Martin Meredith
Elephants *
Elephants are specifically mentioned by Plato as being indigenous to Atlantis. This must have significance for anyone trying to arrive at a credible location for Atlantis. For example, supporters of the Theran Atlantis School cannot show where such large animals could have lived on the small volcanic island. There are no physical remains, no frescos and no historical references. Rodney Castleden who supports the Minoan Hypothesis admits that “no raw elephant ivory has been found (on Thera) and very little in the way of worked ivory”[225.70]. He later speaks of the importation of ivory into Crete[p.172] having bravely denounced Plato’s description (Critias 115a) of herds of elephants on Atlantis as “false”[p.136].
Similarly, Spanuth’s Heligoland location would have been climatically unsuited to elephants. Spanuth himself admits that the elephant reference “is hard to explain“. Nevertheless, Felice Vinci who champions a Northern European origin for Greek mythology believes that Plato’s elephant reference may be a lingering memory of the woolly mammoths that inhabited Arctic regions as recently as 2500-2000 BC(t)(u). In the late 17th century Olof Rudbeck, recognising the problem that Plato’s reference to elephants presented for his Swedish Atlantis, argued that Plato had been speaking figuratively when describing the large voracious animals and had actually been referring to wolves, the Swedish word for wolf being ‘ulf’, which sounds like the beginning of ‘elephant’!!
Elephants in Western Europe were undoubtedly represented by mammoths, remains of which have been recovered from the North Sea – Doggerland and dated to around 40,000 years ago. Coincidentally, a tool made of mammoth bone, used for making rope, has also been dated to 40,000 years ago(i)(n). This discovery(s) by Nicholas Conard from the University of Tubingen was made shortly before Ashley Cowie published his interesting book[1454] on the history of rope-making. Further information on string, ropes and knots was published in March 2017(o). This ingenuity of our very distant ancestors, so often underestimated, is slowly being revealed by modern archaeology. In 2000, in the Czech Republic, it was discovered that woven cloth was being produced on looms 27,000 years ago(v). A few years later a team from Harvard’s Peabody Museum reported the discovery of fibres that ‘were spun, twisted or knotted’ and dated to at least 34,000 years ago(x). 2020 saw evidence emerge which suggested that even as far back as 41,000 – 52,000 years ago the Neanderthals had mastered the making of cords(w). Later the same year, further evidence was offered that string-making may have begun even earlier(y).
Allied to the demise of the Siberian mammoths is the often-repeated fib that when the remains were first discovered, their flesh was still fresh enough to eat, which has recently been debunked by Jason Colavito(j). He has also unearthed the truth behind that other canard relating to a Siberian mammoth, namely that fresh buttercups were found in its mouth(j). He has now(q) traced back the earliest reference to the frozen mammoths to George Cuvier in 1822 [1586.11].
Eckart Kahlhofer, in a forthcoming book[715] advocates a North-West European location for Atlantis, and suggests that where Plato referred to elephants he actually meant deer! Kahlhofer offers, as a simple explanation for this seemingly daft contention, the fact that the Greek for elephant, elephas, is very similar to the Greek elaphos which means deer. He claims that a simple transcription error by a scribe could have caused the mix-up.
The elk was the largest species of deer to be found in the northern hemisphere and is still to be found in Scandinavia. The Great Irish Deer which died out around 5500 BC had an antler span of 11ft and a maximum height of 10ft, though usually less. The tallest African elephant ever recorded was 13 feet at the shoulder, which would appear to give the elephant the edge over the deer heightwise. Furthermore, It is worth pointing out, again, that Plato described his elephants as the ‘largest and most voracious’ animal, so when we realise that an adult elephant eats 250-300 lbs a day, while a moose manages on 40-60 lbs, there seems to be no contest.
Gene Matlock in an attempt to bolster his Mexican location for Atlantis has suggested that Plato’s elephants were in reality the long-snouted tapirs of Meso-America!(c), an idea ‘borrowed’ from Hyde Clarke
While the elephant issue should not be dealt with in isolation it does serve to illustrate the difficulties involved in analysing Plato’s text. Consider the possibility that the early date of 9600 BC for Atlantis is accepted, then the islands that are too small today to accommodate elephants may have been considerably larger and sometimes connected to each other or a mainland during the Ice Age, when sea levels were lower, and consequently capable of supporting pachyderms. In this regard, Sundaland would have been the most suitable candidate. Not only would today’s South China Sea archipelagos have been a single landmass, but there would have been access to the region from the Asian mainland, home today to large numbers of elephants.
