Robert Graves
Laestrygonians
Laestrygonians, we are told by Homer were mythical giants encountered by Odysseus on his return journey to Ithaca.
Wikipedia tells us that “according to Thucydides (6.2.1.) and Polybius (1.2.9) the Laestrygones inhabited southeast Sicily. The name is akin to that of the Lestriconi, a branch of the Corsi people of the northeast coast of Sardinia (now Gallura). Later Greeks believed that the Laestrygonians, as well as the Cyclopes, had once inhabited Sicily.
“According to historian Angelo Paratico, the Laestrygonians were the result of a legend originated by the sight by Greek sailors of the Giants of Mont’e Prama, recently excavated in Sardinia. Earlier, Victor Bérard had also suggested Sardinia.
Some writers have also sought to attribute a historical reality to the Laestrygonians, often proposing locations very different to that of Thucydides and Polybius. Emmet Sweeney [700.23] has noted that Robert Graves who invariably placed the Greek myths in a Mediterranean setting, suggested that the home of the Laestrygonians was to be found in the far north of Europe, in the Land of the Midnight Sun!
Equally exotic is the suggestion from Gerard W.J. Janssen of Leiden University who places the voyages of Odysseus in the Atlantic(b). However, although he situates most of the places visited in the eastern Atlantic, he does claim(a) that Homer‘s Laestrygonians were to be found in Cuba, an interpretation supported by both Théophile Cailleux and Iman Wilkens.
(a) LAISTRUGONIACUBA, LA HAVANA (homerusodyssee.nl)
(b) https://www.academia.edu/38535990/ATLANTIC_OGUGIA_AND_KALUPSO?email_work_card=view-paper
Doggerland
Doggerland is a term applied to a shallow region (Fig.1) of the North Sea between Denmark and the North of England that covers an area of around 10,000 sq. miles. The existence of Doggerland was first suggested in a late 19th-century novel by H.G. Wells entitled A Story of the Stone Age.>>In 1913, the British geologist, Clement Reid, published his study of the North Sea that included a proposed map of the landbridge that had connected Britain with mainland Europe during the last Ice Age.<<
The appellation ‘Doggerland’ was coined by Professor Bryony Coles in 1998. However, the name has been applied recently(f) to nearly the totality of the Celtic Shelf (Fig.2). Ulf Erlingsson who had promoted his theory(b) that Atlantis h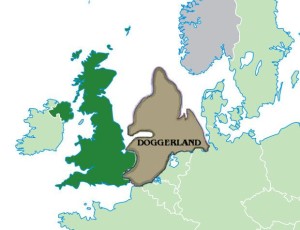 ad been located in Ireland (with 98.9% confidence!) has explained that the Egyptian story of Atlantis is the result of an account of megalithic Ireland conflated with a report of the inundation of Doggerland in 6200 BC resulting from a Norwegian storegga(ad).
ad been located in Ireland (with 98.9% confidence!) has explained that the Egyptian story of Atlantis is the result of an account of megalithic Ireland conflated with a report of the inundation of Doggerland in 6200 BC resulting from a Norwegian storegga(ad).
According to some, this flooding may have been the inspiration behind the ‘impassable shoals’ described by Plato following the submergence of Atlantis.
However, it was Rachael Carson who was probably the first to suggest the Dogger Bank as the home of Atlantis in her 1951 book, The Sea Around Us[1267]. Later a Scandinavian writer, Nils Olof Bergquist, in his 1971 book, Ymdogat-Atlantis[785]. who appeared next to support this idea.
Other writers such as Jean Deruelle(a), Sylvain Tristan(c) and Guy Gervis(d) have also linked the Dogger Bank with Atlantis. Gervis has written two related papers(k)(l) on the subject. The earliest suggestion of such a connection was briefly supported by Robert Graves[342.39-3]. Rob Waugh, a British journalist, has offered an illustrated article(g) with the provocative title of Britain’s Atlantis found at the Bottom of the North Sea, in which he touches on some of the discoveries made on Doggerland.
In 2003, Georg Lohle put forward the idea that Atlantis had been situated in the North Sea between Denmark and Britain and destroyed around 2200 BC. He based this speculation on the content of the controversial Oera Linda Book(ac).
Some have combined Doggerland with exposed land further north, now known as the Viking-Bergen Banks, as having constituted the territory of Atlantis(x).
In 2009 a book[662] was published with the subtitle of The Rediscovery of Doggerland, based on the research of a team led by Professor Vincent Gaffney of the University of Birmingham. In July 2012 the UK’s Daily Mail published(h) an extensive article on Doggerland.
