J.D. Brady
Hershiser, David
David Hershiser is the author of Beyond the Pillars of Hercules: Atlantis and Tyrus in Plato’s Writings, Biblical Verses, and the Works of Helena Blavatsky, Edgar Cayce, and Ruth Montgomery[1016]. In it he adopts the idea of J. D. Brady that Ezekiel’s Tyrus was not the Phoenician city of Tyre, but it can be identified as Atlantis. In a 2015 article in Atlantis Rising magazine(a) Hershiser discusses the core of this theory. Unlike Brady, who proposed that Tyrus/Atlantis was to be identified with Troy, Hershiser places his Tyrus/Atlantis in the Atlantic just outside the Strait of Gibraltar.
*(a) See: Archive 3395*
Mackey, Damien
Damien Mackey (1950- ) is an Australian writer who has written extensively on religious and historical matters. In April 2016, he devoted a blog(a) to the subject of Atlantis and its possible historical underpinnings as well as cultural borrowings from Old Testament sources. In this regard, he echoes the views of J.D. Brady in comparing Plato’s Atlantis with Tyrus in the Bible’s Book of Ezekiel. He has also challenged(c) the chronology presented in Ahmed Osman’s Out of Egypt [1744].
Mackey has also proposed(e) “that the Patriarchs Abraham, Isaac, Jacob, Joseph, and Moses, span the entire period of Egyptian history from the very first king of the First Dynasty of the Old Kingdom (as we have already learned) to, in the case of Moses, the last king (actually a woman) of the so-called Middle Kingdom.”
His MA thesis which concerned The Sothic Star Theory of the Egyptian Calendar(d) is available online.
Mackey has also supported the identification of the biblical Amalekites with the Hyksos(f) noting that “Dr. I. Velikovsky’s identification of the Hyksos conquerors of Egypt with the biblical Amalekites has been widely accepted by revisionists – even those who have since rejected his Ages in Chaos.
David Rohl, whose own biblico-historical revision is some centuries apart from Velikovsky’s, had nonetheless accepted the latter’s identification of the Hyksos conquerors of Egypt with the Amalekites of the Book of Exodus (Pharaohs and Kings: A Biblical Quest, 1997).”
Mackey has written a number of papers aimed at synchronising Egyptian and biblical chronologies(g), some of which are available on the academia.edu website(h).
Additionally, he suggests that Solon could be identified with biblical Solomon(b)!
(a) https://westerncivilisationamaic.blogspot.ie/2016/04/ancient-atlantis.html
(b) https://www.academia.edu/3660164/Solomon_and_Sheba
(c) Archive 6193
(e) Archive 6532 | (atlantipedia.ie)
(f) https://mosesegyptianised.wordpress.com/2016/10/26/the-hyksos-as-amalekites/
(g) (99+) Securing an anchorless Egypt to biblical history | Damien Mackey – Academia.edu *
(h) (99+) Damien Mackey | The University of Sydney – Academia.edu *
Labyrinth *
Labyrinths, are one of the many mysteries of the ancient world, with the earliest examples apparently dating back around 4,000 years(t). In Egypt, around 1800 BC Pharaoh Amenemhet III was responsible for building what is reputed to have been the largest labyrinth at Hawara containing three thousand rooms according to Herodotus, who visited it in the 5th century BC. Herodotus’ description inspired Athanasius Kircher to draw a plan of the underground complex(u).
The Labyrinth along with the double-headed axe, the labyris, are usually associated with Minoan culture. However, the labyrinth is an ancient symbol found around the world in locations such as Italy(s), India(g), Egypt(h), England(q), Finland(r)and even in the New World as Evan Hadingham has shown an example [1309.261] at Pacatnamú in Peru. In Scandinavia, they are known as Troy Towns – Trojeborgar. Sweden has the greatest number with 200(e).
The largest example in Sweden was discovered at the Mesolithic site on Blå Jungfrun Island(j).
Tracy Boyd, in a lengthy paper(m) about Chartres Cathedral, mentions in footnote 27 that “Many of the labyrinths originally installed in cathedrals in France were later destroyed by the Church itself”!
Eberhard Zangger claimed that “most labyrinths are found around the Mediterranean” and “that at the end of the Bronze Age, the labyrinth was a recognised pattern around the eastern Mediterranean.” [484.136] He proceeds to link the labyrinth with Troy, which, in an earlier book [483] he had identified as Atlantis.
India’s second-largest example, measuring 56 feet by 56 feet, was partly uncovered in Gedimedu near Pollachi(i) in 2015. It is estimated to be 2,000 years old and has a design similar to those found on clay tablets found at Pylos, Greece, from 1200 BC.
Labyrinths were also incorporated into very many churches and cathedrals throughout Europe. Lucile Taylor Hansen gives some examples of mazes in the United States[572.276].
