Staffa
Vinci, Felice *
Felice Vinci (1946- ) is an Italian nuclear engineer with a background in Latin and Greek studies  and is a member of MENSA, Italy. He believes that Greek mythology had its origins in Northern Europe.
and is a member of MENSA, Italy. He believes that Greek mythology had its origins in Northern Europe.
His first book on the subject in 1993, Homericus Nuncius[1358], was subsequently expanded into Omero nel Baltico[0018] and published in 1995. It has now been translated into most of the languages of the Baltic as well as an English version with the title of The Baltic Origins of Homer’s Epic Tales[0019]. The foreword was written by Joscelyn Godwin.
Vinci explained that “I have been interested in the Greek poet Homer and Greek mythology since I was seven years old. My elementary school teacher gave me a book about the Trojan War, so the leading characters of Homer’s poem, ‘Iliad,’ were as important for me as Mickey Mouse and Donald Duck.
“In 1992, I found the Greek historian Plutarch‘s key-indication which positioned the island Ogygie in the North Atlantic ocean. I decided to dedicate myself to this research. The ancient Greek that I had studied in secondary school helped me very much. Subsequently, I was helped and encouraged by Professor Rosa Calzecchi Onesti, a famous scholar who has translated both of Homer’s poems, ‘Iliad’ and ‘Odyssey,’ into Italian. Her translations are considered a point of reference for scholars in Italy.”(s)
Readers might find two short reviews of Vinci’s book on an Icelandic website (in English) of interest(t)(u).
However, the idea of a northern source for Homeric material is not new. In the seventeenth century, Olof Rudbeck insisted that the Hyperboreans were early Swedes and by extension, were also Atlanteans. In 1918, an English translation of a paper by Carus Sterne (Dr Ernst Ludwig Krause)(1839-1903) was published with the title of The Northern Origin of the Story of Troy(m).
Vinci offers a compelling argument for re-reading Homer’s Iliad and Odyssey with the geography of the Baltic rather than the Mediterranean as a guide. A synopsis of his research is available on the Internet(a).
His book has had positive reviews from a variety of commentators(j). Understandably, Vinci’s theory is not without its critics some of whose views can also be found on the internet(d)(b)and in particular I wish to draw attention to one extensive review by Andreas Pääbo which is quite critical(k). His objections are based on a firm contention that the Odyssey and the Iliad came from two different authors(v).
Stuart L. Harris has written a variety of articles for the Migration and Diffusion website(c) including a number specifying a Finnish location for Troy following a meeting with Vinci in Rome. M.A. Joramo was also influenced by Vinci’s work and has placed the backdrop to Homer’s epic works in northern European regions, specifically identifying the island of Trenyken, in Norway’s Outer Lofoten Islands, with Homer’s legendary Thrinacia. An Italian article also links the Lofotens with some of Homer’s geographical references(r).
Jürgen Spanuth based his Atlantis theory[015] on an unambiguous identification of the Atlanteans with the Hyperboreans of the Baltic region. More specifically, he was convinced [p88] that the Cimbrian peninsula or Jutland, comprised today of continental Denmark and part of northern Germany had been the land of the Hyperboreans.
As a corollary to his theory, Vinci feels that the Atlantis story should also be reconsidered with a northern European origin at its core. More recently, Vinci wrote a lengthy Preface(p) to Marco Goti‘s book, Atlantide: mistero svelato[1430], which places Atlantis in Greenland! Vinci’s support for this Greenland location for Atlantis is reiterated in a 2025 paper(w). Furthermore, he produced a paper in 2024 proposing Morbihan in Brittany as the location of the Pillars of Herakles(x).
Vinci also makes an interesting observation regarding the size of Atlantis when he points out that ‘for ancient seafaring peoples, the ‘size’ of an island was the length of its coastal perimeter, which is roughly assessable by circumnavigating it’. Consequently, Vinci contends that when Plato wrote of Atlantis being ‘greater’ than Libya and Asia together he was comparing the perimeter of Atlantis with the ‘coastal length’ of Libya and Asia.
Malena Lagerhorn, a Swedish novelist, has written two books, in English, entitled Ilion [1546] and Heracles [1547], which incorporate much of Vinci’s theories into her plots(l). She has also written a blog about the mystery of Achilles’ blond hair(n).
Alberto Majrani is another Italian author, who, influenced by Vinci, is happy to relocate the origins of many Greek myths to the Nordic regions [1875]. Although his focus is on the Homeric epics, he has also touched on Plato’s Atlantis story, proposing, for example, that the Pillars of Heracles were a reference to the thousands of basaltic columns, known as the ‘Giant’s Causeway’ to be found on the north coast of Ireland with a counterpart across the sea in Scotland’s Isle of Staffa.(o)
Not content with moving the geography of Homer and Plato to the Baltic, Vinci has gone further and transferred[1178] the biblical Garden of Eden to the same region(e). Then in a more recent blog(q) he repeats his views on the location of Eden in Lapland and reiterates his core thesis that “the real scenario of the events of the Iliad and the Odyssey was the Baltic-Scandinavian world, the primitive seat of the blond Achean navigators: they subsequently descended into the Mediterranean, where, around the beginning of the sixteenth century BC., they founded the Mycenaean civilization.”
