Peter Daughtrey
Daughtrey, Peter
Peter Daughtrey is a British researcher and the author of Atlantis and the  Silver City in which he identifies a location in Portugal, where he lived until recently, for Atlantis. The publicity blurb looks promising as it reads as follows: “Over 2000 books have previously attempted to find the answer but invariably stumbled by matching only a handful of Plato´s clues for this fabled lost civilisation. This book matches almost 60 and includes the discovery of the ancient capital with its harbour that Plato described in great detail and the great sunken plain with at least one group of submerged ruins. Everything fits – the precise location, climate, topography, crops and animals, even the incredible wealth. It sits uneasily by one of the world’s most lethal seismic fault lines which in the past has wreaked havoc up to ten times more powerful than the recent quake off Japan with tsunamis 100 feet high. The great Atlantis empire is traced together with their leader’s odysseys to civilize South America and Egypt. The unique Atlantean physical characteristics are pinpointed and an ancient alphabet traced from which Phoenicians and Greek developed.” However, a pre-publication critique(a) has been rather less than encouraging.
Silver City in which he identifies a location in Portugal, where he lived until recently, for Atlantis. The publicity blurb looks promising as it reads as follows: “Over 2000 books have previously attempted to find the answer but invariably stumbled by matching only a handful of Plato´s clues for this fabled lost civilisation. This book matches almost 60 and includes the discovery of the ancient capital with its harbour that Plato described in great detail and the great sunken plain with at least one group of submerged ruins. Everything fits – the precise location, climate, topography, crops and animals, even the incredible wealth. It sits uneasily by one of the world’s most lethal seismic fault lines which in the past has wreaked havoc up to ten times more powerful than the recent quake off Japan with tsunamis 100 feet high. The great Atlantis empire is traced together with their leader’s odysseys to civilize South America and Egypt. The unique Atlantean physical characteristics are pinpointed and an ancient alphabet traced from which Phoenicians and Greek developed.” However, a pre-publication critique(a) has been rather less than encouraging.
Now that I have read the book I must declare that Daughtrey has produced a work that offers a spirited argument for considering Portugal’s Algarve as the location of Plato’s Atlantis. In fact, he designates not just the Algarve and the submerged area in front of it as Atlantis, but the whole of that southwest Iberian region, starting immediately outside the straits of Gibraltar. The first half of it is the Costa da Luz in Spain. I note that Greg Little has written a positive review of Daughtrey’s book.(f)
Daughtrey recently elaborated that his “position for the great plain that Plato referred to is now the seabed front of southern Portugal and southern Andalucia as far Gibraltar. I think it would also have extended onto the submerged area of northern Morroco and onto the existing mainland. There would only have been much extended narrow straits from Gibraltar dividing it for a good length.”
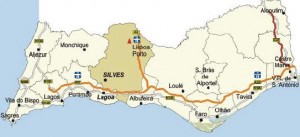
More specifically he identifies the town of Silves, just west of Faro, as the Silver City in the title.
In order to compile Atlantipedia, I have had to read many books supporting a wide range of theories. I can say that Daughtrey’s offering would be in my top dozen Atlantis titles, along with those of Jim Allen, Andrew Collins, Anton Mifsud, Otto Muck and Jürgen Spanuth. They have all made valuable contributions to Atlantology even though I do not accept all of their conclusions.
Nevertheless, without going into a string of nitpicking comments, I would prefer to clearly state where I believe Daughtrey is fundamentally wrong. Which is in accepting Plato’s (or should that be Solon’s) 9,000 years literally. He is not the first to take this approach as the consequence is that either Atlantis attacked Athens (and Egypt) which did not even exist as organised societies at the time or the science of archaeology as we know it must be abandoned. It is interesting that when it suits him, Daughtrey is prepared to revise Plato’s dimensions for the Plain of Atlantis. I prefer to reinterpret all of Plato’s numbers, which I believe are seriously flawed.
In spite of the above, this book is a valuable addition to any Atlantis library.
September 2014 saw the History Channel preparing to broadcast a documentary on Atlantis in the Algarve that includes extensive interviews with Daughtery(b). However, following the airing of the program he seemed rather disappointed(c) that many of what he considered his most important arguments had been omitted from the final cut and that the producers were more interested in extraterrestrials.
Daughtrey’s book has been updated and a second edition [1957] was published in 2021 and contains what he calls “dramatic new evidence”. His book is supported by a website(e), where you will find additional articles, interviews and reviews.>An extensive press release to promote the new edition can be read here.<
In 2015, Daughtrey published a paper entitled ‘Mark Adams’ Atlantis in Morocco Theory Debunked’(g). This is rather misleading as Adams did not endorse any theory [1070]. The author of the Moroccan theory referred to by Daughtrey was the late Michael Hübner, who is not mentioned once. In fact, Daughtrey’s article offers no debunking but was just a promotional piece for his own book. I have a personal interest in this as I had been impressed by Hübner’s carefully constructed theory and had suggested that Adams should meet Hübner. I subsequently identified a serious flaw in Hübner’s theory.
(a) https://www.publishersweekly.com/978-1-60598-415-5
(b) https://www.portugalresident.com/2014/09/03/history-channel-features-algarves-connection-to-atlantis/ See: Archive 2227
(e) https://www.atlantisandthesilvercity.com/
(g) http://atlantisandthesilvercity.com/atlantis-blog/?p=123
Writing in Atlantis
Writing in Atlantis. The text of Plato makes it quite clear that writing was a feature of Atlantean culture. This is just another element in the overall picture presented by Plato of Atlantis as a Bronze Age civilisation, although there is always the possibility that the inclusion of writing might be a Platonic addition, designed to enhance the underlying core tale of a very ancient civilisation destroyed by flooding. If this flooding coincided with the melting of the glaciers at the end of the last Ice Age then it could be dated to around 9500 BC, a date that is in agreement with Solon’s apparent date for the demise of Atlantis.
R. Cedric Leonard(a) has developed the idea that an even older writing system in Western Europe, such as that found on the Glozel Tablets may have had a link with Atlantis. These tablets have been dated to as early as 10,000 BC, but I have some reservations regarding the reliability of this date. Similarly, the writing of the Vinca culture of Eastern Europe is believed to date from around 5500 BC.