Strangely enough, even the Andes, considered by some as the home of Atlantis, reveal the fact that during the last Ice Age, a species of elephant called Cuvieronius lived there but became extinct around 8000 BC. These animals are to be found carved on the great Gateway of the Sun in Tiahuanaco suggesting that they were common in the region. Supporters of an Atlantis link with Tiahuanaco have highlighted this fact.
James Bailey who supports[149][150] the idea of Atlantis in America believes that Plato’s mention of elephants could be a reference to the American mammoth, generally believed to have died out circa 10,000 BC, although Victor von Hagen, the American explorer, contentiously maintained that they survived as late 2000 BC. A similar idea was presented at the 2005 Atlantis Conference by the American researcher, Monique Petersen.
The Schoppes, in support of their theory of Atlantis in the Black Sea region, contend(l) that Indian elephants existed there until 800 BC and support this with a reference to the Egyptian pharaoh Thutmosis III who killed 120 elephants ‘there’ around 1200 BC, which is a strange claim as Thutmosis did not venture beyond Syria and he died circa 1426 BC!
Elephas Antiquus (Palaeoloxodon), is a dwarf species whose remains have been found throughout the islands of the Mediterranean from Sardinia to Cyprus. All those found were dated 200,000 BC or earlier! In sharp contrast, Simon Davis, in an article in New Scientist (3 Jan.1985), dated Mediterranean dwarf elephants to as recent as 6000 BC(p). Some writers, such as Roger Coghill, have tried to use the pygmy elephant as an explanation for Plato’s text (Crit. 114e & 115a) where we find that he describes the elephants as being ‘of its nature the largest and most voracious’. This is not a description of pygmy elephants.
Victoria Louise Herridge is a palaeontologist at the Natural History Museum in London. She has published a lengthy paper in two parts(z)(aa) offering an in-depth technical study of dwarf elephant species found on Mediterranean islands.
However, Ghar Hasan or Hasan’s Cave in southeast Malta has palaeolithic cave paintings that depict elephants, indicating more recent contact with the animals. Whether these represented full-sized or the pygmy variety is unclear. A small booklet[214] by Dr. Anton Mifsud and Dr. Charles Savona-Ventura describes this cave system.
In Dossier Malta – Neanderthal [1587] Mifsud has drawn attention to another cavern, not far away, formerly known as Ghar Dulam, now Ghar Dalam, where thousands of dwarf elephant bones were discovered. Dulam means ‘small elephant’ in Arabic. This is one of the mainstays of his ‘Atlantis in Malta’ theory. Whether these diminutive creatures justify Plato’s description that they were the “largest and most voracious” of animals (Crit.115a) is clearly debatable. For me, this is not a description of pygmy elephants and so in all probability is an indication of a North African location or, as some claim, an Asian one!
The Atlanteans had control in Europe as far as Tyrrhenia and Egypt, which would have included what is now modern Tunisia, the home of the last recorded wild elephants in that region!
The exact extent of Egyptian-controlled territory in Libya at the time of Atlantis is unclear. We do know that “In the mid-13th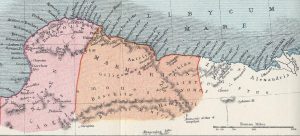 century, Marmarica was dominated by an Egyptian fortress chain stretching along the coast as far west as the area around Marsa Matruh; by the early 12th century, Egypt claimed overlordship of Cyrenaican tribes as well. At one point a ruler chosen by Egypt was set up (briefly!) over the combined tribes of Meshwesh, Libu, and Soped.”(ac)
century, Marmarica was dominated by an Egyptian fortress chain stretching along the coast as far west as the area around Marsa Matruh; by the early 12th century, Egypt claimed overlordship of Cyrenaican tribes as well. At one point a ruler chosen by Egypt was set up (briefly!) over the combined tribes of Meshwesh, Libu, and Soped.”(ac)
A Wikipedia(ab) map suggests that the Egyptian New Kingdom control stretched at least halfway towards Syrtis Major, which has been proposed by some as the location of Atlantis.
Readers should be aware that there is general acceptance that the North African Elephant inhabited the Atlas Mountains until they became extinct in Roman times(e)(h). The New Scientist magazine of 7th February 1985(d) outlined the evidence that Tunisia had native elephants until at least the end of the Roman Empire.
