Massimo Pittau
Pittau, Massimo
Massimo Pittau (1921-2019) was a renowned Italian philologist. Born in Sardinia he has written extensively about his native land. Unfortunately, his work is only available in Italian, however, Google Translate will help the linguistically challenged, such as myself.
One paper, with a link to the English translation below(a) , had valuable comments to offer about the content of Homer’s Odyssey as well as some interesting theories on the origins of the Sardinian Nuragic people. He traces them back to Lydia, now in northwest Turkey and its capital, Sardis.
(a) Massimo Pittau – The Odyssey and Nuragic Sardinia (www-pittau-it.translate.goog) (part English)
Tyrrhenian Sea
>The Tyrrhenian Sea according to Massimo Pittau was named after the Sardinian Nuragics, since in ancient Greek ‘Tyrrenoi’ means ‘builders of towers’. As noted elsewhere, Sardinia was an important part of the Atlantean domain.<
Plato clearly states that Atlantis controlled Europe as far as Tyrrhenia (Critias 114c), which implies that they dominated the southern half of the Italian peninsula. The Sea is surrounded by the islands of Corsica, Sardinia, Sicily and the Lipari Islands as well as continental Europe in the form of the Italian mainland. Not only does it contain islands with an adjacent continent (see Timaeus 24e). It is also accessed through the straits of Messina and Sicily, both of which have been identified as locations for the Pillars of Heracles before Eratosthenes applied that appellation to the region of Gibraltar.
Timaeus 24e-25a as translated by Bury reads “there lay an island which was larger than Libya and Asia together; and it was possible for the travellers of that time to cross from it to the other islands, and from the islands to the whole of the continent over against them which encompasses that veritable ocean (pontos=sea). For all that we have here, lying within the mouth of which we speak, is evidently a haven having a narrow entrance; but that yonder is a real ocean (pelagos=sea), and the land surrounding it may most rightly be called, in the fullest and truest sense, a continent.” Similarly, Lee and Jowett have 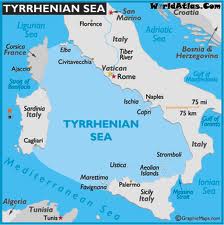 misleadingly translated both pontos and pelagos as ‘ocean’, while the earliest English translation by Thomas Taylor correctly renders them as ‘sea’. Modern translators such as Joseph Warren Wells and a Greek commentator George Sarantitis are both quite happy to agree with Taylor’s translation. However, Peter Kalkavage translates pontos as ‘sea’ but pelagos as ‘ocean’!
misleadingly translated both pontos and pelagos as ‘ocean’, while the earliest English translation by Thomas Taylor correctly renders them as ‘sea’. Modern translators such as Joseph Warren Wells and a Greek commentator George Sarantitis are both quite happy to agree with Taylor’s translation. However, Peter Kalkavage translates pontos as ‘sea’ but pelagos as ‘ocean’!
For me, there is a very strong case to be made for identifying the Tyrrhenian Sea as the ‘sea’ referred to by Plato in the passage quoted above. However, it was probably F.Butavand, in 1925, who first proposed the Tyrrhenian as the sea described by Plato in his La Veritable Histoire de L’Atlantide[205] .
Pushing the boat out a little further, I note that Rome is situated in Central Italy and by tradition was founded by the twins Romulus and Remus!
A 1700 map of the Tyrrhenian Sea is available online.
‘Tyrrhenia’ is sometimes used as a geological term to describe a sunken landmass in the Western Mediterranean Basin(b)(c).
(a) (link broken) *
Scheria
Scheria is the name of a Phaeacian island mentioned by Homer in his Odyssey and identified by some, including Ignatius Donnelly, as Atlantis. Scheria has been noted as only second to Atlantis for the array of locations ascribed to it. For example, Heinrich Schliemann, as well as many ancient and modern commentators, considered Scheria to have been Corfu. K. T. Frost in the early part of the 20th century associated Atlantis with Homer’s Scheria and both with the Minoan Empire, an idea also supported by Walter Leaf(l).
Others, such as Felice Vinci suggest Norway, while Iman Wilkens[610] offers the Canaries.
A recent paper by Gerard Janssen, of Leiden University, also places Scheria in the Canaries, specifically on Lanzarote(f). This is one of an extensive series of papers by Janssen, which links Homer’s geography with locations in the Atlantic(g). An introductory paper(h) might be the best place to start.
