Johann Radlof
Phaëton
Phaëton in Greek mythology was the son of Helios the Greek sun god. Phaëton was also the name given to a comet that impacted or had a close encounter with the Earth in the 13th century BC. The Egyptians knew this comet as Sekhmet. Ancient inscriptions record that some of the consequences of this dramatic encounter were the drying up of the Nile and the desertification of Libya.
Michel-Alain Combes has noted(j) that Phaëton has also been associated “with Anat in Syria, the star of Baal in Canaan (Palestine and Phenicia), Absinthe, The star of the Apocalypse) among the Hebrews, Surt in the countries of the north.” He also suggests that the legends of Typhon (Hesiod) and Phaeton (Ovid), although usually thought to refer to separate events, are just different versions of the same encounter with a comet in the late 13th century BC.
Günter Bischoff has published two lengthy articles(n)(o) on the Atlantisforschung website which includes a comment that might account for the number of locations where apparent sightings of the comet were reported. “Now it is easy to explain why Phaethon should have been sighted over Greece, Egypt, Syria, India and other countries. During its orbits lasting several days, it will have flown over many inhabited areas on its elliptical orbit. Some observers may even have seen it several times and from different directions.”
A 2012 paper by Peter James and M.A, van der Sluijs entitled ”Silver’: A Hurrian Phaethon’ (l) concluded that “there is an attractive pattern of correspondences between the well-known Greek myth of Phaethon and the Hurrian myth of Silver.” Silver was a character in Hurrian mythology, also known as Ushu.
Interestingly, Plato records in Timaeus how Phaëton caused immense devastation but does not link it directly with the destruction of Atlantis but the context implies an event that was in the distant past, considerably earlier than Solon. Some ancient authorities, such as Eusebius and Isidore of Seville, have associated Phaëton with the time of Moses.
The poet Goethe considered the story of Phaëton to have had a real astronomical origin.
>Franz Xavier Kugler was a Jesuit priest who spent over thirty years studying ancient astronomical texts written in cuneiform. In 1927, he published a paper in which he concluded that a 1500 BC asteroidal impact in the Mediterranean inspired the story of Phaëton(r), an idea that could support the theories of Fatih Hodžic.<
>Immanuel Velikovsky has quoted from several of Kugler’s books in Worlds in Collision(t). In 1975 Malcolm Lowery published a more critical view of Kugler’s theories(u), concluding with the comment “thus we see in Kugler the triumph of preconceived ideas over objective investigation of all available evidence – the more surprising as Kugler could accept one interpretation of Plato to back up one aspect of his theory, but was unable to see its obvious similarity to Celsus and Manilius. In the last reckoning, it seems, he was unable to escape the yoke of uniformitarianism.”<
More recently, Bob Kobres has written several articles on the subject of Phaëton having a cometary origin(k). Some of these papers can be found on the Internet(a). Kobres dates this Phaëton event to around 1200 BC.
Stavros Papamarinopoulos from the University of Patras in Greece presented a paper to the 2005 Atlantis Conference held on Melos in which he linked Plato’s Phaëton with an encounter between the earth and cometary fragments around 1200 BC.
Emilio Spedicato opted for 1447 BC as the likely date of the Phaëton explosion. He describes this as a super-Tunguska event, which exploded over southern Denmark(m). He further contends that the after-effects assisted the Israelite Exodus from Egypt.
Spedicato’s identification is comparable with Jürgen Spanuth’s idea that Phaëton was a fragment of Halley’s Comet. Two other followers of Spanuth, Günter Bischoff and Walter Stender have written extensive papers, in German, on a meteorite impact with Northern Europe around 1220 BC, which they identify as Phaëton(c). The same interpretation has been applied specifically to Lake Chiemgau in S.E. Bavaria and is expanded on in papers by Barbara Rappenglück among many others(d)(f).
