Eckart Kahlhofer
Sea Peoples *
The Sea Peoples is the name given by modern scholarship to a group of allies who caused havoc among the nations of the Eastern Mediterranean including Egypt, which they invaded at least twice, in the 2nd millennium BC. The phrase ‘Sea Peoples’ was never used in ancient records, in fact, the coining of the term in 1855 is now generally attributed to French Egyptologist, Emmanuel de Rougé who used the term ‘peuples de la mer’ (literally “peoples of the sea”) in a description of reliefs at Medinet Habu. The phrase was later popularized by another French Egyptologist, Gaston Maspero (1846-1916). Eckart Kahlhofer has recently suggested that even earlier, J. F. Champollion (1790–1832) employed an equivalent term ‘gens navales’ to describe the occupants of the invading swan-necked boats.
Also related to the carvings at Medinet Habu is an interesting study of the Sea Peoples’ ships depicted there, by the nautical archaeologist Professor Andrea Salimbetti’s website has a lengthy paper on Aegean Bronze Age ships(al) as well as the Sea Peoples(am).
Cyprian Broodbank in The Making of the Middle Sea [1127] argues that the Sea People “never actually existed as a single people. Instead, small roving bands were a symptom of the collapse, not the cause, and they were blown out of proportion by Egyptian propagandists working for Ramasses III.” (ai)
Broodbank is a co-author with Giulio Lucarini of a paper(av) about Mediterranean Africa that “draws on a new surge in data to present the first up-to-date interpretative synthesis of this region’s archaeology from the start of the Holocene until the threshold of the Iron Age (9600–1000 bc).”
Andrew Mark Henry offers a video in which he highlights the multiple mysteries surrounding the Sea Peoples primarily due to a lack of original documentation(bf).
Motivation
One website(h) describes the Sea People as groups of dispossessed raiders driven by hunger following crop failures resulting from climate change. The same idea is expanded on by Lu Paradise in an extensive article(v).
A different view was expressed by the Egyptologist Robert Anderson who commented “It would seem that, rather than bands of plunderers, the Sea People were probably part of a great migration of displaced people. The migration was most likely the result of widespread crop failures and famine.”(d)
Evidence is mounting that climate change played a significant part in the Late Bronze Age collapse of civilisations in the Eastern Mediterranean region. There is a school of thought that believes that the widespread societal disintegration was more the result of environmental factors rather than the depredations of the Sea Peoples(ag).
Origins
The Sea Peoples’ exact origin continues to be a matter of intense speculation(ad). The debate regarding their true identity has been ongoing for a long time and will probably continue as long as the chronologies of the Middle East are not fully harmonized to the satisfaction of most. One site offers 10 of the most popular identification theories(bh).
There is, however, some agreement that the Sea Peoples mounted two separate invasion attempts on Egypt around 1208 & 1176 BC (Facchetti & Negri).
Sea Peoples from the Adriatic
“While most of the Sea Peoples came from either the Aegean or the wider Mediterranean, many historians argue that groups from the Adriatic Sea also joined the migration. Specifically, Austrian historian Fritz Schachermeyr asserted in 1982 that the Sherden and Shekelesh were originally from the Adriatic and had connections to the ancient Illyrians.
Although Schachermeyr’s theory is not commonly held among students of the Sea Peoples, there are those who continue to believe that a famine in the Balkans drove several tribes, including the Illyrians, to migrate over land and over water(ba).”
Mycenaean Sea Peoples
The Oxford Companion to the Bible [0605] is certain that the Sea Peoples were originally Mycenaean, who moved south, following the collapse of their civilisation at the end of the Late Bronze Age. They were repelled by the Egyptians and then moved on to the Levant where they later became known as the Philistines. A paper(ab) that also links the Philistines with the Sea Peoples from a biblical perspective is available.
Shelley Wachsmann(aj), also offers evidence that at least some Mycenaeans were involved with the Sea Peoples(ak).
There is a claim that the Sea Peoples also attacked Mycenaean Greece on two occasions and that Athens survived both(ae). Contrast that with the contention that there was a Mycenaean group within the Sea Peoples. The confusion surrounding the Sea Peoples is exemplified by the response to a question on the quora.com website(af).
Sea Peoples from Anatolia (Northern Levant)
Erick Wright, formerly a regular contributor to the now-defunct Atlantis Rising forums(b) had initially thought that Atlantis had been situated in Morocco but further research led him to conclude that Atlantis was located in what today is Southern Turkey and that Atlanteans were among the Sea Peoples who attacked Egypt in 1200 BC. Another Atlantis Rising forum(e) on the subject is also worth a look as is another illustrated site(f) which includes a map of the homelands of the Sea Peoples.
The historian, Sanford Hoist, published a paper in which he argued(j) for an Anatolian origin for the Sea Peoples together with other groups such as the Phoenicians.
David Rohl, a high-profile archaeologist, has proposed an Anatolian homeland for most of the Sea Peoples listed by the Egyptians in his book, The Lords of Avaris [0232].
The most recent addition to our knowledge of the Sea Peoples appears to be imminent with the publication of a paper in the December 2017 issue of the journal Proceedings of the Dutch Archaeological and Historical Society. Written by Frederik Woudhuizen and Eberhard Zangger, the authors offer a translation of a 3200-year-old inscription That may refer to the Sea Peoples and link them with western Turkey. You can read more, now, on the Livescience website(z). In a 2006 paper(ac), The Ethnicity of the Sea Peoples, Woudhuizen included some groups from the Central Mediterranean as part of the Sea Peoples.
Erich Fred Legner offers an extensive paper(au) on the diversity of the Sea Peoples. Brian Janeway explored the idea that the Sea Peoples originated in the Northern Levant(aw).
