Punt
Ancient Seafaring
Ancient Seafaring is a controversial subject owing principally to a dearth of physical evidence. The earliest known boat is the Pesse
Canoe (see right) which was discovered in The Netherlands and thought to be around 10,000 years old. The second oldest boat was also a canoe, found in Malawi and dated to about 8,000 years ago(g). Wikipedia lists all the surviving boats, which shows that until the third millennium BC all that have been found are canoes.
Seafaring and Atlantis are inextricably linked. In Critias 117d Plato anachronistically refers to the shipyards of Atlantis being full of triremes, which were not developed until the 7th century BC, long after the demise of Atlantis. However, the term ‘trireme’ was probably employed by Plato to make his narrative more relevant to his audience. He credits the Atlantean navy with 1200 ships, which for me seems like borrowing and rounding the numbers of either the Achaean fleet of 1186 vessels in Homer’s Iliad or that of the 1207 ships of the later Persian invaders. That ships were used in the war with Athens can be inferred from the fact that Atlantis, or at least its capital, was situated on an island.
Professor Seán McGrail (1928-2021) wrote in his monumental work, Boats of the World “There is no direct evidence for water transport until the Mesolithic even in the most favoured regions, and it is not until the Bronze Age that vessels other than logboats are known” [1949.10]. For those that adhere to a 10th millennium BC date for the Atlantean War with Athens, this lack of naval evidence to support such an early date undermines the idea. An invasion fleet of canoes travelling from beyond the Pillars of Herakles to attack Athens seems rather unlikely!
Apart from the Solar Boats of the Egyptians, such as the Khufu Boat (see left),
discovered at Giza in 1954 and dated to 2500 BC. Fifty years later Kathryn A. Bard, Professor Emerita of Archaeology and Classical Studies at Boston University and Rodolfo Fattovich, an archaeologist at the Orientale University of Naples, discovered an ancient port at Mersa Gawasis on the Red Sea. Evidence at the site indicated that it had been used around 1800 BC as an embarcation point for expeditions to the legendary land of Punt. Andrew Curry has written a review(l) of the work carried on at the site. Curry’s article is headed with the claim that the discovery of the harbour “proves ancient Egyptians mastered oceangoing technology”. In my opinion, this is possibly overstating it as the remains of the vessels found there may have suited the relatively calm Red Sea, a voyage in the Atlantic would probably have been too much.
Nevertheless, Heather Pringle published an article in 2008 in which she reviewed the suggestion by Jon Erlandson(k), an archaeologist at the University of Oregon, that early humans may have travelled the oceans 70,000 years ago(j).
Seldom referred to, but perhaps even more interesting is to be found earlier in Critias 113e which describes the mythological beginnings of Atlantis and which reads “for at that time neither ships nor sailing were as yet in existence”. However, we are given little information to bridge the time up to its development as a major trading entity. It is reasonable to assume a gap of several thousand years.
Recent studies(a) have suggested that primitive seafaring took place in the Mediterranean thousands of years earlier than originally thought and may even have been engaged in by Homo Erectus and Neanderthals in the form of island hopping and coastal-hugging, the latter continuing into historical times.
Plato describes an advanced maritime trading nation with a powerful naval capacity. How much was part of the original story brought from Egypt by Solon or whether it was in any way embellished by Plato is unclear. The earliest known trading empire is that of the Minoans which began in the 3rd millennium BC and has led to many identifying them with the Atlanteans. However, there are very many other details in Plato’s narrative that seriously conflict with this hypothesis.
The limitations of ancient seafaring raise many questions regarding the navigation supports available to these early sailors(b). Initially, sailing, probably for fishing, would have been confined to daytime travel and keeping within the sight of land. With the development of maritime trade, the demand for improved navigation methods also grew.
It has been generally accepted that sailing in the Mediterranean in the Middle Ages was not undertaken between October and March because of the dangerous weather usually encountered at that time of the year. Some cities, such as Pisa, Venice and Genoa had ordinances forbidding commercial voyages in winter! Understandably, many considered that this was also the case in Greek and Roman times when shipbuilding skills and navigational technology were probably more primitive. A 2015 paper by T.M.P. Duggan demonstrates that commercial maritime activity in winter was commonplace in medieval times(m).