An Atlantic location for Homer’s epic poems is advocated by N.R. De Graaf, the Dutch author of the Homeros Explorations website(i). Specifically, he also concluded that Scheria can be identified with Lanzarote in the Canaries concurring with Wilkens and Janssen.
According to Pierluigi Montalbano, his native Sardinia was the Homeric land of the Phaeacians(j). Massimo Pittau offered the same conclusion “However the fact is that the Odyssey- as we have seen before – never mentions Sardinia. How, therefore, can this great and singular historical-documentary inconsistency be overcome? It can be overcome by assuming and saying that the poet of the Odyssey actually mentions Sardinia, but not calling it with his name, which will later become traditional and definitive, but with some other name relating to one of its regions or its population. And this is precisely my point of view, the one I am about to indicate and demonstrate: the poet of the Odyssey mentions Sardinia and its Nuragic civilization when he speaks of the «Scherìa or island of the Phaeacians».”(k)
Armin Wolf (1935- ), the German historian, suggests(b) that Calabria in Southern Italy was Scheria and even more controversially that the Phaeacians were in fact Phoenicians!
Wolf also claims[669.326] that although the country of the Phaeacians is in some translations called an island, the original Greek text never calls it ‘island’ just Scheria, which, Wolf informs us, etymologically means ‘continent’ – perfectly fitting Calabria. Even today, when people from Sicily go to Calabria they say they are going to the ‘continente’. Wolf puts Scheria in the vicinity of Catanzaro, the capital of Calabria. It has been suggested to me in private correspondence(d) that the etymology of Catanzaro is strongly indicative of a Phoenician influence! Catanzaro is also  known as ‘the city of the two seas’, having the Tyrrhenian Sea to the west and the Ionian Sea to the east. It is Wolf’s contention that it was across this isthmus that Odysseus travelled[p.327].
known as ‘the city of the two seas’, having the Tyrrhenian Sea to the west and the Ionian Sea to the east. It is Wolf’s contention that it was across this isthmus that Odysseus travelled[p.327].
A further mystery is that, according to Dr Ernst Assmann quoted by Edwin Bjorkman, “both the vessel of Odysseus, as pictured in Greek art, and the term applied to it, are of Phoenician origin.”
Daniel Fleck(a) lists ten similarities between Scheria and Atlantis. Jürgen Spanuth[015] quoted and added to an even more extensive list of comparisons between the two compiled by R. Hennig. Rainer W. Kühne has also written a paper(c) on the similarities. Walter Leaf perceived a connection between the two and wrote accordingly[434]. Edwin Björkman went further and wrote a book[181] that linked Tartessos, Scheria and Atlantis. More recently, Roger Coghill stressed the similarity of Homer’s Scheria to Plato’s Atlantis in The Message of Atlantis [0494].>>Additional comparisons are offered on the coda.io website(n).<<
Ernle Bradford notes that the name Scheria itself is thought by some to be derived from the Phoenician word ‘schera’, which means marketplace, which is not incompatible with Plato’s description of Atlantis as a hive of commercial activity. [1011.204]
Michael MacRae in his Sun Boat: The Odyssey Deciphered[985] also thinks that Scheria could be identified with Atlantis and as such was probably situated at the western end of the Gulf of Cadiz near Portugal’s Cape Vincent. A number of 20th-century researchers such as Sykes and Mertz have placed the travels of Odysseus in the Atlantic. More recently, Gerard Janssen has followed this school of thought and as part of his theories identifies Scheria as the island of Lanzarote in the Canaries (e).
This identification of Scheria with Atlantis has induced Eberhard Zangger, who advocates Atlantis as Troy, to propose that Troy is also Scheria![483]
However, Ernle Bradford, who retraced the voyage of Odysseus, voiced his view that Corfu was the land of the Phaeacians and noted that “the voice of antiquity is almost as unanimous about Scheria being Corfu as it is about the Messina Strait being the home of Scylla and Charybdis.”