Sea Peoples from Southern Levant (Modern Syria, Lebanon, Israel & Palestine)
Joseph Morris in his thesis(m) presented to the Classics Department of Florida State University in 2006 defined the Sea Peoples as “a coalition consisting of the indigenous populations of Syria-Palestine led by the neo-Hittite states.”
Eric Cline noted in 1117 BC: The Year Civilization Collapsed [1005] that the only member of the Sea Peoples alliance whose identity has been ‘firmly established’ is that of the Peleset who are accepted as Philistines. He also comments that identifying the Shekelesh with Sicily and the Shardana with Sardinia is based in part on the ‘consonantal similarities’ [p.4]. In a 2016 article, Cline wrote, “As for what role the Sea Peoples actually played in the destruction of civilizations around 1200 BCE and shortly thereafter, I personally think that they have been set up as a scapegoat, because of the Egyptian inscriptions, and that they were as much victims as oppressors. I doubt that they were responsible for all of the destructions that we blame on them and I think that they are only one of the many factors that together contributed to a “perfect storm” that ended the Bronze Age. These stressors, as they are sometimes called, probably also included drought, famine, earthquakes, and possible internal rebellions in addition to external invaders, all of which combined to cause a system to collapse.” (az)
In another paper(bi), Cline concluded as follows; “Let us simply restate the obvious, but frequently overlooked, observation that the earliest records attesting to the existence of Israel and the first indications of the phenomenon known as the Sea Peoples occurred simultaneously, in the fifth year of Merneptah’s reign. It is possible that these are not independent events, although they are usually treated as such in published studies of ancient Israel, and instead were related processes.
To the legendary figures of Moses and Joshua associated with the biblical stories of the Exodus and the Conquest of Canaan, we might want to now add the far less legendary but still anonymous and mysterious warriors within the Sea Peoples – the Eqwesh, Teresh, Lukka, Shardana, and Shekelesh coming across the sea from Greece, Turkey, Sicily, and Sardinia – or without the chaos and destructions that they wrought in the land of Canaan, and the power vacuum that they created in the area, the Israelites might never have taken over the region and the history of Western Civilization might have taken a radically different course.”
Sea Peoples or North Sea Peoples?
Until the middle of the 20th century, there was a consensus that the Sea Peoples originated in the Mediterranean region. That is until Jürgen Spanuth published his claim that Atlantis had been located in the North Sea and equated the Atlanteans with the Sea Peoples. This radical idea, with some variations, was adopted by several commentators and unsurprisingly, many were from Northern Europe. Spanuth referred to them as the North Sea Peoples [0015] and offered a range of evidence from the Egyptian inscriptions at Medinet Habu to support this idea. This evidence includes a variety of features that Egyptians used to portray the Sea Peoples such as types of swords, the shape of ships, shields and helmets as well as hair, clothing and shaving fashions. He then identified these Scandinavians as Atlanteans who later attacked Egypt. His opinion in this regard was strongly supported by Felix R. Paturi [1339.218]. More recently, Spanuth’s ideas have also been echoed by Walter Baucum in his Bronze Age Atlantis [0183].
In the 2007 DVD, Atlantis: Secret Star-Mappers of a Lost World, Childress identifies the Baltic as the original home of the Sea Peoples, reminiscent of the theories of Jürgen Spanuth, half a century earlier.
Similarly, Ellis Peterson endorses Spanuth’s Scandinavian location for Atlantis(ax).
Eckart Kahlhofer has now (2022) been investigating the idea of ‘North Sea Peoples’ for thirty years and supports the concept in his free ebook. He claims that in the twelfth century BC, the Egyptians referred to the Sea Peoples as the Nine Bows people, which is a geographical term.
Before the emergence of these Bronze Age seafarers, there was a history of Northern Boat-Peoples who gradually expanded globally after the last Ice Age. A paper by Andres Pääbo charts their story(k). Zach Zorich is a freelance journalist and contributing editor at Archaeology magazine. In January 2016 he wrote an article(r) that would seem to contradict the idea of Northern European ‘Sea People’ invading Egypt, for the simple reason that sailing boats were not developed in Scandinavia until around the time of the Vikings! – “The plank boats and log boats being built in northern Europe were not the most advanced watercraft of their time. The Greeks, Egyptians, and other cultures around the Mediterranean Sea used sailing ships to conduct trade, and sails wouldn’t be used in Northern Europe until the Iron Age, during the seventh or eighth century CE.”
Another site(an) also describes the various ships of the period used by the Egyptians, Greeks and the Sea Peoples. One unusual suggestion on the same site is that some of the Sea Peoples, although allied with groups from across the Mediterranean, came from Britain and Northern Europe(ao)!
The Sea Peoples’ Alliances
I have used the plural because the evidence suggests that over the extended period of the Sea Peoples activities, the alliances did experience some change in members.
Federico Bardanzellu offers several papers on his Museo dei Dolmen website(n) in which he suggests specific homelands for many of the members of the alliance(o).
Bob Idjennaden along with co-author, Mebarek S. Taklit, have produced The Mysterious Sea Peoples attack Egypt [1195], which provides an overview of the various incursions against Egypt during the 2nd millennium BC. The prominent part played by the Berbers or their ancestors in varying alliances that constituted the Sea Peoples is highlighted.
According to Raffaele D’Amato & Andrea Salimbeti [1152.20]+, the Denyen was one of the major groups of the Sea Peoples and have been known in ancient sources by different names; Danai, Danaoi, Danaus, Danaids, Dene, Danaids, Danuna. Others have linked them with the Danaan of Irish mythology. The Tuatha de Danaan invaded Ireland in prehistoric times. Having noted that Dan/Don/Danu were ancient words for water, it is not such a wild supposition that the Tuatha de Danaan were at least a constituent part of the Sea Peoples, an idea promoted by Leonardo Melis. A short review of D’Amato’s and Salimbeti’s book is available(bb).
