Rome
Two Crops a Year
Two Crops a year is one of the characteristics of Atlantean agriculture according to Plato (Critias 118e).
The North African climate was slightly wetter at the time of Hannibal (2nd & 3rd cent. BC), later, Algeria, Egypt and particularly Tunisia, were the ‘breadbasket’ of Rome(b) and may also have been so for the Atlanteans who earlier had control from North Africa to Tyrrhenia! Even today well-irrigated plains in Tunisia can produce two crops a year, usually planted with the autumnal rains and harvested in the early spring and again planted in the spring and harvested in late summer. The Berbers of Morocco produce two crops a year—cereals in winter and vegetables in summer(a).
It is worth noting that Mago, the Carthaginian author of a 28-book work on the agricultural practices of North Africa. had his books brought to Rome after the destruction of Carthage in 146 BC, where they were translated from Punic into Latin and Greek and were widely quoted. It is clear that Mago’s work was a reflection of a highly developed agricultural society in that region, a description that could also be applied to Plato’s Atlantis!
Although two crops are possible annually in other parts of the world, I must emphasise that North Africa is the only part of the Atlantean territory referred to by Plato (Timaeus 25b) that was so productive and continued to be so until the Romans, who depended on it along with Egypt to feed Rome.
>James Bailey who advocated an American location for Atlantis refers [150.63] to the irrigation systems of ancient Mexico and the ability to raise three crops a year in Mexico and the coastal plains of Peru as all echoes of Plato’s description of Atlantis.<
Invasion
Invasion today, as in the past, is usually the consequence of a shortage of resources (food, metals, oil, water), climate change (affecting food supply), overpopulation (also affecting food supply) or political upheaval. Although I do not speak as a military strategist, it would seem obvious that if for any of these reasons, a state is forced into expansionism, it will first look at its nearest neighbours and assess the chances of military success. It is obvious that before the introduction of airborne attacks, propinquity in the form of contiguous territory or short sea journeys has always been critical for a successful invasion(a) and the continued control of occupied territories. This is borne out by the simple historical fact that all the earliest empires, which were located in what we now call the Middle East, expanded through the invasion of its neighbours.
>Even today (27.02.22) Vladimir Putin has expanded his empire into more of the contiguous state of Ukraine, having already annexed Crimea. Some military imperatives never change.<
However, over-expansion can be costly and potentially dangerous. With particular reference to the fall of the Roman Empire, Rachel Nuwer noted in a recent BBC article(c) that. “By the end of the 100 BC, the Romans had spread across the Mediterranean, to the places most easily accessed by sea. They should have stopped there, but things were going well and they felt empowered to expand to new frontiers by land. While transportation by sea was economical, however, transportation across the land was slow and expensive. All the while, they were overextending themselves and running up costs.”
Many people think that military intelligence gathering is a relatively modern development. However, ancient documents, including the Bible, have accounts of spying thousands of years ago. Mary Rose Sheldon has produced an invaluable sourcebook[1445] on the subject, as well as a volume on Spies in the Bible[1446], while Peter Dubovsky, in his Hezekiah and the Assyrian Spies[1568], focuses on espionage described in 2 Kgs 18-19. It is reasonable therefore to assume that Atlantis also exercised due diligence and endeavoured to assess their opponent’s strengths and weaknesses before invading.
Boris Rankov has noted(b) in The Encyclopedia of Ancient History that military intelligence in ancient times had its value limited by the “slowness of communications, which meant that it was often out of date before any response could be brought to bear.” This, of course, ties in with the then established practice of invading those within your immediate proximity; supply lines are shorter and information more up-to-date. In turn, it implies that Atlantis was within relatively easy striking distance of Athens!
Even in modern times, the same constraints determined the actions of invaders. Hitler could not have invaded Russia without first controlling Poland and Romania. Even expansionist Japan, although an island nation, expanded into Korea and Manchuria (China) and following the attack on Pearl Harbour spread even further within the same region.
The ancient land-based empires were dependent on military might, whereas others, such as the Phoenicians, expanded their influence through trade, supported by extensive merchant fleets. However, over time, Phoenician or more correctly Carthaginian rivalry with Rome led to disastrous wars.