The flooding of the Dogger Bank has been attributed to a 6200 BC event apparently caused by either an outpouring of meltwater from Lake Agassiz in North America or a huge tsunami generated by a Norwegian storegga(e). This event was covered in an extensive article in the November 2012 edition of the BBC Focus magazine. The same article has a sidebar on Atlantis which suggests that there is “perhaps just one archaeological theory that has any serious claim on the myth.” Then, not for the first time, the BBC offered tacit support for the Minoan Hypothesis in spite of the fact that, at least ostensibly, it does not match Plato’s description of Atlantis in terms of either time, size or location and offers no rationale for its stance.
In December 2020, a degree of revisionism was offered in a New Scientist article, which suggested that storegga tsunami may have been less than previously thought. Furthermore, it proposes that parts of what is now the submerged Dogger Bank was not completely flooded by the tsunami, but that parts continued as dry land, perhaps for centuries!(y)
“For a long time, scientists assumed that a tsunami of this kind also caused the Dogger Bank, which was still protruding from the sea, to sink completely. According to a study by researchers at the University of Bradford, however, there was no single, all-destroying tsunami.
Rather, by examining sediments, the researchers were able to prove that only the northern part of Doggerland was submerged after the tsunami and that the destructive force of its floods was probably slowed down by hills or forests on the island.
However, after the water receded, the flooded area recovered over the years, as is demonstrated by the fact that evidence of plants and animals can be found again in the sediment layers above the disrupted tsunami layer.” There is a suggestion that Heligoland may be the last remnant of Doggerland.(ab)
It has been estimated that over a period of a couple of hundred years, the English Channel was also created in a comparable manner(n).
The December 2012 edition of National Geographic magazine also published an informative article on Doggerland and the ongoing work by archaeologists in the region. It considers the Storegga or the Lake Agassiz meltwater to be the cause of Doggerland’s final inundation. For me, it was interesting that a map in the article showed a small area around where I live as the last glaciated region of Ireland.
Alfred de Grazia’s online Q-Mag also published an overview of the Doggerland story in 2012(j) that was originally taken from the German magazine Der Spiegel. The same site has another paper(r) by Jean  Deruelle in which he also argues that Doggerland was the location of the Great Plain of Atlantis that stretched from the east of the Dogger Bank and extended as far as what is now Denmark. Plato described the plain as being surrounded by a huge ditch. Then Deruelle, with a flash of ingenuity claims that it was not a ditch but instead was a dyke, designed to hold back the slowing advancing waters of the North Sea that were being fed by deglaciation. He endeavoured to reinforce this claim with the proposal that the Greek word for a ditch, ‘taphros’ can also be used for dyke. This interpretation seems possible according to W.K. Pritchett, a distinguished historian [1622.52.5].
Deruelle in which he also argues that Doggerland was the location of the Great Plain of Atlantis that stretched from the east of the Dogger Bank and extended as far as what is now Denmark. Plato described the plain as being surrounded by a huge ditch. Then Deruelle, with a flash of ingenuity claims that it was not a ditch but instead was a dyke, designed to hold back the slowing advancing waters of the North Sea that were being fed by deglaciation. He endeavoured to reinforce this claim with the proposal that the Greek word for a ditch, ‘taphros’ can also be used for dyke. This interpretation seems possible according to W.K. Pritchett, a distinguished historian [1622.52.5].
Robert John Langdon has proposed that megalith builders from Africa came to Doggerland as the Ice Age ended and when Doggerland submerged they migrated to what is now mainland Britain, eventually constructing Stonehenge(i). But Langdon has gone further and also claims that Doggerland was actually Atlantis(aa).
A 2014 ‘Drowned Landscapes’ exhibition(m) organised by Dr Richard Bates of the Department of Earth Sciences at St Andrew’s University, reveals in greater detail the flora and fauna, as well as the lives of its inhabitants, of this submerged world. Much of the information was gleaned from data provided by oil and gas companies, combined with artefacts recovered from the seafloor.
Comparable discoveries have been made submerged deep under the waters of Hanö Bay near the coast of Havang, Sweden and dated to about 7000 BC(v).
In 2015 it was announced that €2.5 million in funding from the European Union has enabled a number of archaeologists from Britain’s top universities to team up for what will be the most intensive study of Doggerland so far(o)(q). Joined by experts from the University of Ghent and assisted by the Belgian Navy they located the first identifiable submerged settlements on the floor of the North Sea. Until now (2019) the only evidence of human habitation in the region were occasional artefacts caught up in fishermen’s nets.
In 2016, it was revealed(p) that the ancient footprints of both adults and children had been discovered off the coast of Northumberland, formerly a part of Doggerland. Their feet had apparently been shod.
