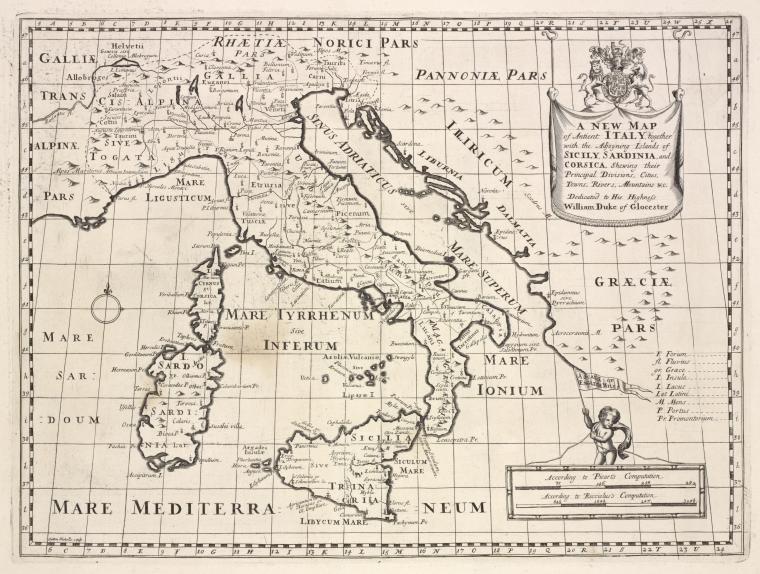
Tyrrhenian Sea
Italy
Italy seems to have an uncertain etymology; Thucydides claims that Italos, the Sicilian king gave his name to Italy, while more recently Emilio Spedicato(h) considers that ”the best derivation we believe to be the one proposed by the Italian nuclear engineer Felice Vinci (1998), in his monograph claiming a Baltic setting for the Homeric epic: he derives Italia from the rare Greek word aithalia, meaning the smoking one.” This is thought to be a reference to Italy’s many volcanoes.
Italy today is comprised of territory south of the Alps on mainland Europe including a very large boot-shaped peninsula, plus Sicily, Sardinia and some smaller island groups, which along with the French island of Corsica virtually enclose the Tyrrhenian Sea.
The earliest proposal that Italy could be linked with Atlantis came from Angelo Mazzoldi in 1840 when he claimed that before Etruria, Italy had been home to Atlantis and dated its demise to 1986 BC. Mazzoldi expressed a form of hyperdiffusion that had his Italian Atlantis as the mother culture which seeded the great civilisations of the eastern Mediterranean region(b).
Some of Mazzoldi’s views regarding ancient Italy were expanded on by later scholars such as Camillo Ravioli, Ciro Nispi-Landi, Evelino Leonardi, Costantine Cattoi, Guido DiNardo and Giuseppe Brex. Ravioli sought to associate the Maltese island of Gozo with his proposed Atlantis in Italy.
The Italian region of Lazio, which includes Rome, has had a number of very ancient structures proposed as Atlantean; Monte Circeo (Leonardi) and Arpino(a) (Cassaro). Another aspect of Italian prehistory is the story of Tirrenide, which was described as a westward extension of the Italian landmass into the Tyrrhenian Sea during the last Ice Age, with a land bridge to a conjoined Sardinia and Corsica. At the same time, there were land links to Sicily and Malta, which were all destroyed as deglaciation took place and sea levels rose.
 It is surprising that so few researchers have commented on Italy’s part in Plato’s Atlantis narrative considering that he twice, without any ambiguity, informs us that the Atlantean domain extended as far as Tyrrhenia (modern Tuscany).
It is surprising that so few researchers have commented on Italy’s part in Plato’s Atlantis narrative considering that he twice, without any ambiguity, informs us that the Atlantean domain extended as far as Tyrrhenia (modern Tuscany).
Crit.114c. So all these, themselves and their descendants dwelt for many generations bearing rule over many other islands throughout the sea and holding sway besides, as was previously stated, over the Mediterranean peoples as far as Egypt and Tuscany. Tim.25a/b. Now in this island of Atlantis there existed a confederation of kings, of great and marvellous power, which held sway over all the island, and over many other islands also and parts of the continent; and, moreover, of the lands here within the Straits they ruled over Libya as far as Egypt, and over Europe as far as Tuscany. (Bury)
The quotation from Timaeus is most interesting because of its reference to a ‘continent’. Some have understandably but incorrectly claimed that this is a reference to America or Antarctica, when quite clearly it refers to southern Italy as part of the continent of Europe. Moreover, Herodotus is quite clear (4.42) that the ancient Greeks knew of only three continents, Europe, Asia and Libya.