In time sailors acquired a familiarity with the night sky that enabled them to use the stars as navigational aids, given clear skies. Gradually, as nighttime travel became more common, the use of beacons and later lighthouses also expanded. The lighthouse at Pharos near Alexandria came to be counted as one of the wonders of the Old World. Similarly, it is thought that the Colossus at Rhodes performed a similar function.
Different navigation skills have been identified in different parts of the world. In the Pacific, the navigational capabilities of the Polynesians are legendary(c). A November article on the BBC website expanded on this ‘ancient art of wayfindlng’ (i). The ancient Chinese employed magnetism(e) and in the cloudy North Atlantic, the Vikings used their ‘sunstones’(d).
In their book, Atlantis in America [244] Ivar Zapp & George Erikson claimed that the stone spheres of Costa Rica had a navigational function [p34] as Zapp discovered that the sightlines of all the stones remaining in their original positions, did point to important ancient sites such as Giza, Stonehenge and Easter Island!
A most imaginative proposal has come from Crichton E.M. Miller who proposed [1918] that the ubiquitous Celtic Cross is an image of an ancient navigational device. He further claims that “This instrument can tell the time, find latitude and longitude, measure the angles of the stars, predict the solstices and equinoxes and measure the precession of the equinoxes. It can also find the ecliptic pole as well as the north and south poles; it can make maps and charts, design pyramids and henges and—used in combination with these sites—can record and predict the cycles of nature and time(f) “. Then for good measure, he proceeded to patent the device.
(a) http://news.yahoo.com/ancient-mariners-did-neanderthals-sail-mediterranean-192112855.html
(b) http://www.ancient-wisdom.com/navigation.htm
(c) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polynesian_navigation
(d) https://www.newscientist.com/article/dn20052-vikings-crystal-clear-method-of-navigation/
(e) http://www.ancient-wisdom.com/magnetism.htm
(f) Atlantis Rising magazine #35 http://pdfarchive.info/index.php?pages/At
(g) https://www.ancient-origins.net/artifacts-ancient-technology/pesse-canoe-0017298
(i) https://www.bbc.com/future/article/20231128-what-we-can-learn-from-the-ancient-art-of-wayfinding
(j) https://www.discovermagazine.com/the-sciences/did-humans-colonize-the-world-by-boat
Ophir
Ophir is referred to in the Bible as a source of gold, silver, precious stones and exotic animals. King Solomon was reputed to have received a cargo of such goodies every three years, a detail which points to Ophir being a considerable distance from Israel.
The exact location of Ophir is the subject of continuing controversy. In broad terms the most popular regions suggested are, or have been, India(g), Africa(f) and the Americas(a), but they were not the only proposed locations, even Australia and the Solomon Islands were considered. Emilio Spedicato has opted for Tibet, where an ancient goldmine fits the bill, which he outlines in his paper entitled Ophir, It’s Location Unveiled(h).
There is also a claim that the Batanes Islands off the Northern Philippines held the site of Ophir(b). Further west, Dhani Irwanto has claimed that Punt was also known as Ophir(d) and was situated on Sumatera (Sumatra) in Indonesia(c). However, he went further and also located Atlantis in Indonesia in his book, Atlantis: The lost city is in the Java Sea [1093]. His chosen site is just north of Bawean Island in the Java Sea.
However, Irwanto was not the first to link Atlantis with Ophir, Theodore L. Urban was the author of a paper delivered to the Lancaster County Historical Society of Pennsylvania in 1897. In it, he denied that Atlantis had been completely destroyed and argued that the biblical Ophir was in fact Atlantis, suggesting that it had been located in the Americas, which explained the three years that the round trip took(e).