It has been suggested by a number of writers that the labyrinth had some connection with Atlantis(a)(b). Such suggestions are interesting but highly speculative. Lewis Spence does so in The History of Atlantis. J. D. Brady touches on this in his book, Atlantis[0738] where he announced that Atlantean gold treasure was to be found within a labyrinth on the Greek island of Lemnos.
What I find interesting is that so many widespread examples of the labyrinth retain the irregular elements of the symbol even when depicted in a rectangular rather than a rounded style. An extensive website covering all aspects of labyrinths and mazes is worth a visit(c). There is also The Labyrinth Society(f) to further whet your appetite.
In 2014 an article(o) by April Holloway described a collection of labyrinths that I consider the most mysterious of all. They are situated on Russia’s Solovetsky Islands (or Solovki), which “are an archipelago located in the Onega Bay of the White Sea, Russia. It is here where there can be found thirty-five Neolithic labyrinths, known as ‘vavilons’ (‘Babylons’) in the local dialect, which date back to around 3,000 BC. The most remarkable are the stone labyrinths of Bolshoi Zayatsky Island, a group of fourteen labyrinths in a 0.4km 2 area.” The Atlas Obscura website offers a number of images(p).
In 2017, an extensive article by John Reppion offers further information on the history and geographical spread of labyrinths(k). Similarly, Gary Vey offers an article with additional information and more images(l).
Some researchers have attempted to link the outline of the labyrinth with the concentric design of the harbour of Plato’s capital city. The harbour was described as a series of perfectly concentric circular features ‘as if created on a lathe’ (Critias 113d), whereas the labyrinth is more spiral with a slightly offset entrance. My conclusion regarding the labyrinth is; fascinating– yes, Atlantis – probably not.
The persistent use of this ancient symbol was highlighted by an aerial image, sent to me by Hank Harrison, of a Catholic school in California.
(a) MMM Group Home Page (archive.org)
(b) www.duepassinelmistero.com/Il%20mito%20di%20Atlantide.htm
(c) Labyrinthos Homepage (archive.org)
(e) https://www.mymaze.de/trojaburg_en.htm
(f) The Labyrinth Society: The Labyrinth Society: Sacred Geometry and Labyrinths (archive.org) *
(h) https://www.ancient-origins.net/ancient-places-africa/lost-labyrinth-ancient-egypt-part-1-002033
(k) https://dailygrail.com/Guest-Articles/2017/7/The-Labyrinths-Troy
(l) Labyrinth: walk on the wild side / Viewzone
(m) our lady of chartres (archive.org)
(o) https://www.ancient-origins.net/ancient-places-asia/ancient-stone-labyrinths-bolshoi-zayatsky-001573
(p) https://www.atlasobscura.com/places/bolshoi-zayatsky-island
(q) https://andrewgough.co.uk/articles_land/
(r) Labyrinths and Ritual in Scandinavia | BLADE HONER (wordpress.com)
Tyre
Tyre was located in what is modern Lebanon and is considered to have been originally a colony of Sidon. According to 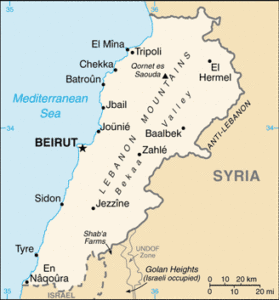 Egyptian records they ruled it during the middle of the second millennium BC, but lost control when their influence in the area declined. Independence brought commercial success that saw Tyre surpass Sidon in wealth and influence and eventually establish its own colonies across the Mediterranean. One of these was Carthage in North Africa, which in time became independent and eventually rivalled the Roman Empire in the west. It also had colonies in Greece and frequently fought with Egypt.
Egyptian records they ruled it during the middle of the second millennium BC, but lost control when their influence in the area declined. Independence brought commercial success that saw Tyre surpass Sidon in wealth and influence and eventually establish its own colonies across the Mediterranean. One of these was Carthage in North Africa, which in time became independent and eventually rivalled the Roman Empire in the west. It also had colonies in Greece and frequently fought with Egypt.
The location of Tyre, on an island with a superb natural harbour and which had great wealth and was supported by its many colonies, has been seen as a mirror of Atlantis. The Old Testament prophecies of Ezekiel, writing around 600 BC, described (26:19, 27: 27-28) the destruction of Tyre in terms that have prompted some to link it with Plato’s description of Atlantis’ demise, written two hundred years later.*The earliest claim that Ezekiel’s Tyrus was a reference to Atlantis was made by Madame Blavatsky in The Secret Doctrine [1495] in 1888.
However, although both J.D. Brady and David Hershiser promote the idea of a linkage between Ezekiel’s Tyrus and Atlantis, they are certain that Tyrus is not the Phoenician city of Tyre. Beyond that, Brady identifies Tyrus/Atlantis with Troy, while Hershiser has placed his Tyrus/Atlantis in the Atlantic just beyond the Strait of Gibraltar(b).