One of the primary military concerns today, as in ancient times, will be to ensure that its men are fed and watered and consequently there will be a need to keep its supply lines as short as possible.
The nearest possible belligerent to the west of Athens was across the Adriatic in Italy. I argue elsewhere that according to Plato, southern Italy constituted part of the Atlantean domain (see Etruscans). I suggest that the Atlantean invasion of Greece was probably launched from there. The motivation is unclear, but we can speculate that success in Greece would have been followed by the control of the entire Aegean, including Crete, offering a huge expansion in trade.
The alternative is that the nearest part of Atlantis was elsewhere, necessitating the bypassing of other territories on the way and stretching supply and communication lines more than desirable. Italy looks the best bet, with forces added from the Atlantean HQ in Sicily or Sardinia, possibly travelling through the Strait of Messina, sometimes identified as the location of the Pillars of Heracles.
In the south, the Atlantean forces in North Africa (Ancient Libya), if not augmenting the attack on Greece, were probably planning their invasion of Egypt (Timaeus 25b & Critias 114c). Success there would have been followed by a two-pronged attack by both northern and southern Atlantean forces on the eastern Mediterranean coast, later known as the Levant, giving them total control of the eastern Mediterranean Basin.
Invasion requirements are the strongest argument against any of the fanciful Atlantis theories that place Plato’s Atlantis in Antarctica, the Andes, or North America. It is ludicrous to claim that any invasion force came across the Atlantic to attack Greeks and Egyptians. That there were remarkable early cultures in both North and South America is absolutely undeniable, however, it is foolishness to claim that they had any connection with Plato’s story.
(a) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_invasions
(b) http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/9781444338386.wbeah26323/abstract
(c)http://www.bbc.com/future/story/20170418-how-western-civilisation-could-collapse
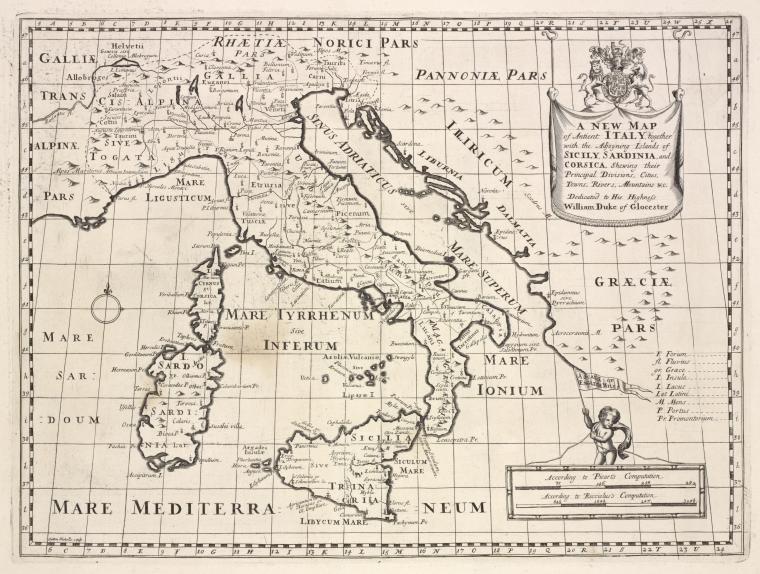
Tyrrhenian Sea
>The Tyrrhenian Sea according to Massimo Pittau was named after the Sardinian Nuragics, since in ancient Greek ‘Tyrrenoi’ means ‘builders of towers’. As noted elsewhere, Sardinia was an important part of the Atlantean domain.<
Plato clearly states that Atlantis controlled Europe as far as Tyrrhenia (Critias 114c), which implies that they dominated the southern half of the Italian peninsula. The Sea is surrounded by the islands of Corsica, Sardinia, Sicily and the Lipari Islands as well as continental Europe in the form of the Italian mainland. Not only does it contain islands with an adjacent continent (see Timaeus 24e). It is also accessed through the straits of Messina and Sicily, both of which have been identified as locations for the Pillars of Heracles before Eratosthenes applied that appellation to the region of Gibraltar.