On the other hand, Egerton Sykes thought that the Tuatha de Danaan were refugees from Atlantis, an idea he expressed in his 1949 edition of Ignatius Donnelly’s Atlantis. A paper offering a sober Irish (not an oxymoron) view of the Tuatha de Danaan should also be read(bc).
Sykes was convinced that Murias one of the four legendary cities of the de Danann had been located in Bimini. This highly speculative idea failed to bear fruit as have all efforts to identify the location of the other three cities, Falias, Finias and Gorias.
Speculation regarding the identity of individual tribes in the federation can be found on various websites(i)(f). One of the most comprehensive is provided by two Italian military historians, D’Amato & Salimbeti in their 2015 booklet [1152]+ and on the internet(l) and both are to be highly recommended. They highlight the complexities involved in definitively identifying the members of the varying alliances that were loosely described as the ‘Sea Peoples’ over a three-hundred-year period.
Atlantis and the Sea Peoples
The German classical scholar, Wilhelm Christ, was probably the first to identify the invading Sea Peoples with the Atlanteans(p), predating Jürgen Spanuth’s theory by the better part of a century. Christ’s idea was also supported to varying degrees by Theodor Gomperz, Spyridon Marinatos, John V. Luce, and Herwig Görgemanns. A translation of the relevant text of Christ’s 1886 paper was recently published by Jason Colavito(bd).
Quite a number of other writers have identified the Atlanteans as the Sea Peoples whose invasion of the Eastern Mediterranean has been recorded in some detail by the Egyptians. One such high-profile identification in the 20th century was by Spyridon Marinatos. One of the latest to join this school is Dr Rainer W. Kühne who not only makes the same identification but, using satellite images, believes that he has pinpointed the capital of Atlantis in Southern Spain. His website has a list of comparisons of Atlanteans to the Sea Peoples(a), which is worth consideration.
‘Rider’, the anonymous author of an article(ae) concerning ‘the campaigns of the Sea Peoples’ on the allempires.com website also suggests that Plato’s Atlanteans can be identified with the Sea Peoples.
Frank Joseph contends that conflict between the Egyptians and the Sea Peoples was part of the Trojan War [0108.11] and has identified the Meshwesh, one of the Sea Peoples, as Atlantean [1535]. His speculation extended to describing ‘the Atlantean Sea Peoples’ as culture bearers who were responsible for, among other matters, the famous Serpent Mound of Ohio(ay).
Eberhard Zangger argues that the Sea Peoples were survivors of the Trojan War that fled to various parts of both the central and eastern Mediterranean(g). He has written further on this identification and more on the Luwian Studies website(s). Zangger claims that the Sea Peoples were an alliance of Libyans and Western Anatolian (Luwian) states(w)(y), which seems odd since Plato describes the Atlanteans as mightier than Libya and Asia combined. If Zangger is correct in identifying Troy as Atlantis [0483], he is also implying that according to Plato, a part (Troy) is greater than the whole (Libya and Asia combined), Troy being part of Asia! Something is wrong with his theory.
In a 2022 article in Popular Archaeology (Oct.15 2022)(bg) Zangger returns to the identification of Luwians as part of the Sea Peoples.
In 2020, Sean Welsh maintained that survivors of the eruption of Thera, which held the capital of Atlantis ‘morphed’ into the Sea Peoples [1874].
Other Theories
A more recent (2017) paper(aa) on a conservative website suggests that the Sea Peoples were ‘early Western Europeans’.
W.S. Baird has also offered a western Mediterranean identification for the Sea Peoples, whom he considers to have originally been colonists from the Aegean who settled in the southeast of Spain and are known as the El Argar culture! Their society suffered some form of collapse around 1350 BC and according to Baird is in some way connected with the emergence of the Sea Peoples!(ap)
The most radical suggestion regarding the Sea Peoples has come from Jim Allen, who promotes a South American location for Atlantis. He also seemingly equates at least some of the Sea Peoples with his South American Atlanteans [077.123], and has drawn attention to the similarity of some of the Sea Peoples’ headgear with that of Amazonian ‘Indians’(c)!
The Malagabay website published a lengthy article(t) in July 2016, offering evidence along with some conjecture, supporting the equally extreme idea that the Sea Peoples had originated in India and having migrated westward, some of them reached the Aegean and became known as Dorians! The author of the article appears to have followed the ideas of Edward Pococke (1604-1691) published in his India in Greece [1231].
Another unexpected twist is the claim by the discoverer of the Phaistos Disk, Luigi Pernier, that the characters used on the Disk are similar to the representations of the Sea Peoples at Medinet Habu.
Peter Adamis, an Australian ex-military serviceman has devoted a section of his website to the question of the Sea Peoples’ identity. It offers a large number of related videos and papers(be).
Two contributors to the Sea Peoples debate in the 1970s were Alessandra Nibbi (1923-2007) [1670] and Nancy K. Sandars (1914-2015) [1671] who, although they had their differences, appear to have agreed on: “(a) the ‘Sea Peoples’ were not one particular people, (b) their label as being ‘of the sea’ is misleading, and (c) earlier attempts to blame the cataclysmic collapse throughout the East Mediterranean in the Late Bronze Age on the Sea Peoples is untenable.”
Sources
The earliest book devoted entirely to the Sea Peoples, which I am aware of, was Immanuel Velikovsky’s Peoples of the Sea. However, Velikovsky was more concerned with revising the chronologies of the Middle East and so focused on dating the invasion of the Sea Peoples rather than identifying their origins. Velikovsky has an interesting footnote in his Peoples of the Sea [758.4], which reads; “When Ramses III speaks of ‘Peoples of the Sea’ he specifies the Tkeker, the Shekelesh, the Teresh, the Weshesh and the Sherden (or Sardan); he specifies the Denyen as ‘Peoples of the Isles.'” It would be interesting to know the reason for the distinction.
