Salah Salim Ali
Islam *
Islam itself does not offer any evidence in support of Atlantis’ existence. However, the Qur’an was not intended as a history book(a). Nevertheless, several renowned medieval Arabic writers such as Al-Biruni, Al-Idrisi and Al-Mas’udi have been referred to as offering indirect but relevant evidence for the submergence of Atlantis in the Mediterranean following the breaching of a dam at Gibraltar. A more contemporary Iraqi scholar, Salah Salim Ali, in a twenty-page essay entitled Arabic References to Plato’s Lost Atlantis[077], discusses a possible link between Atlantis and “the City of Brass” referred to by medieval Arabic writers.
In 2014 an Indonesian website offered a more recent view of the Qur’an and Atlantis(b).
Adlantis was imagined by Ignatius Donnelly to be another form of Atlantis. He noted that the first inhabitants of Arabia were known as Adites. They were named after Ad who was fourth in line from Noah. Without any convincing reason, Donnelly states [0021.276] that “these Adites were probably the people of Atlantis or Adlantis.” The Qur’an (89:6-9) does refer to Ad(c) – Do you not see what your Lord did with ‘Ad-Iram of the Columns whose like was not created in any land? Iram has been identified as the city of Ubar discovered some decades ago(e), but, while Ad, Iram and Ubar may refer to the same place there is no way that either can be linked to Plato’s Atlantis.
It is claimed that the Qur’an contains scientific knowledge that was not known fourteen hundred years ago(d).
(a) The Qur’an on the Lost City of Atlantis – Understanding Islam -under construction (archive.org) *
(c) Archive 3021 | (atlantipedia.ie)
City of Brass
The City of Brass is a term found in the writings of medieval Arabic writers. The Iraqi scholar Salah Salim Ali has written an essay[077] suggesting a link with Atlantis and its Orichalcum coated walls. Over half a century ago Egerton Sykes made a similar submission in his Atlantis journal, quoting sources such A Thousand and One Nights.(a)
>(a) Atlantis, Vol.4, No.3, Stember 1951<
Arabic References (L)
Arabic References to Atlantis are discussed by the contemporary Iraqi scholar, Salah Salim Ali, in a twenty- page essay entitled Arabic References to Plato’s Lost Atlantis[077]. He quotes a number of medieval Arabic writers who refer to such places as the ‘City of Brass’ and the enigmatic ‘City of Baht’ (baht = stone of laughter). The city of Brass obviously echoing Plato’s description of the walls of Atlantis being covered with Orichalcum. Although the contexts of these references are somewhat confusing, Salah Salim Ali concludes that they probably refer to Atlantis and indicate a location in either Andalusia or North-West Africa.
Orichalcum
Orichalcum is, according to legend, reputed to have been ‘invented’ by Cadmus noted in Greek mythology as the legendary Phoenician founder of Boeotian Thebes. This metal is one of the many mysteries in Plato’s Atlantis narrative. It is mentioned five times in the Critias [114e, 116c-d, 119c] as a metal extensively used in Atlantis. I am not aware of any reference to it anywhere else in his writings, a fact that can be advanced as evidence of the veracity of his Atlantis story. Plato took the time to explain to his audience why the kings of Atlantis have Hellenised names. However, he introduces Orichalcum into the story without explanation, which suggests that the metal was something well-known to the listeners. It is therefore natural to expect that metals might play an important part in determining the credibility of any proposed Atlantis location.
Bronze was an alloy of copper and tin, while brass was a mixture of copper and zinc, their similarity is such that museums today refer to artefacts made of either refer to them as copper alloys.