The late Bernhard Beier published an article on the Atlantisforschung website regarding Spanuth’s Phaeton theory that proposes a North Sea impact around 4.5km south of Helgoland with the consequent destruction of Atlantis. Beier concludes his comments with “Spanuth’s assumption that the Phaethon legend represents a mythical representation of catastrophic events from pre-Hellenic times corresponds exactly to Plato’s view of things and can therefore still be regarded as open to discussion. His chronological assignment of these events to the end of the ‘Bronze Age’ still seems worthy of discussion. On the other hand, the equation of the assumed Phaethon 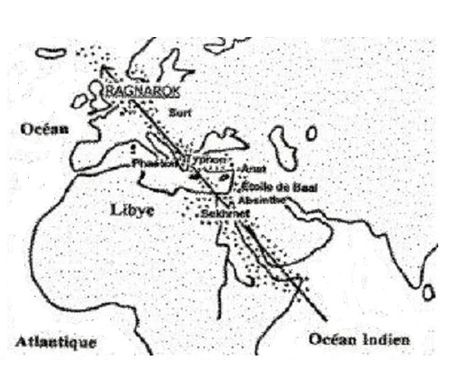 impact with the Atlantis catastrophe, which he made quite naturally and without further ado, lacks any exegetical basis, even if it may initially appear quite logical in the context of Spanuth ‘s theory.”(p) There are aspects of the Phaëton story that are still debated. Was the Phaëton of Greek mythology inspired by a close encounter with a comet? Did it destroy Atlantis? Are we dealing with an impact or just a very close encounter? What was the flight path of the comet? One suggested route is shown here, where it was given different names along the way.
impact with the Atlantis catastrophe, which he made quite naturally and without further ado, lacks any exegetical basis, even if it may initially appear quite logical in the context of Spanuth ‘s theory.”(p) There are aspects of the Phaëton story that are still debated. Was the Phaëton of Greek mythology inspired by a close encounter with a comet? Did it destroy Atlantis? Are we dealing with an impact or just a very close encounter? What was the flight path of the comet? One suggested route is shown here, where it was given different names along the way.
Holger Kalweit, who also follows Spanuth in identifying Heligoland as a remnant of Atlantis, claims it was destroyed in 1222 BC by Phaëton.
Clube & Napier [0290] have proposed a slightly later date of 1369 BC for the encounter with Phaëton.
Dale Drinnon has argued(g) against any connection between Phaeton and the destruction of Atlantis saying “There are two different kinds of catastrophes being described and distinguished from one another and the Phaethon event is categorically differentiated from the Destruction of Atlantis in the Atlantis dialogues of Plato. There is no good reason to equate the two and certainly no textual justification for doing so.”
Allan & Delair refer to the central cause of the catastrophe described in their book[014] as Phaëton, which they claim was cosmic ejecta from a supernova in the Vela constellation. Maurice A. Williams in his review(q) of their book noted how the authors deduced that ancient Mesopotamian observers named this cosmic intruder Marduk as it caused great disruption in the Solar System, including the destruction of the planet ‘Tiamat’ creating the Asteroid Belt and capturing Tiamat’s satellite ‘Kingu’, which in turn disintegrated near Earth causing the biblical Deluge. This deadly journey was also seen by the Greeks and called Phaëton by them.
Amanda Laoupi offers an extensive article on the history of the Phaëton myth and its interpretation in both ancient and modern times.
Phaëton was also the name given by Johann Gottlieb Radlof (1775-1829) to a planet that he believed disintegrated after a collision with a comet, within human memory, resulting in the asteroid belt.
Today, we have an asteroid called 3200 Phaeton which is the source of the annual Geminid meteor shower(s).
(a) Comet Phaethon’s Ride (defendgaia.org)
(b) https://www.migration-diffusion.info/article.php?year=2011&id=259
(c) http://www.efodon.de/html/archiv/vorgeschichte/bischoff/2003-SY5%20bischoff_phaeton.pdf
(d) http://impact-structures.com/news/Stoettham_c.pdf
(f) https://guginew.blogspot.ie/2011/09/fall-of-phaethon-greco-roman-geomyth.html
(g) Archive 3605
(j) http://www.astrosurf.com/macombes/Article_Sekhmet,_Phaeton,_Surt_et_les_autres.htm (French)
(k) Archive 3365.
