F. Butavand
Tyrrhenian Sea
>The Tyrrhenian Sea according to Massimo Pittau was named after the Sardinian Nuragics, since in ancient Greek ‘Tyrrenoi’ means ‘builders of towers’. As noted elsewhere, Sardinia was an important part of the Atlantean domain.<
Plato clearly states that Atlantis controlled Europe as far as Tyrrhenia (Critias 114c), which implies that they dominated the southern half of the Italian peninsula. The Sea is surrounded by the islands of Corsica, Sardinia, Sicily and the Lipari Islands as well as continental Europe in the form of the Italian mainland. Not only does it contain islands with an adjacent continent (see Timaeus 24e). It is also accessed through the straits of Messina and Sicily, both of which have been identified as locations for the Pillars of Heracles before Eratosthenes applied that appellation to the region of Gibraltar.
Timaeus 24e-25a as translated by Bury reads “there lay an island which was larger than Libya and Asia together; and it was possible for the travellers of that time to cross from it to the other islands, and from the islands to the whole of the continent over against them which encompasses that veritable ocean (pontos=sea). For all that we have here, lying within the mouth of which we speak, is evidently a haven having a narrow entrance; but that yonder is a real ocean (pelagos=sea), and the land surrounding it may most rightly be called, in the fullest and truest sense, a continent.” Similarly, Lee and Jowett have  misleadingly translated both pontos and pelagos as ‘ocean’, while the earliest English translation by Thomas Taylor correctly renders them as ‘sea’. Modern translators such as Joseph Warren Wells and a Greek commentator George Sarantitis are both quite happy to agree with Taylor’s translation. However, Peter Kalkavage translates pontos as ‘sea’ but pelagos as ‘ocean’!
misleadingly translated both pontos and pelagos as ‘ocean’, while the earliest English translation by Thomas Taylor correctly renders them as ‘sea’. Modern translators such as Joseph Warren Wells and a Greek commentator George Sarantitis are both quite happy to agree with Taylor’s translation. However, Peter Kalkavage translates pontos as ‘sea’ but pelagos as ‘ocean’!
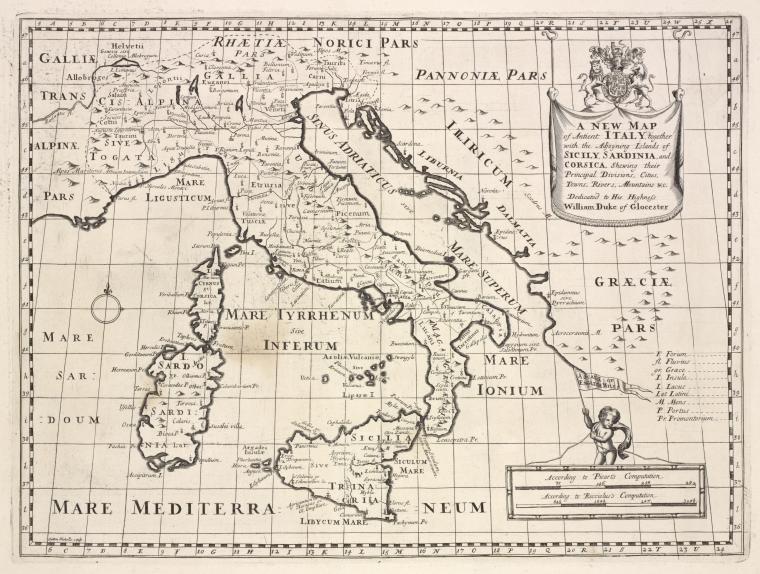
For me, there is a very strong case to be made for identifying the Tyrrhenian Sea as the ‘sea’ referred to by Plato in the passage quoted above. However, it was probably F.Butavand, in 1925, who first proposed the Tyrrhenian as the sea described by Plato in his La Veritable Histoire de L’Atlantide[205] .
Pushing the boat out a little further, I note that Rome is situated in Central Italy and by tradition was founded by the twins Romulus and Remus!
A 1700 map of the Tyrrhenian Sea is available online.
‘Tyrrhenia’ is sometimes used as a geological term to describe a sunken landmass in the Western Mediterranean Basin(b)(c).
(a) (link broken) *
Chaouat, Dr. Émile Mir
Dr. Émile Mir Chaouat follows the views of Butavand and agrees that Plato’s 9,000 years should be taken as months and consequently dates the destruction of Atlantis to 1400 BC. He agrees, in common with many other writers, that the Sahara once had a large inland sea which contained Atlantis. He believes that its Mediterranean port was located at Cerne. He points out that Athena and Neith the goddess of Sais were identical and suggests that the name of the legendary North African queen Tin Hanan may be a corruption of Athena [(A)tin-ha(nan)]. In 1925 Byron Khun de Prorok claimed to have found the tomb of Tin Hanan, renowned queen of the Tuaregs, in the Hoggar Mountains. Chaouat’s published his views in a 1953 booklet, Lumiére sur l’Atlantide [227].
Robert Charroux was intrigued by Chaouat’s book[1039.122].
However, Atlantisforschung tells us that “this was apparently only the first volume of a multi-part Atlantological publication series from his pen because WorldCat also contains references to three other related publications of his, namely: L’Atlantide. Deuxième partie (1957), L’Atlantide. 3. Lumière sur l’Atlantide, les Atlantes en Afrique, Libye des Anciens (1957) and Lumière sur l’Atlantide / 4, Les Atlantes en Europe (also 1957). Unfortunately, none of these works currently seem to be available in an antiquarian form, but they are at least still available in some university libraries.” (a)
(a) Émile Mir Chaouat – Atlantisforschung.de (atlantis-forschung.de)
Arecchi, Alberto *
 Alberto Arecchi, born in 1947, is an architect and professor of Design and history of Art, in Pavia in Italy, where he lives. He is president of the Cultural Association Liutprand. He has spent fifteen years in Africa working on international development projects. He is the author of many books relating to European History.