According to James Bramwell[195.91], Albert Rivaud demonstrated that the term ‘orichalcum’ was known before Plato and not just invented by him. Similarly, Zhirov notes that both Homer and Hesiod refer to the metal[0458.46], as does Ibycus, the 6th century BC poet, who compares its appearance to gold suggesting a brasslike alloy. Thomas Taylor (1825) noted that in a fragment from a lost book of Proclus, he seems to refer to orichalcum under the name of migma(c).>Virgil in his Aeneid mentioned that the breastplate of Turnus was “stiff with gold and white orachalc”.<
Wikipedia also adds that “Orichalcum is also mentioned in the Antiquities of the Jews – Book VIII, sect. 88 by Josephus, who stated that the vessels in the Temple of Solomon were made of orichalcum (or a bronze that was like gold in beauty). Pliny the Elder points out that the metal had lost currency due to the mines being exhausted. Pseudo-Aristotle in ‘De mirabilibus auscultationibus’ describes orichalcum as a shining metal obtained during the smelting of copper with the addition of ‘calmia’, a kind of earth formerly found on the shores of the Black Sea, which is attributed to be zinc oxide.”
Friedrich Netolitzky (1875-1945) offered an independent interpretation of the oriharukon (orichalcum) in Plato’s Atlantis account, which he identified as an artificial modification of white gold (known as Asem in ancient Egypt).
Atlantisforschung also offers a lengthy article on orichalcum(p).
Orichalcum, or its equivalent Latin Aurichalcum, is usually translated as ‘golden copper’ referring to either its colour or composition (80% copper and 20% zinc) or both. However, Webster’s Dictionary translates it as ‘mountain-copper’ from ‘oros’ meaning mountain and ‘chalchos’ meaning copper.
Sir Desmond Lee described the metal as ‘imaginary’ without explaining away the classical references or the fact that ”In numismatics, orichalcum is the name given to a brass-like alloy of copper and zinc used for the Roman sestertius and dupondius(r). Very similar in composition to modern brass, it had a golden-yellow color when freshly struck. In coinage, orichalcum’s value was nearly double reddish copper or bronze. Because production cost was similar to copper or bronze, orichalcum’s formulation and production were highly profitable government secrets.”(m)
Modern writers have offered a range of conflicting explanations for both the origin and nature of orichalcum. A sober overview of the subject is provided by the Coin and Bullion Pages website(d).
In 1926 Paul Borchardt recounted Berber traditions that recalled a lost City of Brass. Salah Salim Ali, the Iraqi scholar, points[0077] out that a number of medieval Arabic writers referred to an ancient ‘City of Brass’ echoing the Orichalcum-covered walls of Plato’s Atlantis.
Ivan Tournier, a regular contributor to the French journal Atlantis proposed that orichalcum was composed of copper and beryllium. Tournier’s conclusion seems to have been influenced by the discovery in 1936 at Assuit in Egypt of a type of scalpel made from such an alloy(e). An English translation of Tournier’s paper was published in Atlantean Research (Vol 2. No.6, Feb/Mar.1950). In the same edition of A.R. Egerton Sykes adds a few comments of his own on the subject(r).
An unusual suggestion was made by Michael Hübner who noted that “small pieces of a reddish lime plaster with an addition of mica were discovered close to a rampart” in his chosen Atlantis location of South Morocco. He links this with Plato’s orichalcum but does so without any great enthusiasm.
Jim Allen, promoter of the Atlantis in Bolivia theory, claims that a natural alloy of gold and copper is unique to the Andes. Tumbaga is the name given by the Spaniards to a non-specific alloy of gold and copper found in South America. However, an alloy of the two that has 15-40% copper, melts at 200 Co degrees less than gold. Dr. Karen Olsen Bruhns, an archaeologist at San Francisco State University wrote in her book, Ancient South America[0497], “Copper and copper alloy objects were routinely gilded or silvered, the original colour apparently not being much valued. The gilded copper objects were often made of an alloy, which came to be very important in all of South and Central American metallurgy: tumbaga. This is a gold-copper alloy that is significantly harder than copper, but which retains its flexibility when hammered. It is thus ideally suited to the formation of elaborate objects made of hammered sheet metal. In addition, it casts well and melts at a lower temperature than copper, always a consideration when fuel sources for a draught were the wind and men’s lungs. The alloy could be made to look like pure gold by treatment of the finished face with an acid solution to dissolve the copper, and then by hammering or polishing to join the gold, giving a uniformly gold surface”.