On Sunday, January 13th, 2019. the UK’s Sunday Express delighted its readers with two Atlantis stories(t)(u). First, the online edition of the paper had a story by one of its reporters, with an ‘Atlantis Discovered’ headline claiming that the remains of an ancient 8,000-year-old city, home to ‘tens of thousands’ of people, had been discovered in the North Sea, in a huge region sometimes referred to as Doggerland. The reporter cites Dr Richard Bates in support of this account. Unfortunately, the 2012 comments by Dr Bates never mentioned ‘a city’, but a vast area occupied by ‘tens of thousands’ of people, presumably early farmers(s). Then the same edition of the same paper by the same ‘reporter’ with another ‘Atlantis Found?’ headline, offered a video clip of the Maltese island of Filfla, while the commentator told us that Plato had said that a devastating earthquake had destroyed Atlantis it was finished off by an eruption. This is factually incorrect as Plato never mentioned an eruption. These two accounts are a sad reflection of the quality of media reporting today.
In 2020, David Keys, author of Catastrophe [1330] wrote an article for the UK’s Independent newspaper outlining the most recent research into the 6200 BC tsunami that destroyed Doggerland. “It is estimated that multiple giant waves inundated some 2,700 square miles of land – from Scotland in the north to Norfolk in the south.
New underwater research carried out by the universities of Bradford, Warwick, St Andrews and Wales has for the first time discovered that the tsunami devastated parts of East Anglia and adjacent land which is now submerged beneath the southern part of the North Sea.” (z)
In 2021, the UK’s Guardian reported on an “exhibition, ‘Doggerland: Lost World in the North Sea’, at the Rijksmuseum van Oudheden (National Museum of Antiquities) in Leiden, southern Holland, includes more than 200 objects, ranging from a deer bone in which an arrowhead is embedded, and fossils such as petrified hyena droppings and mammoth molars, to a fragment of a skull of a young male Neanderthal. Studies of the forehead bone, dredged up in 2001 off the coast of Zeeland, suggests he was a big meat eater.”(ae)
Graham Phillips‘ latest offering is The Mystery of Doggerland: Atlantis in the North Sea [2063], published in late July 2023.
(b) http://atlantisinireland.com/
(c) http://spcov.free.fr/site_nicoulaud/en/empire.php
(d) See: https://web.archive.org/web/20180320072706/https://nwepexplore.com/
(g) https://www.bibliotecapleyades.net/atlantida_mu/esp_atlantida_38.htm
(i) http://www.the-stonehenge-enigma.info/#!/2013/06/stonehenge-atlantis-momentous-discovery.html
Also See:https://atlantipedia.ie/samples/archive-2071/
(j) https://www.q-mag.org/doggerland-lost.html
(k) See: Archive: 2073
(l) See: Archive 2074
(n) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Doggerland
(q) https://www.q-mag.org/doggerland-to-be-digitally-repopulated.html
(s) https://www.guidememalta.com/en/all-you-need-to-know-about-the-mysterious-islet-of-filfla
(t) https://www.bbc.com/news/uk-scotland-edinburgh-east-fife-18687504
(v) https://www.thevintagenews.com/2017/01/17/the-discovery-of-the-submerged-stone-age-atlantis/
(x) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tbenuEzWgQk
(y) Tiny island survived tsunami that helped separate Britain and Europe | New Scientist
(aa) Chapter 3 – Atlantis – Dawn of the Lost Civilisation (archive.org) *
(ab) https://www.dw.com/en/doggerland-how-did-the-atlantis-of-the-north-sea-sink/a-55960379
(ac) Atlantis is a myth or real past (archive.org)
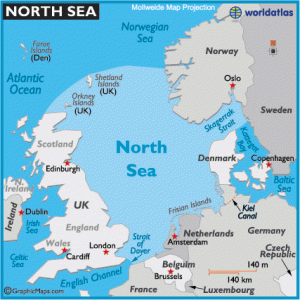
North Sea *
The North Sea has been advocated by a variety of writers as the original site of Atlantis. Jürgen Spanuth specified his native Heligoland as its location in his well-researched work, Atlantis of the North[015]. However, Spanuth was not the first to make this suggestion as Heinrich Pudor, had advocated Helgoland as Atlantis in the 1930’s [1693][1694], but was unreferenced by Spanuth.
Robert Scrutton drew heavily on the contents of the controversial Oera Linda Book to support his view of an Atlantis or Atlantean colony in the Frisian Islands of the North Sea[117][118].