Early in the 20th century Hanns Hörbiger also cited Ezekiel as justification for identifying Tyre as Atlantis.*
Recently, a sunken city has been discovered between Tyre and Sidon and according to its discoverer, Mohammed Sargi, is the 4,000 year old City of Yarmuta referred to in the Tell al-Amarna letters.
Carl Fredrich Baer, the imaginative 18th century writer, proposed a linkage between Tyre and Tyrrhenia. This idea has been 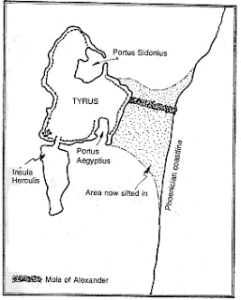 revived recently by the claims of Jaime Manuschevich[468] that the Tyrrhenians were Phoenicians from Tyre. Other supporters of a Tyrrhenian linkage with Tyre are J.D.Brady, Thérêse Ghembaza and most recently Dhani Irwanto. J.S. Gordon also claims[339.241] that Tyre was so named by the Tyrrhenians.
revived recently by the claims of Jaime Manuschevich[468] that the Tyrrhenians were Phoenicians from Tyre. Other supporters of a Tyrrhenian linkage with Tyre are J.D.Brady, Thérêse Ghembaza and most recently Dhani Irwanto. J.S. Gordon also claims[339.241] that Tyre was so named by the Tyrrhenians.
In Greek mythology it is said that Cadmus, son of the Phoenician king Agenor, brought the alphabet to Greece, suggesting a closer connection than generally thought.
J.P. Rambling places the Pillars of Heracles on Insula Herculis, now a sunken island, immediately south of Tyre(a).
(a) https://redefiningatlantis.blogspot.ie/search/label/Heracles
*(b) See: Archive 3395*
Troy *
Troy is believed to have been founded by Ilus, son of Troas, giving it the names of both Troy and Ilios (Ilium) with some minor variants.
“According to new evidence obtained from excavations, archaeologists say that the ancient city of Troy in northwestern Turkey may have been more than six centuries older than previously thought. Rüstem Aslan, who is from the Archaeology Department of Çanakkale Onsekiz Mart University (ÇOMU), said that because of fires, earthquakes, and wars, the ancient city of Troy had been destroyed and re-established numerous times throughout the years.” This report pushes the origins of this famous city back to around 3500 BC(s).
Dating Homer’s Troy has produced many problems. Immanuel Velikovsky has drawn attention to some of these difficulties(aa). Ralph S. Pacini endorsed Velikovsky’s conclusion that the matter could only be resolved through a revised chronology. Pacini noted that “the proposed correction of Egyptian chronology produces a veritable flood of synchronisms in the ancient middle east, affirming many of the statements by ancient authors which had been discarded by historians as anachronisms.”(z)
The precise date of the ending of the Trojan War continues to generate comment. A 2012 paper by Rodger C. Young and Andrew E. Steinmann has offered evidence that the conclusion of the conflict occurred in 1208 BC, which agrees with the date recorded on the Parian Marble(ah). This obviously conflicts with the date calculated by Eratosthenes of 1183 BC. A 2009 paper(ai) by Nikos Kokkinos delves into the methodology used by Eratosthenes to arrive at this date. Peter James has listed classical sources that offered competing dates ranging from 1346 BC-1127 BC, although Eratosthenes’ date had more general acceptance by later commentators [46.327] and still has support today.
New dating for the end of the Trojan War has been presented by Stavros Papamarinopoulos et al in a paper(aj) now available on the Academia.edu website. Working with astronomical data relating to eclipses in the 2nd millennium BC, they have calculated the ending of the War to have taken place in 1218 BC and Odysseus’ return in 1207 BC.
The city is generally accepted by modern scholars to have been situated at Hissarlik in what is now northwest Turkey. Confusion over identifying the site as Troy can be traced back to the 1st century AD geographer Strabo, who claimed that Ilion and Troy were two different cities!(t) In the 18th century, many scholars consider the village of Pinarbasi, 10 km south of Hissarlik, as a more likely location for Troy.
The Hisarlik “theory had first been put forward in 1821 by Charles Maclaren, a Scottish newspaper publisher and amateur geologist. Maclaren identified Hisarlik as the Homeric Troy without having visited the region. His theory was based to an extent on observations by the Cambridge professor of mineralogy Edward Daniel Clarke and his assistant John Martin Cripps. In 1801, those gentlemen were the first to have linked the archaeological site at Hisarlik with historic Troy.”(m)
The earliest excavations at Hissarlik began in 1856 by a British naval officer, John Burton. His work was continued in 1863 until 1865 by an amateur researcher, Frank Calvert. It was Calvert who directed Schliemann to Hissarlik and the rest is history(j).