(l) https://www.researchgate.net/publication/274336666_’Silver’_A_Hurrian_Phaethon
(m) https://interval.louisiana.edu/conferences/2007_Stenger/Slides_of_talks/mose8-6.pdf
(t) Franz Xaver Kugler | The Velikovsky Encyclopedia *
(u) “F. X. KUGLER — ALMOST A CATASTROPHIST”) (defendgaia.org) *
Velikovsky, Immanuel
Immanuel Velikovsky (1895-1979) was born in what is now Belarus. He was by profession a doctor of medicine, specialising in psychiatry. However, his fame is based on being  arguably the most controversial catastrophist of the 20th century. He daringly proposed that the Earth had several close encounters with other planetary bodies that resulted in catastrophic consequences, including interference with the rotation of our planet. He speculated that Atlantis was probably destroyed during one of these cataclysmic events.[037][038]
arguably the most controversial catastrophist of the 20th century. He daringly proposed that the Earth had several close encounters with other planetary bodies that resulted in catastrophic consequences, including interference with the rotation of our planet. He speculated that Atlantis was probably destroyed during one of these cataclysmic events.[037][038]
John Kettler is an American writer on alternative science and was a frequent contributor to Atlantis Rising magazine. In issue #30(z) of that publication, he reviewed the disgusting manner in which members of the scientific community endeavoured to prevent the publication of Velikovsky’s books. In order to give you the full flavour of the nastiness of their methods, I add three paragraphs here.
“The scientific and academic reaction to the book (Worlds in Collision) was generally presaged by the extortion practised prior to and after publication against the Macmillan Company. As the book began to garner public and in some circles, even scientific interest and acclaim, all pretence of genteel discussion went by the boards. Out came the mailed fists, the naked threats and oceans of mud and offal. The attacks targeted three main groups: the public, the scientific and academic community, and Immanuel Velikovsky himself. Nor were such niceties as actually reading the book before denouncing it and its author employed.
Even before the Macmillan Company published the book, renowned astronomer Harlow Shapley arranged multiple intellectual well poisonings by an astronomer, a geologist, and an archaeologist, not one of whom had read the book, in a learned journal. This was a pattern used over and over again.
Shapley and his minions also engineered the sacking of the veteran senior editor (25 years at the Macmillan Company) who accepted Worlds in Collision for publication and got the director of the famous Hayden Planetarium fired for the high crime of proposing to mount a display there, on Velikovsky’s unique cosmological theory. Meanwhile, Velikovsky was systematically attacked in the scientific journals, via distortion, lies, misrepresentation, incompetence and ad hominem attacks, while there never seemed to be space in which he could reply, in order to defend himself.” J. Douglas Kenyon included Kettler’s revealing essay in Forbidden History [802.53].
Some have seen the influence of Ignatius Donnelly’s Ragnarok, written seventy years earlier, in Velikovsky’s cosmic collision theories. Some commentators have noted how Velikovsky seemed reluctant to credit earlier writers, such as W. C. Beaumont and Johann Radlof (1775-1846)(b)[1438], with their contributions to the development of the theory of planetary catastrophism. Rens Van Der Sluijs has written an interesting two-part paper(d)(e) listing the catastrophists who preceded Velikovsky demonstrating a certain lack of originality on his part! Others take a more critical view of his ideas(g). In 1950, he responded to this criticism with a defensive piece(n), but I consider it inadequate as he continued to ignore the work of Radlof and Beaumont. Some years ago Ev Cochrane and Phil ‘Pib’ Burns also discussed Velikovsky’s reluctance to credit earlier writers for ideas used by him, compared with the recognition given by Clube & Napier to the work of Velikovsky(x).
Van Der Sluijs has written a two-part(k)(l) article on Velikovsky’s radical views regarding Venus as a comet-like body and how Aztec sources support some of his contentions.
Carl Sagan (1934-1996), was a well-known American astronomer, author and lecturer. He is considered a leading debunker of Velikovsky’s theories. He devoted much of his Broca’s Brain [1662] to this end. Charles Ginenthal (1934-2017) produced an extensive rebuttal of Sagan’s criticisms in Carl Sagan & Immanuel Velikovsky [1485]. However, criticism of Velikovsky continues with varying degrees of ferocity, such as that of Leroy Ellenberger, a former supporter of Velikovsky, who contends that the data from the Greenland ice cores fail to support Velikovsky(s).