A 116 bullet-pointed support for Vinci from a 2007 seminar, “Toija and the roots of European civilization” has been published online(h). In 2012 John Esse Larsen published a book[1048] expressing similar views.
 An extensive 2014 audio recording of an interview with Vinci on Red Ice Radio is available online(f). It is important to note that Vinci is not the first to situate Homer’s epics in the Atlantic, northern Europe and even further afield. Henriette Mertz has Odysseus wandering across the Atlantic, while Iman Wilkens also gave Odysseus a trans-Atlantic voyage and just as controversially locates Homer’s Troy in England[610]. Edo Nyland has linked the story of Odysseus with Bronze Age Scotland[394].
An extensive 2014 audio recording of an interview with Vinci on Red Ice Radio is available online(f). It is important to note that Vinci is not the first to situate Homer’s epics in the Atlantic, northern Europe and even further afield. Henriette Mertz has Odysseus wandering across the Atlantic, while Iman Wilkens also gave Odysseus a trans-Atlantic voyage and just as controversially locates Homer’s Troy in England[610]. Edo Nyland has linked the story of Odysseus with Bronze Age Scotland[394].
Christine Pellech has daringly proposed in a 2011 book[0640], that the core narrative in Homer’s Odyssey is a description of the circumnavigation of the globe in a westerly direction(i). These are just a few of the theories promoting a non-Mediterranean backdrop to the Illiad and Odyssey. They cannot all be correct and quite possibly all are wrong. Many have been seduced by their novelty rather than their provability. For my part I will, for now, stick with the more mundane and majority view that Homer wrote of events that took place mainly in the central and eastern Mediterranean. Armin Wolf offers a valuable overview of this notion(g).
It is worth noting that Bernard Jones has recently moved [1638] Troy to Britain, probably in the vicinity of Cambridge! Like many others, he argues that Homer’s Iliad and Odyssey were not set in the Mediterranean as so many of the details that he provides are incompatible with the characteristics of that sea. However, Jones has gone further and claimed that there are details in Virgil’s Aeneid, which are equally inconsistent with the Mediterranean[p.6-10], requiring a new location!
Felice Vinci is also a co-author (with Syusy Blady, and Karl Kello) of Il meteorite iperboreo [1906] in which the Kaali meteor is discussed along with its possible association with the ancient Greek story of Phaeton.>>This is just one of the many other subjects that Vinci has commented on, as a quick look at the academia.edu website(y) reveals.<<
(a) The Location of Troy | Felice Vinci (archive.org)
(b) https://mythopedia.info/Vinci-review.pdf
(c) http://www.migration-diffusion.info/article.php?authorid=113
(d) https://homergeography.blogspot.ie/
(e) The Indo-European paradise and the Garden of Eden (archive.org) *
(f) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=P6QPtcZWBPs
(g) Wayback Machine (archive.org) See: Note 5
(h) https://www.slideshare.net/akela64/1-aa-toija-2007-English
(i) https://www.migration-diffusion.info/books.php
(j) https://www.migration-diffusion.info/article.php?id=44
(k) https://www.paabo.ca/reviews/BalticHomericVinci.html
(l) Ilion & HERACLES: the books (archive.org)
(m) The Open Court magazine. Vol.XXXII (No.8) August 1918. No. 747
(n) The mystery of Achilles’s blond hair – Ilion & HERACLES: the books (archive.org)
(o) https://ilionboken.wordpress.com/insight-articles/guest-article-where-were-the-pillars-of-hercules/
(p) Atlantis: Mystery Unveiled – The Tapestry of Time (larazzodeltempo.it)
(s) https://www.encyclopedia.com/arts/educational-magazines/vinci-felice-1946
(v) (26) The Odyssey’s Northern Origins and a Different Author Than Homer | Andres Pääbo – Academia.edu
(w) https://lupinepublishers.com/anthropological-and-archaeological-sciences/pdf/JAAS.MS.ID.000339.pdf
(x) https://lupinepublishers.com/anthropological-and-archaeological-sciences/pdf/JAAS.MS.ID.000314.pdf
Beaumont, William Comyns *
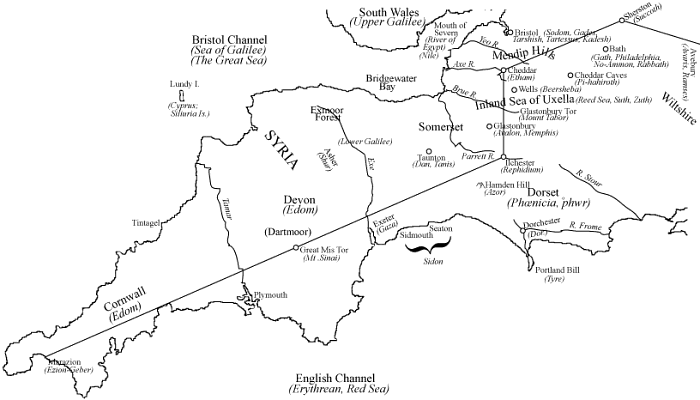
William Comyns Beaumont (1873-1956) was a British journalist, author and the uncle of the novelist Daphne Du Maurier. He is frequently referred to as an eccentric and not without reason. He published an extraordinary book, Britain – The Key to World History [088], in which he claimed among other things, that Edinburgh was the original Jerusalem, London was Damascus and rather worryingly that Bristol was Sodom (see map).
