Edward Dumergue
Lake Tritonis *
Lake Tritonis is frequently referred to by the classical writers. Ian Wilson refers to Scylax of Caryanda as having “specifically described Lake Tritonis extending in his time over an area of 2,300 km2.“ He also cites Herodotus as confirming it as still partly extant in his time, a century later, describing it as a ‘great lagoon’, with a ‘large river’ (the Triton) flowing into it.[185.185]
Lake Tritonis was considered the birthplace of Athene, the Greek Goddess of Wisdom, after whom Athens is named. The exact location of the lake is disputed but there is some consensus that the salty marshes or chotts of central Tunisia and North-East Algeria are the most likely candidates. It appears that these marshes originally formed a large inland sea connected to the Mediterranean but due to seismic activity in the area were cut off from the sea. Diodorus Siculus records this event in his third book.
I should also mention that Lake Tritonis along with the Greek island of Lemnos and the river Thermodon in northern Turkey, now known as Terme Çay, have all been associated with the Amazons(d).
Edward Herbert Bunbury, a former British MP, included a chapter(a) on Lake Tritonis in his 1879 book on the history of ancient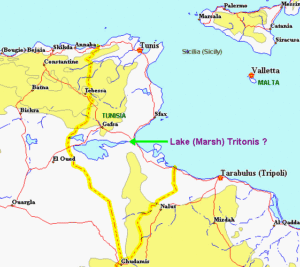 geography [1531.v1.316]+.
geography [1531.v1.316]+.
In 1883, Edward Dumergue published[659]+ a brief study of the Tunisian chotts, which he concluded were the remnants of an ancient inland sea that had been connected to the Mediterranean Sea at the Gulf of Gabes.
Lucile Taylor Hansen in The Ancient Atlantic[572], has included a speculative map taken from Reader’s Digest showing Lake Tritonis, around 11.000 BC, as a megalake covering much of today’s Sahara, with the Ahaggar Mountains turned into an island. Atlantis is shown to the west in the Atlantic.
In 1967 Egerton Sykes published a paper entitled The Sahara Inland Sea in which he describes a vast inland sea of ‘remarkable proportions’ and “is attested not only by classical references but also by the fact that beneath most of it lies a layer of brackish water ranging from 200 to 500 feet below the ground. The various oases are believed to be located on patches where the depth is only about 50 feet, conducive to plant survival. The climatic change seems to have happened quite recently, around 5000 BC. B.C., since the classics contain numerous references to its [the inland sea] existence.”(e)
I should mention here that the Atlantis theory of George Sarantitis is entirely dependent on extensive inland waterways including the chotts of Tunisia and Algeria as well as a number of other large lakes and rivers in what is now the Sahara.
In modern times, Alberto Arecchi has taken the idea further[079] and suggested that the inland sea, where the chotts are now, was the original ‘Atlantic Sea’ and that the city of Atlantis was situated on an extended landmass to the east of Tunisia and connected to Sicily due to a lower sea level. Arecchi’s identification of the chotts with Lake Tritonis has now been adopted by Lu Paradise in a May 2015 blog(c). The Qattara Depression of Northern Egypt also contains a series of salt lakes and marshes and is believed by others to have been Lake Tritonis.
Cindy Clendenon is the author of a book [801.397] on hydromythology in which she concludes that “the now-extinct Lake Tritonis once was a Cyrenaican lagoon-sabkha complex near today’s Sabkha Ghuzayyil and Marsa Brega, Libya”(b), not in Tunisia! Clyde Winters also placed Lake Tritonis in Libya(f).
[659]+ https://archive.org/details/chottstunisorgr01dumegoog
[1531.v1.316]+ https://archive.org/stream/historyofancient01bunb#page/n6/mode/1up/search/Tritonis Vol.1
(a) Lake Tritonis – Jason and the Argonauts (archive.org) *
(b) https://www.abebooks.com/9780981842103/Hydromythology-Ancient-Greek-World-Earth-0981842100/plp
(d) https://www.myrine.at/Amazons/mobilIndex.html
(e) The Saharan Inland Sea – Atlantisforschung.de (atlantisforschung-de.translate.goog)
(f) https://africanbloodsiblings.wordpress.com/2013/11/21/fertile-african-crescent-by-clyde-winters/
Chott el Jerid
Chott el Jerid is one of a series of ancient salt lakes (sometimes spelt shott or shat) in Tunisia that stretches from the Gulf of Gabés westward into Algeria, south of the Atlas Mountains. It is the second-largest salt lake in the world after Salt Lake in Utah. It is maintained that ancient Lake Tritonis was located in this region and possibly incorporated Chott el Jerid and at some point may even have extended as far as an enlarged Lake Chad.
These chotts are not, strictly speaking, lakes at all today. They are flat depressed areas, which for most of the year are areas of dried mud covered with a thick skin of salt, suggesting an earlier connection with the Mediterranean.
The principal chotts are Chott el Djerid, Chott ech Chergui, Chott Melrhir, Chott el Fejej and Chott el Hodna.