Alberto Arecchi, born in 1947, is an architect and professor of Design and history of Art, in Pavia in Italy, where he lives. He is president of the Cultural Association Liutprand. He has spent fifteen years in Africa working on international development projects. He is the author of many books relating to European History.
Arecchi has also written about Atlantis in Atlantide, Un mondo scomparso, in which he builds on investigations originally begun in the 1920s by F. Butavand and Jean Gattefosse. Arecchi’s book [079] contains some radical ideas:
(i) it supports the theory of an extensive Sicilian land bridge between Europe with Africa,
(ii) it locates Atlantis off the coast of modern Tunisia and
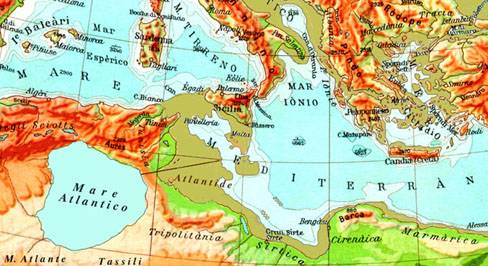
(iii) it posits the existence of a large inland sea, the original Atlantic ‘Sea’, in part of what is now the northern Sahara, where the chotts of Algeria and Tunisia now are.
He claims that all this ended around 1225 BC when seismic activity in the region caused the land bridge to disappear and the dam that contained the inland sea to rupture and Atlantis to vanish. His date is based on the interpretation of Plato’s 9,000 ‘years’ as 9,000 lunar cycles. Arecchi further claims that the Gibraltar Dam was breached around 2500 BC. He also envisages the Maltese Islands connected to both Sicily and Tunisia before this breach.
An outline of his understanding of the Atlantis story, in Italian and English, can be found on the Internet(e) in a 2004 paper entitled Empire of Atlantis: From the Mediterranean to the New World, in which he reviews the evidence for early Mediterranean influences in the Americas and particularly the work of the controversial Barry Fell, who identified North African scripts on markers at a number of locations in North America. Arecchi sees this as support for his Atlantis location off the coast of today’s Tunisia and that there was trans-Atlantic Atlantean influence!
In fairness, the contentious opinions of Fell deserve a look, so a vindication of his epigraphic work(h) should also be read, as well as further corroboration by more recent DNA studies(i).
Part of Arecchi’s theory includes a landbridge between Italy and North Africa, in his own words – “At that time, the sea today known as the Mediterranean Sea had to be divided into two parts, placed at different levels and deprived of mutual communications. The western Mediterranean and the Tyrrhenian were – as they are today – in communication with the Ocean, through Gibraltar, opened more than a thousand years before. The eastern part – i.e. the Greeks’ Mediterranean – was properly an “interior sea”, like a lake, from the Small Syrte to the Syro-Palestinian coasts, including lower Adriatic and Candia Sea (while the Aegean territory, all emerging, was a plain, crowned by volcanic mountains). Its waters would be approximately 300 m under the level of today. We will note this level as “level zero”, in order to measure the relative altitudes.” (see map)
The suggested Sicilian land bridge was more than a possibility if the Gibraltar Dam was a fact. By cutting off the waters of the Atlantic, desiccation in the Mediterranean would have brought the level of its water below that of the Atlantic, creating at least two very large inland lakes and exposing the Sicilian land bridge. Diaz-Montexano supports the idea of this isthmus or land bridge, an idea reinforced by the comments of both Strato and Seneca.
However, in November 2011, I came across an Italian website(b) that included two articles by Arecchi which offer maps of two different locations for Atlantis. Nave di Atlantide? includes the North African site mentioned above. La Vera Atlantide incorrectly attributes Atlantis as a unified and much enlarged Balearic archipelago to Arecchi. I contacted Professor Arecchi, who confirmed that he is only advocating a site 100 miles SE of Malta (see map). The reference to Mallorca in the other article he attributes to a “free-interpretation” of his only thesis.
Arecchi claims that the people known as ‘Tjehenu’ or ‘Tenehu’ by the Egyptians were the Atlanteans of Plato’s narrative, an idea echoed by Ulrich Hoffman.
Arecchi’s book, referred to above, is now available as a free pdf file(c), unfortunately, it is in Italian and pdf files are sometimes difficult to translate. Several papers relating to his architectural interests can be found on the academia.edu website. Two short reviews of Arecchi’s book by Flavio Barbiero and Emilio Spedicato are available online(j).
I believe this book to be an important contribution to the Atlantis debate so if I can find an efficient means of translating it, I will post it here. In the meanwhile, an abstract of his book, in English, is available online(d). A more extensive précis of his theories, in English and Italian, can be read in Archive 6912.
As a supporter of the idea of Atlantis in the Central Mediterranean, I find Arecchi’s concepts quite credible, although I would like to know more about the scientific evidence underlying them. An English translation of his book would help.
(a) https://www.liutprand.it/Atlantis.htm
(b) PETROGLIFI DI QUIACA (archive.org) *
(d) https://www.liutprand.it/articoliMondo.asp?id=111
(e) https://www.liutprand.it/impero_atl.pdf (Ital) & https://atlantipedia.ie/samples/archive-2529/(Eng)
(g) http://www.antikitera.net/news.asp?ID=9728
(h) http://www.equinox-project.com/DRFEL.HTM
(i) The Arabian Horizon – The Cherokee Compass | MalagaBay (archive.org)