Georg Lohle in his book[446] on world history identifies a location between England and Denmark that was inundated about 2000 BC. He also makes extensive use of the Oera Linda Book. His German language website(a) has a wide range of photos and diagrams. Lohle daringly resurrects the old idea of the Earth being hollow and then combines it with another controversial concept, namely that it is still expanding(b).
In the middle of the 20th century we find Robert Graves and Rachel Carson were probably the first to suggest the Dogger Bank as the location of Atlantis. More recently Jean Deruelle(e), Sylvain Tristan(c) and Guy Gervis(d) have all opted for a location near the Dogger Bank, now more popularly known as Doggerland.
The most recent challenger for the Atlantis title is located in the vicinity of Rockall, an uninhabited islet north west of Ireland.
(a) See: https://web.archive.org/web/20161113122829/https://www.erdexpansion.de/atlantis.htm
(b) See: https://web.archive.org/web/20180307141731/https://www.grisda.org/origins/15053.htm
(c) Atlantis ist ein Mythos oder reelle Vergangenheit (archive.org) *
(d) See: Archive 3606
(e) atlantide (archive.org) *
Graves, Robert
 Robert von Ranke Graves (1895-1985), the renowned poet and mythologist, placed Atlantis[342] in the region of modern Tunisia and Libya. He first did this in a 1953 article(c) that followed the writings of Diodorus Siculus. He firmly believed that the salts marshes of North Africa were the remnants of Lake Tritonis where Atlantis had existed before a destructive catastrophe that led to the dispersal of its survivors in various directions. However, Jean Deruelle[278] claims that Graves was the first, if briefly(b), to suggest the Dogger Bank as the location of Atlantis.*It seems that he quickly abandoned this idea>because the North Sea inundation was too early(d.89).<
Robert von Ranke Graves (1895-1985), the renowned poet and mythologist, placed Atlantis[342] in the region of modern Tunisia and Libya. He first did this in a 1953 article(c) that followed the writings of Diodorus Siculus. He firmly believed that the salts marshes of North Africa were the remnants of Lake Tritonis where Atlantis had existed before a destructive catastrophe that led to the dispersal of its survivors in various directions. However, Jean Deruelle[278] claims that Graves was the first, if briefly(b), to suggest the Dogger Bank as the location of Atlantis.*It seems that he quickly abandoned this idea>because the North Sea inundation was too early(d.89).<
Further confusion is added by an entry in Wikipedia that claims(a) that Graves argued that Atlantis was the Island of Pharos off the western coast of the Nile Delta, that is before Alexander the Great connected the island to mainland Egypt by building a causeway.>What he did say was that “perhaps as the result of a submarine earthquake, the enormous harbour works built by the Keftiu (‘sea-people’, meaning the Cretans and their allies) on the island of Pharos and, subsided under seven fathoms of water.”(d.89)<
In The Greek Myths, Graves considered the likelihood that the Atlantis story was comprised of several components from different legends. It may be relevant to include Graves’ definition of myths, which was “whatever religious or heroic legends are so foreign to a student’s experience that he cannot believe them to be true.”
(a) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Location_hypotheses_of_Atlantis
(b) https://www.q-mag.org/the-great-plain-of-atlantis-was-it-in-doggerland.html
(c) The Atlantic Monthly, October 1953, (pp.71-74)
(d) Robert Graves – The Greek Myths 1955, revised 1960 (abcdocz.com) *
Plain of Atlantis
The Plain of Atlantis is one of the principal features recorded by Plato in great detail. He describes it being “3000 stades in length and at its midpoint 2000 stades in breath from the coast” (Critias 118a, trans. Lee). The shape of the plain is frequently given as ‘rectangular’ or ‘oblong’ and contained an efficient irrigation system that was fed by mountain streams. The fertility of the plain gave the inhabitants two crops annually.
The dimensions given by Plato would translate into 370 x 555 km (230 x 345 miles). However, the late Ulf Richter has recently proposed(a) that the dimensions originally given to Solon by the priests of Sais used the Egyptian ‘khet’ (52.4 meters) as the unit of measurement. Possibly Solon recorded the figures without mentioning the units employed. In Ireland, we changed over to the metric system some years ago, but builders still speak and write of using ‘2×4’ lengths of timber without specifying that they are referring to inches. Such unqualified notations made at present could be interpreted in the future as 2×4 centimetres. This illustrates how reasonable Richter’s suggestion is. The acceptance of it would give us a more credible 105 x 157 km (65 x 97 miles) as the dimensions of this plain. Richter also maintains that the plain was in fact a river delta, which explains the remarkable fertility of the land.
