Ali Bey el Abbassi
Sahara Desert
The Sahara Desert and in particular its northern regions have attracted its share of attention from Atlantis investigators. However unlikely it may appear as a possible location for Atlantis it must be kept in mind that the Sahara of prehistory was very different from what we see today. Not only was it wetter at various periods in the past, but also there is clear evidence for the existence of a large inland sea extending across the borders of modern Algeria and Tunisia. This evidence is in the form of the chotts or salt flats in both countries. This proposed sea is considered by some to have been the Lake Tritonis referred to by classical writers. It is suggested that some form of tectonic/seismic activity, common in the region, was responsible for isolating this body of seawater from the Mediterranean and eventually turning it into the salt flats we see today.
An even more extensive inland sea, further south, was proposed by Ali Bey el Abbassi and based on his theory a map was published in 1802 which can be viewed online(c).
More recently, Riaan Booysen has published an illustrated paper on the ancient inland Saharan seas as indicated on the 16th-century maps of Mercator and Ortelius(i). King’s College London runs The Sahara Megalakes Project which studies the Megalakes and the Saharan Palaeoclimate record(m).>>The largest of these was possibly Lake Chad which at its most extensive is estimated to have been greater than the combined Great Lakes of North America.<<
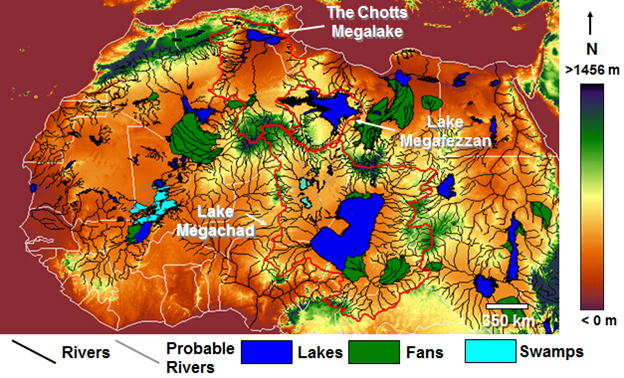 A 2013 report in New Scientist magazine(d) revealed that 100,000 years ago the Sahara had been home to three large rivers that flowed northward, which probably provided migration routes for our ancestors. Depending on how long the African Humid Period lasted, this article may be read in conjunction with George Sarantitis‘ theory regarding the Voyage of Hanno that he claims took place in the interior of Africa.
A 2013 report in New Scientist magazine(d) revealed that 100,000 years ago the Sahara had been home to three large rivers that flowed northward, which probably provided migration routes for our ancestors. Depending on how long the African Humid Period lasted, this article may be read in conjunction with George Sarantitis‘ theory regarding the Voyage of Hanno that he claims took place in the interior of Africa.
Other studies(h) have shown the previous existence of a huge river system in the Western Sahara, which flowed into the Atlantic on the Mauritanian coast.
An article in the Sept. 2008 edition of National Geographic pointed out that the Saharan climate has been similar for the past 70,000 years except for a period beginning 12,000 years ago when a number of factors combined to alter this fact. A northerly shift by seasonal monsoons brought additional rain to an area the size of the contiguous USA. This period of a greener Sahara lasted until around 4,500 years ago.
More recent studies claim that “there’s geologic evidence from ocean sediments that these orbitally-paced Green Sahara events occur as far back as the Miocene epoch (23 million to 5 million years ago), including during periods when atmospheric carbon dioxide was similar to and possibly higher than today’s levels. So, a future Green Sahara event is still highly likely in the distant future.” (p)
>>However, in the Sept. 2024 edition of National Geographic an article Peter Gwin notes that “the Sahara hasn’t always been a desert. In fact, it transforms from desert to lush savanna about every 21,000 years. A quirk in Earth’s planetary mechanics periodically causes its axis to tilt slightly, increasing the amount of radiation directed to the Northern Hemisphere, which in turns pulls Africa’s seasonal rains northward.”<<
Henri Lhote contributed an article to Reader’s Digest‘s, The World’s Last Mysteries [1083], regarding the ‘green’ Sahara that existed prior to 2500 BC. Two German climatologists Rudolph Kuper and Stefan Kröpelin have estimated that this last greening of the Sahara began around 8500 BC and ended sometime between 3500 BC and 1500 BC(r)(u) .