Enrico Mattievich also believed that orichalcum had been mined in the Peruvian Andes(b).
Jürgen Spanuth tried to equate Orichalch with amber. Paul Dunbavin links Orichalcum with Wales. Robert Ishoy implies a connection between obsidian and Orichalcum, an idea also promoted by Christian & Siegfried Schoppe.
The most exotic suggestion has come from Felice Vinci who equates it with platinum[019.286] which was probably brought from the Ural Mountains. The most recent (2023) identification of orichalcum, which Plato tells us was used as wall cladding in Atlantis, came from Graham Phillips who also suggested[2063] that it was platinum! Incidentally, platinum was not discovered by Europeans until the eighteenth century in South America.
Albert Slosman thought that there was a connection between Moroccan oricalcita, a copper derivative, and Plato’s orichalcum. Peter Daughtrey has offered [893.82] a solution from a little further north in Portugal where the ancient Kunii people of the region used ori or oro as the word for gold and at that period used calcos for copper.
Thorwald C. Franke has suggested[750.174] that two sulphur compounds, realgar and orpiment whose fiery and sometimes translucent appearance might have been Plato’s orichalcum. His chosen location for Atlantis, Sicily, is a leading source of sulphur and some of its compounds. I doubt this explanation as realgar disintegrates with prolonged exposure to sunlight, while both it and orpiment, a toxin, could not be described as metals in any way comparable with gold and silver as stated by Plato.
Frank Joseph translates orichalcum as ‘gleaming or superior copper’ rather than the more correct ‘mountain copper’ and then links Plato’s metal with the ancient copper mines of the Upper Great Lakes. Joseph follows Egerton Sykes in associating ‘findrine’, a metal referred to in old Irish epics, with orichalcum. However, findrine was usually described as white bronze, unlike the reddish hue of orichalcum.
Ulf Erlingsson suggested [319.61] that orichalcum was ochre, which is normally yellow, but red when burnt. He seems to have based this on his translation of the text Critias116b. In fact, the passage describes the citadel flashing in a fiery manner, but it does not specify a colour!
Other writers have suggested that orichalcum was bronze, an idea that conflicts with a 9600 BC date for the destruction of Atlantis since the archaeological evidence indicates the earliest use of bronze was around 6000 years later.
Thérêse Ghembaza has kindly drawn my attention to two quotations from Pliny the Elder and Ovid that offer possible explanations for Plato’s orichalcum(n). The former refers to a Cypriot copper mixed with gold which gave a fiery colour and is called pyropus, while Ovid also refers to a cladding of pyropus. She also mentions auricupride(Cu3Au), an alloy that may be connected with orichalcum.
Zatoz Nondik, a German researcher, has written a book about Plato’s ‘orichalcum’, From 2012 to Oreichalkos[0841], in which he describes, in detail, how the orichalcum may be related to Japanese lacquer and suitable for coating walls as described in the Atlantis(b) narrative!
The fact is that copper and gold mixtures, both natural and manmade, have been found in various parts of the world and have been eagerly seized upon as support for different Atlantis location theories. A third of all gold is produced as a by-product of copper, lead, and zinc production.
It is also recorded that on ancient Crete, in the Aegean, two types of gold were found, one of which was a deep red developed by the addition of copper. Don Ingram suggests that the reddish gold produced in ancient Ireland is what Plato was referring to.
Irrespective of what orichalcum actually was, I think it is obvious that it was more appropriate to the Bronze Age than 9,600 BC. Furthermore, it occurs to me that Plato, who was so careful to explain or Hellenise foreign words so as not to confuse his Athenian audience, appears to assume that orichalcum is not an alien term to his audience.
The result of all of this is that Orichalcum has been advanced to support the location of Atlantis in North and South America, Sundaland, Ireland, Britain and the Aegean. Once again an unintentional lack of clarity in Plato’s text hampers a clear-cut identification of the location of Atlantis.