However, an article in New Scientist (20.02.10) reports that a study of cave markings at 146 sites in France revealed that a total of just 26 signs were used with a varying frequency between 33,000 BC and 8000 BC. The symbols were only found in Southern France as most of the north was glaciated for much of this period. If these findings are substantiated it will raise questions regarding the date of the arrival of modern man into Europe.
Genevieve von Petzinger a Canadian paleoanthropologist and rock art researcher has studied geometric signs found in caves and other sites dating back 40,000 years. In a 2019 paper, her work is discussed including that she has identified “32 recurring symbols in all cultures of 40,000 years ago.” That was the easy part, now they must be interpreted(g).
It is generally thought that there is no evidence of any developed writing system until around 3500 BC in Harappa in the Indus Valley, while a few hundred years later the Sumerians were using a sophisticated cuneiform script and the Egyptians had developed a system of hieroglyphics(d). In 2010, Orly Goldwasser had an article published in the Biblical Archaeology Review (BAR) in which she traced the development of the Canaanite alphabet from Egyptian hieroglyphics!(n)
In turn, the Phoenicians developed their script circa 1000 BC and from them, the Greeks developed their Linear A & B. However, the discovery in 1993 of the Dispilio Tablet(j) in Greece has pushed back the use of writing in Greece to around 5200 BC, which is long before the people recognised as Phoenicians emerged in the 2nd millennium BC(i)!
In 2017, an ancient ivory comb was discovered and dated to around 1700 BC. It was later spotted that the object had been inscribed with the earliest complete sentence in a Canaanite dialect(l).
This debate regarding the origins of writing, both when and where will continue for some considerable time. An article on the Ancient Origins website in September 2022 ended with the following comment – “Conventional history dictates that these kinds of Neolithic discoveries are merely evidence of proto-writing, a term which refers to a way of communicating limited information, rather than proof of an entire language. But should additional artifacts comparable to the Dispilio tablet emerge, they could completely change the history of writing and with it the story of humanity.”(k)
Crete had crude writing around 3000 BC, but it would be another 1000 years before the earliest alphabetic inscription discovered so far would be inscribed on a rock, in what is now Southern Egypt. This has been dated to the 1900s BC, two hundred years earlier than expected. This particular epigraph has prompted speculation that what we know as an alphabet originated in Egypt, but it is not unreasonable to think that this revision will not be the last. However, the March/April 2010 edition of the respected Biblical Archaeology Review has an article that identifies the early alphabet as a development of hieroglyphics(c).
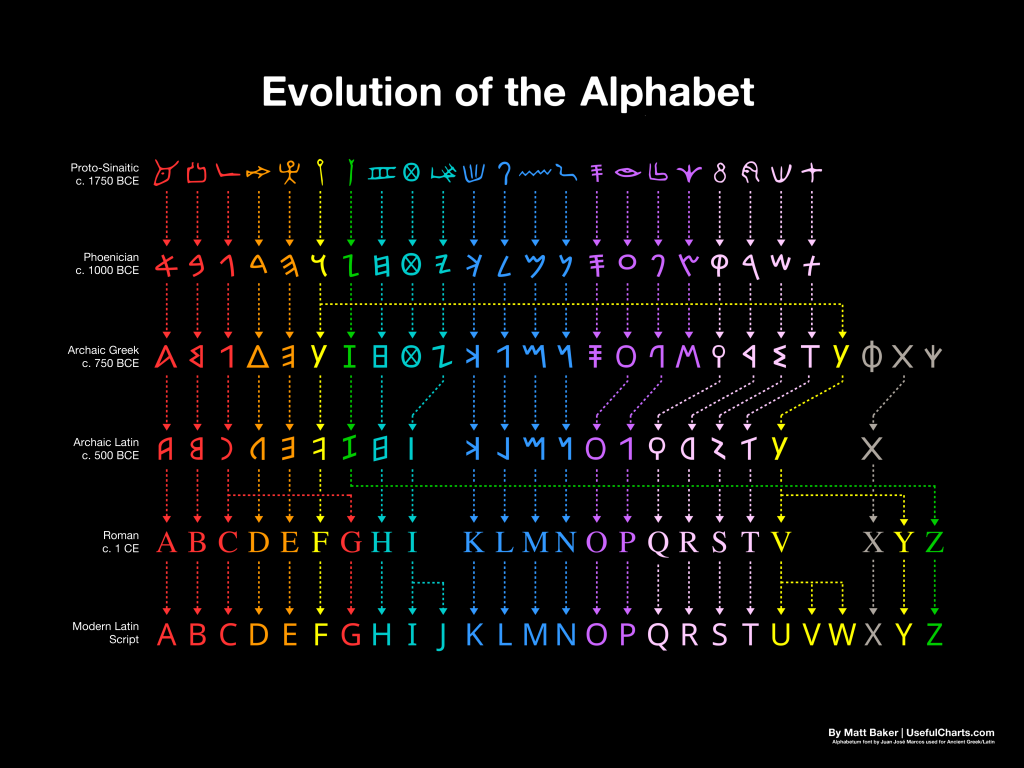
This evolution from hieroglyphs to modern European scripts is now available as a chart by Matt Baker(o).*
Although the Phoenicians have often been credited with the invention of the precursor to modern Western scripts around 1,100 BC, it now appears more likely that they were responsible for the adaptation of an even earlier character system. The earliest known Hebrew writing has now been dated to the 10th century BC(b).
Peter Daughtrey in his book, Atlantis and the Silver City [893] has devoted chapter seventeen to offering the claim that the earliest alphabet developed in southwest Iberia and by extension in Atlantis. An abbreviated version can be read on his website(h).
In Meso-America, the Olmecs appear to have been the first to develop a writing system around 900 BC, 600 years earlier than the Maya. However, the late emergence of a script there would appear to argue against a common Atlantean source for cultures on both sides of the Atlantic.
In 1905, Flinders Petrie and his wife, also an archaeologist, discovered strange signs on the side of a mine in the Sinai Peninsula, which they identified as alphabetical. After a decade of study, Sir Allan Gardiner published a decipherment of the symbols in 1916(f). They became known as proto-Sinaitic script and dated to between 1850 and 1550 BC. However, there were individual ‘letters’ whose identities were disputed. In 2017, Douglas Petrovich claimed to have solved all outstanding issues [1767]. Today, Orly Goldwasser, an Israeli Egyptologist, is arguably the leading promoter of the idea that this was the earliest example of an alphabet discovered so far(e).