A team from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Research led by Professor Martin Claussen published a number of papers in the late 1990s following their production of a successful computer simulation of prehistorical North Africa(v). According to a report on the climateark website (now offline), one of their conclusions was “that the change to desert climate in the Sahara was triggered by changes in the Earth’s orbit and the tilt of Earth’s axis.”
Some, such as Kröpelin, have suggested a connection between the latest aridification of the Sahara and the migration of settlers to the Nile Valley(w), where, coincidentally, the ancient Egypt we know about was founded around 3100 BC.
Others have endeavoured to link the last drying of the Sahara with the destruction of Atlantis!
More recently, human activity has been blamed as a major contributory factor for the desertification of the Sahara region less than 10,000 years ago.(n)
Related to the above is a recent study of sediments off the west coast of Africa, which resulted in the discovery of what was “primarily a new “beat,” in which the Sahara vacillated between wet and dry climates every 20,000 years, in sync with the region’s monsoon activity and the periodic tilting of the Earth.” (o)
In Mauritania, a huge natural feature known as the Richat Structure has been claimed as the remnant of Atlantis by George Sarantitis [1470] as well as by Alexander & Rosen and others. >>However, Ulf Richter has pointed out that it is too wide (35km), too elevated (400metres) and too far from the sea (500km) to be seriously considered as the location of Atlantis. Apart from which, a scientific study of the Structure reveals it to be a natural feature(x).<<
In 1868, it was proposed by D.A. Godron, the French botanist, that the Sahara was the location of Atlantis. In 2003, the non-existent archaeologist Dr.Carla Sage announced that she was hoping to lead an international expedition to the Sahara in search of Atlantis. Her contention was that “Atlantis was the capital of a vast North African empire with ports on the Gulf of Sidra”. This report is now confirmed to have been a hoax! I am indebted to Stel Pavlou for uncovering the origin of this story(e).
The idea of an African Atlantis was highlighted in 2021 with the publication of Atletenu [1821], in which the author, Diego Ratti, identified the Hyksos as Atlanteans with their capital at Avaris in the eastern Nile Delta. At the other end of North Africa, the chotts of Tunisia and Algeria were nominated by Holden Zhang as the location of Atlantis in a YouTube clip(q).
Gary Gilligan, the well-known catastrophist, wrote a thought-provoking article(k) on the origin of the Saharan sands, which he claims are extraterrestrial in origin and expands on the idea in his 2016 book Extraterrestrial Sands [1365]. A March 2024 report(t). on the BBC website has revealed that a particular type of sand dune has now been dated. They are known as ‘star’ or ‘pyramid’ dunes – “are named after their distinctive shapes and reach hundreds of metres in height.” They are found in Africa, Asia and North America, as well as on Mars – but experts had never before been able to put a date on when they were formed. Now scientists have discovered that a dune called Lala Lallia in Morocco formed 13,000 years ago.”
David Mattingly, an archaeologist at Leicester University has found that an ancient people known as the Garamantes had an extensive civilisation in the Sahara(l). He has evidence of at least three cities and twenty other settlements. The Garamantes reached their peak around 100 BC and then gradually diminished in influence as fossil water supplies reduced until in the 7th century AD they were subjected to Islamic domination. Some researchers such as Frank Joseph have identified the Garamantes as being linked with the Sea Peoples. Bob Idjennaden has published short but informative Kindle books about both the Garamantes [1194] and the Sea Peoples [1195], without a suggestion of any connection between the two.
A 2017 article on the Popular Archaeology website told us that “New research investigating the transition of the Sahara from a lush, green landscape 10,000 years ago to the arid conditions found today, suggests that humans may have played an active role in its desertification.” (n).