Trude & Moshe Dothan have added another valuable book to the Sea Peoples’ literature with their People of the Sea which has the interesting sub-title of The Search for the Philistines [1524]. Related to their work, is the result of recent excavations at Ashkelon, an important Philistine city, which suggests that the city had received migrants from southern Europe during the Bronze Age, who may have constituted a component of the Sea Peoples(ah). Clearly, further investigation will be required to confirm these indications.
An extensive review of all the available material relating to the Sea Peoples was also published online in October 2015(q). The MalagaBay website (now closed) had also a wide-ranging illustrated article(u) about the Sea Peoples, although without reaching any firm conclusions.
[1152.20]+ https://img.4plebs.org/boards/tg/image/1498/88/1498880873171.pdf
(a) Location and Dating of Atlantis (archive.org)
(c) http://www.atlantisbolivia.org/headgear.htm (link broken) see part atlantis bolivia part 4 conclusion, mummies,uente magna and links
(d) https://web.archive.org/web/20181014190855/http://www.touregypt.net/featurestories/seapeople.htm
(g) http://archive.aramcoworld.com/issue/199503/who.were.the.sea.people.htm
(h) http://www.historyfiles.co.uk/KingListsMiddEast/AnatoliaSeaPeoples.htm
(i) Archive 2813 | (atlantipedia.ie) *
(j) http://www.phoenician.org/sea_peoples.htm
(k) Archive 2337 (all three parts)
(l) http://www.salimbeti.com/micenei/index.htm
(n) http://www.museodeidolmen.it/englishdefault.html
(o) http://www.museodeidolmen.it/englishpopomare.html
(p) Abhandlungen der bayerischen Akademie der Wissenschaften, Vol.. XVII, 2nd part, Munich 1886, pp. 451-512. (German)
(q) http://www.salimbeti.com/micenei/sea.htm
(s) https://luwianstudies.org/the-sea-peoples-inscriptions-and-excavation-results/
(t) https://malagabay.wordpress.com/2016/07/07/catastrophic-english-india-in-greece/
(u) https://malagabay.wordpress.com/2016/02/18/deja-vu-vikings/
(w) https://luwianstudies.org/the-sea-peoples-inscriptions-and-excavation-results/
(x) http://rlebling.blogspot.ie/2012/03/where-was-ogygia-isle-of-calypso.html
(z) https://www.livescience.com/60629-ancient-inscription-trojan-prince-sea-people.html
(aa) Archive 3429
(ab) https://img.4plebs.org/boards/tg/image/1498/88/1498880873171.pdf
(ac) https://www.academia.edu/7287651/The_Ethnicity_of_the_Sea_Peoples_dissertation_
(ad) https://listverse.com/2016/06/06/10-theories-regarding-the-sea-peoples/
(ae) The Campaigns of the Sea Peoples – All Empires (archive.org)
(ah) https://advances.sciencemag.org/content/5/7/eaax0061
(ai) https://www.reddit.com/r/history/comments/c3fm5j/who_were_the_mysterious_sea_people_during_the/ (halfway down page)
(aj) https://www.academia.edu/4594906/The_Ships_of_the_Sea_Peoples
(ak) https://www.academia.edu/4635111/Were_the_Sea_Peoples_Mycenaeans_The_Evidence_of_Ship_Iconography
(al) http://www.salimbeti.com/micenei/ships.htm
(am) http://www.salimbeti.com/micenei/sea.htm
(an) Ancient Ships: The Ships of Antiquity (archive.org)
(ap) https://minoanatlantis.com/Origin_Sea_Peoples.php
(ar) https://www.academia.edu/173946/M_J_Adams_and_M_E_Cohen_The_Sea_Peoples_in_Primary_Sources
(as) Cambridge Ancient History Ist edition, Vol.II, p.8
(at) https://www.academia.edu/34555497/The_Sea_Peoples_Superior_on_Land_and_at_Sea
(au) File: <seapeopl (archive.org)
(aw) https://www.academia.edu/38648258/Sea_Peoples_of_the_Northern_Levant
(ax) https://hiddenhistorysecrets.blogspot.com/2008/01/hidden-history-scandinavia-atlantis.html
(ay) Atlantis Rising magazine #36 http://pdfarchive.info/index.php?pages/At
(ba) https://listverse.com/2016/06/06/10-theories-regarding-the-sea-peoples/
(bc) https://www.irishcentral.com/opinion/others/tuatha-de-danann-irish-gods-aliens
(bd) Atlantis and the Sea Peoples – JASON COLAVITO
(be) SEA PEOPLES – ABALINX (archive.org)
(bf) https://www.thearchaeologist.org/blog/who-were-the-sea-peoples
(bh) Wayback Machine (archive.org)
(bi) https://www.academia.edu/355166/2009_Cline_Sea_Peoples_and_Israelites_article
Fauna of Atlantis
The Fauna of Atlantis as described by Plato has done little to pinpoint its location and is clearly a subject for further investigation. However, pinpointing is the wrong word since Atlantis stretched from North Africa as far north as central Italy, so there is probably a wide geographical spread to the fauna noted by Plato.
In Critias he refers to ‘flocks’ (111c) implying sheep and/or goats; bees (111c), elephants (114e); horses (117b); bulls (119d). He also mentions sable clothing (120b) but these were possibly imported.
The most problematic of these is the reference to elephants, a term that could be loosely applied to a number of related species including mastodons, mammoths, the Indian, the African and dwarf elephants. The habitat of the latter diminutive creatures stretched from Siberia as far south as the equator. The remains of dwarf elephants have been found on the islands of the Mediterranean from Sardinia to Cyprus.
Pygmy elephant is the term applied to some species found today in parts of Asia and Africa. However ‘pygmy’ or ‘dwarf’ elephants could hardly be described as “largest and most voracious” of animals (Critias 115a).