However, some high-profile authorities, such as Sir Moses Finley (1912-1986), have denounced the whole idea of a Trojan War as fiction in his book, The World of Odysseus [1139]. Predating Finley, in 1909, Albert Gruhn argued against Hissarlik as Troy’s location(i).
Not only do details such as the location of Troy or the date of the Trojan War continue to be matters for debate, but surprisingly, whether the immediate cause of the Trojan War, Helen of Troy was ever in Troy or not, is another source of controversy. A paper(ab) by Guy Smoot discusses some of the difficulties. “Odysseus’, Nestor’s and Menelaos’ failures to mention that they saw or found Helen at Troy, combined with the fact that the only two witnesses of her presence are highly untrustworthy and problematic, warrant the conclusion that the Homeric Odyssey casts serious doubts on the version attested in the Homeric Iliad whereby the daughter of Zeus was detained in Troy.”
The Swedish scholar, Martin P. Nilsson (1874-1967) who argued for a Scandinavian origin for the Mycenaeans [1140], also considered the identification of Hissarlik with Homer’s Troy as unproven.
A less dramatic relocation of Troy has been proposed by John Chaple who placed it inland from Hissarlik. This “theory suggests that Hisarlik was part of the first defences of a Trojan homeland that stretched far further inland than is fully appreciated now and probably included the entire valley of the Scamander and its plains (with their distinctive ‘Celtic’ field patterns). That doesn’t mean to say that most of the battles did not take place on the Plain of Troy near Hisarlik as tradition has it but this was only the Trojans ‘front garden’ as it were, yet the main Trojan territory was behind the defensive line of hills and was vastly bigger with the modern town of Ezine its capital – the real Troy.” (af)
Troy as Atlantis is not a commonly held idea, although Strabo, suggested such a link. So it was quite understandable that when Swiss geo-archaeologist, Eberhard Zangger, expressed this view [483] it caused quite a stir. In essence, Zangger proposed(g) that Plato’s story of Atlantis  was a retelling of the Trojan War.
was a retelling of the Trojan War.
For me, the Trojan Atlantis theory makes little sense as Troy was to the northeast of Athens and Plato clearly states that the Atlantean invasion came from the west. In fact, what Plato said was that the invasion came from the ‘Atlantic Sea’ (pelagos). Although there is some disagreement about the location of this Atlantic Sea, all candidates proposed so far are west of both Athens and Egypt.(Tim.24e & Crit. 114c)
Troy would have been well known to Plato, so why did he not simply name them? Furthermore, Plato tells us that the Atlanteans had control of the Mediterranean as far as Libya and Tyrrhenia, which is not a claim that can be made for the Trojans. What about the elephants, the two crops a year or in this scenario, where were the Pillars of Heracles?
A very unusual theory explaining the fall of Troy as a consequence of a plasma discharge is offered by Peter Mungo Jupp on The Thunderbolts Project website(d) together with a video(e).
Zangger proceeded to re-interpret Plato’s text to accommodate a location in North-West Turkey. He contends that the original Atlantis story contains many words that have been critically mistranslated. The Bronze Age Atlantis of Plato matches the Bronze Age Troy. He points out that Plato’s reference to Atlantis as an island is misleading, since, at that time in Egypt where the story originated, they frequently referred to any foreign land as an island. He also compares the position of the bull in the culture of Ancient Anatolia with that of Plato’s Atlantis. He also identifies the plain mentioned in the Atlantis narrative, which is more distant from the sea now, due to silting. Zangger considers these Atlantean/Trojans to have been one of the Sea Peoples who he believes were the Greek-speaking city-states of the Aegean.
Rather strangely, Zangger admits (p.220) that “Troy does not match the description of Atlantis in terms of date, location, size and island character…..”, so the reader can be forgiven for wondering why he wrote his book in the first place. Elsewhere(f), another interesting comment from Zangger was that “One thing is clear, however: the site of Hisarlik has more similarities with Atlantis than with Troy.”
There was considerable academic opposition to Zangger’s theory(a). Arn Strohmeyer wrote a refutation of the idea of a Trojan Atlantis in a German-language book [559].
An American researcher, J. D. Brady, in a somewhat complicated theory, places Atlantis in the Bay of Troy.
In January 2022, Oliver D. Smith who is unhappy with Hisarlik as the location of Troy and dissatisfied with alternatives offered by others, proposed a Bronze Age site, Yenibademli Höyük, on the Aegean island of Imbros(v). His paper was published in the Athens Journal of History (AJH).
To confuse matters further Prof. Arysio Nunes dos Santos, a leading proponent of Atlantis in the South China Sea places Troy in that same region of Asia(b).
Furthermore, the late Philip Coppens reviewed(h) the question marks that still hang over our traditional view of Troy.