The discovery of megalithic structures discovered at Nabta Playa (Nabta Lake) in the Egyptian Sahara has provided evidence for the existence of a sophisticated society in that area around 5000 BC. In the same region, near the Dakhleh Oasis, archaeologists have produced data that supports the idea that pre-Pharaonic Egypt had Desert Origins rather than being an importation from Mesopotamia or elsewhere(a).
Nabta Playa is not unique, in fact, the largest megalithic ellipse in the world is to be found at Mzorah, 27 km from Lixus in Morocco(b). It appears that the construction methods employed at both Mezorah and Nabta Playa are both similar to that used in the British Isles. An even more impressive site is Adam’s Calendar in South Africa which has been claimed as 75,000-250,000 years old.
West of Cairo near the border with Libya is the Siwa Oasis, where it has now been demonstrated that “it is in fact home to one of Ancient Egypt’s astounding solar-calendar technologies– the solar equinox alignment between the Timasirayn Temple and the Temple of Amun Oracle in Aghurmi.”(j).
I think we can expect further exciting discoveries in the Sahara leading to a clearer picture of the prehistoric cultures of the region and what connections there are, if any, with Plato’s Atlantis. In the meanwhile in the Eastern Egyptian Desert, Douglas Brewer, a professor of archaeology at the University of Illinois, has discovered over 1,000 examples of rock art, including numerous depictions of boats although the sites, so far undisclosed, are remote from water.
Even more remarkable is the report(e) of March 2015 that a survey of the Messak Settafet escarpment in the central Sahara revealed that there were enough discarded stone tools in the region “to build more than one Great Pyramid for every square kilometre of land on the continent”! Coincidentally, around the same time, it was reported that over a thousand stone tools had been found in the Northern Utah Desert(g). What the Utah discovery lacked in quantity was made up for in quality with the finding of the largest known Haskett point spearhead, measuring around nine inches in length.
(a) Saudi Aramco World (2006, Vol. 57, No.5 p.2-11)
(c) https://web.archive.org/web/20201019061756/http://catalog.afriterra.org/zoomMap.cmd?number=1036
(d) NewScientist.com, 16 September 2013, https://tinyurl.com/mg9vcoz
(e) https://books.google.com/books?id=GvMDAAAAMBAJ&pg=PA46&dq=dr.+carla+sage+archaeologist&hl=en&sa=X&ei=GSENVKiaO9W0yASJgoIY&ved=0CCYQ6AEwAA#v=onepage&q=dr.%20carla%20sage%20archaeologist&f=false
(f) https://www.cam.ac.uk/research/news/saharan-carpet-of-tools-is-the-earliest-known-man-made-landscape
(i) 7. The lakes in the middle of the Sahara desert – Page 8 (archive.org)
(l) See: Archive 3268
(n) https://popular-archaeology.com/issue/winter-2017/article/did-humans-create-the-sahara-desert
(o) https://phys.org/news/2019-01-sahara-swung-lush-conditions-years.html#jCp
(p) https://www.livescience.com/will-sahara-desert-turn-green.html
(q) Revive Eden 3 Convincing Atlantis – YouTube
(r) https://www.smithsonianmag.com/history/uncovering-secrets-of-the-sphinx-5053442/
(s) https://las.illinois.edu/news/2006-09-01/oasis-art-egyptian-desert
(t) Star dune: Scientists solve mystery behind Earth’s largest desert sands – BBC News
(u) Shift From Savannah to Sahara Was Gradual, Research Suggests – The New York Times (nytimes.com)
(x) Eye Of The Sahara or Richat Structure » Geology Science *
North Africa
North Africa has received considerable attention as a possible location for Atlantis since the beginning of the 19th century. Gattefosse and Butavand are names associated with early 20th-century North African theorists. They, along with Borchardt, Herrmann and others have proposed locations as far west as Lixus on the Atlantic coast of Morocco, on through Tunisia and Libya and even as far east as the Nile delta.