Velikovsky and Einstein were acquaintances and as Nathaniel Lloyd wrote in his three-part blog on chronological revisionism(y) that when Velikovsky “asked Einstein to read his work and give an opinion. Einstein suggested that Velikovsky might have a hard time finding a publisher, specifically because “every sensible physicist” would realize that the catastrophes Velikovsky described would have completely destroyed the Earth’s crust. Nevertheless, Einstein was kind about his criticism, and Velikovsky was undeterred. But years later, in Einstein’s very last interview, his opinion was less delicate: ‘It really isn’t a bad book,’ he said, laughing. ‘The only trouble with it is, it is crazy’.”
More recently, Paul Dunbavin, author of Towers of Atlantis [1627], has published a paper(r), entitled Catastrophism without Velikovsky, which is highly critical of Velikovsky’s work.
Velikovsky was initially inclined to link the disappearance of Atlantis with the eruption of Thera but later came to support a location between the Azores and the Mid-Atlantic Ridge(i). He was an early questioner of Plato’s figure of 9,000 years for the age of Atlantis, suggesting that it was exaggerated by a factor of ten[0037.152]. ”Whatever the source of the error, the most probable date of the sinking of Atlantis would be in the middle of the second millennium, 900 years before Solon when the earth twice suffered great catastrophes as a result of ‘the shifting of the heavenly bodies.’ These words of Plato received the least attention, though they deserved the greatest.”
Velikovsky offered intriguing evidence that on at least one occasion the early Egyptians experienced the sun rising in the west and set in the east(q)!
His other major contribution was in his questioning of the accepted Bronze Age chronologies of the eastern Mediterranean[039]. Later writers, such as David Rohl and Peter James have built on his chronology work, while Gary Gilligan has added support for Velikovsky’s planetary theories[1385] as well. Others have accused Velikovsky of being over-dependent on his belief in the inerrancy of biblical chronology.
In a recent (2023) paper(ac). on the Academia.edu website, Donald Keith Mills was highly critical of Velikovsky’s research on the Hyksos and Amalakites in Ages in Chaos. Mills had earlier written critically of Velikovsky’s Worlds in Collision(ab).
“In Ages in Chaos, Velikovsky made numerous detailed claims which he supported by footnote references to his sources. Those sources were of two kinds: those that would be easily available to most of his readers, such as the Bible and the works of Josephus; and those that would be difficult or impossible for most readers to access, including technical journals and the works of medieval Arabian, Persian, and Egyptian writers.
“Access to such materials began to change in the late 20th Century, and I have been able to download almost all of Velikovsky’s “Arabic” sources from the Internet Archive Digital Library (https://archive.org/ ), together with some he didn’t explicitly use. Those original sources, in the same editions as he cited, revealed that his uses of allusions, references, and quotations often failed to agree with what the sources actually said.”
“Repeatedly, when faced with conflicting accounts of pre-Islamic (and essentially prehistoric) events, Velikovsky selected only those that met his purposes. The damaging aspect of this criticism is the fact that, almost without exception, he did so without discussing the alternatives, without providing reasons for rejecting them, and without even acknowledging their existence.“
One website(a)provides us with a considerable amount of Velikovsky’s unpublished work, while another offers an encyclopedia of his work(c). A more general German site(f), in English, is also worth a visit.
The three of Velikovsky’s most popular books as well as some of his lesser-known papers are available as pdf files(j)(m).
Jan Sammer was an assistant to Velikovsky (1976-1978) and an archivist and editor for the Velikovsky Estate (1980-1983). He advises us that he was involved in the completion of Velikovsky’s unpublished book, In the Beginning(h), which was eventually published in 2020 [1956]. The book’s contents were originally intended to be part of Worlds in Collision. In it, you will find more details of Velikovsky’s claim that within the memory of man, there was a time when we had no Moon, which he claimed was subsequently ‘captured’ by the Earth. He wrote a short paper in 1973 entitled Earth without a Moon and published by the editors of Pensée in Velikovsky Reconsidered [1877.86], but without any reference to Hanns Hörbiger.
According to Velikovsky, Venus was a relatively recent newcomer to our Solar System and the orbit of Mars had been disturbed, which would suggest that before the arrival of Venus, Bode’s Law would have been invalidated! C.J. Ransom tackled this head-on in The Age of Velikovsky [1880.90]. However, his defence of Bode and Velikovsky was rejected by Dr M. M. Nieto(t).