However, there is general acceptance that the North African Elephant inhabited the Atlas Mountains until they became extinct in Roman times(b)(e). Atlantis sceptic, Ronald H. Fritze, an Atlantis sceptic, acknowledges[709.25] the existence of elephants in North Africa until the Romans.
The species of elephant used by Hannibal has been a source of debate for years(c). The Numidians of North Africa (202 BC–46 BC) also used local elephants in warfare (d). It would seem to me that the North African Elephant, rather than the Asian or African species, would have been more suited to the trek across the Alps. Needless to say the Atlas Mountains were part of the Atlantean sphere of influence (Timaeus 25a-b).
Eckart Kahlhofer believes that the elephants referred to by Plato were in fact deer, claiming that a scribal error resulted in the Greek word elaphos (deer) being transcribed as elephas (elephant).
>Hyde Clarke proposed that Plato’s ‘elephants were in fact tapirs in an effort to bolster his Hispaniola location for Atlantis. Gene Matlock ‘borrowed’ this idea to suit his Mexican Atlantis. Tapirs are only found in S.E. Asia as well as Central and South America. Apart from that, Plato described his elephants as ‘the largest and most voracious’ (Crit. 114e & 115a), which would clearly exclude tapirs or deer.<
R. Cedric Leonard has written an interesting paper(a) on the early domestication of animals and its possible connection with Atlantis.
*(a) https://web.archive.org/web/20161210225952/https://www.atlantisquest.com/Taming.html*
(b) https://interesting-africa-facts.com/Africa-Landforms/Atlas-Mountains-Facts.html
(c) https://www.nytimes.com/1984/09/18/science/the-mystery-of-hannibal-s-elephants.html
Elephants *
Elephants are specifically mentioned by Plato as being indigenous to Atlantis. This must have significance for anyone trying to arrive at a credible location for Atlantis. For example, supporters of the Theran Atlantis School cannot show where such large animals could have lived on the small volcanic island. There are no physical remains, no frescos and no historical references. Rodney Castleden who supports the Minoan Hypothesis admits that “no raw elephant ivory has been found (on Thera) and very little in the way of worked ivory”[225.70]. He later speaks of the importation of ivory into Crete[p.172] having bravely denounced Plato’s description (Critias 115a) of herds of elephants on Atlantis as “false”[p.136].
Similarly, Spanuth’s Heligoland location would have been climatically unsuited to elephants. Spanuth himself admits that the elephant reference “is hard to explain“. Nevertheless, Felice Vinci who champions a Northern European origin for Greek mythology believes that Plato’s elephant reference may be a lingering memory of the woolly mammoths that inhabited Arctic regions as recently as 2500-2000 BC(t)(u). In the late 17th century Olof Rudbeck, recognising the problem that Plato’s reference to elephants presented for his Swedish Atlantis, argued that Plato had been speaking figuratively when describing the large voracious animals and had actually been referring to wolves, the Swedish word for wolf being ‘ulf’, which sounds like the beginning of ‘elephant’!!
Elephants in Western Europe were undoubtedly represented by mammoths, remains of which have been recovered from the North Sea – Doggerland and dated to around 40,000 years ago. Coincidentally, a tool made of mammoth bone, used for making rope, has also been dated to 40,000 years ago(i)(n). This discovery(s) by Nicholas Conard from the University of Tubingen was made shortly before Ashley Cowie published his interesting book[1454] on the history of rope-making. Further information on string, ropes and knots was published in March 2017(o). This ingenuity of our very distant ancestors, so often underestimated, is slowly being revealed by modern archaeology. In 2000, in the Czech Republic, it was discovered that woven cloth was being produced on looms 27,000 years ago(v). A few years later a team from Harvard’s Peabody Museum reported the discovery of fibres that ‘were spun, twisted or knotted’ and dated to at least 34,000 years ago(x). 2020 saw evidence emerge which suggested that even as far back as 41,000 – 52,000 years ago the Neanderthals had mastered the making of cords(w). Later the same year, further evidence was offered that string-making may have begun even earlier(y).
Allied to the demise of the Siberian mammoths is the often-repeated fib that when the remains were first discovered, their flesh was still fresh enough to eat, which has recently been debunked by Jason Colavito(j). He has also unearthed the truth behind that other canard relating to a Siberian mammoth, namely that fresh buttercups were found in its mouth(j). He has now(q) traced back the earliest reference to the frozen mammoths to George Cuvier in 1822 [1586.11].
Eckart Kahlhofer, in a forthcoming book[715] advocates a North-West European location for Atlantis, and suggests that where Plato referred to elephants he actually meant deer! Kahlhofer offers, as a simple explanation for this seemingly daft contention, the fact that the Greek for elephant, elephas, is very similar to the Greek elaphos which means deer. He claims that a simple transcription error by a scribe could have caused the mix-up.
The elk was the largest species of deer to be found in the northern hemisphere and is still to be found in Scandinavia. The Great Irish Deer which died out around 5500 BC had an antler span of 11ft and a maximum height of 10ft, though usually less. The tallest African elephant ever recorded was 13 feet at the shoulder, which would appear to give the elephant the edge over the deer heightwise. Furthermore, It is worth pointing out, again, that Plato described his elephants as the ‘largest and most voracious’ animal, so when we realise that an adult elephant eats 250-300 lbs a day, while a moose manages on 40-60 lbs, there seems to be no contest.
Gene Matlock in an attempt to bolster his Mexican location for Atlantis has suggested that Plato’s elephants were in reality the long-snouted tapirs of Meso-America!(c), an idea ‘borrowed’ from Hyde Clarke
While the elephant issue should not be dealt with in isolation it does serve to illustrate the difficulties involved in analysing Plato’s text. Consider the possibility that the early date of 9600 BC for Atlantis is accepted, then the islands that are too small today to accommodate elephants may have been considerably larger and sometimes connected to each other or a mainland during the Ice Age, when sea levels were lower, and consequently capable of supporting pachyderms. In this regard, Sundaland would have been the most suitable candidate. Not only would today’s South China Sea archipelagos have been a single landmass, but there would have been access to the region from the Asian mainland, home today to large numbers of elephants.