Philo of Alexandria (20 BC-50 AD) in his On the Eternity of the World(g) wrote “Are you ignorant of the celebrated account which is given of that most sacred Sicilian strait, which in old times joined Sicily to the continent of Italy?” (v.139).>The name ‘Italy’ was normally used until the third century BC to describe just the southern part of the peninsula(e).<Some commentators think that Philo was quoting Theophrastus, Aristotle’s successor. This would push the custom of referring to Italy as a ‘continent’ back near to the time of Plato. More recently, Armin Wolf, the German historian, when writing about Scheria relates(f) that “Even today, when people from Sicily go to Calabria (southern Italy) they say they are going to the ‘continente’.” This continuing usage is further confirmed by a current travel site(d) and by author, Robert Fox[1168.141]. I suggest that Plato used the term in a similar fashion and can be seen as offering the most rational explanation for the use of the word ‘continent’ in Timaeus 25a.
When you consider that close to Italy are located the large islands of Sicily, Sardinia and Corsica, as well as smaller archipelagos such as the Egadi, Lipari and Maltese groups, the idea of Atlantis in the Central Mediterranean can be seen as highly compatible with Plato’s description.
If we accept that Plato stated unambiguously that the domain of Atlantis included at least part of southern Italy and also declared that Atlantis attacked from beyond the Pillars of Heracles, then this appellation could not be applied at that time to any location in the vicinity of the Strait of Gibraltar but must have been further east, probably not too far from Atlantean Italy. This matches earlier alternative locations recorded by classical writers who placed the ‘Pillars’ at the straits of Messina or Sicily. I personally favour Messina, unless there is stronger evidence that some of the islands in or near the Strait of Sicily such as the Maltese or Pelagian Islands or Pantelleria were home to the ‘Pillars’.
(a) http://www.richardcassaro.com/hidden-italy-the-forbidden-cyclopean-ruins-of-giants-from-atlantis
(b) Archive 2509P (Eng) Archive 2943 (Ital)
(c) Archive 2946
(d) Four Ways to Do Sicily – Articles – Departures (archive.org)
(e) https://profilbaru.com/article/Name_of_Italy *
(f) Wayback Machine (archive.org)
(g) http://www.earlychristianwritings.com/yonge/book35.html
(h) http://2010-q-conference.com/ophir/ophir-27-10-09.pdf
Gruhn, Albert
Dr. Albert Gruhn was reported to have placed Atlantis in the Western Mediterranean Basin, according to a report in New Zealand’s North Otago Times of August 8th 1911(a). Apparently it was quoting from the ‘North German Gazette’ where he stated his belief that the Western Basin had once been dry land and that Atlantis had been situated between the Balearic Islands and Sardinia or in what is now the Tyrrhenian Sea.
>Atlantisforschung has further information on the details of Gruhn’s theory(c).<
A couple of years earlier he had disputed(b) that Homer’s Troy had been located at Hissarlik, instead he opted for Duden.
(a) https://paperspast.natlib.govt.nz/cgi-bin/paperspast?a=d&d=NOT19110819.2.22.16
(b) https://www.jstor.org/stable/496830?seq=14#page_scan_tab_contents
(c) Addendum zu Albert Gruhn (Februar 2017) – Atlantisforschung.de *
Tyrrhenian Sea
>The Tyrrhenian Sea according to Massimo Pittau was named after the Sardinian Nuragics, since in ancient Greek ‘Tyrrenoi’ means ‘builders of towers’. As noted elsewhere, Sardinia was an important part of the Atlantean domain.<
Plato clearly states that Atlantis controlled Europe as far as Tyrrhenia (Critias 114c), which implies that they dominated the southern half of the Italian peninsula. The Sea is surrounded by the islands of Corsica, Sardinia, Sicily and the Lipari Islands as well as continental Europe in the form of the Italian mainland. Not only does it contain islands with an adjacent continent (see Timaeus 24e). It is also accessed through the straits of Messina and Sicily, both of which have been identified as locations for the Pillars of Heracles before Eratosthenes applied that appellation to the region of Gibraltar.