A fascinating anecdote relating to the use of a term similar to ‘orichalcum’ to describe a mixture of copper and gold was used by a metalsmith in Dubai as recently as 2007 and is recounted on the Internet(a).
The Wikipedia entry(f) for ‘orichalcum’ adds further classical references to this mysterious metal.
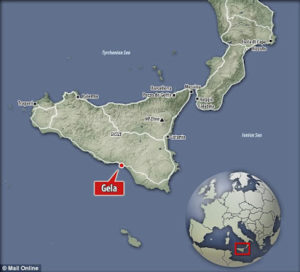 2015 began with a report that 47 ingots of ‘orichalcum’ had been found in a shipwreck off the coast of Sicily, near Gela, and dated to around 600 BC(g). What I cannot understand is that since we never knew the exact composition of Plato’s alloy, how can anyone today determine that these salvaged ingots are the same metal? Thorwald C. Franke has more scholarly comments on offer(h). Jason Colavito has also applied his debunking talents to the subject(i). In June of the same year,
2015 began with a report that 47 ingots of ‘orichalcum’ had been found in a shipwreck off the coast of Sicily, near Gela, and dated to around 600 BC(g). What I cannot understand is that since we never knew the exact composition of Plato’s alloy, how can anyone today determine that these salvaged ingots are the same metal? Thorwald C. Franke has more scholarly comments on offer(h). Jason Colavito has also applied his debunking talents to the subject(i). In June of the same year,  Christos Djonis, in an article(j) on the Ancient Origins website, wrote a sober review of the media coverage of the shipwreck. He also added some interesting background history on the origin of the word ‘orichalcum’.
Christos Djonis, in an article(j) on the Ancient Origins website, wrote a sober review of the media coverage of the shipwreck. He also added some interesting background history on the origin of the word ‘orichalcum’.
An analysis revealed(k) that those ingots were composed of 75-80% copper, 15-20% zinc, and traces of nickel, lead and iron, but no proof that this particular alloy was orichalcum. The recovery of a further 39 ingots from the wreck was reported in February 2017 and the excavation of the sunken ship continues.
An extensive paper(o) on the Gela discovery reported: “that Professor Sebastiano Tusa, an archaeologist at the office of the Superintendent of the Sea in Sicily, claimed the metal they had discovered in the remains of the ship was probably the mythical and highly prized red metal orichalcum.” However, dissent was not long coming, as the paper also notes that “ Enrico Mattievich, a former physics professor at the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, believes the metal has its origins in the Chavin civilisation that developed in the Peruvian Andes in around 1,200 BC. He claims the metal alloy is made from copper, gold and silver. He claims that the discovery off the coast of Gela is not true orichalcum.” I think that both are probably wrong as we do not know the exact chemical composition of Plato’s orichalcum and both are just engaging in speculation.
The most recent explanation for the term comes from Dhani Irwanto who has proposed that orichalcum refers to a form zircon(l) that is plentiful on the Indonesian island of Kalimantan, where he has hypothesised that the Plain of Atlantis was located [1093.110].
(a) Problems with Atlantis – Aquiziam (archive.org)
(b) https://www.migration-diffusion.info/article.php?year=2011&id=268
(c) https://www.sacred-texts.com/cla/flwp/flwp26.htm
(d) https://www.coinandbullionpages.com/gold-alloys/orichalcum.html
(e) Atlantis Research Vol 2. No.6, Feb/Mar 1950, p.86
(f) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Orichalcum
(g) See: Archive 2460
(h) https://www.atlantis-scout.de/atlantis_newsl_archive.htm
(k) From Fiction to Fact: Ancient Metal Identified with XRF – Analyzing Metals (archive.org) *
(l) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zircon
(m) https://www.forumancientcoins.com/numiswiki/view.asp?key=orichalcum
(n) See: Archive 3456
(p) Oriharukon – Atlantisforschung.de (atlantisforschung-de.translate.goog)
(q) http://www.oocities.org/motorcity/factory/2583/orich.htm
(r) http://www.jaysromanhistory.com/romeweb//engineer/art11.htm