Rich McQuillen has adopted Richter’s suggestion that there was some unspecified translation confusion regarding the use of the Egyptian ‘khet’ or the Greek ‘stade’ by Solon. The revised dimensions led McQuillen to propose territory adjacent to Canopus at the mouth of the Nile as the location of the Plain of Atlantis. Canopus along with nearby Pharos and Herakleoin were destroyed by liquefaction resulting from an earthquake. McQuillen’s ideas also coincide with Richter’s additional proposal that Atlantis was situated on a river delta(a).
Paul Dunbavin offered a number of possible explanations of how the obvious exaggeration of Plato’s numbers occurred(f). He suggests that “Regardless of how the original story came to be recorded by the priests of Sais, they too must have translated the dimensions from a native (Atlantian) source. The chain of preservation goes something like this:
- Recorded in unknown local units of measure
- Transmitted by traders or colonists to archaic Egypt
- Recorded by the Saite priests when the temple was built
- Transcribed numerous times up to the era of Solon
- converted to Greek units by/for Solon
- Interpreted by Plato for his narratives
- Translated for modern readers by Greek scholars
Errors could have been introduced at any of these intermediate stages in the preservation of the history. Therefore other than to conclude that the measurements are sensibly too large by a huge multiple then it becomes fruitless to seek a submerged rectangular plain of any precise scale; be it in the Atlantic or Mediterranean.”
However, I am not convinced that the problem with Plato’s numbers is a matter of misunderstanding the units of measurement used. As I pointed out in Joining the Dots [p89] “The numbers attributed to the Atlantean military appear to be just as extravagant as Plato’s other figures for time, distance, and area. Now, where months can be substituted for years and khets for stades, soldiers are units in any language and so Plato’s excessive manpower figures cannot be explained away by claiming there had been some confusion over the unit of measurement employed.”
My conclusion is that we should be looking at the possible manner in which an alien numerical notation system was misunderstood somewhere along that chain of transmission listed above by Dunbavin. For those that claim that Plato concocted the entire Atlantis story, it should be obvious that if he had, he would have offered more credible data, but, apparently in deference to Solon, repeated the numbers recorded by him.
Galanopoulos and Bacon commenting [263.36] on the plain described in Critias 118a-e concluded that Plato had been referring to a second plain, “Next, the plain surrounding the city does not appear to be the same as the one close to the Ancient Metropolis since this lay in the centre of the island at a distance of 50 stades (6 miles) from the sea. Whereas the plain surrounding the City was 3,000 stades (340 miles) and 2,000 stades (227 miles) wide; and so the centre of this plain must have been very much more than six miles from the sea. The attempt to reconcile these statements by suggesting that the Ancient Metropolis was not in the centre of the island but close to the sea in the middle of one of the sides of the island likewise will not work in view of the passage (Critias 113d) which states that the belts of water encircling the metropolis were everywhere equidistant from the centre of the island.”
Jim Allen, who supports an Andean location for Atlantis, offers a strong argument against other principal Atlantis candidates by critically examining the plains included in alternative location theories(c). However, it must be pointed out that Allen had to divide Plato’s dimensions for the plain by two in order to shoehorn it into his chosen location.
While I accept that there is evidence that there was flooding on the Altiplano, it took place some thousands of years before the Bronze Age Atlantis described by Plato and certainly long before he wrote “this is why the sea in that area is to this day impassible to navigation, which is hindered by mud just below the surface, the remains of the sunken island.” (Timaeus 25d – Desmond Lee) This is not a description that can be applied to anywhere on the Altiplano during the 1st millennium BC. Apart from that, Plato’s account clearly states that Atlantis was submerged and was still so in his own day, making Allen’s critique somewhat redundant.
An interesting suggestion, although badly flawed, was made by Jean Deruelle who proposed ‘Doggerland‘ in the North Sea as the location of Atlantis, adding an interesting twist to Plato’s description of the Plain. “Deruelle, an engineer and a geologist by profession, offers a hypothesis that is rational, highly precise, and based on his areas of expertise. No other hypothesis than Deruelle’s tackles so credibly the most outlandish elements in Plato’s description of Atlantis: the description of a vast plain, surrounded by a man-made ditch, 180 meters broad and thirty meters deep, large enough to circulate supertankers: it was not a ditch, but a dyke, build over centuries to protect a large part of Doggerland against the slowly rising waters of the North Sea.”(d)
Diaz-Montexano maintains that Plato never said that the plain was shaped like a rectangle.
