C.C.M. Hardy
Hardy, C. C. M
C. C. M Hardy was a contributor to Egerton Sykes’ Atlantis magazine from its year of inception.
Hardy subscribed to the view that there had been a dam at Gibraltar that was breached around 4500 BC with such a force that it also led to the destruction of a landbridge between Tunisia and Italy.
>In issue 2 of Egerton Sykes’ (Atlantean) Research (July/August 1948) he argued strongly against Ignatius Donnelly’s chosen Atlantis location of Azores. In sharp contrast, he believed that remnants of Atlantis will be found in the seas around Greece.<
In 1966 he investigated the possibility of setting up a University Chair of Atlantean Studies either in the USA or Europe(a). Unfortunately, the idea did not appeal to conservative academia and was consequently shelved. I think that there is even more validity in the idea today.
It is remarkable, therefore, that commencing January 2017 the University of Oxford offered a short course on Plato’s Atlantis. The lecturer is Stephen P. Kershaw, a specialist in Greek mythology(b), which suggests that the lectures may only be concerned with the mythological content of the Atlantis narrative without due regard for any possible historical underpinnings. Kershaw had A Brief History of Atlantis published as a Kindle book in September 2017.
(a) https://www.seachild.net/atlantology/
(b) https://web.archive.org/web/20180315161815/https://www.conted.ox.ac.uk/courses/platos-atlantis
Gibraltar Landbridge or Dam *
A Gibraltar Landbridge or Dam is generally accepted to have existed on several occasions during the earth’s history. There is a broad consensus among geologists that the last time an enclosed and desiccated Mediterranean had its barrier to the Atlantic breached was around 5.3 million years ago. A paper by Daniel García-Castellanos on the refilling of the Mediterranean deserves a read(u).
Today, we generally think of the Strait of Gibraltar as the only gateway between the Atlantic and the  Mediterranean, while in fact there is evidence that millions of years ago the Strait was closed but that there were earlier access routes between the two bodies of water(n). The Betic Corridor in the north, which later became part of the Spanish Guadalquivir Basin and the Rifian Corridor in the south, in what is now Morocco(t).
Mediterranean, while in fact there is evidence that millions of years ago the Strait was closed but that there were earlier access routes between the two bodies of water(n). The Betic Corridor in the north, which later became part of the Spanish Guadalquivir Basin and the Rifian Corridor in the south, in what is now Morocco(t).
However, a number of experts in different fields (noted by Van Sertima) have opted to suggest a more recent landbridge, perhaps 120,000 years ago, in order to explain some of the faunal migrations from Africa to the Iberian Peninsula[322].
When the last opening of the Mediterranean was demonstrated by Kenneth Hsu to have taken place 5.5 million years ago, the idea of a landbridge at Gibraltar being destroyed within the memory of man seemed rather unlikely. However, when I saw the 2012 bathymetric maps of the Mediterranean produced by Brosolo, Mascle & Loubrie(v) relating to the Younger Dryas Period, it raised new questions for me.
However, Hsu’s date for the last flooding of the Mediterranean has, understandably, found little support from young-Earth creationists, such as Lambert Dolphin(o). and Barry Setterfield, who have striven to reconcile the irreconcilable with obscure ideas, such as changes in the speed of light!
The 18th-century writer Georges-Louis Buffon speculated as early as 1749 on the existence of a Gibraltar Dam. Alexander Braghine refers [156.21] to Bishop Tollerat, a contemporary of Bory de Saint Vincent, claiming that a Gibraltar landbridge was breached by an earthquake and led to the submergence of Atlantis. Unfortunately, I have been unable to track down Tollerat.
Even popular fiction featured the idea of a Gibraltar landbridge. In 1869, Mark Twain in chapter 7 of Innocents Abroad [1123] voiced a then-current theory that there had been dry land between Gibraltar and North Africa allowing the passage northward of the so-called ‘Barbary apes’ that live on the ‘Rock’ today.
In 1921, H.G.Wells, in The Outline of History, offered a graphic, although speculative, description of the breaching of the Gibraltar Dam(g). He wrote that “This refilling of the Mediterranean, which by the rough chronology we are employing in this book may have happened somewhen between 30,000 and 10,000 B.C., must have been one of the greatest single events in the pre-history of our race.”