Timaeus 24e-25a as translated by Bury reads “there lay an island which was larger than Libya and Asia together; and it was possible for the travellers of that time to cross from it to the other islands, and from the islands to the whole of the continent over against them which encompasses that veritable ocean (pontos=sea). For all that we have here, lying within the mouth of which we speak, is evidently a haven having a narrow entrance; but that yonder is a real ocean (pelagos=sea), and the land surrounding it may most rightly be called, in the fullest and truest sense, a continent.” Similarly, Lee and Jowett have  misleadingly translated both pontos and pelagos as ‘ocean’, while the earliest English translation by Thomas Taylor correctly renders them as ‘sea’. Modern translators such as Joseph Warren Wells and a Greek commentator George Sarantitis are both quite happy to agree with Taylor’s translation. However, Peter Kalkavage translates pontos as ‘sea’ but pelagos as ‘ocean’!
misleadingly translated both pontos and pelagos as ‘ocean’, while the earliest English translation by Thomas Taylor correctly renders them as ‘sea’. Modern translators such as Joseph Warren Wells and a Greek commentator George Sarantitis are both quite happy to agree with Taylor’s translation. However, Peter Kalkavage translates pontos as ‘sea’ but pelagos as ‘ocean’!
For me, there is a very strong case to be made for identifying the Tyrrhenian Sea as the ‘sea’ referred to by Plato in the passage quoted above. However, it was probably F.Butavand, in 1925, who first proposed the Tyrrhenian as the sea described by Plato in his La Veritable Histoire de L’Atlantide[205] .
Pushing the boat out a little further, I note that Rome is situated in Central Italy and by tradition was founded by the twins Romulus and Remus!
A 1700 map of the Tyrrhenian Sea is available online.
‘Tyrrhenia’ is sometimes used as a geological term to describe a sunken landmass in the Western Mediterranean Basin(b)(c).
(a) (link broken) *
Kings of Atlantis
The Kings of Atlantis were, according to Plato, originally the sons of Poseidon and Cleito. They were ten in number and consisted of five sets of male twins. The firstborn was Atlas who was given authority over the others, each of whom controlled their own territory. Some commentators reacted with such incredulity to this story, that they have either dismissed this detail or in some cases the entire Atlantis tale as pure fantasy. Of course, it is highly improbable, if not virtually impossible to accept that Clieto had five sets of all-male twins. However, we are dealing here with a myth that is an echo of the legends of many other cultures describing their antediluvian origins. Lenormant & Chevallier wrote [424] of this over a hundred years ago:
“…The ten kingdoms of Atlantis are perpetuated in all the ancient traditions. ‘In the number given by the Bible for the Antediluvian patriarchs we have the first instance of a striking agreement with the traditions of various nations. Other nations, to whatever epoch they carry back their ancestors…are constant to the sacred number of ten… In Chaldea (Babylon), Berosus, writing in the third century BC, numerates ten Antediluvian kings whose fabulous reigns extended to thousands of years. The legends of the Iranian race commence with the reign of ten Peisdadien (Poseidon?) kings…. In India we meet with the nine Brahmadikas, who, with Brahma, their founder, make ten, and who are called the Ten Petris, or Fathers. The Chinese count ten emperors, partaking of the divine nature, before the dawn of historical time. The Germans believed in the ten ancestors of Odin, and the Arabs in the ten mythical kings of the Adites”.
Cosmas Indicopleustes, in the 6th century AD, contended[1245] that Atlantis was the Garden of Eden and that Plato’s 10 kings of Atlantis were the 10 generations between Adam and Noah!
It may be just a coincidence, but Plato tells us that the domain of Atlantis extended as far as Tyrrhenia (modern Tuscany), just south of which was Rome, a city, which according to legend was also founded by twin brothers, Romulus and Remus. It has been claimed that the story of their origins is a variation of the story in the Hindu epic Ramayana concerning the twin sons of king Sri Rama, Luva and Kusha(c).
In the same region, Sicily has the legend of the divine Palici twins (Palikoi in Greek).