Timaeus 24e-25a as translated by Bury reads “there lay an island which was larger than Libya and Asia together; and it was possible for the travellers of that time to cross from it to the other islands, and from the islands to the whole of the continent over against them which encompasses that veritable ocean (pontos=sea). For all that we have here, lying within the mouth of which we speak, is evidently a haven having a narrow entrance; but that yonder is a real ocean (pelagos=sea), and the land surrounding it may most rightly be called, in the fullest and truest sense, a continent.” Similarly, Lee and Jowett have 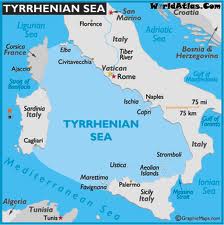 misleadingly translated both pontos and pelagos as ‘ocean’, while the earliest English translation by Thomas Taylor correctly renders them as ‘sea’. Modern translators such as Joseph Warren Wells and a Greek commentator George Sarantitis are both quite happy to agree with Taylor’s translation. However, Peter Kalkavage translates pontos as ‘sea’ but pelagos as ‘ocean’!
misleadingly translated both pontos and pelagos as ‘ocean’, while the earliest English translation by Thomas Taylor correctly renders them as ‘sea’. Modern translators such as Joseph Warren Wells and a Greek commentator George Sarantitis are both quite happy to agree with Taylor’s translation. However, Peter Kalkavage translates pontos as ‘sea’ but pelagos as ‘ocean’!
For me, there is a very strong case to be made for identifying the Tyrrhenian Sea as the ‘sea’ referred to by Plato in the passage quoted above. However, it was probably F.Butavand, in 1925, who first proposed the Tyrrhenian as the sea described by Plato in his La Veritable Histoire de L’Atlantide[205] .
Pushing the boat out a little further, I note that Rome is situated in Central Italy and by tradition was founded by the twins Romulus and Remus!
A 1700 map of the Tyrrhenian Sea is available online.
‘Tyrrhenia’ is sometimes used as a geological term to describe a sunken landmass in the Western Mediterranean Basin(b)(c).
(a) (link broken) *
Tirrenide
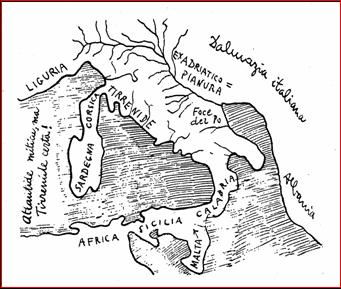 Tirrenide is the name given to a large landmass that was supposedly submerged off the west coast of Italy, which subsequently gave its name to the Tyrrhenian Sea. Some of these ideas were proposed in 1840 by Angelo Mazzoldi in Delle Origini Italiche who also placed Atlantis in this ancient Italy.
Tirrenide is the name given to a large landmass that was supposedly submerged off the west coast of Italy, which subsequently gave its name to the Tyrrhenian Sea. Some of these ideas were proposed in 1840 by Angelo Mazzoldi in Delle Origini Italiche who also placed Atlantis in this ancient Italy.
The name ‘Tirrenide’ was first proposed by C.J. Forsyth Major in 1882.
>The idea of the existence of such a large sunken land is seemingly supported by Pliny the Elder in Natural History (III, Of Italy) where he compared the shape of Italy to an oak leaf: “I may premise by observing that this land very much resembles in shape an oak leaf, being much longer than it is broad…” which seems a far cry from the boot-like shape used to describe Italy today.<
Some commentators, such as Pier Paolo Cavallin(e) [1049] and Evelino Leonardi, have tried to link the story with Atlantis. Leonardi’s contribution to the belief that there was an Italian Atlantis is explored in depth by Marco Pucciarni(d). Von Klaproth speculated that it had been a vast island that filled most of the Western Mediterranean. Others suggest the vicinity of Calabria or part of a landbridge between Italy and North Africa.
The legend of Tirrenide is frequently linked with the island of Sardinia (along with Corsica). This is the view of Leonardo Melis who considers his Tirrenide to have been a rival empire of Atlantis(c).
Constantino Cattoi expressed some odd views involving an extension of Atlantis reaching into the Mediterranean as far as Italy and added that just offshore from Ansedonia, 70 miles north of Rome may have been the location of the Atlantean capital! This concept has now been adopted by Francesco Palambo.
Cattoi also announced that he had located three of the cities of Tirrenide between Porto Santo Stefano and Isola del Giglio, but he died without being able to find funding for the underwater exploration that would have proved his hypothesis(b).
A more recent view of Tirrenide at the end of the last Ice Age is available online(a).