Strangely enough, even the Andes, considered by some as the home of Atlantis, reveal the fact that during the last Ice Age, a species of elephant called Cuvieronius lived there but became extinct around 8000 BC. These animals are to be found carved on the great Gateway of the Sun in Tiahuanaco suggesting that they were common in the region. Supporters of an Atlantis link with Tiahuanaco have highlighted this fact.
James Bailey who supports[149][150] the idea of Atlantis in America believes that Plato’s mention of elephants could be a reference to the American mammoth, generally believed to have died out circa 10,000 BC, although Victor von Hagen, the American explorer, contentiously maintained that they survived as late 2000 BC. A similar idea was presented at the 2005 Atlantis Conference by the American researcher, Monique Petersen.
The Schoppes, in support of their theory of Atlantis in the Black Sea region, contend(l) that Indian elephants existed there until 800 BC and support this with a reference to the Egyptian pharaoh Thutmosis III who killed 120 elephants ‘there’ around 1200 BC, which is a strange claim as Thutmosis did not venture beyond Syria and he died circa 1426 BC!
Elephas Antiquus (Palaeoloxodon), is a dwarf species whose remains have been found throughout the islands of the Mediterranean from Sardinia to Cyprus. All those found were dated 200,000 BC or earlier! In sharp contrast, Simon Davis, in an article in New Scientist (3 Jan.1985), dated Mediterranean dwarf elephants to as recent as 6000 BC(p). Some writers, such as Roger Coghill, have tried to use the pygmy elephant as an explanation for Plato’s text (Crit. 114e & 115a) where we find that he describes the elephants as being ‘of its nature the largest and most voracious’. This is not a description of pygmy elephants.
Victoria Louise Herridge is a palaeontologist at the Natural History Museum in London. She has published a lengthy paper in two parts(z)(aa) offering an in-depth technical study of dwarf elephant species found on Mediterranean islands.
However, Ghar Hasan or Hasan’s Cave in southeast Malta has palaeolithic cave paintings that depict elephants, indicating more recent contact with the animals. Whether these represented full-sized or the pygmy variety is unclear. A small booklet[214] by Dr. Anton Mifsud and Dr. Charles Savona-Ventura describes this cave system.
In Dossier Malta – Neanderthal [1587] Mifsud has drawn attention to another cavern, not far away, formerly known as Ghar Dulam, now Ghar Dalam, where thousands of dwarf elephant bones were discovered. Dulam means ‘small elephant’ in Arabic. This is one of the mainstays of his ‘Atlantis in Malta’ theory. Whether these diminutive creatures justify Plato’s description that they were the “largest and most voracious” of animals (Crit.115a) is clearly debatable. For me, this is not a description of pygmy elephants and so in all probability is an indication of a North African location or, as some claim, an Asian one!
The Atlanteans had control in Europe as far as Tyrrhenia and Egypt, which would have included what is now modern Tunisia, the home of the last recorded wild elephants in that region!
The exact extent of Egyptian-controlled territory in Libya at the time of Atlantis is unclear. We do know that “In the mid-13th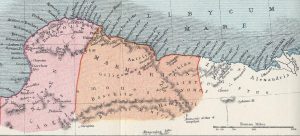 century, Marmarica was dominated by an Egyptian fortress chain stretching along the coast as far west as the area around Marsa Matruh; by the early 12th century, Egypt claimed overlordship of Cyrenaican tribes as well. At one point a ruler chosen by Egypt was set up (briefly!) over the combined tribes of Meshwesh, Libu, and Soped.”(ac)
century, Marmarica was dominated by an Egyptian fortress chain stretching along the coast as far west as the area around Marsa Matruh; by the early 12th century, Egypt claimed overlordship of Cyrenaican tribes as well. At one point a ruler chosen by Egypt was set up (briefly!) over the combined tribes of Meshwesh, Libu, and Soped.”(ac)
A Wikipedia(ab) map suggests that the Egyptian New Kingdom control stretched at least halfway towards Syrtis Major, which has been proposed by some as the location of Atlantis.
Readers should be aware that there is general acceptance that the North African Elephant inhabited the Atlas Mountains until they became extinct in Roman times(e)(h). The New Scientist magazine of 7th February 1985(d) outlined the evidence that Tunisia had native elephants until at least the end of the Roman Empire.
H.R. Stahel in Atlantis Illustrated [560] is the only commentator that I have encountered who suggested that elephants were used in the construction of the magnificent buildings described by Plato. This would make sense as Stahel calculated that surrounding the city of Atlantis “the aggregate length of the walls was almost 50 miles; they were 50 feet broad and twice as high. To build them, and their gates and towers, was a feat as impressive as the construction of the canals. The quantity of stone required was roughly 27 times that used in an Egyptian pyramid.” [p94]
In Elephant Destiny[1301] Martin Meredith records that one of the earliest references to the African elephant came from Hanno, the 5th century BC Carthaginian explorer, who related how he came across marshes at the foot of the Atlas Mountains, which “were haunted by elephants and multitudes of other grazing beasts.” Meredith also mentions that stables for as many as 300 elephants were to be found within the city of Carthage itself.
Nevertheless, the species of elephant used by Hannibal has been a source of debate for years(f). The Numidians of North Africa (202 BC–46 BC) also used local elephants in warfare(g). It would seem to me that the North African Elephant, rather than the Asian or African species, would have been more suited to the trek across the Alps. Needless to say, the Atlas Mountains were part of the Atlantean sphere of control (Timaeus 25a-b) and so may be the reason that Plato mentioned them. It is also reported that during the reign of the Ptolemies in Egypt (323 BC-30 BC), they imported war elephants from Eritrea in East Africa(r).