>Aelian in his Natura Animalium has recorded [0619 xv.2] how the natives who live on the shores of ‘Ocean’ have a legend that tells of the Atlantean kings, who, to symbolise their authority from Poseidon, wore a crown reminiscent of the white band that ran around the forehead of the male ‘ram fish’ while their queens wore headgear made from the skins of ’marine ewes’.
“Ram-fishes, whose name has a wide circulation, although information about them is not very definite except in so far as displayed in works of art, spend the winter near the strait between Corsica and Sardinia and actually appear above water. And round about them swim dolphins of very great size.” (15.2)(f)
Although these animals have not been clearly identified, their size suggests a species of whale. I suggest that it was a fin whale which has a grey or white chevron marking on top of its head and is frequently found in the Strait of Bonifacio, between Corsica and Sardinia, at the southern end of the Pelagos Sanctuary.
“Fin whales, the second largest animal on the planet after blue whales, are represented in the Mediterranean by a resident population separated from the Atlantic.“(e)
So, it would appear obvious from this excerpt that Aelian did not have any doubt regarding the reality of Atlantis. Perhaps even more interesting is that Aelian seems to also associate these kings of Atlantis with Corsica and Sardinia. For me, this is compatible with a Central Mediterranean location for Atlantis.<
Although Babylon is supposed to have had ten kings before the Flood, it must be noted that they reigned successively rather than concurrently, as was the case in Atlantis.
Attention has been drawn to the fact that Manetho (c. 300 BC), the Egyptian historian called the first sequence of Egyptian god-kings ‘Auriteans’, which has been seen as suspiciously like a corruption of ‘Atlanteans‘.
Plato gives the names of the first ten kings as; Atlas, Gadeiros (Eumelos), Ampheres, Euaimon, Mneseos, Autochthon, Elasippos, Mestor, Azaes, Diaprepres (Critias 114b).
Some writers have attempted to link these names with specific regions; such as Atlas with Morocco, Eumelos (Gadeiros) with Gades (Cadiz) and Elasippos with Lisbon. Beyond these three there is very little agreement. Lewis Spence correctly points out “Plato expressly states that these names had been Egyptianised from the Atlantean language by the priest of Sais, and subsequently Hellenised in Critias, so that there is little hope that they were transmitted in anything like their original form.” Spence also commented on the similarity of the Phoenician gods and the early kings of Atlantis, an idea suggested earlier by Ignatius Donnelly.
Reginald Fessenden claimed to have identified at least six of Plato’s Atlantean king-list with names in the Caucasus.(d)
Even more distant locations were proposed by the French cartographer Guillaume Sanson (1633-1703), who generously distributed the Americas among the ten brothers, allocating Mexico to Atlas.
R. Cedric Leonard is convinced that Manetho’s list of Egyptian god-kings is in fact a list of the first kings of Atlantis and expands on this idea on his website(a). However, in his 1979 book, Quest for Atlantis[0130], Leonard has suggested that the kings of Atlantis were human-alien hybrids and that humans are the result of alien genetic experiments!!
Another site(b) identifies the kings of Atlantis with the pantheon of Phoenician gods, an idea first mooted by Ignatius Donnelly (part IV. chap. III). But Donnelly, also suggested, unconvincingly, that the gods of the Greeks were just the deified kings of Atlantis (part IV, chap. II), while it is also possible that they were just personifications of natural phenomena.
An unusual feature of the Atlantean kings is the meeting every fifth and sixth year. Plato explains this as a way of honouring odd and even numbers. However, Bacon & Galanopoulos suggest[263.152] that in fact, this may have been the result of an awareness of the eleven-year cycles of rains. I believe that this explanation is equally weak and the subject requires further investigation.
(a) https://web.archive.org/web/20170608084749/http:/www.atlantisquest.com:80/Hiero.html
(b) https://phoenicia.org/godidea.html#Atlantis
(c) https://vediccafe.blogspot.ie/2014/05/the-ramayana-in-roots-of-pre-christian.html
(d) The Deluged Civilisation of the Caucasus Isthmus [1012] (chap 3.29) *
(e) https://tethys.org/activities-overview/research/fin-whales/ *