Manuel Sánchez de Ocaña was the Spanish Lieutenant General during the 1909 war in Africa. In a rare 1935 book, Accion de España en Africa(a) (Spanish Action in Africa) he refers to the ancient isthmus that linked Spain and North Africa as well as landbridges linking Europe and America on which he believed Atlantis had been situated.
François de Sarre (1947- ) was a noted French evolutionary zoologist who proposed that a landbridge had existed at Gibraltar, which was only destroyed in relatively recent times, possibly in the second millennium BC. In support of his view, he quotes Pomponius Mela, Diodorus Siculus and Pliny. He has also published a paper, in English, supporting his opinion with a spectrum of faunal evidence(k).
Others have ventured further and proposed that a dam existed within the experience of man and that its last destruction led to the sinking of Atlantis which many claim was located in the Mediterranean. H. S. Bellamy refers to Strato quoted by Strabo, declaring that originally the strait did not exist but that the barrier was broken through in a cataclysm. Bellamy also quotes Seneca describing how Spain was separated from Africa by earthquakes. Neither of these references could have originated without human witnesses.
Alexander Braghine also added to the idea of a relatively recent landbridge when he wrote[156.139] “We possess a whole series of records of the width of these Straits, left by ancient and medieval writers of various centuries. At the beginning of the fifth century B.C. the width was only half a mile, but the writer Euton in 400 B.C., estimated it at 4 miles; Turiano Greslio, in 300 B.C., at 5 miles; and Titus Livius, at the beginning of the Christian Era, at 7 miles. Victor Vitensa, in A.D. 400, gives the width of the Straits as equal to 12 miles, and at present it is 15 miles wide.” John Jensen offers the same information as a graphic(q).
C. M. Hardy subscribed to the view that there had been a dam at Gibraltar that was breached around 4500 BC with such a force that it also led to the destruction of a landbridge between Tunisia and Italy. He believed that remnants of Atlantis will be found in the seas around Greece.
C. S. Rafinesque, the famous naturalist, claimed that there was a Gibraltar landbridge that was destroyed 654 years after Noah’s Flood. These claims are to be found in chapter 14 of Vol II of The American Nations published in 1836. This volume can now be downloaded for free(e). A creationist website(i) links the breaching of the landbridge with Noah’s Deluge, which the author claims not only flooded the Mediterranean but also spilled into the Black Sea, the Red Sea and also the Persian Gulf. (see below)
 The standard argument against the landbridge theory is that although the Atlantic was dramatically lower during the last Ice Age it was not sufficient to expose a land bridge between Spain and Africa at Gibraltar. However, it should be noted that the underwater sill between the Atlantic and the Mediterranean would have been much higher than now. When we consider that the breaching of a landbridge at Gibraltar would have caused an incredible flow of water through the breach (hundreds of times the flow of Niagara Falls), scouring its bottom, so that by the time the levels in the Atlantic and the Mediterranean had equalised, the erosion of the sill between them would have been considerable and when viewed today would misleadingly suggest that the Mediterranean had not have been completely cut off from the Atlantic during the last Ice Age. In the future, the consequence of this is that when (not if) the next Ice Age begins the ocean levels will have to drop even lower if the Mediterranean is to be isolated from the Atlantic once again. An example of what a sudden release of large bodies of water can do is visible in the scablands of North America, created by the breaching of the glacial dam retaining Lake Missoula.
The standard argument against the landbridge theory is that although the Atlantic was dramatically lower during the last Ice Age it was not sufficient to expose a land bridge between Spain and Africa at Gibraltar. However, it should be noted that the underwater sill between the Atlantic and the Mediterranean would have been much higher than now. When we consider that the breaching of a landbridge at Gibraltar would have caused an incredible flow of water through the breach (hundreds of times the flow of Niagara Falls), scouring its bottom, so that by the time the levels in the Atlantic and the Mediterranean had equalised, the erosion of the sill between them would have been considerable and when viewed today would misleadingly suggest that the Mediterranean had not have been completely cut off from the Atlantic during the last Ice Age. In the future, the consequence of this is that when (not if) the next Ice Age begins the ocean levels will have to drop even lower if the Mediterranean is to be isolated from the Atlantic once again. An example of what a sudden release of large bodies of water can do is visible in the scablands of North America, created by the breaching of the glacial dam retaining Lake Missoula.