(a) See: Archive 2510 (b) https://www.paginecuriose.it/2019/07/28/atlantide-vicino-allargentario/ (Italian)
(c) La Sardegna e Atlantide (archive.org) (Italian)
(e) Pier Paolo Cavallin – Atlantisforschung.de (atlantisforschung-de.translate.goog)
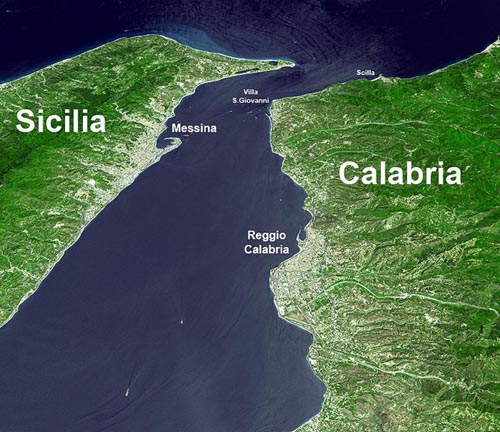
Strait of Messina
The Strait of Messina is, at its narrowest point, just 2 miles wide. A number of classical writers refer to a time when Sicily was still connected to Italy. In fact legend has it that Heracles was responsible for their separation. However, Cyprian Broodbank has pointed out in his monumental work, The Making of the Middle Sea, that “Today, the Messina strait dividing it (Sicily) from peninsular Italy is a minimum of 3 km (2 miles) wide and 72 metres (235 ft) in depth at its shallowest point. On the face of it, therefore, Sicily and mainland Italy should have fused under full glacial conditions. Yet this spot lies on a plate boundary and has already risen several metres over the last 150 years for which accurate measurements exist. Add a 127,000-71,000-year-old beach now elevated 90m (300ft) above the sea near the strait and we might start to wonder whether Sicily was ever solidly attached to the other land.”[1127.91] Nevertheless, he does suggest that early man possibly had stepping-stones in the form of islets and shallows between the two landmasses.
The Strait of Messina had a reputation in antiquity for having dangerous currents, which are thought to be the inspiration for Homer‘s sea monsters, Scylla and Charybdis. Heinrich Schliemann supported this identification[1243]. The currents there are still very dangerous, but nevertheless the strait is a busy waterway with both commercial and pleasure craft, indicating that the conditions there can be mastered. The hazards were situated at the northern end of the Strait, where today there is a town appropriately called Scilla on the Calabrian side.
The strait is sometimes offered as an earlier site for the Pillars of Heracles prior to the Western Mediterranean becoming more frequently navigated by the ancient Greeks, at which time the term was transferred to the Strait of Gibraltar. Winfried Huf is a keen supporter of ‘Pillars’ having been located at Messina. A constituent part of the Western Mediterranean was the Tyrrhenian Sea, which, for the Greeks, would have been most easily accessed through the Strait of Messina.
The earliest westward expansion of the Greeks was understandably to what became known as Magna Graecia in Sicily and southern Italy. The Phoenician expansion was along the north African coast eventually establishing Carthage at the Strait of Sicily. The ships available at that time were not designed for the open sea, but were usually kept within sight of land. I am inclined to think that the early Greeks would have had the Strait of Messina as the location of their Pillars of Heracles leading to the little known Western Mediterranean (or Tyrrhenian Sea), apparently referred to by some as the ‘Atlantic Sea’, whereas the Strait of Sicily might have led to conflict with the Phoenicians!
It is interesting that from around 330 BC and for nearly a thousand years(b) the Strait of Messina was known as Fretum Siculum, which translates as the Sicilian Strait. Philo of Alexandria (20 BC-50 AD) in his On the Eternity of the World(c) wrote “Are you ignorant of the celebrated account which is given of that most sacred Sicilian strait, which in old times joined Sicily to the continent of Italy?” (v.139).
>Alexander V. Podossinov in his paper on straits and their significance for the ancients commented “the Carthaginians for a long time did not permit the Greeks to pass through the Straits of Messina and had power over the whole western Mediterranean.”(d)<
Support for the idea of the Western Mediterranean being the ‘Sea of Atlantis’ with the ‘Pillars’ at the Strait of Messina is presented on a French forum(a), which offers the map below.
(a) https://histoiresecrete.leforum.eu/t716-quelques-questions-se-poser-sur-le-Tim-e-Critias.htm
(b) https://pleiades.stoa.org/places/462494
Marcellus
Marcellus was a Greek geographer, about whom very little is known. He wrote just before or just after the start of the Common Era, offering what is probably the earliest independent reference to Atlantis after Plato. He states that it consisted of ‘seven islands and also three others of immense extent’, the middle one of which was dedicated to the Atlantean god Poseidon. The magnitude of this island was ‘one thousand stadia ‘, and the inhabitants of it preserved the remembrance of their ancestors, or the Atlantic island that had existed there, and was truly prodigiously great; which for many periods had domination over all the islands in the Atlantic Sea.’
*The above passage from Marcellus’ now lost Ethiopic History, is cited by Proclus in his commentary on Timaeus.