Felice Vinci has placed Troy in the Baltic and his views have been endorsed by the American researcher Stuart L. Harris in a number of articles on the excellent Migration and Diffusion website(c). Harris specifically identifies Finland as the location of Troy, which he claims fell in 1283 BC although he subsequently revised this to 1190 BC, which is more in line with conventional thinking. The dating of the Trojan War has spawned its own collection of controversies.
However, the idea of a northern source for Homeric material is not new. In 1918, an English translation of a paper by Carus Sterne (Dr Ernst Ludwig Krause)(1839-1903) was published under the title of The Northern Origin of the Story of Troy(n). Iman Wilkens is arguably the best-known proponent of a North Atlantic Troy, which he places in Britain. Another scholar, who argues strongly for Homer’s geography being identifiable in the Atlantic, is Gerard Janssen of the University of Leiden, who has published a number of papers on the subject(u). Robert John Langdon has endorsed the idea of a northern European location for Troy citing Wilkens and Felice Vinci (w). However, John Esse Larsen is convinced that Homer’s Troy had been situated where the town Bergen on the German island of Rügen(x) is today.
Most recently (May 2019) historian Bernard Jones(q) has joined the ranks of those advocating a Northern European location for Troy in his book, The Discovery of Troy and Its Lost History [1638]. He has also written an article supporting his ideas in the Ancient Origins website(o). For some balance, I suggest that you also read Jason Colavito’s comments(p).
Steven Sora in an article(k) in Atlantis Rising Magazine suggested a site near Lisbon called ‘Troia’ as just possibly the original Troy, as part of his theory that Homer’s epics were based on events that took place in the Atlantic. Two years later, in the same publication, Sora investigated the claim for an Italian Odyssey(l). In the Introduction to The Triumph of the Sea Gods [395], he offers a number of incompatibilities in Homer’s account of the Trojan War with a Mediterranean backdrop.
Roberto Salinas Price (1938-2012) was a Mexican Homeric scholar who caused quite a stir in 1985 in Yugoslavia, as it was then when he claimed that the village of Gabela 15 miles from the Adriatic’s Dalmatian coast in what is now Bosnia-Herzegovina, was the ‘real’ location of Troy in his Homeric Whispers [1544].
More recently another Adriatic location theory has come from the Croatian historian, Vedran Sinožic in his book Naša Troja (Our Troy) [1543]. “After many years of research and exhaustive work on collecting all available information and knowledge, Sinožic provides numerous arguments that prove that the legendary Homer Troy is not located in Hisarlik in Turkey, but is located in the Republic of Croatia – today’s town of Motovun in Istria.” Sinožic who has been developing his theory over the past 30 years has also identified a connection between his Troy and the Celtic world.
Similarly, Zlatko Mandzuka has placed the travels of Odysseus in the Adriatic in his 2014 book, Demystifying the Odyssey[1396].
Fernando Fernández Díaz is a Spanish writer, who has moved Troy to Iberia in his Cómo encontramos la verdadera Troya (y su Cultura material) en Iberia [1810] (How we find the real Troy (and its material Culture) in Iberia.).
Like most high-profile ancient sites, Troy has developed its own mystique, inviting the more imaginative among us to speculate on its associations, including a possible link with Atlantis. Recently, a British genealogist, Anthony Adolph, has proposed that the ancestry of the British can be traced back to Troy in his book Brutus of Troy[1505]. Petros Koutoupis has written a short review of Adolph’s book(ad).
Caleb Howells, a content writer for the Greek Reporter website, among others, has written The Trojan Kings of Britain [2076] due for release in 2024. In it he contends that the legend of Brutus is based on historical facts. However, Adolph came to the conclusion that the story of Brutus is just a myth(ae), whereas Howells supports the opposite viewpoint.
Iman Wilkens delivered a lecture(y) in 1992 titled ‘The Trojan Kings of England’.
It is thought that Schliemann has some doubts about the size of the Troy that he unearthed, as it seemed to fall short of the powerful and prestigious city described by Homer. His misgivings were justified when many decades later the German archaeologist, Manfred Korfmann (1942-2005), resumed excavations at Hissarlik and eventually exposed a Troy that was perhaps ten times greater in extent than Schliemann’s Troy(r).
An anonymous website with the title of The Real City of Troy(ag) began in 2020 and offers regular blogs on the subject of Troy, the most recent (as of Dec. 2023) was published in Nov. 2023. The author is concerned with what appear to be other cities on the Plain of Troy unusually close to Hissarlik!