>Jason Colavito has published articles written by Thomas Crawford Johnston in 1892(i) that he later developed into his 1913 book Did the Phoenicians Discover America [1902+] in which he places Ophir in America!<
(a) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ophir#Americas
(b) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5ZqYQpmRCx0
(c) https://atlantisjavasea.com/2015/11/14/land-of-punt-is-sumatera/
(d) https://atlantisjavasea.com/2019/06/16/land-of-ophir/
(e) https://openlibrary.org/works/OL10326701W/American_Indians (p.91)
(f) https://www.historicmysteries.com/lost-mine-ophir/
(g) https://www.britannica.com/place/Ophir
(h) OPHIR 27-10-09 (2010-q-conference.com) *
(i) Phoenicians in America – JASON COLAVITO *
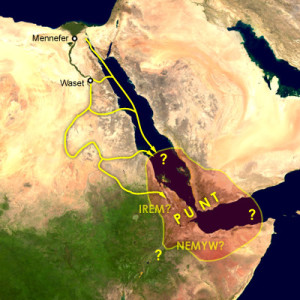
Punt *
Punt is the name given to a land with which the ancient Egyptians traded. The leading theory is that it was located to the southeast of Egypt, roughly occupying what is now called ‘the Horn of Africa, although there is also a popular view that it was situated on the Arabian Peninsula. Others suggest that a combination of parts of both regions might be nearer the truth. An article from November 2016 elaborates on the claim for this identification(e).
Along with the many luxury goods that Punt supplied to Egypt were baboons, so it was interesting to read in 2020 that “a new study tracing the geographic origins of Egyptian mummified baboons finds that they were sourced from an area that includes the modern-day countries of Ethiopia, Eritrea, Djibouti, Somalia, and Yemen, providing new insight into Punt’s location.”(i). The investigation centred on the strontium levels found in the ancient remains.
A November 2023 an article by Miriam Fauzia returned to the possibility that the baboons offered clues to the location of Punt and once again focused on East Africa, specifically the Eritrean location of the legendary port city known to the Romans as Adulis(n).
Thor Heyerdahl in The Tigris Expedition [1921] also identified the region around Djibouti as the land of Punt.
In 2013, a short book [1567] by Ahmed Ibrahim Awale, placed Punt in the same region, namely, in Hargeisa, the capital of Somaliland. A favourable and well-illustrated review(f) of Awale’s book is worth a read. The worldhistory.org website has pointed out that the name of the Puntland State of Somalia may preserve a memory of the original mythical Punt(h).
However, Immanuel Velikovsky wrote at length about Punt and its location in Palestine in Ages in Chaos [0039]. He maintains that Punt is consistently described as being to the east of Egypt, which would rule out Somalia. Added to this, he claimed that the Queen of Sheba and Queen Hatshepsut were one and the same person, a view endorsed by historical researcher Dr. Eva Danelius (1898-1995).
Others, such as Eulalio Eguia jr, identify the Queen of Sheba with Nefertiti(l). Velikovsky’s comments are certainly worth a read. Emmet Sweeney has adopted both Velikovsky’s location for Punt and his identification of the Queen of Sheba(j). Damien Mackey offers new evidence to support Velikovsky’s claims(m).
By way of contrast, David Lorton has offered a series of criticisms of Velikovsky’s Punt/Sheba ideas(k).
Frank Joseph in his Atlantis Encyclopedia[0104.37] claims that “the Lands of Punt (are) often associated with the islands of Atlantis.” Joseph expands on this in an Atlantis Rising article(a) where he refers to an ancient Egyptian story of “The Shipwrecked Sailor” in which the ‘Serpent King’ is identified as master of the island of Punt, which again Joseph claims to be Atlantis.
More recently, a small number of commentators have identified Punt/Atlantis with Indonesia(b)(c). Dhani Irwanto, who is a leading advocate of an Indonesian Atlantis[1093] published in November 2015 an extensive article online(d) in which he specifically names the Indonesian island of Sumatera (Sumatra) as the land of Punt. He has now expanded this into a book, Land of Punt: In Search of the Divine Land of the Egyptians [1628]. Irwanto goes further and also identifies the mysterious land of Ophir in the Bible as Punt.
Xavier Séguin proposed that Punt along with Atlantis, Mu and Hyperborea were in fact satellites(g)!!!