One interpretation is that in this extract the Atlantic ‘Sea’ is the Tyrrhenian Sea and that the three ‘immense’ islands referred to are Corsica, Sardinia and Sicily! Outside the Aegean, the Central Mediterranean is the only location within striking distance of Athens that has three very large islands together with numerous smaller ones.*
Adriatic Sea *
The Adriatic Sea was mainly dry land during the last Ice Age until it was inundated between 8500-6000 BC. The last decade has seen a number of sites in  the Adriatic region nominated as possible locations for Atlantis. A sunken town near Zadar would appear to be the latest candidate(d).
the Adriatic region nominated as possible locations for Atlantis. A sunken town near Zadar would appear to be the latest candidate(d).
Fatih Hodzic, a Slovenian writer, has offered of a new theory(a), which places Atlantis in the southern Adriatic Basin. He contends that the destruction of Atlantis was a consequence of an asteroid impact, recorded in Greek mythology as Phaëton, impacting in either the Ionian or the Tyrrhenian Sea just west of Sicily.
Recently, Alessio Toscano has suggested that the Pillars of Heracles were situated at the Strait of Otranto and that Plato’s ‘Atlantic’ was in fact the Adriatic Sea(c).
The Italian side of the Adriatic has also had claims made of an association with Atlantis such as with Valbruna. Daniela Bortoluzzi has written a lengthy article suggesting a possible link between Atlantis and Venice(h). More detailed is the claim by Morven Robertson that Atlantis had been situated between Padua and Ferrara, not far from Venice.
Mljet is a Croatian island close to Dubrovnik and believed by some to be Homer’s Ogygia, which in turn has been identified as Atlantis. This same island offers a competing claim to be the place where St. Paul was shipwrecked on his way to Rome, rather than Malta. At the risk of offending my Maltese friends, I consider the Mljet claim to have some considerable merit. Apart from anything else, at that time ships, for reasons of safety, preferred to stay close to shore, which suggests that to use the Strait of Otranto would provide the shortest open sea journey available, after that the Strait of Messina would bring them straight up the Italian coast to Rome! I find it hard to understand how at any point on that route that a storm could have threatened to carry them to Syrtis Minor (Southern Tunisia) which was about 400 miles at the nearest point.
Dubrovnik was recently claimed to have a number of pyramids in its vicinity by Pero Metkovic as well as the location of Atlantis. His rather rambling blog(g) offers no evidence apart from over-imaginative speculation.
Another claim is that satellite imagery has revealed a network of lines near Durrés, west of Tirana in Albania, which are the remnants of Plato’s Atlantean canals. The co-ordinates are 41.08-41.02 N and 19.23 E. A blogsite(b) is also home to a number of articles adding support for this Durrés theory.
Andi Zineli, in a now defunct website, advocated an Albanian solution to the mystery of Atlantis. He employed the Oera Linda Book to support his theory.
While the above suggestions are interesting, they are not convincing. Does it not seem strange that had Atlantis been located in the Adriatic, next door to Greece, that the Greeks in general and Plato in particular would have been unaware of it?
The Adriatic was also the backdrop to Homer’s Odyssey according to a new book[1396] by Zlatko Mandzuka, himself a native of the region. Even more radical is the claim that Troy itself had been located in Bosnia-Herzegovina or adjacent Croatia, the former by Roberto Salinas Price in 1985[1544], while more recently the latter is promoted by Vedran Sinožic[1543].
When the sunken ruins of a city, dated to around 1500 BC were discovered in 2015, near Croatia’s oldest city, Zadar, it generated the usual flurry of Atlantis speculation.
There was a media report(f) in early 2017 in which Mark Kempf claimed to have discovered the remains of Atlantis 30 miles off the coast of Croatia. Kempf is a treasure hunter and hopes that the discovery by him and his team will yield a fortune. I consider this report to be somewhat dubious.
>Nevertheless, although it cannot be directly linked to Atlantis, I feel obliged to add a May 2023 report that a “prehistoric road was discovered under layers of sea mud at the sunken Neolithic site of Soline, and helped connect the Hvar settlement to the now-isolated island of Kor?ula in Croatia(i). The ‘road’ has been dated to around 5000 BC.<
(a) http://en.atlantida.spletnestrani.com/atlantida/
(b) http://atlantisinalbania.blogspot.com/2008/07/name-and-location.html
(c) http://templeofapollobelenus.blogspot.ie/
(d) https://www.reddit.com/r/worldnews/comments/3u7rce/archeologists_in_croatia_announced_their/
(f) https://empirenews.net/lost-city-of-atlantis-uncovered-in-mediterranean-sea/
(i) 7,000-Year-Old Ancient Road Found Buried Underneath the Mediterranean Sea! | Weather.com