One of the earliest writers was Ali Bey El Abbassi who discussed Atlantis and an ancient inland sea in the Sahara. The concept of such an inland sea, usually linked with Lake Tritonis, has persisted with the Chotts of Tunisia and Algeria as prime suspects.
>There is some acceptance that a seismic or tectonic upward thrust in the vicinity of the Gulf of Gabés created a barrier that cut off this inland sea from the Mediterranean, leaving the trapped water to gradually evaporate. However, the chotts still receive some runoff from the Atlas mountains in winter, which liquefies the salty crust. Diodorus Siculus records this event (Bk.3.55) “The story is also told that the marsh Tritonis disappeared from sight in the course of an earthquake, when those parts of it which lay towards the ocean were torn asunder.” [1731a.179] However, this is more a description of the removal of a barrier, rather than the creation of one! Ludwig Borchardt suggested that this event took place around 1250 BC(c).<
If such an event did not occur, how do we explain the salt-laden chotts? However, proving a connection with Atlantis is another matter.
Whether this particular geological upheaval was related to the episode that destroyed parts of ancient Malta is questionable as the Maltese event was one of more massive subsidence.
It should be kept in mind that Plato described the southern part of the Atlantean confederation as occupying North Africa as far eastward as Egypt (Tim.25b & Crit.114c).
The exact extent of Egyptian-controlled territory in Libya at the time of Atlantis is unclear. We do know that “In the mid-13th century, Marmarica was dominated by an Egyptian fortress chain stretching along the coast as far west as the area around Marsa Matruh; by the early 12th century, Egypt claimed overlordship of Cyrenaican tribes as well. At one point a ruler chosen by Egypt was set up (briefly!) over the combined tribes of Meshwesh, Libu, and Soped.”(b) Another site(a) suggests that Egyptian control stretched nearly as far as Syrtis Major, which itself has been proposed by some as the location of Atlantis.
All this, of course, conflicts with the idea of the Atlanteans invading from beyond ‘Pillars of Heracles’ situated at Gibraltar since they apparently already controlled at least part of the Western Mediterranean as far as Italy and Egypt.
One of the principal arguments against Atlantis being located in North Africa is that Plato clearly referred to Atlantis as an island. However, as Papamarinopoulos has pointed out that regarding the Greek word for island, ‘nesos’ “a literary differentiation between ‘island’ and ‘peninsula’ did not exist in alphabetic Greek before Herodotus’ in the 5th century BC. Similarly, there was not any distinction between the coast and an island in Egyptian writing systems, up to the 5th century BC.” In conversation with Mark Adams[1070.198], Papamarinopoulos explains that in the sixth century BC, when Solon lived, ‘nesos’ had five geographic meanings. “One, an island as we know it. Two, a promontory. Three, a peninsula. Four, a coast. Five, land within a continent, surrounded by lakes, rivers or springs.”
Personally, from the context, I am quite happy to accept that the principal city of the Atlantean alliance existed on an island as we understand the word. This was probably north of Tunisia, where a number of possible candidates exist. However, it may be unwise to rule out a North African city just yet!
Another argument put forward that appears to exclude at least part of North Africa is that Plato, according to many translations, he refers to Atlantis as ‘greater’ than ‘Libya’ and ‘Asia‘ combined, using the Greek word, ‘meizon‘, which had a primary meaning of ‘more powerful’ not greater in size. Atlantis could not have been situated in either Libya or Asia because ‘a part cannot be greater than the whole’. However, if Plato was referring to military might rather than geographical extent, as seems quite likely, North Africa may indeed have been part of the Atlantean alliance, particularly as Plato describes the control of Atlantis in the Mediterranean as far as Tyrrhenia and Egypt.