The insistence by some on the great antiquity of ancient scripts is driven by those Atlantis researchers who blindly accept the 9,600 BC date for the destruction of a literate Atlantis given by Plato. If an early date for writing cannot be more fully substantiated then Plato’s date must be reappraised.
>An “Atlantean language was created for the film Atlantis: The Lost Empire by Marc Okrand, who worked with John Emerson, a designer at Disney, to produce an alphabet for the language. The language is spoken and written by the people of Atlantis in the film and is integral to the plot.”(m)<
(a) https://web.archive.org/web/20170615131537/http:/atlantisquest.com:80/classical.html
(b) https://phys.org/news/2010-01-ancient-hebrew-biblical-inscription-deciphered.html
(c) https://members.bib-arch.org/publication.asp?PubID=BSBA&Volume=36&Issue=02&ArticleID=06 (link broken) *
(d) https://www.abc.net.au/science/news/stories/s17999.htm
(f) Who Invented the Alphabet? | History | Smithsonian Magazine
(h) http://atlantisandthesilvercity.com/atlantis-blog/?p=28
(j) https://www.thearchaeologist.org/blog/dispilio-tablet-the-oldest-known-written-text
(k) https://www.ancient-origins.net/artifacts-ancient-writings/dispilio-tablet-00913
(m) https://omniglot.com/conscripts/atlantean.htm
(n) https://www.torahinmyheart.com/v/vspfiles/downloadables/00_Origins_of_the_Aleph-Bet.pdf
(o) https://mymodernmet.com/history-of-the-alphabet-usefulcharts/ *
Tartessos
Tartessos or Tartessus is generally accepted to have existed along the valley of the Guadalquivir River where the rich deposits of copper and silver led to the development of a powerful native civilisation, which traded with the Phoenicians, who had colonies along the south coast of Spain(k).
A continuing debate is whether Tartessos was developed by a pre-Phoenician indigenous society or was a joint venture by locals along with the Phoenicians.(o) One of the few modern English-language books about Tartessos was written by Sebastian Celestino & Carolina López-Ruiz and entitled Tartessos and the Phoenicians in Iberia [1900].
A 2022 BBC article offers some additional up-to-date developments in the studies of Tartessos(v).
It is assumed by most commentators that Tartessos was identical to the wealthy city of Tarshish that is mentioned in the Bible. There have been persistent attempts over the past century to link Tartessos with Atlantis. The last king of Tartessia, in what is now Southern Spain, is noted by Herodotus to have been Arganthonios, who is claimed to have ruled from 630 BC until 550 BC. Similarly, Ephorus a 4th century BC historian describes Tartessos as ‘a very prosperous market.’ However, if these dates are only approximately true, then Atlantis cannot be identified with Tartessos as they nearly coincide with the lifetime of Solon, who received the story of Atlantis as being very ancient.
However, the suggested linkage of Tartessos with Atlantis is disputed by some Spanish researchers, such as Mario Mas Fenollar [1802] and Ester Rodríguez González(n). Mas Fennolar has claimed that at least a thousand years separated the two. Arysio dos Santos frequently claimed that Atlantis was Tartessos throughout his Atlantis and the Pillars of Hercules [1378].
The existence of a ‘Tartessian’ empire is receiving gradual acceptance. Strabo writes of their system of canals running from the Guadalquivir River and a culture that had written records dating back 6,000 years. Their alphabet was slightly different to the ‘Iberian’. The Carthaginians were said to have been captured by Tartessos after the reign of Arganthonios and after that, contact with Tartessos seems to have ended abruptly!
The exact location of this city is not known apart from being near the mouth of the Guadalquivir River in Andalusia. The Guadalquivir was known as Baetis by the Romans and Tartessos to the Greeks. The present-day Gulf of Cadiz was known as Tartessius Sinus (Gulf of Tartessus) in Roman times. Cadiz is accepted to be a corruption of Gades that in turn is believed to have been named after Gaderius. This idea was proposed as early as 1634 by Rodrigo Caro (image left), the Spanish historian and poet, in his Antigüedades y principado de la Ilustrísima ciudad de Sevilla, now available as a free ebook(i).
In 1849, the German researcher Gustav Moritz Redslob (1804-1882) carried out a study of everything available relating to Tartessos and concluded that the lost city had been the town of Tortosa on the River Ebro situated near Tarragona in Catalonia. The idea seems to have received little support until recently, when Carles Camp published a paper supporting this contention(w). It was written in Valenciano, which is related to Catalan and can be translated with Google Translate using the latter option.
A few years ago, Richard Cassaro endeavoured to link the megalithic walls of old Tarragona with the mythical one-eyed Cyclops and for good measure suggest a link with Atlantis(l). Concerning the giants, the images of doorways posted by Cassaro are too low to comfortably accommodate giants! Cassaro has previously made the same claim about megalithic structures in Italy(m)
The German archaeologist Adolf Schulten spent many years searching unsuccessfully for Tartessos, in the region of the Guadalquivir. He believed that Tartessos had been founded by Lydians in 1150 BC, which became the centre of an ancient culture that was Atlantis or at least one of its colonies. Schulten also noted that Tartessos disappeared from historical records around 500 BC, which is after Solon’s visit to Egypt and so could not have been Atlantis.
Richard Hennig in the 1920s also supported the idea of Tartessos being Atlantis and situated in southern Spain. However, according to Atlantisforschung he later changed his opinion opting to adopt Spanuth’s Helgoland location instead(x).
Otto Jessen, a German geographer, also believed that there had been a connection between Atlantis and Tartessos. Jean Gattefosse was convinced that the Pillars of Heracles were at Tartessos, which he identifies as modern Seville. However, Mrs E. M. Whishaw, who studied in the area for 25 years at the beginning of the 20th century, believed that Tartessos was just a colony of Atlantis. The discovery of a ‘sun temple’ 8 meters under the streets of Seville led Mrs Whishaw to surmise[053] that Tartessos may be buried under that city. Edwin Björkman wrote a short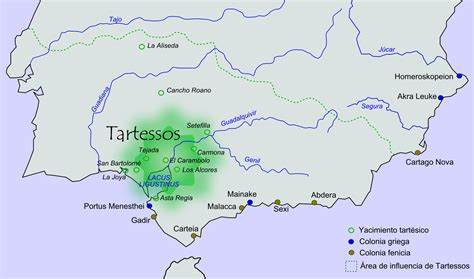 book, The Search for Atlantis[181] in which he identified Atlantis with Tartessos and also Homer’s Scheria.
book, The Search for Atlantis[181] in which he identified Atlantis with Tartessos and also Homer’s Scheria.