(a) See: Archive 2790
(b) https://www.bibliotecapleyades.net/atlantida_mu/esp_atlantida_3a.htm
(c) http://www.lost-civilizations.net/true-history-atlantis-2.html
(d) https://atlantisjavasea.com/2015/11/14/land-of-punt-is-sumatera/
(f) The Mystery of the Land of Punt Unravelled – book review | Land of Punt (archive.org)
(h) https://www.worldhistory.org/punt/?visitCount=48&lastVisitDate=2021-4-9&pageViewCount=64
(i) https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2020/12/201215082048.htm
(j) https://www.hope-of-israel.org/expeditionpunt.html
(k) Hatshepsut, the Queen of Sheba, and Immanuel Velikovsky (archive.org) (new link)
(l) Nefertiti – The Queen of Sheba | PDF | Tutankhamun | Akhenaten (scribd.com) *
(m) (83) Solomon and Sheba | Damien Mackey – Academia.edu
Irwanto, Dhani
Dhani Irwanto (1962- ) is an Indonesian hydraulic engineer, who is the latest proponent of the  Sundaland location for Atlantis, in his April 2015 book, Atlantis: The lost city is in the Java Sea[1093]. A review of his book online(a), shows quite clearly that the author has made a serious effort to match Plato’s narrative with his chosen location for Atlantis, namely off the southern coast of the island of Kalimantan in the Java Sea. Irwanto also uses his professional expertise to analyse Plato’s many references to the waterways of the Atlantean capital and its extensive plain. The review also includes a number of maps and video clips used to support Irwanto’s views.
Sundaland location for Atlantis, in his April 2015 book, Atlantis: The lost city is in the Java Sea[1093]. A review of his book online(a), shows quite clearly that the author has made a serious effort to match Plato’s narrative with his chosen location for Atlantis, namely off the southern coast of the island of Kalimantan in the Java Sea. Irwanto also uses his professional expertise to analyse Plato’s many references to the waterways of the Atlantean capital and its extensive plain. The review also includes a number of maps and video clips used to support Irwanto’s views.
Irwanto has also adopted(c) the 32-point checklist of dos Santos and expanded it to 60 points. He has now published a YouTube video supporting his theory(d). The first 30 pages of his book can be read online(f).
Irwanto also claims that the biblical Garden of Eden and the legendary island of Taprobane were situated on the island of Kalimantan*. In an extensive online(b) article in November 2015, he identified the Indonesian island of Sumatra as the land of Punt, which he thinks was also known as the Ophir referred to in the Old Testament (1 Kings 9.26 & 10.11).
In June 2017, Irwanto published an illustrated paper(e) on Aurea Chersonesus, referred to by Ptolemy in his 2nd century Geographia . Irwanto has matched the details in Ptolemy’s description with a place in western Sumatra called Tanjungemas renowned for its gold mines in ancient times.
On his website, since the publication of his book, Irwanto had continued to add a number of detailed articles that are of interest to students of Atlantology. One example came in late 2021, when he added an extensive paper entitled Decoding Plato’s Narrative to Find Atlantis, using a visual format, infographics(g) that is worth a look.
(a) https://ahmadsamantho.wordpress.com/2015/06/10/a-new-theory-of-atlantis-disclosed/
(b) https://atlantisjavasea.com/2015/11/14/land-of-punt-is-sumatera/
(d) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JT23A12-tDc&feature=youtu.be
(e) https://atlantisjavasea.com/2017/06/08/aurea-chersonesus-is-in-sumatera/
(f) https://www.academia.edu/18597541/Atlantis_in_Java_Sea
(g) https://atlantisjavasea.com/2021/10/17/decoding-platos-narrative-to-find-atlantis-in-infographics/
Aden
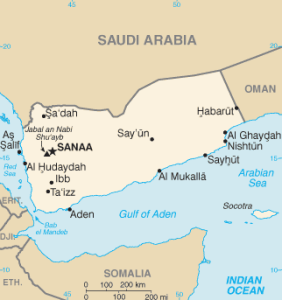 Aden was formerly a British possession and is now part of war-torn Yemen. Stan Deyo, author of The Vindicator Scrolls[784], in 1989 located Atlantis in Aden. A Dutch amateur Egyptologist, Alexander Muster, also promotes a similar idea through a variety of Internet forums. A former French police chief, Jacques Hébert, has proposed that the Yemeni island of Socotra was part of the Atlantean civilisation.