(a) https://starshinetours.com/first-signs-of-weakening/ (Link broken)
(b) https://www.penn.museum/sites/expedition/egyptians-and-libyans-in-the-new-kingdom/
(c) Ludwig Borchardt – Dictionary of Art Historians (archive.org) *
Atlas Mountains
The Atlas Mountains stretch for over 1,500 miles across the Maghreb of North-West Africa, from Morocco through Algeria to 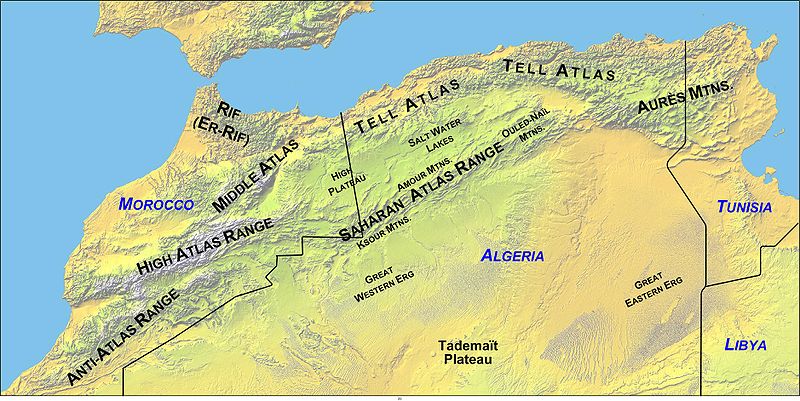 Tunisia. The origin of the name is unclear but seems to be generally accepted as having been named after the Titan.
Tunisia. The origin of the name is unclear but seems to be generally accepted as having been named after the Titan.
Herodotus states (The Histories, Book IV. 42-43) that the inhabitants of ancient Mauretania (modern Morocco) were known as Atlantes and took their name from the nearby mount Atlas. Jean Gattefosse believed that the Atlas Mountains were also known as the Meros and that a large inland sea bounded by the range had been known as both the Meropic and the Atlantic Sea. Furthermore, he contended that Nysa had been a seaport on this inland sea.
The Maghreb, or parts of it, have been identified as the location of Atlantis by a number of commentators. One of the earliest was Ali Bey El Abbassi, who wrote of the Atlas Mountains being the ancient island of Atlantis when what is now the Sahara held a huge interior sea in the centre of Africa.
Ulrich Hofmann concluded his presentation at the 2005 Atlantis Conference with the comment that “based on Plato’s detailed description it can be concluded that Atlantis was most likely identical with the Maghreb.”[629.377] Furthermore, he has proposed that the Algerian Chott-el-Hodna has a ring structure deserving of investigation.
To add a little bit of confusion to the subject, the writer Paul Dunbavin declared[099] that Atlas was a name applied by ancient writers to a number of mountains.
My contention is that the Atlas Mountains of northwest Africa are the mountains referred to by Plato in Critias 118, where he describes the mountains north of the Plain of Atlantis as being the most numerous, the highest and most beautiful. Certainly, within the Mediterranean region, they are the only ones that could match the superlatives used by Plato. In isolation, the Atlas ranges can justifiably be proposed as the peaks referred to by Plato, but there is much more to justify this identification.
The North African climate was slightly wetter in the 2nd & 3rd centuries BC, later, Algeria, Egypt and particularly Tunisia, became the ‘breadbaskets’ of Rome (b). Even today well-irrigated plains in Tunisia can produce two crops a year, usually planted with the autumnal rains and harvested in the early spring and again planted in the spring and harvested in late summer. The Berbers of Morocco produce two crops a year — cereals in winter and vegetables in summer(a).