The largest, the Chott el Jerid, is just a few feet below the level of the ![chott_el_jerid[1]](https://atlantipedia.ie/samples/wp-content/uploads/2010/06/chott_el_jerid11-300x240.jpg) Mediterranean, according to Wikipedia. However, François Roudaire, a 19th-century French geographer, surveyed the chott and reported that the entire salt lake was 15 metres above the level of the Mediterranean. This fact was confirmed by Edward Dumergue in his 1883 booklet, The Chotts of Tunis[659]. In the same publication [p.5] he mentions Roudaire “showing how these chotts could be formed into one great inland sea, extending from near Biskra and Chegga in Algeria, through Tunis, to the Gulf of Gabes, about 300 miles in length and about 60 in breadth, forming a new gulf into the Mediterranean, with an area somewhat greater than the Irish Sea.”
Mediterranean, according to Wikipedia. However, François Roudaire, a 19th-century French geographer, surveyed the chott and reported that the entire salt lake was 15 metres above the level of the Mediterranean. This fact was confirmed by Edward Dumergue in his 1883 booklet, The Chotts of Tunis[659]. In the same publication [p.5] he mentions Roudaire “showing how these chotts could be formed into one great inland sea, extending from near Biskra and Chegga in Algeria, through Tunis, to the Gulf of Gabes, about 300 miles in length and about 60 in breadth, forming a new gulf into the Mediterranean, with an area somewhat greater than the Irish Sea.”
It is worth noting that Diodorus Siculus records that around 1250 BC catastrophic seismic activity across North-West Africa from the Gulf of Gabés to the Atlantic radically changed the topography of the region. Some investigators see this event as being responsible for the cutting-off of these inland seas from the Mediterranean creating today’s salt lakes. This idea is not as fanciful as it might seem at first sight when you consider the geological instability of the Central Mediterranean region. A well-known example is to be found at the Macellum of Pozzuoli near Naples which has been rising and falling over the past two millennia, due to movements in the volcanic caldera on which it sits.
Wintertime can produce up to a metre of water in these chotts, which by liquefying the mud makes them perfectly impassable. There is a clear suggestion that these chotts represent an inland sea that was once connected to the Mediterranean. It is believed that seismic activity in the area cut this connection. All around these salt lakes there are numerous springs, rushing from the sandy hillocks. Virtually all these springs are very near boiling point. The town of Gabés is close to a grand oasis, which is maintained by water from a stream emptying itself into the sea at Gabés after a short run.
More than one writer has placed Atlantis in this region. Paul Borchardt and Albert Hermann in the early 1920s and more recently Alberto Arecchi have advocated this idea. Borchardt reported that the local name of Chott el Jerid was Bahr Atala or Sea of Atlas.
Arecchi concurs with this explanation and is convinced that the inland sea was the original ‘Atlantic Ocean’. He quotes the Book of Jubilees to support this contention(a).
>In 2020, David Winder published Mysterien der Bronzezeit (Mysteries of the Bronze Age) [1936] in which he firmly locates Atlantis in the region of Chott- el-Jerid. In an article on the Atlantisforschung website, he expands on his theory and includes a chronology of key events in the 2nd millennium BC(f).<
A year late, Hong-Quan Zhang also placed Atlantis firmly within what is now the northwest region of Africa, specifically identifying the capital’s location at the eastern end of Chott el Jerid in modern Tunisia(e).
A contributor to a June 2012 forum(b) provided a link(c) to an interesting satellite image, as well as the following list of fifteen points favouring the chotts as a location for Atlantis:
1) Atlantis did not sink to “the bottom of the ocean” instead it became a “muddy shoal only several feet below the water surface”
2) It’s to the West of both Egypt and Greece
3) The Chotts used to be a large “mega-lake” and you can use a sea-level map to simulate how large this lake used-to be
4) That mega-lake is very likely to be the mythical “Lake Tritonis” that the Greeks ascribed to this area
5) Herodotus spoke of Tritonis in relation to peoples near mount Atlas who referred to themselves as Atlanteans
6) There are Carthaginian coins from this area with Elephants (and older petroglyphs with Elephants and diverse fauna)
7) One phase of the local art was highly similar to the Minoan\Sea Peoples influence
8) The local Deity is syncretically equal to Neith (who was deemed syncretically equal to Athena by Egypt in the tale)
9) Another local Deity is syncretically equal to Poseidon
10) The tale of the Amazons is corroborated genetically from Tuscany to Corfu to this Region (the Amazons fought the Atlanteans)
11) The Berbers often claim to have a heritage from Atlantis (not a big deal, so does half the Mediterranean and South America… etc)
12) Several ancient sources claim that this “mega-lake” emptied via a geological cataclysm. The event precedes the Sea Peoples epoch.
13) The name ‘Gabes’ is arguably linguistically closer to ‘Gades’ than Cadiz (Spain).
14) Gafsa (Caspa) was legendarily the home of the Libyan Herakles and resided between two mountains
15) It’s closer proximity to Egypt and Greece make it more plausible as a Bronze Age power than Gibraltar where it would be essentially like living on the moon in that age. (In no order).
(a) https://www.liutprand.it/articoliMondo.asp?id=430
(b) https://forums.thedarkmod.com/topic/13909-what-is-your-favorite-historical-mystery/
(d) https://forums.thedarkmod.com/topic/13909-what-is-your-favorite-historical-mystery/
(e) https://medcraveonline.com/IJH/is-atlantis-related-to-the-green-sahara.html
(f) Atlantis: From Myth to Reality – Atlantisforschung.de (atlantisforschung-de.translate.goog) *