The Spanish researcher Paulino Zamarro contends, in his 2000 book, Del Estrecho de Gibraltar a la Atlantida that a Gibraltar dam was created by silting when the Atlantic was very much lower during the last Ice Age and that it lasted until 7,500 years ago when it was breached and destroyed Atlantis, which he locates in the Cyclades, with the island of Melos containing its capital city. Details of his theory can be found on the Internet(d). A larger version of Zamarro’s map is shown on the right.
that a Gibraltar dam was created by silting when the Atlantic was very much lower during the last Ice Age and that it lasted until 7,500 years ago when it was breached and destroyed Atlantis, which he locates in the Cyclades, with the island of Melos containing its capital city. Details of his theory can be found on the Internet(d). A larger version of Zamarro’s map is shown on the right.
Other researchers such as Constantin Benetatos maintain that this idea is supported by comments of ancient writers who suggest that at one time the Mediterranean had no existence. The philosopher Strato supported by Seneca refers to the sundering of such a dam linking Europe and Africa. The same idea was expressed by Diodorus Siculus, who said that Africa and Europe were joined and separated by Heracles. Such ideas could only have arisen if there had been a Gibraltar Dam far more recently than the conventionally accepted 5.3 million years ago. The lowering of the ocean levels at the beginning of the last Ice Age and the exposure of a landbridge or dam between Spain and Morocco would have had the effect of drying out the Mediterranean due to the fact that loss of water through evaporation in the region is greater than the amount of water from rivers that feed into it.
It is worth considering that although the catastrophic breaching of the Bosporus and consequent expansion of the Black Sea is generally accepted as fact, there are no specific legends to support it apart from a reappraisal of the Flood of Noah. Therefore, it is not unreasonable to point out that there is little by way of local myth or legend relating to the breaching of a Gibraltar Dam which is not proof that such an event did not occur. Although, as you will see below, a number of highly regarded Arabic scholars have endorsed the idea of a breached dam at Gibraltar.Furthermore, the area around the mouth of the Mediterranean is geologically unstable and could have been subjected to seismic activity that could have breached or even blocked the strait.
Alberto Arecchi agrees(a) with the concept of a historical land bridge at Gibraltar, but places its breach to around 2300 BC. John Jensen puts it about a millennium later and suggested that the sundering of the Gibraltar Dam was probably outward from the Mediterranean into the Atlantic(q) rather than the more generally accepted other direction. As already intimated, Constantin Benetatos also supported(b) the existence of the Gibraltar Dam.
Joseph S. Ellul the Maltese writer was probably the first modern author to link the breaching of a Gibraltar landbridge with the destruction of Atlantis, which he claims to have been located adjacent to Malta. He identifies this submergence of Atlantis by the waters of the Atlantic with Noah’s Flood. Ellul interprets Genesis 7:11, 8:2, which refers to the “fountains of the great deep” bursting forth, as a reference to the collapse of the Gibraltar Dam.
David Hatcher Childress also supports the idea of such a landbridge and has ventured a date of around 9000 BC for its collapse[620.261] and the consequent flooding of a desiccated Mediterranean.
Georgeos Diaz-Montexano, who has been searching for Atlantis off the coast of Spain and Gibraltar, has favourably referred to Zamarro’s silting theory and included the illustration, shown above, from Zamarro’s book on his websites. A further reference to silting can be read on another website(f).
When the Mediterranean eventually filled up, it is highly probable that it was then that the pressure of its waters led to the flooding of the Black Sea. It is reported that there are scouring marks at the entrance to the Black Sea that are very similar to those at Gibraltar. The date of the putative collapse of the Gibraltar Dam would therefore be marginally earlier, while the Mediterranean basins filled, than the accepted date for the breaching of the Bosporus currently calculated to have been around 5600 BC.
Robert Sarmast’s apparently dormant theory of Atlantis submerged off the coast of Cyprus under what is now a mile of water is totally dependent on the existence of a Gibraltar Dam during the last Ice Age and it being subsequently breached when the level of the Atlantic rose or the even more improbable lowering of the seafloor by a mile, as a consequence of seismic/tectonic activity in the region.
On the basis of evidence(c) offered by the quoted classical writers, the fact that sea levels rose hundreds of feet after the last Ice Age and examples of water damage to temples on elevated ground in Malta and nuraghi in Sardinia it is not unreasonable to conclude that a rupturing of a landbridge at Gibraltar within the last ten thousand year was possible if not probable.