H.R. Stahel in Atlantis Illustrated [560] is the only commentator that I have encountered who suggested that elephants were used in the construction of the magnificent buildings described by Plato. This would make sense as Stahel calculated that surrounding the city of Atlantis “the aggregate length of the walls was almost 50 miles; they were 50 feet broad and twice as high. To build them, and their gates and towers, was a feat as impressive as the construction of the canals. The quantity of stone required was roughly 27 times that used in an Egyptian pyramid.” [p94]
In Elephant Destiny[1301] Martin Meredith records that one of the earliest references to the African elephant came from Hanno, the 5th century BC Carthaginian explorer, who related how he came across marshes at the foot of the Atlas Mountains, which “were haunted by elephants and multitudes of other grazing beasts.” Meredith also mentions that stables for as many as 300 elephants were to be found within the city of Carthage itself.
Nevertheless, the species of elephant used by Hannibal has been a source of debate for years(f). The Numidians of North Africa (202 BC–46 BC) also used local elephants in warfare(g). It would seem to me that the North African Elephant, rather than the Asian or African species, would have been more suited to the trek across the Alps. Needless to say, the Atlas Mountains were part of the Atlantean sphere of control (Timaeus 25a-b) and so may be the reason that Plato mentioned them. It is also reported that during the reign of the Ptolemies in Egypt (323 BC-30 BC), they imported war elephants from Eritrea in East Africa(r).
Dustin Kolb, is a German researcher, who also advocates a Mexican location for Atlantis and endeavoured, unconvincingly, to explain away Plato’s mention of elephants as a reference to bulls and bison!
The latter half of 2010 saw a new piece of nonsense hit the blogosophere when a claim that the Atlanteans had flying machines made of elephant skins suddenly appeared and before you could say “cut and paste” it was ‘adopted’ by a variety of websites(a)(b). So Dumbo was not the first flying elephant! In fact, this daft idea was just a recycling of one of Edgar Cayce’s ‘revelations’ (Reading 364-6)(m).
(a) https://www.articledashboard.com/Article/Speaking-of-Atlantis/1872335 (Offline October 2017)
(b) https://www.saching.com/Articles/Historical-Proof-of-Atlantis-2888.html
(c) https://viewzone.com/atlantis22.html
(d) New Scientist, 7 February 1985
(e) https://interesting-africa-facts.com/Africa-Landforms/Atlas-Mountains-Facts.html
(f) https://www.nytimes.com/1984/09/18/science/the-mystery-of-hannibal-s-elephants.html
(g) https://nabataea.net/explore/history/the-elephant-and-the-nabataeans/
(h) 5 Animals That Once Roamed Morocco but No Longer Exist (archive.org)
(i) https://www.seeker.com/how-rope-was-made-40000-years-ago-1943454415.html
(j) https://www.jasoncolavito.com/blog/dining-on-frozen-mammoth-steaks-the-evolution-of-a-strange-rumor
(l) https://web.archive.org/web/20190830053312/https://www.black-sea-atlantis.com/black-sea-atlantis/
(m) Edgar Cayce Reading 364-6 (hpage.com)
(n) https://www.q-mag.org/40000-years-of-rope-making.html
(o) https://www.hakaimagazine.com/features/the-long-knotty-world-spanning-story-of-string/
(p) New Scientist (3 Jan.1985)
(q) https://www.jasoncolavito.com/blog/the-claim-of-flash-frozen-mammoths-is-older-than-i-thought
(r) https://www.livescience.com/64407-ancient-egypt-fortress-war-elephants.html
(s) https://www.seeker.com/how-rope-was-made-40000-years-ago-1943454415.html
(u) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wrangel_Island#Flora_and_fauna
(v) https://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/790569.stm
(w) The Oldest String Ever Found May Have Been Made By Neanderthals | WUNC *
https://www.capradio.org/news/npr/story?storyid=828400733
(x) https://web.archive.org/web/20090930011321/https://www.thecrimson.com/article.aspx?ref=529173
(y) 120,000-calendar year-outdated necklace tells of the origin of string (archive.org)
(z) https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/id/eprint/133456/1/133456_Vol.1.pdf
(aa) https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/id/eprint/133456/2/133456_Vol.2.pdf
(ab) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/New_Kingdom_of_Egypt
(ac) https://www.penn.museum/sites/expedition/egyptians-and-libyans-in-the-new-kingdom/