Steven A. Arts, the author of Mystery Airships in the Sky, also penned an article for Atlantis Rising in which he suggests that the Tarshish of the Old Testament is a reference to Tartessos and by extension to Atlantis(r)!
More recently Karl Jürgen Hepke has written at length, on his website(a), about Tartessos. Dr Rainer W. Kühne, following the work of another German, Werner Wickboldt, had an article[429] published in Antiquity that highlighted satellite images of the Guadalquivir valley that he has identified as a possible location for Atlantis. Kühne published an article(b) outlining his reasons for identifying Tartessos as the model for Plato’s Atlantis.
Although there is a consensus that Tartessos was located in Iberia, there have been some refinements of the idea. One of these is the opinion of Peter Daughtrey, expressed in his book, Atlantis and the Silver City[0893] in which he proposes that Tartessos was a state which extended from Gibraltar around the coast to include what is today Cadiz and on into Portugal’s Algarve having Silves as its ancient capital.
It was reported(c) in January 2010 that researchers were investigating the site in the Doñana National Park, at the mouth of the Guadalquivir, identified by Dr Rainer Kühne as Atlantis in a 2011 paper(s). In the same year, Professor Richard Freund of the University of Hartford garnered a lot of publicity when he visited the site and expressed the view that it was the location of Tartessos which he equates with Atlantis. The Jerusalem Post in seeking to give more balance to the discussion quoted archaeology professor Aren Maeir who commented that “Richard Freund is known as someone who makes ‘sensational’ finds. I would say that I am exceptionally skeptical about the thing, but I wouldn’t discount it 100% until I see the details, which haven’t been published as far as I know.”(u)
A minority view is that Tarshish is related to Tarxien (Tarshin) in Malta, which, however, is located some miles inland with no connection to the sea. Another unusual theory is offered by Luana Monte, who has opted for Thera as Tartessos. She bases this view on a rather convoluted etymology(e) which morphed its original name of Therasia into Therasios, which in Semitic languages having no vowels would read as ‘t.r.s.s’ and can be equated with Tarshish in the Bible, which in turn is generally accepted to refer to Tartessos.
Giorgio Valdés favours a Sardinian location for Tartessos(f), an idea endorsed later by Giuseppe Mura in his 2018 book, published in Italian, Tartesso in Sardegna [2068], the full title of which translates as Tartessos in Sardinia: Reasons, circumstances and methods used by ancient historians and geographers to remove Tartessos (the Tarshish of the Bible) from Caralis and place it in Spanish Andalusia. Caralis is an old name for Cagliari, the Sardinian capital.
Andis Kaulins has claimed that further south, in the same region, Carthage was possibly built on the remains of Tartessos, near the Pillars of Heracles(j).
A more radical idea was put forward in 2012 by the Spanish researcher, José Angel Hernández, who proposed(g)(h) that the Tarshish of the Bible was to be found in the coastal region of the Indus Valley, but that Tartessos was a colony of the Indus city of Lhotal and had been situated on both sides of the Strait of Gibraltar!
A recent novel by C.E. Albertson[130] uses the idea of an Atlantean Tartessos as a backdrop to the plot.
A relatively recent claim associating Tartessos with Atlantis came from Simcha Jacobovici in a promotional interview(p) for the 2017 National Geographic documentary, Atlantis Rising. In it, Jacobovici was joined by James Cameron as producer, but unfortunately, the documentary did not produce anything of any real substance despite a lot of pre-broadcast hype.
There is an extensive website(d) dealing with all aspects of Tartessos, including the full text of Schulten’s book on the city. Although this site is in Spanish, it is worthwhile using your Google translator to read an English version.
“Today, researchers consider Tartessos to be the Western Mediterranean’s first historical civilization. Now, at an excavation in Extremadura—a region of Spain that borders Portugal, just north of Seville—a new understanding of how that civilization may have ended is emerging from the orange and yellow soil. But the site, Casas del Turuñuelo, is also uncovering new questions.”(q) First surveyed in 2014 it was in late 2021, a report emerged of exciting excavations there that may have a bearing on the demise of Tartessos. Work is currently on hold because of a dispute with landowners, with only a quarter of the site uncovered. The project director is Sebastian Celestino Perez. The Atlas Obscura website offers further background and details of discoveries at the site(t).
(a) http://web.archive.org/web/20170716221143/http://www.tolos.de/History%20E.htm
(b) Meine Homepage (archive.org)
(d) TARTESSOS.INFO: LA IBERIA BEREBER (archive.org)
(e) http://xmx.forumcommunity.net/?t=948627&st=105
(f) http://gianfrancopintore.blogspot.ie/2010/09/atlantide-e-tartesso-tra-mito-e-realta.html
(g) http://joseangelh.wordpress.com/category/mito-y-religion/
(h) http://joseangelh.wordpress.com/category/arqueologia-e-historia/
(j) Pillars of Heracles – Alternative Location (archive.org)
(k) Archive 3283 | (atlantipedia.ie)
(n) (PDF) Tarteso vs la Atlántida: un debate que trasciende al mito (researchgate.net)
(o) (PDF) Definiendo Tarteso: indígenas y fenicios (researchgate.net)
(p) Lost City of Atlantis And Its Incredible Connection to Jewish Temple (israel365news.com)
(q) The Ancient People Who Burned Their Culture to the Ground – Atlas Obscura
(r) Atlantis Rising magazine #36 http://pdfarchive.info/index.php?pages/At
(t) https://www.atlasobscura.com/articles/tartessos-casas-del-turunuelo
(u) https://www.jpost.com/jewish-world/jewish-news/the-deepest-jewish-encampment
(v) https://www.bbc.com/travel/article/20220727-the-iberian-civilisation-that-vanished
(w) https://www.inh.cat/articles/La-localitzacio-de-Tartessos-es-desconeguda.-Pot-ser-Tartessos-Tortosa- *
(x) Richard Hennig – Atlantisforschung.de (atlantisforschung-de.translate.goog) *
Portugal
Portugal, in the 12th century, began as a county, that is, governed by a count. Wikipedia notes that it “refers to two successive medieval counties in the region around Braga and Porto, today corresponding to littoral northern Portugal, within which the identity of the Portuguese people formed. The first county existed from the mid-ninth to the mid-eleventh centuries as a vassalage of the Kingdom of Asturias and later the Kingdoms of Galicia and León, before being abolished as a result of rebellion. A larger entity under the same name was then re-established in the late 11th century and subsequently elevated by its count in the mid-12th century into an independent Kingdom of Portugal.”