In 2012, Laird Scranton, published The Velikovsky Heresies[1642], in which he reviews Velikovsky’s controversial theories in the light of scientific discoveries since his death. Not unexpectedly, Scranton does find evidence that supports some of Velikovsky’s contentions.
Ralph E. Juergens, an American engineer, supported Velikovsky with the idea that electromagnetic and electrostatic forces and not conventional celestial mechanics alone were responsible for the cosmic encounters witnessed and recorded by our ancestors(u).
In the late 1990s Sean Mewhinney (1944-2016), a Canadian researcher published a series of papers(w) that was highly critical of Velikovsky’s theories. Much of his criticism was focused on ice-core data. Once again, Charles Ginenthal took up the challenge, responding with an extensive paper entitled Minds in Denial, later the title of an ebook [1897] that include the original paper. Ginenthal also published a book on the Electro-Gravitic Theory of Celestial Motion and Cosmology and its possible application to Velikovsky’s theories(v).
In 2021, Bob Forrest(aa), a British retired mathematics teacher had re-published a book of over 700 pages entitled Velikovsky’s Sources, which deals with Worlds in Collision. It had been originally issued as a series of seven booklets between 1981 and 1985. These have now been combined in one volume and edited by Donald Keith Mills and available on the Academia.edu website(ab). The content is a critique of Velikovsky’s work and now forty years later Forrest still believes “that Velikovsky was spectacularly wrong.”
Some readers may wish to see a video by Wallace Thornhill, of Electric Universe fame, in which he discusses Velikovsky’s Astrophysics(o). There are several related papers and books, including some Velikovskian material, freely available online(p).
>We are also fortunate to have a biography of Velikovsky’s eventful life published in 2010 by his daughter, Ruth Velikovsky Sharon [2048].<
(b) https://www.mythopedia.info/radlof.htm
(c) https://www.velikovsky.info/Main_Page
(d) https://www.thunderbolts.info/wp/2013/01/22/on-the-shoulders-of-suppressed-giants-part-one-2/
(e) https://www.thunderbolts.info/wp/2013/01/23/on-the-shoulders-of-suppressed-giants-part-two-2/ (f) http://www.velikovsky.de/en/velikovsky.html
(g) See: https://web.archive.org/web/20180305142157/https://abob.libs.uga.edu/bobk/velidelu.html
(h) https://www.varchive.org/itb/tnote.htm
(i) https://www.varchive.org/ce/baalbek/atlantis.htm
(j) https://www.pdfarchive.info/index.php?pages/Ve
(k) https://www.thunderbolts.info/wp/2016/12/19/smoke-without-fire-part-one/
(l) https://www.thunderbolts.info/wp/2016/12/21/smoke-without-fire-part-two/
(m) https://www.scribd.com/doc/124804145/Ages-in-Chaos-Velikovsky-pdf
(n) https://www.varchive.org/ce/precursors.htm
(o) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Gouqy4OghyY
(p) Free Electric Universe theory ebooks and related research papers (archive.org)
(q) The Sun rose in the west? Egyptian evidence? (archive.org)
(r) https://www.third-millennium.co.uk/home-2
(s) http://www.defendgaia.org/bobk/velstcol.html
(t) The Titius-Bode Law (archive.org)
(u) http://www.thunderbolts.info/pdf/Reconciling%20Celetial%20Mechanics.pdf
(v) TheElectroGraviticTheoryofCelestialMotionandCosmology.pdf (rogerswebsite.com)
(w) http://www.pibburns.com/smmia.htm
(x) How much do Clube and Napier owe Velikovsky? (pibburns.com)
(y) https://www.historicalblindness.com/blogandpodcast//the-chronological-revision-chronicles-part-one-the-fomenko-timeline (new link) *
(z) Atlantis Rising magazine #30 http://pdfarchive.info/index.php?pages/At
(aa) Home Page (bobforrestweb.co.uk)
(ab) (82) [Forrest 2021] Velikovsky’s Sources: Worlds in Collision | Donald Keith Mills – Academia.edu
(ac) (99+) VELIKOVSKY AND THE AMALEKITES | Donald Keith Mills – Academia.edu