A paper by John Black concluded with the following paragraph that fairly sums up what we actually know about the Phaeacians. “Who were the Phaeacians and where was their place of abode? No definite answers and no clues have been found but yet their extraordinary seafaring abilities and the intriguing description by Homer make them appear to be either a fascinating advanced civilization of the past yet to be discovered, or a fiction of the imagination for the sake of a good story. It is worth mentioning that Homer’s description of Troy was also once considered to be a work of fiction. However, the city of Troy has now been discovered, turning myth into reality.” (m)
(a) http://web.archive.org/web/20250613012321/https://atlantipedia.ie/samples/archive-2087/
(b) Wayback Machine (archive.org)
(c) (PDF) Did Ulysses Travel to Atlantis? (researchgate.net)
(d) Private correspondence Jan. 2016
(e) https://www.homerusodyssee.nl/id16.htm
(f) https://www.academia.edu/38347562/ATLANTIC_SCHERIA_AND_THE_FAIAKANS_LANZAROTE_AND_THE_FAYCANS
(g) https://leidenuniv.academia.edu/GerardJanssen
(h) https://www.academia.edu/38537104/ATLANTIC_TROY
(i) https://www.homeros-explorations.nl
(k) Massimo Pittau – The Odyssey and Nuragic Sardinia (www-pittau-it.translate.goog)
(l) Miscellanea Homerica, VI, The Classical Journal, Vol. 23, No. 8 (May, 1928), pp. 615-617 (3 pages)
(m) https://www.ancient-origins.net/myths-legends/mythic-scheria-and-legendary-phaeacians-001034
(n) https://coda.io/@together/collective-research/homers-oddysey-atlantis-comparison-14 *
Lydia
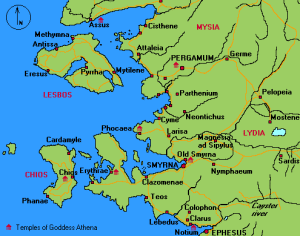 Lydia was a small but powerful kingdom in the west of modern Turkey. It flourished in the 6th and 7th centuries BC. The inhabitants were famous as merchants and credited with having invented gold and silver coinage and the concept of permanent retail shops.
Lydia was a small but powerful kingdom in the west of modern Turkey. It flourished in the 6th and 7th centuries BC. The inhabitants were famous as merchants and credited with having invented gold and silver coinage and the concept of permanent retail shops.
Tantalis is referred to by Pliny as the capital of ancient Lydia in Western Turkey. It was later known as Magnesium ad Sipylum. Tantalis was allegedly named after the legendary King Tantalus, who shared remarkable similarities with Atlas; they were both Titans, supported the heavens and had mountains named after them(a). This powerful city was flooded following an earthquake and is now reputed to be located beneath the now dried-up Lake Saloe. Also, note that Atlantis is an anagram of Tantalis – coincidence? British archaeologist Peter James has identified Tantalis as the>>inspiration for the Atlantis story<<and that it was located just north-east of Smyrna, now the modern port of Izmir [0047].
Early in the 20th century the German archaeologist Adolf Schulten spent many years searching unsuccessfully, in the region of the Guadalquivir, for Tartessos. He believed that Tartessos had been founded by Lydians in 1150 BC, which became the centre of an ancient culture that was Atlantis or at least one of its colonies.
It must be pointed out that apart from his famous visit to Egypt, Solon travelled extensively throughout the eastern Mediterranean including Lydia where he encountered Croesus the fabulously wealthy monarch. It is possible that during these trips further information regarding the history of the region was gathered and included in his notes that were to pass down through Plato’s family.
Herodotus claimed that the Etruscans migrated from Lydia to Tyrrhenia, a claim that is supported by recent studies of DNA carried out at Pavia University in Italy. Dr. Barry Fell, the renowned, and controversial expert in ancient scripts, translated Etruscan inscriptions using the language of the ancient Hittites who ruled Anatolia, including Lydia, in the 2nd millennium BC.
Angelo Paratico recently proposed a connection between the Lydian capital Sardis and Sardinia during a lecture delivered in Hong Kong in 2004(a). This idea was put forward earlier by archaeologist David Rohl [0232]. Massimo Pittau also supports the idea of Lydian Sardis was the original home of nuragic Sardinians!(c)
Wikipedia includes the following information “According to Timaeus, one of Plato’s dialogues, Sardinia and its people as well, the “Sardonioi” or “Sardianoi”, might have been named after “Sardò”, a legendary woman from Sardis, capital of the ancient Kingdom of Lydia in Anatolia.”(b)
(a) Is there a link between ancient Sardis and Sardinia? – Gingko Edizioni (archive.org) *
(b) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sardinian_people
(c) Massimo Pittau – The Odyssey and Nuragic Sardinia (www-pittau-it.translate.goog)