Beaumont located the Pillars of Heracles at Northern Ireland’s Giant’s Causeway along with its counterpart on the Isle of Staffa in Scotland(h). This suggestion was revived(k) nearly twenty years ago by veteran forum contributor ‘Jameske’ and more recently by Marco Goti. This identification has now also been adopted by Alberto Majrani(i). However, the first to associate the Giant’s Causeway with Atlantis was probably John Whitehurst (1713-1788)(j). James McCulloh (1793-1870) noted [1588.30] that General George Vallancey was disposed to support Whitehurst’s association of the Giant’s Causeway with ‘lost Atalantis’.
In addition, Beaumont was convinced that 18th Dynasty Pharaohs ruled the Welsh Britons. The foreword to the ‘Key’ is available online(d) as is a 1949 newspaper review(e).
In an earlier work[089] he had identified ancient Britain as Atlantis and claimed that Atlantis was destroyed by a cometary impact in 1322 BC. This book introduced Beaumont as possibly the first British catastrophist, who expanded on this subject of celestial collisions in a subsequent book[090].
It has been claimed that Beaumont’s theory of celestial impacts partly inspired Immanuel Velikovsky’s writings[037], but characteristically, without receiving any recognition from that quarter.
Some years ago Benny J. Peiser drew attention to how Beaumont’s work had been overlooked and probably plagiarised citing a list of 25 similarities between the theories of Beaumont and Velikovsky previously noted by Alfred De Grazia(a).
In 1975, the American psychologist, Robert Stephanos (1925-2011)(c), founded the Comyns Beaumont Society in Philadelphia. Stephanos appears to have accepted Beaumont’s ideas including their more bizarre elements. In 1994 Stephanos published an article in Fate magazine(f), in which he also claimed that Velikovsky had ‘borrowed’ many of Beaumont’s catastrophist ideas.
The authorship of the works of Shakespeare has been questioned by both Ignatius Donnelly[0023] and Beaumont[1224].
Beaumont’s books are hard to find, however, all four of them have now been made available as reprints(b) and are a must for students of the history of catastrophism and its part in the Atlantis story.
Beaumont had completed the manuscript for another book, The Great Deception[1227], shortly before his death. This has now been edited for publication by Janice Mendez and is now available in print and online. In it, Beaumont returned to the subject of catastrophism along with some radical historical revisionism and has its objective described by his grandson, Christopher Toyne, as “to propound the ultimate subterfuge by Emperor Constantine the Great to reconstruct the story of Jesus away from the British Isles and place it in the now Middle Eastern ‘Holy Lands.’ This is THE GREAT DECEPTION.” I expect the reviews to be entertaining.
A more recent (Jan.2017) review(g) of Beaumont’s odd ideas might be worth a read.
(a) See: Archive 2315 and Comyns Beaumont | The Velikovsky Encyclopedia
(b) https://web.archive.org/web/20181004052944/https://www.twelvearound1.com/comb.html
(c) https://www.irishoriginsofcivilization.com/comyns-beaumont.html
(d) https://self-realisation.com/ourstory/britain-key-to-world-history/
(f) Catastrophists in Collision: Did Velikovsky borrow from Beaumont’s original works? Fate [March 1994], 66-72
(g) https://blog.world-mysteries.com/ancient-writings/scotlands-catastrophic-comet-conspiracy/
(h) https://www.theflatearthsociety.org/library/pamphlets/Is%20Britain%20the%20Lost%20Atlantis.pdf
(i) Guest Article: Where were the Pillars of Hercules? – Ilion & HERACLES: the books (archive.org) *
(k) Re: Atlantis = Ireland? – Graham Hancock Official Website