The Mediterranean, between Sicily and North Africa, has been offered by a number of commentators, such as Alberto Arecchi and Alex Hausmann, as the location of the Plain of Atlantis. There is evidence of large areas of land having been submerged within the region between Malta and the Pelagie Islands. I include here a passing reference from Ernle Bradford who sailed the region which may be of interest to supporters of a Central Mediterranean Atlantis. When discussing the Egadi Islands off the west coast of Sicily he describes Levanzo, the smallest of the group as being “once joined to Sicily, and the island was surrounded by a large fertile plain. Levanzo, in fact, was joined to more than Sicily. Between this western corner of the Sicilian coast and the Cape Bon peninsula in Tunisia there once lay rich and fertile valleys-perhaps, who knows, long lost Atlantis?” [1011.57]
The number of different locations that have been proposed for the plain is obviously a reflection of the number of sites suggested for the city of Atlantis. I list the most popular below with the added comment that, at best, only one can be correct while all may be wrong.
Plain of Atlantis
Mauritania (David Edward)
Mesara Plain on Crete (Braymer)
Central Plain of Ireland (Erlingsson)
Sea of Azov (Flying Eagle & Whispering Wind)
Altiplano of Bolivia (Jim Allen)
Andalusian Plain (Diaz-Montexano)
North Sea (Doggerland) (Jean Deruelle)
Plain of Catania, Sicily
Plain of Campidano, Sardinia (Giuseppe Mura)
Souss-Massa Plain, Morocco (Michael Hübner) (Mario Vivarez)
Greenland (Mario Dantas)
Beni, Bolivia (David Antelo)
Mesopotamia in Argentina (Doug Fisher)
Black Sea (Werner E. Friedrich) (George K. Weller)
Plain of Troy (J.D.Brady)
South of England (E.J. deMeester)
Carthage (Pallatino & Corbato)
Celtic Shelf (Dan Crisp)
Western Plain, Cuba (Andrew Collins)
Portugal (Peter Daughtrey)
Off the coast of Wales (Paul Dunbavin)
Florida (Dennis Brooks)
Atlantic Floor (Michael Jaye)
Baffin Bay, Greenland (Ian Fox)
Between Sicily and Malta (Axel Hausmann)
Pannonian Plain, Hungary+(Ticleanu, Constantin & Nicolescu)
Guadalete River Plain (Karl Jürgen Hepke)
Mouth of the Nile (Rich McQuillen) (Robert Graves)
South China Sea Indonesia (Dhani Irwanto) (Bill Lauritzen)
Saudi Arabia (Stan Deyo)
Venezuelan Basin (Caribbean) Brad Yoon (P.P. Flambas)
Yucatan Peninsula (Mark Carlotto)(b)
(a) https://web.archive.org/web/20160326200714/https://www.atlantis-schoppe.de/richter.pdf
(b) A Commentary on Plato’s “Myth” of Atlantis – Before Atlantis
(c) https://web.archive.org/web/20200707234820/http://www.atlantisbolivia.org/plaincomparison.htm
(d) https://www.q-mag.org/the-great-plain-of-atlantis-was-it-in-doggerland.html
(f) file:///C:/Users/Tony/Downloads/An_Atlantis_Miscellany.pdf *
Pharos
 Pharos in the Nile Delta has been suggested by R. McQuillen as the location of Atlantis. It should be noted that the cities of Canopus and Herakleion in the same area were submerged, apparently due to liquefaction(h), following an earthquake between 731 and 743 BC. If something similar occurred to Atlantis situated at Pharos it might explain the shoals of mud reported by Plato and may even have been the reason for the erection of the famous lighthouse there, completed around 280 BC.
Pharos in the Nile Delta has been suggested by R. McQuillen as the location of Atlantis. It should be noted that the cities of Canopus and Herakleion in the same area were submerged, apparently due to liquefaction(h), following an earthquake between 731 and 743 BC. If something similar occurred to Atlantis situated at Pharos it might explain the shoals of mud reported by Plato and may even have been the reason for the erection of the famous lighthouse there, completed around 280 BC.
This lighthouse at Pharos took 20 years to build and is reported to have been as much as 450 feet in height, topped with a statue of Poseidon (or Zeus). It is claimed that there was also a furnace on top which, according to Robert Temple [928], suggested that some form of mirror reflected light out to sea. There is evidence from writers as early as Homer that nocturnal sea travel was commonplace in ancient times(d), so some system of beacons to assist this, would have been a natural development.
Themistocles (524-459 BC) is traditionally credited with having established the first Greek lighthouse at Athens’ port, Piraeus, in the 5th century BC, which was a column with a beacon on top.
The coining of ‘pharology’ as a term to describe the study of lighthouses is generally credited to the British hydrographer John Purdy (1773-1843).