Aden was formerly a British possession and is now part of war-torn Yemen. Stan Deyo, author of The Vindicator Scrolls[784], in 1989 located Atlantis in Aden. A Dutch amateur Egyptologist, Alexander Muster, also promotes a similar idea through a variety of Internet forums. A former French police chief, Jacques Hébert, has proposed that the Yemeni island of Socotra was part of the Atlantean civilisation.
>Yemen’s long history was highlighted just before the end of the last century, when a group of megaliths were discovered, by chance, on the coastal plain of western Yemen(c).<
In 2008, Gary Vey and John McGovern claimed to have evidence that the Ark of the Covenant had been buried in Yemen (the ancient kingdom of Saba)(b).
>Immanuel Velikovsky placed the Garden of Eden in Aden(d).<
A recent Russian website(a) also places Atlantis in the Gulf of Aden opposite the legendary land of Punt in what is now Somalia.
(a) https://sites.google.com/view/atlantis-aden/main
(b) Proto-Canaanite / First Tongue / Ark of the Covenant (viewzone.com)
Sundaland
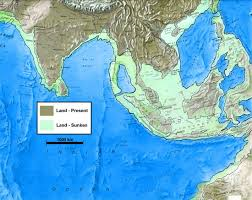 Sundaland is the name of a large biogeographical region of South East Asia, a large portion of which had been above sea level during the last Ice Age and later inundated as the glaciers retreated. The term was apparently first used[1629] in 1949 by R.W. van Bemmelen (1868-1941) and later by other authorities.
Sundaland is the name of a large biogeographical region of South East Asia, a large portion of which had been above sea level during the last Ice Age and later inundated as the glaciers retreated. The term was apparently first used[1629] in 1949 by R.W. van Bemmelen (1868-1941) and later by other authorities.
It is worth noting that it is now generally accepted that South East Asia was probably the entry point of modern humans from Africa. Human traces have been found in Papua New Guinea that have been dated to around 40,000 BC.
Some authors have specifically claimed a clear link between Sundaland and Plato’s Atlantis. The Sunda Sub-Oceanic Plain is large enough to match Plato’s description of Atlantis. Its topography, climate, flora and fauna together with aspects of local mythologies, all permit a convincing case to be made to support this idea.
C.W. Leadbeater (1854-1934) who was a prominent theosophist was perhaps the first to suggest a link between Atlantis and Indonesia in his book, The Occult History of Java [1094], which is now available online(f).
Other investigators have written on the prehistory of the region of whom the best known is probably Stephen Oppenheimer who firmly locates the Garden of Eden in this region[004], although he makes little reference to Atlantis. More recently, Robert Schoch, in collaboration with Robert Aquinas McNally, wrote a book[455] in which they suggest that pyramid building may have had its origins in a civilisation that flourished on parts of Sundaland that are now submerged.
The first book to specifically identify Sundaland with Atlantis was written by Zia Abbas[001]. However, prior to its publication, the Internet offered at least two sites that discussed in detail the case for Atlantis in South East Asia. William Lauritzen(a) and the late Professor Arysio Nunes dos Santos(b) developed extensive websites. Lauritzen has also written an e-book that is available from his site, while Santos developed his views on an Asian Atlantis in another recent book[320]. Dr Sunil Prasannan has an interesting essay on Graham Hancock’s website(c). A more esoteric site(d) also offers support for the Sundaland theory.
An Indonesian researcher, Panji R. Hadinoto, has published on his website(e) a 32 point checklist purporting to ‘prove’ that Atlantis was located on Sundaland. Unfortunately, this checklist is not original but copied from the work of Professor dos Santos.
April 2015 saw further support for an Indonesian Atlantis with the publication of a book[1093] by a hydraulic engineer, Dhani Irwanto, who endeavours to identify features of the lost city with details in Plato’s account with a site in the Java Sea off the coast of the island of Kilmantan. He has now published a YouTube video in support of his theory(h).
In 2019, Irwanto published two new books, the first, Sundaland: Tracing the Cradle of Civilisations [1618], in which he offers a compelling case for considering emigrants from a submerging Sundaland as bringers of embryonic civilisation to other lands, where it flourished and developed local variants. It crossed my mind that Irwanto’s contention might explain the origins of the likes of the Sumerian civilisation, among others, which have never been satisfactorily settled!