Dustin Kolb, is a German researcher, who also advocates a Mexican location for Atlantis and endeavoured, unconvincingly, to explain away Plato’s mention of elephants as a reference to bulls and bison!
The latter half of 2010 saw a new piece of nonsense hit the blogosophere when a claim that the Atlanteans had flying machines made of elephant skins suddenly appeared and before you could say “cut and paste” it was ‘adopted’ by a variety of websites(a)(b). So Dumbo was not the first flying elephant! In fact, this daft idea was just a recycling of one of Edgar Cayce’s ‘revelations’ (Reading 364-6)(m).
(a) https://www.articledashboard.com/Article/Speaking-of-Atlantis/1872335 (Offline October 2017)
(b) https://www.saching.com/Articles/Historical-Proof-of-Atlantis-2888.html
(c) https://viewzone.com/atlantis22.html
(d) New Scientist, 7 February 1985
(e) https://interesting-africa-facts.com/Africa-Landforms/Atlas-Mountains-Facts.html
(f) https://www.nytimes.com/1984/09/18/science/the-mystery-of-hannibal-s-elephants.html
(g) https://nabataea.net/explore/history/the-elephant-and-the-nabataeans/ *
(h) 5 Animals That Once Roamed Morocco but No Longer Exist (archive.org) *
(i) https://www.seeker.com/how-rope-was-made-40000-years-ago-1943454415.html
(j) https://www.jasoncolavito.com/blog/dining-on-frozen-mammoth-steaks-the-evolution-of-a-strange-rumor
(l) https://web.archive.org/web/20190830053312/https://www.black-sea-atlantis.com/black-sea-atlantis/
(m) Edgar Cayce Reading 364-6 (hpage.com)
(n) https://www.q-mag.org/40000-years-of-rope-making.html
(o) https://www.hakaimagazine.com/features/the-long-knotty-world-spanning-story-of-string/
(p) New Scientist (3 Jan.1985)
(q) https://www.jasoncolavito.com/blog/the-claim-of-flash-frozen-mammoths-is-older-than-i-thought
(r) https://www.livescience.com/64407-ancient-egypt-fortress-war-elephants.html
(s) https://www.seeker.com/how-rope-was-made-40000-years-ago-1943454415.html
(u) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wrangel_Island#Flora_and_fauna
(v) https://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/790569.stm
(w) https://www.capradio.org/news/npr/story?storyid=828400733
(x) https://web.archive.org/web/20090930011321/https://www.thecrimson.com/article.aspx?ref=529173
(y) 120,000-calendar year-outdated necklace tells of the origin of string (archive.org)
(z) https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/id/eprint/133456/1/133456_Vol.1.pdf
(aa) https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/id/eprint/133456/2/133456_Vol.2.pdf
(ab) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/New_Kingdom_of_Egypt
(ac) https://www.penn.museum/sites/expedition/egyptians-and-libyans-in-the-new-kingdom/
Deer
Deer(Greek elephos) are apparently not mentioned in his Atlantis narrative, however, he does refer to elephants (elephas). Jürgen Spanuth, who advocated a North-West Europe location for Atlantis was unable to satisfactorily reconcile his Helgoland location with Plato’s elephants. Now another German researcher, Eckart Kahlhofer, has offered a simple explanation, namely that a transcription error led to the Greek word for elephant (elephas) being mistaken for their word for deer (elephos). However, as Atlantis story originated in Egypt, what may be more relevant is the fact that the Egyptian hieroglyphics for deer (seshau) and elephant (abu) are so totally different that confusion between the two is not possible.
The elk was the largest species of deer in Northern Europe and is still found in Scandinavia. The Great Irish Deer which died out around 5500 BC was 10 feet (3 metres) tall and had an antler span of 11 feet.
Kahlhofer, Eckart
Eckart Kahlhofer (1936- ) is a German entertainer(a) and Atlantis researcher who has recently added his support to the concept of Atlantis in North-West Europe echoing some of the ideas of Jürgen Spanuth. He identifies the invasions of the Sea Peoples with that of the Atlanteans during the 12th century BC. Like Spanuth he  also equates orichalcum with amber. Among his more creative ideas is to identify the Shardana as coming from Sweden and similarly argue that the Philistines came from northwest Europe.
also equates orichalcum with amber. Among his more creative ideas is to identify the Shardana as coming from Sweden and similarly argue that the Philistines came from northwest Europe.
Additionally, he contends that the elephants referred to by Plato were in fact deer, claiming that a scribal error resulted in the Greek word elaphos (deer) being transcribed as elephas (elephant).
He strongly rejects the commonly accepted interpretation of Caphtor, contending that the term refers to the ‘pillar of heaven’ in the North Sea holding up the sky and personified by Atlas.(See: Archive 2809)
Kahlhofer also attacks the views of, Rudolf Steiner, Lewis Spence, Eberhard Zangger, the Schoppes and Aristotle.
Publication of his book[715], Atlantis in the Third Millennium, was imminent and due to have been available in English and German. However, he has now published an ebook with the title of Mit Atlantis–die andere Dimension (Atlantis: The Other Dimension) in German.
In October 2013, Kahlhofer published an English translation of a sample of his work. His latest book Der Atlantis Codex is now available as a free pdf file(b).
>Khalhofer has identified the ‘Nine Bows’ people referred to by Merenpth “as the coalition of Lebu, Turscha, Sekeles, Peleset, Theker, Denen, Sardana, Wasasa and Meschwesch coming from the north”, whom he had conquered. We would come to know them as the Sea Peoples(f).
Khalhofer notes that later Ramses III (Year 8) in the year 1175 BC, defeated the Sea Peoples whom he knew as the Nine Bow peoples from the North(g).<
He updated his website(c) and the English translation of Der Atlantis Codex in December 2019. Further amendments were added in January 2021(d).