Impressive megalithic sites are to be found in Portugal, among which is the large Almendres Cromlech (Cromeleque dos Almendres) near Evora. It still has 93 huge stones that form two concentric rings. They were erected there around 4000-5000 BC making them about 2000 years older than Stonehenge(a).
>A recent article(e) on Graham Hancock’s website by Leonard Wolf describes a number of megalithic sites in Portugal that he personally explored including some in the Evora district in 2022. In 2015, the same Mr. Wolf published a lengthy paper(f) advocating a site off the coast of Mexico’s Yucatan Peninsula as the location of Atlantis.<
According to Mel Nicholls [0944], the Bell Beaker culture originated in Portugal around 2800 BC and has nominated the Beaker people in Britain as Atlantean, whereas Donald Ingram argues that their successors in Britain, the Wessex II culture were Atlantean.
Portugal entered the Atlantis Stakes with a claim by a Basque researcher, Luis Aldamiz, that a little-known ancient civilisation, known as the Villa Nova 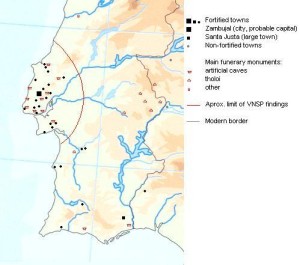 de São Pedro (VNSP) culture matched much of Plato’s description of Atlantis(b). Its capital was Zambujal, which was located on a mountain in the centre of the Estramadura peninsula, near modern Lisbon. Originally it was described as a ‘perriruthos’, which indicates something surrounded by water. Aldamiz notes that ten tombs were found there; reminiscent of the ten kings of Atlantis. Zambujal had large complex fortifications. Aldamiz claims that this civilisation fought against the Greeks during the Middle Bronze Age. He further believes that the destruction of his Atlantis was caused by an event that was similar to the 1755 Lisbon earthquake that caused such death and destruction.
de São Pedro (VNSP) culture matched much of Plato’s description of Atlantis(b). Its capital was Zambujal, which was located on a mountain in the centre of the Estramadura peninsula, near modern Lisbon. Originally it was described as a ‘perriruthos’, which indicates something surrounded by water. Aldamiz notes that ten tombs were found there; reminiscent of the ten kings of Atlantis. Zambujal had large complex fortifications. Aldamiz claims that this civilisation fought against the Greeks during the Middle Bronze Age. He further believes that the destruction of his Atlantis was caused by an event that was similar to the 1755 Lisbon earthquake that caused such death and destruction.
Lereno Barradas was a Portuguese writer who speculated in the early 1970s that Tartessos could be identified with Atlantis and that it had been located in the Tagus estuary near the site of modern Lisbon. He also suggested that these ancient Atlanteans had travelled to America.
In 1989 another Portuguese researcher, José Antunes, proposed that Atlantis had been situated in what is now northwest of Lisbon between Sintra and Mafra.
A more radical theory has been put forward by Roger Coghill, the British bioelectromagnetic investigator, who suggests on his website that Atlantis was located in the vicinity of Faro in the Algarve. Coghill expanded on his theory in his book, The Message of Atlantis[494]. He has also drawn attention to a book [1562] by Antonio Jose Lopes Navarro, published in 1983, in which he has brought together a number of classical references to the prehistory of the Algarve.
Portugal got further attention in 2013 when another British researcher, Peter Daughtrey, who then lived in Portugal, published Atlantis and the Silver City [893] in which he designates not just the Algarve and the submerged area in front of it as Atlantis, but the whole of that south-west Iberian region.
Daughtrey’s book has been updated and contains what he calls “dramatic new evidence”. His book is supported by a website(d), where you will find additional articles, interviews and reviews.
The late Steven Sora suggested [0395] that the Etruscans were refugees from their original homeland in Iberia, where he also located Troy/Atlantis. He specified Lisbon, Setubal and Troia, all in modern Portugal, as Trojan/Atlantean territory, conflating the Trojan and Atlantean wars, although placing those conflicts 4,000 km away from the battleground at Hissarlik, where Eberhard Zangger claims his Troy, which he also deemed to be identical with Atlantis was located!
Apart from the mainland claims the Portuguese Atlantic archipelagos of Azores and Madeiras have also been identified by several commentators as probable Atlantis locations.
Manuel J.Gandra has produced a valuable bibliography(c) of Portuguese sources dealing with Atlantis.
(a) https://www.atlasobscura.com/places/almendres-cromlech
(b) https://www.geocities.ws/luis_aldamiz/Atlantis/Atlantis.html
(c) Wayback Machine (archive.org)
(d) https://www.atlantisandthesilvercity.com
Little, Drs. Gregory and Lora *
Dr. Gregory and Dr. Lora Little are a husband and wife team who for twenty years have been members of the Association for
Research and Enlightenment which was set up to promote the ideas of Edgar Cayce. They are the authors of the Association’s newsletter(a) and have written several books[060] on the search for Atlantis in the Bahamas region. Greg was initially sceptical about Cayce’s readings on ancient history, but as a result of the archaeological discoveries of the last decade, he is now convinced of their fundamental veracity. However, in November 2010 he stated(b) “I don’t even know for certain that Atlantis existed.”A video clip(f) from the History Channel shows Little presenting some of his views.
So, after spending years searching for Edgar Cayce’s Atlantis in the Bahamas, he reveals that he is unsure of its existence and to confuse us further, he is also quoted as describing Peter Daughtrey’s Atlantis and the Silver City in AP Magazine as matching “all of Plato”(h)!
Greg Little is also the author of a comprehensive encyclopedia(c) of Native American mounds and earthworks[791].
He has also delved into the subject of giants’ remains discovered in Indian mounds in the 19th and early 20th centuries(d). Jason Colavito has challenged(e) his ideas and a state of undeclared war now appears to exist between them.