In a study of ancient lighthouses (pharology) by Ken Trethewey(a), now a retired marine engineer, he indicates that there were probably precursors to the Alexandrian edifice, but that there is no archaeological evidence to support this contention. Just as New York’s Empire State Building could not have been built without the preceding decades of evolution of building methods, similarly, the magnificent Pharos lighthouse must have had forerunners.
Another suggestion is that altars, temples and latterly Christian churches frequently situated at the end of promontories may have functioned initially as navigational aids, keeping in mind that early Mediterranean seafarers preferred coastal hugging to open sea travel. I would think it strange if such locations were not used for beacons.
A book review by Terrance M.P. Duggan draws attention to the use of the word ‘pharos’ as far back as Homer’s time, centuries before the Alexandrine structure was built(c). Duggan has also noted in an extensive study of ancient beacons(d) how “sailing at night was practiced in antiquity, first by the Phoenicians” and that “later, sailing at night is mentioned repeatedly by Homer in the Odyssey.” It must be obvious that such regular nocturnal travel could not have been achieved without the availability of some system of warning beacons.
Duggan also notes the use of false beacons such as in the story of “Palamedes’s father, the King of Naupilus or Euboea, then lit a series of false beacons leading to the shipwreck off Euboea of much of the Achaean fleet returning from the Trojan War, using false maritime navigational beacons to serve as a wrecker’s device, and with the use of these false navigational beacons quite clearly indicating the presence at this date of considerable numbers of genuine navigational beacons along coastlines to provide an expected navigational guide for ships sailing through the night.“
What I also found interesting was another quote by Duggan of a passage from Al-Mas’udi, circa 947 AD – “At the point where the Mediterranean Sea joins the Atlantic Ocean, there is a lighthouse of stone and copper (bronze), built by the giant Hercules (probably to be associated with the location of the Phoenician Temple of Melkart-Herakles on the North African side). It is covered with inscriptions and statues whose hand gestures proclaim to those coming from the Mediterranean who wish to enter the Atlantic Ocean, ‘There is no way beyond me’” This is a clear association of Heracles with a lighthouse and raises the question of whether this was a more widespread occurrence, which seems possible.
At the other end of the Mediterranean, the Colossus of Rhodes is also thought by some(g) to have functioned as a lighthouse, but at the very least was a daytime navigational marker, Heracles was also worshipped on the island as the founder of its first settlement.
The Tower of Hercules is an ancient Roman lighthouse on a peninsula about 2.4 km (1.5 mi) from the centre of the town of A Coruña, Galicia, in north-western Spain. There is also a claim that a Roman lighthouse existed at Akko (Acre), now in northern Israel, which is discussed elsewhere and supported by numismatic and archaeological evidence(i).
Massimo Rapisarda & Marcello Ranieri have now published a paper(f) pointing to possible land-based navigational aids, most likely, Phoenician, at the Sicilian promontory of Capo Gallo. They also refer to “the renowned Phoenician ability to navigate at night.”
Trethewey, a leading pharologist, published Ancient Lighthouses [1667] in 2018. Furthermore, he has also published a series of eight lengthy papers on pharology on the academia.edu website(e).
>The prolific Dr. Uday Dokras in his work on the lighthouse at Alexandria wrote that it “was certainly not the first such aid to ancient mariners but it was probably the first monumental one. Thasos, the north Aegean island, for example, was known to have had a tower-lighthouse in the Archaic period, and beacons and landmarks were widely used by cities to help sailors across the Mediterranean. Ancient lighthouses were built primarily as navigational aids for where a harbour was located rather than as a warning of hazardous shallows or submerged rocks, although, because of the dangerous waters of Alexandria’s harbour, the Pharos performed both functions.” (l)<
Other papers by Marco Vigano also investigate the subject of proto-lighthouses(b)(j), furthermore, a book review by Terrance M.P. Duggan, draws attention to the use of the word ‘pharos’ as far back as Homer’s time, centuries before the Alexandrine structure was built(c). Duggan has also written a paper on The Missing Navigational Markers(d).
A recent book, The Electric Mirror on the Pharos Lighthouse[948], edited by Larry Brian Radka, argues spiritedly for the use of electricity at Pharos!
Robert Graves suggested a number of locations as having Atlantean connections. Included in that list is Pharos(k).