The most dramatic suggestion regarding the creation of the Strait of Gibraltar has been offered by Terry Westerman(h), who proposed that the rupturing of the landbridge was caused by two meteor impacts.
Finally, it is worth considering the comments of a number of respected Arabic scholars such as Al-Biruni, and Al-Mas’udi who lent support to the idea of a Gibraltar landbridge. Additionally, Al-Idrisi recounts how the Gibraltar landbridge was breached by Alexander the Great. While the introduction of Alexander, who was very highly regarded by the Arabs, is obviously a folkloric embellishment, it demonstrates an underlying belief in the existence of such an isthmus in the distant past. Adding strength to this idea is that al-Idrisi was born in Ceuta on the African side of the Strait of Gibraltar and consequently would undoubtedly have been fully aware of local traditions regarding a landbridge there in ancient times.
However, all that must be reconciled with the scientific findings of Kenneth Hsu who dated the last opening of the Gibraltar Strait to 5.5 million years ago(m). This date has been unchallenged as far as I’m aware.
A paper published online in May 2022 would appear to contradict the idea that a landbridge blocking the  Gibraltar Strait had collapsed, flooding the Mediterranean and contributing to the destruction of Atlantis.
Gibraltar Strait had collapsed, flooding the Mediterranean and contributing to the destruction of Atlantis.
This paper(a) includes a map showing the gradual encroachment inland by the Mediterranean at Spain’s Pego-Olvia (opposite Ibiza), between 9000 BC and 8100 BC. This was the result of post-glacial melting of the glaciers gradually raised sea levels allowing water to slowly move inland over the flat coastal plain at a rate of about a kilometre every century. Little has changed since then, indicating that any suggested landbridge could not have been breached after 8100 BC without a more significant expansion inland by the Mediterranean. It also suggests that in a scenario where a Mediterranean Atlantis was flooded during that period and particularly during the second millennium BC, it should still be in relatively shallow waters!
(a) https://www.liutprand.it/articoliMondo.asp?id=111
(b) See: Archive 2365
(c) https://www.freerepublic.com/focus/news/601935/posts
(d) See: https://web.archive.org/web/20180820052424/https://www.atlantidaegeo.com/autor.html
(f) https://wiki.answers.com/Q/What_was_the_depth_of_the_Mediterranean_Sea_during_the_last_Ice_Age
(g) https://archive.org/details/OutlineOfHistory
(h) The Formation of the Strait of Gibraltar (archive.org)
(i) https://www.makesyouthinkblog.com/?m=201204 (link broken) See Archive 2536
(k) https://www.migra(o)tion-diffusion.info/article.php?year=2015&id=477
(m) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Messinian_salinity_crisis
(n) https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/2014PA002719/full
(o) http://www.ldolphin.org/meddead.html
(r) Wayback Machine (archive.org)
(s) https://www.grisda.org/origins-01067
(t) https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/2014PA002719
(u) https://mappingignorance.org/2014/02/07/how-the-mediterranean-was-refilled/
(v) Morpho-Bathymetric Map of the Mediterranean – CCMG (ccgm.org) *
Aegean Sea
The Aegean Sea is located in the eastern Mediterranean, bounded by the Greek mainland in the north and west, Turkey in the east and extending to Crete in the south. In 1899, R.F. Scharff claimed that it was commonly accepted that the Aegean had been dry land until after the appearance of man(c). Zhirov wrote of this landmass being referred to as ‘Aegeida’ before it subsided to form the Aegean Sea [0458.96], but he doubted that it occurred before ‘thinking man’ arrived there.
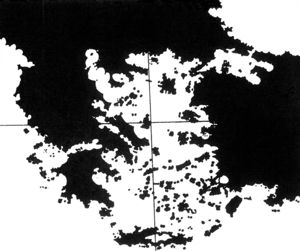 The 15th-century map of Ibn Ben Zara appears to show the islands of Aegean as larger and more numerous than today!
The 15th-century map of Ibn Ben Zara appears to show the islands of Aegean as larger and more numerous than today!
The importance of the Aegean to the ancient Greeks is highlighted by Plato when he described their relationship as one where the Greeks “are like frogs around a pond.” (Phaedo 109a-b)
However, it has been noted(i) that the Homeric poems (and the works attributed to Hesiod) studiously avoid any reference to the Aegean Sea, an avoidance that appears all the more striking when juxtaposed with the fact that there are other named seas in the poems.