(a) https://web.archive.org/web/20150912081113/https://bmcr.brynmawr.edu/1995/95.02.18.html
(b) http://www.atlan.org/articles/atlantis/
(c) http://www.migration-diffusion.info/article.php?authorid=113
(d) https://www.thunderbolts.info/wp/2013/09/16/troy-homers-plasma-holocaust/
(e) Troy – Homers Plasma holocaust – Episode 1 – the iliad (Destructions 17) (archive.org)
(f) https://www.moneymuseum.com/pdf/yesterday/03_Antiquity/Atlantis%20en.pdf
(g) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mo-lb2AAGfY
(h) https://www.philipcoppens.com/troy.html or See: Archive 2482
(i) https://www.jstor.org/stable/496830?seq=14#page_scan_tab_contents
(j) https://turkisharchaeonews.net/site/troy
(k) Atlantis Rising Magazine #64 July/Aug 2007 See: Archive 3275
(l) Atlantis Rising Magazine #74 March/April 2009 See: Archive 3276
(m) https://luwianstudies.org/the-investigation-of-troy/
(n) The Open Court magazine. Vol.XXXII (No.8) August 1918. No. 747 See: https://archive.org/stream/opencourt_aug1918caru/opencourt_aug1918caru_djvu.txt
(o) https://www.ancient-origins.net/ancient-places-europe/location-troy-0011933
(q) https://www.trojanhistory.com/
(r) Manfred Korfmann, 63, Is Dead; Expanded Excavation at Troy – The New York Times (archive.org)
(t) https://web.archive.org/web/20121130173504/http://www.6millionandcounting.com/articles/article5.php
(u) https://leidenuniv.academia.edu/GerardJanssen
(x) http://odisse.me.uk/troy-the-town-bergen-on-the-island-rugen-2.html
(y) https://phdamste.tripod.com/trojan.html
(z) http://www.mikamar.biz/rainbow11/mikamar/articles/troy.htm (Link broken)
(aa) Troy (varchive.org)
(ab) https://chs.harvard.edu/guy-smoot-did-the-helen-of-the-homeric-odyssey-ever-go-to-troy/
(ac) https://www.ancient-origins.net/myths-legends-europe/aeneas-troy-0019186
(ad) https://diggingupthepast.substack.com/p/rediscovering-brutus-of-troy-the#details
(ae) https://anthonyadolph.co.uk/brutus-of-troy/
(af) Someplace else? Alternative locations for Troy – ASLAN Hub
(aj) http://www.academia.edu/7806255/A_NEW_ASTRONOMICAL_DATING_OF_THE_TROJAN_WARS_END
Bible *
The Bible offers no direct reference to Atlantis, but this is not to be seen as proof of its non-existence, when you consider that in spite of the fact that the Hebrews were in Egypt for hundreds of years, the Bible does not mention the pyramids either and they most certainly did then and still do, exist.
The Bible has been invoked as a justification for everything from war to slavery. It has been one of the most divisive books ever, having been instrumental in the creation of hundreds, if not thousands, of competing Christian sects over the last two millennia. It is assumed that any theory, religious or secular that can be shown to have a biblical foundation will automatically have enhanced credibility.
Jean De Serres, the 16th-century historian, was probably the first to link Atlantis with the Bible when he wrote that Atlantis had been located in the Holy Land. Lewis Spence[259.33] accused Huet, Borchart and Vossius, in the 16th and 17th centuries of using ‘ingenious misreading of the Pentateuch’ to claim that the Platonic story of Atlantis was, in reality, a version of patriarchal history. In a similar vein, in 1726 a French lawyer, Claude Olivier, wrote of his conviction that the ten tribes of Israel were to be equated with the ten kingdoms of Atlantis.
The Book of Genesis in particular has inspired speculation regarding a possible link between the Bible and the Atlantis narrative. Ignatius Donnelly in his seminal Atlantis: The Antidiluvian World, devoted Chapter Six to ‘demonstrating’ that Genesis held a history of Atlantis(o).
Therefore, I advise that any new scriptural interpretation must be treated with extreme caution. With that in mind, I mention that an American researcher, J. D. Brady, who claims to be a scriptural scholar and as such has identified Atlantis, drawing on chapters 26-28 of Ezekiel. He refers to the Atlanteans as Tyrrhenians and names their leader as Satan! He claims that the Tyre referred to in these chapters was an island named Tyrus that Plato knew as Atlantis. He offers a range of data to suggest that this Tyrus was not the Tyre we know today located in Lebanon. Brady claims with great certainty that the remains of Atlantis are to be found in the Bay of Troy! A 2014 book[1016] by David Hershiser, Beyond the Pillars of Hercules, has taken up this idea that the reference in Ezekiel was concerned with Atlantis.
Not content with identifying Atlantis, Brady also claims to know the location of the Ark of the Covenant, saying that “It is currently secreted in an underground treasure crypt on Lemnos Island.”(b)
H.S. Bellamy, the Austrian researcher, also produced a volume[097], The Book of Revelation is History, devoted to demonstrating that the last book of the New Testament is a coded description of the catastrophes that accompanied the capture of our Moon! He claimed that the reference to the ten horns is an allusion to the ten Atlantean kings. He also interpreted the Book of Jeremiah I & II as well as Ezekiel as containing references to aspects of the Atlantis story. Earlier, Kurt Bilau had also been seduced by the theories of Hans Hörbiger and also like Bellamy endeavoured to use the Book of Revelations to support this belief.