Little recently teamed up with Andrew Collins as co-author of Denisovan Origins [1672], which has led to another joint offering, Origins of the Gods due for publication soon, in which the authors explore “how our ancestors used shamanic rituals at sacred sites to create portals for communication with non-human intelligences”!
A number of his older articles are available online(g).
(a) Ancient Mysteries | Edgar Cayce Readings |Edgar Cayce’s A.R.E. | Edgar Cayce’s A.R.E. (archive.org) *
(b) https://www.mysterious-america.com/final2010atlanti.html
(c) https://www.amazon.com/exec/obidos/ASIN/0940829460/edgarcayceshallo
(d) https://www.apmagazine.info/index.php/component/content/article?id=546
(e) https://www.jasoncolavito.com/blog/greg-little-is-still-mad-about-my-2013-post-on-giant-bones
(f) https://www.history.com/topics/atlantis
(g) Atlantis Related Articles Authored by Dr Little (systemagicmotives.com)
(h) ATLANTIS FOUND. Where is Atlantis? Peter Daughtrey (atlantisandthesilvercity.com)
Phaeacia
Phaeacia was a land described by Homer in his epic poem Odyssey, which is usually equated with the legendary island of Scheria, identified by many with Atlantis. .
Ignatius Donnelly was probably the first to suggest a linkage between Phaeacia and Atlantis. Jürgen Spanuth as well as Hennig and Kluge shared this view of Donnelly‘s, Based on Hennig’s work Spanuth listed 32 items of similarity between Phaeacia and Atlantis in his Atlantis – The Mystery Unravelled[017.143] and Atlantis of the North[015.218]. However, N. Zhirov remarked that an equally long list of discrepancies could also be compiled, leaving the question still open.
There is something of a consensus among scholars that Phaeacia is a reference to the Greek island of Corfu. However, Hennig did not accept that Scheria could be identified with the Adriatic island, instead, he suggested that it was beside Spain.
An Atlantic location for Homer’s epic poems is advocated by N.R. De Graaf(d), the Dutch author of the Homeros Explorations website(c). Specifically, he concluded that Scheria can be identified with Lanzarote in the Canaries concurring with Iman Wilkens.
Armin Wolf who has studied extensively the geography of Homer’s Odyssey concluded a paper(b) on the subject as follows – “Scheria, the country of the Phaeacians, this ideal land described by Homer, was no fantasy, but nothing else but Greater Greece, Magna Graecia.”
>However, Felice Vinci, has strongly set Phaeacia in the geographical context of Norway [019.21-4] and offers a number of similarities between the Vikings and the Phaeacians. Kalju Pattustaja agrees with this identification of the Phaeacians(e) and cites Andres Pääbo as being of a similar view. However, it should be noted that Pääbo is highly critical of much of Vinci’s work(f).<
Roger Coghill is a more recent supporter of Scheria being another name for Atlantis, which he locates near Faro in Portugal. His views have been contrasted in the media(a) with those of Peter Daughtrey, who locates Atlantis not too far away in Silves.
(a) https://web.archive.org/web/20190803175205/https://meravista.com/en/blogentry/legendary-city-atl
(b) Wayback Machine (archive.org)
(c) Homeros Explorations – Homer, facts or fiction? (homeros-explorations.nl)
(d) Homer, facts or fiction? | ancient america
(e) The Nordic Origin of Mycenaean Civilization -The Forgotten Finnic Roots (Link Broken) *
Red, White and Black
The Red, White and Black stone which Plato said had adorned the buildings of its port city, has led Atlantis seekers to eagerly follow up this apparently obvious clue. However, as with so many aspects of the Atlantis story, this particular detail does not provide us with anything like a clear pointer to any specific location.
Jürgen Spanuth relates[015.125] how the ancient Canarians decorated their temple with red, white and black rock, the colours of tufa, pumice and lava. The cliffs of Santorini are also known to display red, white and black rock. These three materials are frequently found in the vicinity of volcanoes(b) and may be considered a valuable clue to the location of Atlantis. However, this combination of rock colours is not exclusive to volcanic localities as Jim Allen has demonstrated at Pampa Augallas in the Andes and Peter Daughtrey at his Silves site in Portugal[0893.120].
Although Atlantis was destroyed by an earthquake, volcanoes are often located in the same general region such as in the Central Mediterranean which is both seismically and volcanically very active and, in my opinion, the prime candidate as the home of Atlantis. This view is endorsed by Plato himself who twice (Tim.25b & Crit.114c) told us that the territory of the Atlantean alliance stretched from North Africa as far as Tyrrhenia in Italy. I further propose that this was on a north/south axis.
Jim Allen has found the same three rock colours at his Bolivian site and further afield, Ian Wilson points out[185] that red, white and black bricks were used extensively in Çatal Hüyük. Not to be excluded, Diaz-Montexano has produced photos on his website of pre-Roman structures near Gibraltar that incorporate red, white and black blocks in their construction. Jonas Bergman has indicated that similarly coloured stone is to be found in Morocco. Other locations include the Azores, Algeria and Sardinia.
Andrew Jones, a professor of archaeology, has noted that the builders of Carn Ban, one of the ‘Clyde Cairns’ on Scotland’s Isle of Arran employed red white and black stones in its design – pure coincidence I’m sure! Robert Hensey in his book on Newgrange [1766.39] refers to Jones and the growing interest in the use of colour in ancient monuments.
>Fatih Hodzic in an attempt to enhance his claim of an Adriatic Atlantis has noted; “The Atlanteans used stone for building: ‘one kind was white, another black, and a third red’. White and black stone is still quarried on Island Bra? (Croatia) and red stone in the Bay of Kotor (Montenegro).”(c)<
Some(a) have sought to link the red, white and black of the Nazi swastika with Plato’s reference!
(b) How are volcanoes and earthquakes related? | Volcano World | Oregon State University (archive.org)
Orichalcum
Orichalcum is, according to legend, reputed to have been ‘invented’ by Cadmus noted in Greek mythology as the legendary Phoenician founder of Boeotian Thebes. This metal is one of the many mysteries in Plato’s Atlantis narrative. It is mentioned five times in the Critias [114e, 116c-d, 119c] as a metal extensively used in Atlantis. I am not aware of any reference to it anywhere else in his writings, a fact that can be advanced as evidence of the veracity of his Atlantis story. Plato took the time to explain to his audience why the kings of Atlantis have Hellenised names. However, he introduces Orichalcum into the story without explanation, which suggests that the metal was something well-known to the listeners. It is therefore natural to expect that metals might play an important part in determining the credibility of any proposed Atlantis location.