>Kahlhofer continued to work on the text leading to a point where it is now (August 2021) a trilogy(e). It was no great surprise when Atlantis Codex 2022 was published. This is a 275-page book originally in German, but if you contact the author, he will send you an English translation(g).<
(a) https://www.imdb.com/name/nm0434764/
(b) DER ATLANTIS CODEX (archive.org) (English & German)
(c) http://www.atlantis-atlantis.de/
(d) Mail – Tony O’Connell – Outlook (live.com)
(f) THE ATLANTEANS ALIAS NINEBOWS | Meine Webseite (atlantis-atlantis.de) *
(g) ATLANTIS 2022 | Meine Webseite (atlantis-atlantis.de) *
Keftiu – Caphtor
Caphtor is a place referred to in the Bible (Jeremiah 47.4, Amos 9.7) and located by traditional Hebrew sources to have been near Pelusium in the eastern Nile Delta. Some think that Jeremiah’s reference to “the coasts of Caphtor” implied that Caphtor was an island. The late Walter Baucum also identified Caphtor with the Egyptian Kaft-ur in the Delta, once occupied by the Philistines [183.309]. A. H. Sayce, a respected 19th century Assyriologist, among others, also placed Caphtor in the Delta.
Keftiu was an Egyptian placename and since the 18th century has been frequently associated with Crete. Half a century ago James E. Jennings of Akron University wrote a paper in which he concluded that “it appears that there is sufficient evidence to support the contention that Caphtor was Crete”(f).
While many commentators today equate Caphtor with Crete, the evidence is far from clear. As Manuel Robbins points out [856.316], the identification of Caphtor with Crete “is based on not one but a string of assumptions. If any of these assumptions are wrong, the conclusion fails, and these assumptions are shaky.”
Baucum offers evidence that the Egyptians also used Keftiu when referring to north of the Orontes River (Syria), Cyprus, Cilicia (S.W. Turkey) as well as Crete. He also attributes the exclusive association of Caphtor with Crete to Champollion’s guessed at identification of the Philistines as the Sea Peoples! A chapter in a book [1057] by Nissim Raphael Ganor that bluntly states that “The Philistines and the ‘Sea Peoples’, not the same entity” is worth reading for anyone studying this particular controversy(i).
Manuel Robbins has concluded [p336] that the most likely location for Keftiu was either Cyprus, Syria or Eastern Anatolia, but that it is essentially a mystery.
In Ramage’s Atlantis: Fact or Fiction? [0522.105] J. Rufus Fears points out that the land called Keftiu was in a tributary relationship with the Egyptian pharaoh.
Matters become confused when we find that there is also a popular theory that Caphtor and Keftiu referred to the same place. Robbins disputed such an identification. He offers pictorial evidence from tombs on the west bank of the Nile opposite Thebes that might equally suggest Syria as the home of Caphtor [p334], but this is also far from conclusive.
Frankly, I find all the competing opinions(h) extremely confusing and unsatisfactory and believe that a solution to these conflicting ideas is far from a resolution.
Some others have been in favour of identifying Keftiu with Cyprus, among whom, Immanuel Velikovsky argued(g) that if Cyprus was not Caphtor, then it is the only island of any importance in the Eastern Mediterranean not mentioned in the Bible [039.210]. Caphtor/Keftiu: A New Investigation [1052] by John Strange also supports this identification with Cyprus. Walter Baucum claims that “Keftiu was the coastline from Tyre northwards to Anatolia, and included the islands of Crete and Cyprus” [p107].
Yair Davidy in his Introduction to Baucum’s book[183.x] and his own Lost Israelite Identity [1375.208] claims that there was another Keftiu in Northern Europe. Jürgen Spanuth claimed that Caphtor and the Norse ‘holmr Asgard’ mean the same [015.94], namely, “the island of the heaven-pillar”. More recent support for a Northern Europe Caphtor is offered by Eckart Kahlhofer who, like Spanuth, also claims it as the location of Atlantis and adds that it was also the home of the Philistines!
Making matters worse was the introduction of Atlantis into the discussion, bringing with it its own range of conflicting ideas. There is also a number of commentators, including Bruce Wayne(d) and Alex Hawk(e), who take Keftiu to be another name for Minoan Crete and equate it with Atlantis. Robert Ishoy considers Nuragic Sardinia as Keftiu/Atlantis(b).
Although Plato was the first to use the term ‘Atlantis’, there are antecedents to his account of a drowned civilisation. There is an Egyptian legend, which Solon probably heard while travelling in Egypt, and was passed down to Plato years later. It concerns the island nation of Keftiu, home to one of the four pillars that held up the sky. It was said to be a glorious advanced civilization, which was destroyed and sank beneath the ocean. It has been suggested that Plato embellished Solon’s story from “the land of the four pillars that held up the sky” into “the land of the Titan, Atlas, who held up the sky.” The Egyptian legend refers to an island west of Egypt, but not necessarily west of the Mediterranean. It may be relevant to point here that Crete is more northerly of Egypt whereas some of the suggested Atlantis locations such as the Maltese Islands or Sardinia are in fact located westward.
It seems that the debate(a) regarding the identification of Keftiu is set to continue for some time. Muddying the waters further is a serious claim of a Minoan connection with Japan(c) with a particular reference to the Linear A script!
(a) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Caphtor
(b) http://www.atlantisdiscovered.org/thesis.htm
(c) http://atlantipedia.ie/samples/archive-3930-2/
(d) http://atlantipedia.ie/samples/archive-2868/
(e) http://www.angelfire.com/hi/alhawk/atlanthira.html
(f) https://biblicalstudies.org.uk/pdf/grace-journal/12-2_23.pdf
(g) https://www.varchive.org/ce/baalbek/caphtor.htm
(h)Archive 2403l