However, R Cedric Leonard does offer(a) an interesting comparison of a passage in the Old Testament with the classical writers:
“And it came to pass when men began to multiply on the face of the earth, and daughters were born unto them, that the sons of God saw the daughters of men that they were fair, and they took them wives of all which they chose…
There were giants in the earth in those days; and also after, when the sons of God came in unto the daughters of men, and they bare children to them, the same mighty men (heroes) which were of old, men of renown.” (Genesis 6:1-2,4)
This passage has been frequently invoked to support the daft idea that extraterrestrial visitors had intercourse with human females, a contention that was debunked by Klaus Aschenbrenner some years ago(l).
“The mixture between gods and men, which is reported in the sixth chapter of Genesis of the Old Testament, is to be interpreted in a similar way: “Then the children of God looked after the daughters of men, how beautiful they were, and took them for wives, which they wanted … and begot them children.”
The fact that offspring resulted from this union clearly speaks for the earthly origin of those Divine beings. There is a genetic barrier that makes it difficult for similar species to mix. For example, if one tries to cross closely related animal species, such as horses and donkeys, the stallions of the resulting mixed forms of mule or hinny are sterile. We must therefore not expect any offspring from a connection between humans and higher extraterrestrial beings because of the certainly greater genetic differences.”
Leonard points out that this same passage in Genesis coincides with Plato’s history of the Atlanteans and highlights that Hesiod referred to the Titans, of which Atlas was one, as the ‘sons of heaven’.
Leonard also offers a more rational translation of Job 26:5-6 that strengthens this view that the Atlanteans and Titans are identical:
“The Titans tremble beneath the waters and the inhabitants thereof. Hell is naked before him, and destruction hath no covering”.
2011 saw the publication of Atlantis: The Eyewitnesses[749] by Walter Parks in which he also quoted extensively from the Book of Job, having claimed that it was written in 9619 BC and contained an eyewitness account of the catastrophe that destroyed Atlantis!
In 2007, David Stewart Jnr., a prominent Mormon writer, offered support for Flem-Ath’s ‘Atlantis in Antarctica’ theory in an article on his scripture history website(p).
Thorwald C. Franke has reviewed a range of theories that have sought to associate various aspects of Bible history with elements of the Atlantis story. Most are rather speculative, but Franke concludes(d) that “the Bible should not be underestimated: There could indeed be indirect hints to Plato’s Atlantis in the Bible!” Furthermore, he also suggested that “A basic error is to consider the Bible as a source of information on the most ancient times of humankind. In truth, vast parts of the Bible were written only very late (since the 6th century BC). For the question of Atlantis, this is much too late!”
The biblical references to Tarshish are also used by those who equate it with Tartessos and in turn identify it as Atlantis. The location of Tarshish is a highly contentious issue with scholars unable to arrive at any clear consensus. However, there is some agreement that Tartessos had been located in Southern Spain. Some proponents of that idea not only consider Tarshish identical to Tartessos but to Atlantis as well. Richard Freund is a proponent of a Spanish Tartessos, which he also identifies with Atlantis and of course with the biblical Tarshish. This Bible connection was taken further in James Cameron’s 2017 (a) documentary, Atlantis Rising, which shows Simcha Jacobovici also linking Tarshish with Atlantis(h) and offering as ‘evidence’ for a linkage between Atlantis and the Jewish Temple, the design of the Hebrew menorah(g), which he claims is a representation of one half the concentric rings of Plato’s city of Atlantis. This foolish idea is not new, as it has already been suggested by Prof. Yahya Ababni(f). Georgeos Diaz-Montexano has also considered this as a possibility(k).
Turning the tables on the idea of the Bible supporting the story of Atlantis, Marjorie Braymer[198.30] wrote that Cosmas Indicopleustes (6th cent. AD) was the first to use Plato’s Atlantis to support the veracity of the Bible.
Another line of investigation might be the suggested parallels between Greek mythology and Genesis(c). A 2023 paper by Neil Godfrey offers some comments on Plato’s Timaeus and the Biblical Creation Accounts [2066] by Russell E. Gmirkin supporting the idea that the creation of the world and the story of the first humans in Genesis both draw directly on Plato’s famous account of the origins of the universe, mortal life and evil containing equal parts science, theology and myth(n).
A paper on the Academia.edu website(e) by M. De Rosa argues that Atlantis was the ‘Beast’ in the Book Of Revelation!