Bronze was an alloy of copper and tin, while brass was a mixture of copper and zinc, their similarity is such that museums today refer to artefacts made of either refer to them as copper alloys.
According to James Bramwell[195.91], Albert Rivaud demonstrated that the term ‘orichalcum’ was known before Plato and not just invented by him. Similarly, Zhirov notes that both Homer and Hesiod refer to the metal[0458.46], as does Ibycus, the 6th century BC poet, who compares its appearance to gold suggesting a brasslike alloy. Thomas Taylor (1825) noted that in a fragment from a lost book of Proclus, he seems to refer to orichalcum under the name of migma(c).>Virgil in his Aeneid mentioned that the breastplate of Turnus was “stiff with gold and white orachalc”.<
Wikipedia also adds that “Orichalcum is also mentioned in the Antiquities of the Jews – Book VIII, sect. 88 by Josephus, who stated that the vessels in the Temple of Solomon were made of orichalcum (or a bronze that was like gold in beauty). Pliny the Elder points out that the metal had lost currency due to the mines being exhausted. Pseudo-Aristotle in ‘De mirabilibus auscultationibus’ describes orichalcum as a shining metal obtained during the smelting of copper with the addition of ‘calmia’, a kind of earth formerly found on the shores of the Black Sea, which is attributed to be zinc oxide.”
Friedrich Netolitzky (1875-1945) offered an independent interpretation of the oriharukon (orichalcum) in Plato’s Atlantis account, which he identified as an artificial modification of white gold (known as Asem in ancient Egypt).
Atlantisforschung also offers a lengthy article on orichalcum(p).
Orichalcum, or its equivalent Latin Aurichalcum, is usually translated as ‘golden copper’ referring to either its colour or composition (80% copper and 20% zinc) or both. However, Webster’s Dictionary translates it as ‘mountain-copper’ from ‘oros’ meaning mountain and ‘chalchos’ meaning copper.
Sir Desmond Lee described the metal as ‘imaginary’ without explaining away the classical references or the fact that ”In numismatics, orichalcum is the name given to a brass-like alloy of copper and zinc used for the Roman sestertius and dupondius(r). Very similar in composition to modern brass, it had a golden-yellow color when freshly struck. In coinage, orichalcum’s value was nearly double reddish copper or bronze. Because production cost was similar to copper or bronze, orichalcum’s formulation and production were highly profitable government secrets.”(m)
Modern writers have offered a range of conflicting explanations for both the origin and nature of orichalcum. A sober overview of the subject is provided by the Coin and Bullion Pages website(d).
In 1926 Paul Borchardt recounted Berber traditions that recalled a lost City of Brass. Salah Salim Ali, the Iraqi scholar, points[0077] out that a number of medieval Arabic writers referred to an ancient ‘City of Brass’ echoing the Orichalcum-covered walls of Plato’s Atlantis.
Ivan Tournier, a regular contributor to the French journal Atlantis proposed that orichalcum was composed of copper and beryllium. Tournier’s conclusion seems to have been influenced by the discovery in 1936 at Assuit in Egypt of a type of scalpel made from such an alloy(e). An English translation of Tournier’s paper was published in Atlantean Research (Vol 2. No.6, Feb/Mar.1950). In the same edition of A.R. Egerton Sykes adds a few comments of his own on the subject(r).
An unusual suggestion was made by Michael Hübner who noted that “small pieces of a reddish lime plaster with an addition of mica were discovered close to a rampart” in his chosen Atlantis location of South Morocco. He links this with Plato’s orichalcum but does so without any great enthusiasm.
Jim Allen, promoter of the Atlantis in Bolivia theory, claims that a natural alloy of gold and copper is unique to the Andes. Tumbaga is the name given by the Spaniards to a non-specific alloy of gold and copper found in South America. However, an alloy of the two that has 15-40% copper, melts at 200 Co degrees less than gold. Dr. Karen Olsen Bruhns, an archaeologist at San Francisco State University wrote in her book, Ancient South America[0497], “Copper and copper alloy objects were routinely gilded or silvered, the original colour apparently not being much valued. The gilded copper objects were often made of an alloy, which came to be very important in all of South and Central American metallurgy: tumbaga. This is a gold-copper alloy that is significantly harder than copper, but which retains its flexibility when hammered. It is thus ideally suited to the formation of elaborate objects made of hammered sheet metal. In addition, it casts well and melts at a lower temperature than copper, always a consideration when fuel sources for a draught were the wind and men’s lungs. The alloy could be made to look like pure gold by treatment of the finished face with an acid solution to dissolve the copper, and then by hammering or polishing to join the gold, giving a uniformly gold surface”.
Enrico Mattievich also believed that orichalcum had been mined in the Peruvian Andes(b).
Jürgen Spanuth tried to equate Orichalch with amber. Paul Dunbavin links Orichalcum with Wales. Robert Ishoy implies a connection between obsidian and Orichalcum, an idea also promoted by Christian & Siegfried Schoppe.
The most exotic suggestion has come from Felice Vinci who equates it with platinum[019.286] which was probably brought from the Ural Mountains. The most recent (2023) identification of orichalcum, which Plato tells us was used as wall cladding in Atlantis, came from Graham Phillips who also suggested[2063] that it was platinum! Incidentally, platinum was not discovered by Europeans until the eighteenth century in South America.
Albert Slosman thought that there was a connection between Moroccan oricalcita, a copper derivative, and Plato’s orichalcum. Peter Daughtrey has offered [893.82] a solution from a little further north in Portugal where the ancient Kunii people of the region used ori or oro as the word for gold and at that period used calcos for copper.
Thorwald C. Franke has suggested[750.174] that two sulphur compounds, realgar and orpiment whose fiery and sometimes translucent appearance might have been Plato’s orichalcum. His chosen location for Atlantis, Sicily, is a leading source of sulphur and some of its compounds. I doubt this explanation as realgar disintegrates with prolonged exposure to sunlight, while both it and orpiment, a toxin, could not be described as metals in any way comparable with gold and silver as stated by Plato.