The second book, Land of Punt [1628], is another interesting offering in which the author suggests that Punt and the biblical Ophir can be equated with Atlantis, located in Sundaland. However, this idea conflicts with a growing consensus(k) that places Punt in the region of the Horn of Africa or across the Red Sea in Arabia.
A 2016 series of graphics shows the gradual inundation of Sundaland from 18,000 BC onwards(g).
Thorwald C. Franke has drawn attention(j) to a recent controversy in Malaya where historian Zaharah Sulaiman has claimed that the Malay set of mtDNA is 63,000 years old, dating back to a time long before the submergence of Sundaland. It seems that Sulaiman had built her claim on some of Oppenheimer’s writings. This veiled suggestion of some sort of racial superiority, through antiquity, was disputed locally.(i)
Ahmad Yanuana Samantho published Atlantis Nusantara [1869] in 2015, which purports to build on the work of Arysio dos Santos with additional data that the author (or publisher) describes as ‘spectacular’. Unfortunately, the 538-page book is only available in Indonesian. Nusantara is generally used to describe the Indonesian archipelago.
(a) Welcome to Earth360.com (archive.org)
(b) https://www.atlan.org
(c) https://www.grahamhancock.com/underworld/DrSunilAtlantis.php
(d) See: https://web.archive.org/web/20060508140324/https://www.tylwythteg.com/atlantis/southchina.html
(e) https://jakarta45.wordpress.com/2009/10/26/pengkajian-benua-atlantis-tempo-doeloe-di-nusantara/
(f) https://theosophists.org/library/books/occult-history-of-java/
(g) https://i.imgur.com/5l16wXp.gifv
(h) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JT23A12-tDc&feature=youtu.be
(i) Arguing against Malays’ ‘Sundaland origins’ | Opinion | Malay Mail (archive.org) *
(j) Atlantis Newsletter Archive – Atlantis-Scout (atlantis-scout.de) (No.120)
(k) The Arabian Horizon – The Lost Lands: Punt | MalagaBay (archive.org)
Heyerdahl, Thor
 Thor Heyerdahl (1914-2002)was not an advocate for any particular theory regarding Atlantis, except to state[387] that in his view Plato’s text was more supportive of an Atlantic location rather than a Mediterranean one. However, in the same book, Early Man and the Ocean, he lists 53 cultural similarities between civilisations in Mesoamerica and those in the eastern Mediterranean. He did so in order to advance his belief in a diffusionist approach to the study of cultural development. His observations were not the first as parallels between cultures of both sides of the Atlantic were noted as soon as the Spanish invasion of America took place. Years earlier, Ignatius Donnelly, in the first attempt[021] at a more scientific approach to the Atlantis question, drew up similar lists.
Thor Heyerdahl (1914-2002)was not an advocate for any particular theory regarding Atlantis, except to state[387] that in his view Plato’s text was more supportive of an Atlantic location rather than a Mediterranean one. However, in the same book, Early Man and the Ocean, he lists 53 cultural similarities between civilisations in Mesoamerica and those in the eastern Mediterranean. He did so in order to advance his belief in a diffusionist approach to the study of cultural development. His observations were not the first as parallels between cultures of both sides of the Atlantic were noted as soon as the Spanish invasion of America took place. Years earlier, Ignatius Donnelly, in the first attempt[021] at a more scientific approach to the Atlantis question, drew up similar lists.
>Thor Heyerdahl’s 1947 Kon-Tiki expedition gave credence to his theory of indigenous Americans and Polynesians being in contact with each other prior to European colonisation and is still relevant today, as his Kon-Tiki expedition completes 75 years, the Kon-Tiki Museum based in Oslo has said.
The strongest validation the theory received was in 2020 when an American research group made a comprehensive study of Polynesian DNA, the museum said in a statement on April 28, 2022.(b)<
The existence of similarities between societies on the two landmasses is unquestionable; that there were ancient contacts between the two is more than probable, but it is not logical to view it as conclusive evidence of a mid-Atlantic location for Atlantis.
>Heyerdahl has also identified the region around Djibouti as the land of Punt. [1921]<
Many of Heyerdahl’s ideas came under attack, as outlined in a 2002 Smithsonian article(a).