A 280-page overview of the Aegean civilisations from the Neolithic to the Hellenistic period(f) is worth a look.
It can be reasonably argued that initially, the Greeks had little knowledge of the world beyond the Aegean, which might explain why Plato did not seem to know the exact identity of the Atlanteans. In this regard, a quote from an AtlantisOnline forum seems relevant – “There is evidence, moreover, that the Greeks were restricted by the Phoenicians to the Aegean Sea for a period of many centuries from 1200 BC onwards, and Naval Historians attribute this to the availability exclusively to the Phoenicians of two elements in ship construction, namely long straight cedar timbers (compared to short sinuous olive timbers available to the Greeks) and Bronze for fixings, claddings and battering rams, which were used in battle to perforate hulls, sinking the enemy.”(e)
Many researchers have suggested the Aegean as a possible location for Atlantis with Thera and Crete as the leading contenders. In fact, it is Thera, with its dramatic volcanic eruption, in the middle of the second millennium BC that still  manages to command considerable support after nearly one hundred years since it was first mooted. Its advocates view it as the most likely source of inspiration for Plato’s tale, in spite of the fact that it conflicts with many of the details described by him.
manages to command considerable support after nearly one hundred years since it was first mooted. Its advocates view it as the most likely source of inspiration for Plato’s tale, in spite of the fact that it conflicts with many of the details described by him.
One regular blogger, ‘mapmistress’, proposed (2010) that the Pillars of Heracles were situated at Rhodes with Atlantis situated north of the island in the Aegean. This suggestion is based on the claim that all English translations of Timaeus 24e are ‘botched’ and that the original does not say “larger than Libya and Asia together” but instead should read “north of Libya and west of Asia”! In fact, she goes further with the claim that the very word ‘Atlantis’ was invented by Benjamin Jowett!(d)
Three Italian linguists, Facchetti, Negri, and Notti, presented a paper to the Atlantis conference on Melos outlining their reasons for supporting an Aegean backdrop to the Atlantis story. Another paper was presented by four members of the Hellenic Centre for Marine Research which demonstrates how three-quarters of the Cyclades Plateau was submerged between 16000 BC and 6000 BC as the sea levels rose after the last Ice Age. Kurt Lambeck and Anthony Purcell also presented a paper along similar lines.
>However, not everyone is happy with Atlantis being placed in the Aegean. About 20 years ago an anonymous contributor to the now-defunct geocities website wrote the following piece regarding the matching of Atlantis with the eruption of Thera(o).
“To arrive at this conclusion is simple enough – take the numbers Plato uses for the dimensions and antiquity of Atlantis, divide them by ten, then keep all the fabulous details about the architecture and pretend it applies to the structures and artifacts recovered by archaeology – then throw out all the details about its conquering armies, its location, and its complete disappearance. No wonder there’s such an exact match!”<
Paulino Zamarro has offered a very radical theory, outlined in his book [024], which claims that Atlantis was located in the Aegean, with its capital on Melos, at a time when sea levels were lower and the islands more extensive in area, with some of them joined together. He postulates an isthmus or land bridge between Gibraltar and Morocco, which he believes was breached around 5500 BC. An idea supported by Strato and Seneca. He contends that this breach not only flooded the Aegean but also was also responsible for the subsequent inundation of the Black Sea, which until then was a smaller freshwater lake.
Diamantis Pastras, a Greek-Australian confectioner presented to the Atlantis Conference in 2005 [0629.295] his theory that Atlantis had been situated in the Aegean Cyclades along with nearby Astipalea in the Dodecanese, which he maintains constituted a single larger landmass 3,500 years ago.
Recent studies have revealed(b) the extent of very early seafaring in the Aegean can be pushed back to around 10,000 BC with evidence of obsidian trading at that period. However, the lower sea level at that time would have meant that the Aegean islands would have been much larger with shorter distances, if any, between them, so it may be unwise to read too much into the obsidian evidence.
A 2018 article pushes back Mediterranean seagoing even further(h). Consider how this evidence may relate to Plato’s comment that when Atlantis was established “at that time neither ships nor sailing were as yet in existence” (Crit.113e). However, December 2022 brought a claim of even earlier seafaring in the Aegean, possibly as far back as 450,000 years ago, according to a team from the University of Patras in Greece led by George Ferentinos(n).