There is general acceptance that the North African elephants inhabited the Atlas Mountains until they became extinct in Roman times(d)(e). The New Scientist magazine of 7th February 1985(c) outlined the evidence that Tunisia had native elephants until at least the end of the Roman Empire. These were full-sized animals and not to be confused with the remains of pygmy elephants found on some Mediterranean islands. Plato refers to many herds of elephants, which he describes (Critias 115a) as being ‘the largest and most voracious’ of all the animals of Atlantis,>which is not a description of pygmy elephants.<
On top of all that, the only unambiguous geographical clues to the extent of the Atlantean confederation are that it controlled southern Italy as far as Tyrrhenia (Etruria) and northwest Africa as far as Egypt as well as some islands (Tim.25b & Crit.114c). So we have fertile plains with magnificent mountains to the north, inhabited by elephants and controlled by Atlanteans. Q.E.D.
(a) https://www.britannica.com/place/Atlas-Mountains
(b) https://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Tunisia
(c) New Scientist 3 Jan.1985 and New Scientist, 7 February.1985 *
(d) https://interesting-africa-facts.com/Africa-Landforms/Atlas-Mountains-Facts.html
Ali Bey El Abbassi
Ali Bey El Abbassi (1766-1818) was one of the assumed names of Domingo  Badia y Leblich, a Spanish traveller and thought to be a spy for Joseph Bonaparte. Early in the 19th century, he published The Ancient Island of Atlantis[012] an account of his journeys in North Africa and the Middle East.
Badia y Leblich, a Spanish traveller and thought to be a spy for Joseph Bonaparte. Early in the 19th century, he published The Ancient Island of Atlantis[012] an account of his journeys in North Africa and the Middle East.
*He wrote of the Atlas Mountains being the ancient island of Atlantis when the Sahara was a huge interior sea in the centre of Africa, known as Mar de la Nigricia. A map of 1802 based on Ali Bey’s description of this inland sea is available on the Internet(a). The same map shows Atlantis extending from Tunisia and Libya into the Mediterranean filling most of the Gulf of Sirtis.>Alberto Arecchi, in more recent times, has proposed a similar geographical spread for Atlantis(c).<
Ali Bey appears to have been the first to suggest North Africa as the location of Atlantis an idea that then lay dormant for half a century until 1868 when D.A. Godron advocated Morocco as its home.
>A 2004 essay by M. Carme Montaner & Anna Maria Casassas describes the life and times of Ali Bey(b).<
(a) https://catalog.afriterra.org/zoomMap.cmd?number=1036 *
Algeria *
Algeria is the largest nation by area in Africa and the tenth largest in the world. Most of the population lives in the fertile north, while most of the country is rather arid, including part of the Sahara. Over two thousand years ago, when the climate was more benign, Algeria along with its neighbour, Tunisia, as well as Egypt, were the ‘breadbaskets’ of Rome.
Since the early 18th century Atlantis has been associated by a number of researchers with Algeria, often linked with Tunisia and/or Morocco. These included Ali Bey El Abbassi, Robert Schmalz, Giovanni Ugas and the American researcher Gerald Wells(a) who specified the western Algerian province of El Bayadh as the location of Atlantis. He offered its exact coordinates as 31.84°N Latitude and 103.03°E Longitude and added that the Garden of Eden had existed in the same region!
 A more frequent suggestion is that the chotts of Algeria and Tunisia had been the location of the legendary Lake Tritonis when the Sahara was a more fertile place with a wetter climate. Ulrich Hofmann supports this view while Alberto Arecchi contends that Lake Tritonis was the ‘Atlantic Sea’ referred to by Plato, with the Pillars of Heracles situated at the Gulf of Gabes. A related claim has been made recently by Hong-Quen Zhang(b).
A more frequent suggestion is that the chotts of Algeria and Tunisia had been the location of the legendary Lake Tritonis when the Sahara was a more fertile place with a wetter climate. Ulrich Hofmann supports this view while Alberto Arecchi contends that Lake Tritonis was the ‘Atlantic Sea’ referred to by Plato, with the Pillars of Heracles situated at the Gulf of Gabes. A related claim has been made recently by Hong-Quen Zhang(b).
(a) Atlantis-Bakhu | Wells Research Laboratory (archive.org) * ^6 pages
(b) https://medcraveonline.com/IJH/is-atlantis-related-to-the-green-sahara.html