Frank Joseph translates orichalcum as ‘gleaming or superior copper’ rather than the more correct ‘mountain copper’ and then links Plato’s metal with the ancient copper mines of the Upper Great Lakes. Joseph follows Egerton Sykes in associating ‘findrine’, a metal referred to in old Irish epics, with orichalcum. However, findrine was usually described as white bronze, unlike the reddish hue of orichalcum.
Ulf Erlingsson suggested [319.61] that orichalcum was ochre, which is normally yellow, but red when burnt. He seems to have based this on his translation of the text Critias116b. In fact, the passage describes the citadel flashing in a fiery manner, but it does not specify a colour!
Other writers have suggested that orichalcum was bronze, an idea that conflicts with a 9600 BC date for the destruction of Atlantis since the archaeological evidence indicates the earliest use of bronze was around 6000 years later.
Thérêse Ghembaza has kindly drawn my attention to two quotations from Pliny the Elder and Ovid that offer possible explanations for Plato’s orichalcum(n). The former refers to a Cypriot copper mixed with gold which gave a fiery colour and is called pyropus, while Ovid also refers to a cladding of pyropus. She also mentions auricupride(Cu3Au), an alloy that may be connected with orichalcum.
Zatoz Nondik, a German researcher, has written a book about Plato’s ‘orichalcum’, From 2012 to Oreichalkos[0841], in which he describes, in detail, how the orichalcum may be related to Japanese lacquer and suitable for coating walls as described in the Atlantis(b) narrative!
The fact is that copper and gold mixtures, both natural and manmade, have been found in various parts of the world and have been eagerly seized upon as support for different Atlantis location theories. A third of all gold is produced as a by-product of copper, lead, and zinc production.
It is also recorded that on ancient Crete, in the Aegean, two types of gold were found, one of which was a deep red developed by the addition of copper. Don Ingram suggests that the reddish gold produced in ancient Ireland is what Plato was referring to.
Irrespective of what orichalcum actually was, I think it is obvious that it was more appropriate to the Bronze Age than 9,600 BC. Furthermore, it occurs to me that Plato, who was so careful to explain or Hellenise foreign words so as not to confuse his Athenian audience, appears to assume that orichalcum is not an alien term to his audience.
The result of all of this is that Orichalcum has been advanced to support the location of Atlantis in North and South America, Sundaland, Ireland, Britain and the Aegean. Once again an unintentional lack of clarity in Plato’s text hampers a clear-cut identification of the location of Atlantis.
A fascinating anecdote relating to the use of a term similar to ‘orichalcum’ to describe a mixture of copper and gold was used by a metalsmith in Dubai as recently as 2007 and is recounted on the Internet(a).
The Wikipedia entry(f) for ‘orichalcum’ adds further classical references to this mysterious metal.
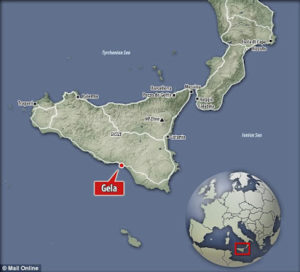 2015 began with a report that 47 ingots of ‘orichalcum’ had been found in a shipwreck off the coast of Sicily, near Gela, and dated to around 600 BC(g). What I cannot understand is that since we never knew the exact composition of Plato’s alloy, how can anyone today determine that these salvaged ingots are the same metal? Thorwald C. Franke has more scholarly comments on offer(h). Jason Colavito has also applied his debunking talents to the subject(i). In June of the same year,
2015 began with a report that 47 ingots of ‘orichalcum’ had been found in a shipwreck off the coast of Sicily, near Gela, and dated to around 600 BC(g). What I cannot understand is that since we never knew the exact composition of Plato’s alloy, how can anyone today determine that these salvaged ingots are the same metal? Thorwald C. Franke has more scholarly comments on offer(h). Jason Colavito has also applied his debunking talents to the subject(i). In June of the same year,  Christos Djonis, in an article(j) on the Ancient Origins website, wrote a sober review of the media coverage of the shipwreck. He also added some interesting background history on the origin of the word ‘orichalcum’.
Christos Djonis, in an article(j) on the Ancient Origins website, wrote a sober review of the media coverage of the shipwreck. He also added some interesting background history on the origin of the word ‘orichalcum’.
An analysis revealed(k) that those ingots were composed of 75-80% copper, 15-20% zinc, and traces of nickel, lead and iron, but no proof that this particular alloy was orichalcum. The recovery of a further 39 ingots from the wreck was reported in February 2017 and the excavation of the sunken ship continues.
An extensive paper(o) on the Gela discovery reported: “that Professor Sebastiano Tusa, an archaeologist at the office of the Superintendent of the Sea in Sicily, claimed the metal they had discovered in the remains of the ship was probably the mythical and highly prized red metal orichalcum.” However, dissent was not long coming, as the paper also notes that “ Enrico Mattievich, a former physics professor at the Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, believes the metal has its origins in the Chavin civilisation that developed in the Peruvian Andes in around 1,200 BC. He claims the metal alloy is made from copper, gold and silver. He claims that the discovery off the coast of Gela is not true orichalcum.” I think that both are probably wrong as we do not know the exact chemical composition of Plato’s orichalcum and both are just engaging in speculation.
The most recent explanation for the term comes from Dhani Irwanto who has proposed that orichalcum refers to a form zircon(l) that is plentiful on the Indonesian island of Kalimantan, where he has hypothesised that the Plain of Atlantis was located [1093.110].
(a) Problems with Atlantis – Aquiziam (archive.org)
(b) https://www.migration-diffusion.info/article.php?year=2011&id=268
(c) https://www.sacred-texts.com/cla/flwp/flwp26.htm
(d) https://www.coinandbullionpages.com/gold-alloys/orichalcum.html
(e) Atlantis Research Vol 2. No.6, Feb/Mar 1950, p.86
(f) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Orichalcum
(g) See: Archive 2460
(h) https://www.atlantis-scout.de/atlantis_newsl_archive.htm
(k) From Fiction to Fact: Ancient Metal Identified with XRF – Analyzing Metals (archive.org) *
(l) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zircon
(m) https://www.forumancientcoins.com/numiswiki/view.asp?key=orichalcum
(n) See: Archive 3456
(p) Oriharukon – Atlantisforschung.de (atlantisforschung-de.translate.goog)
(q) http://www.oocities.org/motorcity/factory/2583/orich.htm
(r) http://www.jaysromanhistory.com/romeweb//engineer/art11.htm