(a) https://www.academia.edu/Documents/in/Ancient_lighthouses
(d) https://www.academia.edu/7665901/On_the_Missing_Navigational_Markers?auto=download
(e) https://www.academia.edu/Documents/in/Lighthouses
(g) https://www.athensjournals.gr/mediterranean/2019-5-1-2-Kebric.pdf
(h) Science Notes 2001: The Sunken Cities of Egypt (ucsc.edu)
(i) https://www.researchgate.net/publication/236849769_The_Roman_Lighthouse_in_Akko_Israel
(j) http://www.arigenova.it/wail/Articoli/Pharology.pdf
(k) Pharos and the Atlantis legend – Atlantisforschung.de (atlantisforschung-de.translate.goog)
(l) https://archive.org/stream/lighthouse-of-alexandria-book/Lighthouse%20of%20Alexandria-BOOK_djvu.txt *
Rockall *
Rockall is an uninhabited islet in the North Atlantic, northwest of Donegal in Ireland. It appears to have been first marked on a map in 1640(c). It is first mentioned in literature in 1716 and referred to by locals as Rocabarraigh, which is also the name of “a mythical rock which is supposed to appear three times, the last being at the end of the world.”(m).
This ostensibly insignificant piece of stone is around 80ft by 100ft at the base and approximately
70ft in height. Nevertheless, its ownership is disputed by Ireland, Iceland, the Faroe Islands and the United Kingdom.
Rocabarraidh which was a mythic island referred to in the folklore of the Lordship of the Isles, a Scottish title, is generally accepted to be an early allusion to Rockall. The Atlantic rock is considered as part of the Hebridean parish of South Harris.
In June 1997, Greenpeace declared Rockall to be the independent state of Waveland(f).
Jean Deruelle credits Robert Graves with being the earliest, although only briefly, to consider the Rockall Bank as the location of Atlantis(e).
Recently, a new claim has been made in connection with Rockall, namely, that it is a remnant of the Atlantis highlands, with the plain so vividly described by Plato, now situated under the sea to the southwest of the rock. Two extensively illustrated French websites(a)(b) expound this theory. Which, however, are somewhat less than convincing. However, a 1938 newspaper report(d) suggests that a proposed linkage with Atlantis goes back much further!
In December 2016, Jonathan Northcote published 16.484ºW 58.521ºN, Atlantis, Found?[1369], in which he offers spirited support for this location using a mass of geological data and underwater topography. He also suggests that Gades may have been Ireland. In January 2019, Northcote revised his book with additional material and published this second edition with the title of Atlantis, Found? An investigation into ancient accounts, bathymetry and climatology [1611].
Stuart L. Harris, the prolific American researcher, has, in recent private correspondence with me, supported the vicinity of Rockall as the location of Atlantis, dating its demise to around 9577 BC. He later expanded on this in a highly speculative paper published on the Academia.edu website.
At the end of September 2018, the UK’s Daily Star, a well-known comic for adults, tried to revive the idea of Atlantis in Frisland(g). They based their brief article on the speculations of Matt Sibson, presented as an ‘expert’, who admits that “there are still some questions that need clearing up.” I would like to know why Frislanders in the middle of the last Ice Age would want to attack a non-existent Athens 4,000 km away. If Sibson is considered to be an expert historian, my cat is a brain surgeon. Jason Colavito had a few words to add regarding Sibson’s pathetic claims(h).
Incredibly, a week later the same ‘newspaper’ cited Sibson again, this time claiming that Rockall was the remains of Atlantis(i), an equally silly idea that is not new. The UK’s online Express recycled this nonsense in January 2020(k).
Kevin A. & Patrick J. Casey have published a series of papers on the Academia.edu website outlining a globally catastrophic event that occurred thirteen thousand years ago, which they refer to as the ’13K Event’, but is more popularly known as the onset of the Younger Dryas period. In February 2019, they published Atlantis Revisited (j), in which they claim that Rockall was the location of Atlantis.
Less extreme is a claim by John Esse Larsen that in support of the theory that Homer’s Odyssey refers to adventures in the North Atlantic he suggests that Rockall is referenced in Odyssey 10.513(l).
(a) https://web.archive.org/web/20191013063335/http://rockallatlantis.com/francais/cerclespiraleos.html
(c) http://adsabs.harvard.edu/full/1955IrAJ….3..202L or Wayback Machine (archive.org) *
(e) https://www.q-mag.org/the-great-plain-of-atlantis-was-it-in-doggerland.html
(f) See: https://web.archive.org/web/20180420165734/https://www.waveland.org/history.html
(h) https://www.jasoncolavito.com/blog/dissecting-this-past-weekends-faulty-claims-about-ancient-history
(j) https://www.academia.edu/38380799/13k_Theory_Atlantis_Revisited.pdf
(l) http://odisse.me.uk/rockall-the-monster-boulder-in-the-north-atlantic-2.html