More recently, a Dutch commentator, Leon Elshout, has also written extensively, in Dutch and English, linking Atlantis and Babylon(i) with details in the Book of Revelation. He claims “that there is a dualistic principle behind Atlantis, expressed by the twin pillars of Hercules and the twin kings, so that Atlantis was mirrored in time and space from Babylon AND Jerusalem.” He also claims that chapters 2 & 7 of the Book of Daniel offer mirror images of the Athenian-Atlantean conflict(m).
Among a number of odd ideas expressed by him is the suggestion that Tarshish was in Britain(j).
(a) See: https://web.archive.org/web/20170607013948/https://www.atlantisquest.com:80/Myth.html
(b) The Ark of the Covenant – on the trail again! – Ritmeyer Archaeological Design (archive.org) *
(c) https://njbiblescience.org/presentations/Greek%20Mythology%20and%20Genesis.pdf
(d) https://www.atlantis-scout.de/atlantis_bible.htm
(e) https://www.academia.edu/6336088/ATLANTIS_AS_THE_BEAST_IN_REVELATIONS
(f) https://mosestablet.info/en/menorah-tablet.html
(g) https://www.wnd.com/2017/02/ocean-explorer-atlantis-found-and-linked-to-jewish-temple/
(h) Lost City of Atlantis And Its Incredible Connection to Jewish Temple (archive.org)
(j) https://roodgoudvanparvaim.nl/8-tarshish-as-great-britain-and-the-paradox-with-atlantis/
(l) They didn’t come from other stars – Atlantisforschung.de (atlantisforschung-de.translate.goog)
(m) 1903.0463v1.pdf (vixra.org)
(o) https://sacred-texts.com/atl/ataw/ataw306.htm
(p) http://scripturehistory.com/atlantisinantarctica.php (link broken)
Brady, J. D. *
Joseph Daniel (Dan) Brady is an American researcher with a particular interest in scripture-related non-fiction mysteries. He has now turned his attention to the question of Atlantis. In a somewhat complicated theory, he makes a distinction between the Phoenician Tyre and the Tyre (Tyrus) whose destruction is described by Ezekiel (26 & 27). He compares the demise of Ezekiel’s Tyre with Plato’s destruction of Atlantis. Brady proceeds to identify the Plain of Troy, formerly a bay, as the final resting place of Atlantis.
In a 2023 email, Brady offered the following clarification of his view of Tyrus and Tyre – “Eze 26:7 (of the KJV translation) says Nebuchadrezzar’s army attacked Tyrus on the day it was destroyed. Eze 26:21 says Tyrus will never be found again. All of the canals dug into the surface of Atlantis weakened its stability, The earthquakes imploded the surface and the floods washed the surface away. The bay at Troy was in the Illiad but is now missing. The fort at Troy needed to be dug out and my conclusion is Plato was referring to this bay when he wrote the subsidence of the island prevents sailing that way anymore. The bay at Troy was filled in by the surface of Atlantis. Tyre is in Lebanon, never lost, finding it is easy. Tyre and Tyrus were different places.
Eze 28:12-13 presents the King of Tyrus as being in Eden. This leads to Satan being the King of Tyrus. In Eze 26, God presents that he was responsible for destroying Atlantis. Eze 28:14 presents Satan as the covering cherub. The lie that Tyre was Tyrus was a cover story that all bible translations, except the King James Version, have accepted. Eze 29:18-20 confirms that Tyrus was destroyed during Nebuchadrezzar’s life. He died c562 BC, Tyre still exists after 2500 years. The story that Tyrus was Tyre does not make sense, but it has succeeded in covering the demise of Tyrus. All bible translations, except KJV, have kicked Tyrus out of the Bible.”
In 2010 Brady published his ideas in a book with the ingenious title of Atlantis, which was available as a paperback[738] and an ebook. Further details can be read on the imdb.com website, which also offers images and videos(e).
He also claims to have located the Garden of Eden as well as having found evidence within the Bible of life on other planets!
Helena Blavatsky was possibly the first to link the biblical Tyrus with Atlantis in The Secret Doctrine[1495]. Brady’s idea that Ezekiel’s Tyrus was not the Phoenician city of Tyre has been taken up by David Hershiser in a 2015 article in Atlantis Rising magazine(d), reprising his book Beyond the Pillars of Hercules[1016]. However, while Brady locates his Tyrus/Atlantis at Troy, Hershiser has placed his Tyrus/Atlantis in the Atlantic just beyond the Strait of Gibraltar.
In 2014 Brady published a revised edition of his book with a new title, Atlantis: The Renamed Island[986], in which he claims that Atlantean gold treasure was hidden in a labyrinth on the Greek island of Lemnos. He further claims that Plato located Atlantis between Lemnos and Troy, in front of the Dardanelle Straits!(b) Jason Colavito has reviewed Brady’s claim of treasure(c).
(b) Atlantis: The ReNamed Island book by Joseph Daniel Brady (thriftbooks.com) *
(d) See Archive 3395
(e) https://www.imdb.com/name/nm14658916/ *