In 1998 William Ryan and Walter Pitman published[025] their evidence for the enlargement of the Black Sea with seawater. The book received widespread attention that led to a subsequent expedition to the area by Robert Ballard, the famous discoverer of the Titanic.
However, Zamarro’s ideas have received very little notice, probably because he has only been published in Spanish. His theory regarding the silting and closure of the mouth of the Mediterranean deserves further consideration, as its confirmation would have a profound effect on the course of future studies of the prehistory of the region and in particular Atlantology.
C.C.M. Hardy was a regular contributor to Sykes‘ Atlantis journal, in which he suggested that remnants of Atlantis would be found in the seas around Greece. Hans-Henning Klein favours the island of Samothrace in the northern Aegean as the home of Atlantis(l).
A half-hearted attempt to link the Greek island of Thasos with Atlantis is to be found on the German de.pluspedia.org website(j).
A recent recruit to the ‘Atlantis in the Aegean’ camp is Christos A, Djonis with his theory[935] that Atlantis lay in the Aegean Sea, to the north of Thera, which itself contained the capital city of the Atlantean confederation. He makes no reference to Zamarro, who proposed a similar location fifteen years ago and consequently, considers Djonis’ work as a form of plagiarism! Apart from that, my gripe is that Djonis wastes over half his book discussing UFOs and ancient astronauts. Another proponent of a Theran Atlantis is Elias Stergakos, who also published his short book[1035] on the Minoan Hypothesis in 2014.
In the same year, the Italian architect Costa Kyrki published a paper entitled Lost Atlantis in which he proposed that the sunken Atlantis was situated between the island of Samos and Miletus on mainland Turkey(k).
J.P. Rambling on his Redefining Atlantis website(g) has now added his support to the concept of an Aegean Atlantis, situated on a large landmass, now mostly submerged, and which included what is now Santorini.
It is worth noting that Jürgen Spanuth In defending his North Sea location for Atlantis scornfully denounced the possibility of an Aegean Atlantis in Atlantis of the North [015.247]. “Neither Thera nor Crete lie in the ‘Atlantic sea’ but in the sea of Crete, which is clearly referred to in Crit.111a and is obviously not the Atlantic sea of Tim.24. Neither island lies at the mouth of a great river; neither was ‘swallowed up by the sea and vanished’ (Tim.25d): the Aegean never became ‘impassable to navigation’ (ibid.) Solon and Plato could never have said of the Aegean that passage there was hindered by ‘impenetrable mud’ (Crit.108e) for both had sailed through it – their contemporaries would have laughed at them if they had made such an absurd assertion.” Spanuth failed to highlight that Plato referred to the shoal of mud in the present tense indicating that it was still a hazard in his day!
What I cannot understand is that if Atlantis had existed in the Aegean, why did Plato not simply say so?
The Atlantisforschung website offers a selection of articles dealing with many aspects of the Aegean and its possible connection with Atlantis(m).
(a) https://atlantipedia.ie/samples/document-250811/
(b)https://www.stonepages.com/news/archives/004698.html
(c) https://www.gutenberg.org/files/33236/33236-h/33236-h.htm#Page_61
(d) https://pseudoastro.wordpress.com/2009/02/01/planet-x-and-2012-the-pole-shift-geographic-spin-axis-explained-and-debunked/ (about half way down page)
(e) https://atlantisonline.smfforfree2.com/index.php?topic=3238.1260
(f) https://www.slideshare.net/darkyla/greeks-9775861
(g) https://redefiningatlantis.blogspot.ie/
(h) https://www.sciencemag.org/news/2018/04/neandertals-stone-age-people-may-have-voyaged-mediterranean
(j) Atlantis Verortung in der Ägäis (Thasos) – PlusPedia
(k) https://www.behance.net/gallery/17045455/LOST-ATLANTIS
(l) ATLANTIS ERAT ! – Es gab ATLANTIS! – Samothrake ist Atlantis – Atlantisforschung.de
(n) Ancient Humans May Have Sailed The Mediterranean 450,000 Years Ago : ScienceAlert
(o) Sunken Civilizations — www.geocities.com/sunkenciv/index.html (archive.org) *
