Syrtis Minor
Syrtis
Syrtis was the name given by the Romans to two gulfs off the North African coast; Syrtis Major which is now known as the Gulf of Sidra off Libya and Syrtis Minor, known today as the Gulf of Gabes in Tunisian waters. They are both shallow sandy gulfs that have been feared from ancient times by mariners. In the Acts of the Apostles (Acts 27.13-18) it is described how St. Paul on his way to Rome was blown off course and feared that they would run aground on ‘Syrtis sands.’
However, they were shipwrecked on Malta or as some claim on Mljet in the Adriatic.
The earliest modern reference to these gulfs that I can find in connection with Atlantis was by Nicolas Fréret in the 18th century when he proposed that Atlantis may have been situated in Syrtis Major. Giorgio Grongnet de Vasse expressed a similar view around the same time. Since then there has been little support for the idea until recent times when Winfried Huf designated Syrtis Major as one of his five divisions of the Atlantean Empire.
However, the region around the Gulf of Gabes has been more persistently associated with aspects of the Atlantis story. Inland from Gabes are the chotts, which were at one time connected to the Mediterranean and considered to have been part of the legendary Lake Tritonis, sometimes suggested as the actual location of Atlantis.
In the Gulf itself, Apollonius of Rhodes placed the Pillars of Herakles(a) , while Anton Mifsud has drawn attention[0209] to the writings of the Greek author, Palefatus of Paros, who stated (c. 32) that the Columns of Heracles were located close to the island of Kerkennah at the western end of Syrtis Minor. Lucanus, the Latin poet, located the Strait of Heracles in Syrtis Minor. Mifsud has pointed out that this reference has been omitted from modern translations of Lucanus’ work!
Férréol Butavand was one of the first modern commentators to locate Atlantis in the Gulf of Gabés[0205]. In 1929 Dr. Paul Borchardt, the German geographer, claimed to have located Atlantis between the chotts and the Gulf, while more recently Alberto Arecchi placed Atlantis in the Gulf when sea levels were lower(b) . George Sarantitis places the ‘Pillars’ near Gabes and Atlantis itself inland, further west in Mauritania, south of the Atlas Mountains. Antonio Usai also places the ‘Pillars’ in the Gulf of Gabes.
In 2018, Charles A. Rogers published a paper(c) on the academia.edu website in which he identified Tunisia as Atlantis with it capital located at the mouth of the Triton River on the Gulf of Gabes. He favours Plato’s 9.000 ‘years’ to have been lunar cycles, bringing the destruction of Atlantis into the middle of the second millennium BC and coinciding with the eruption of Thera which created a tsunami that ran across the Mediterranean destroying the city with the run-up and its subsequent backwash. This partly agrees with my conclusions in Joining the Dots!
Also See: Gulf of Gabes and Tunisia
(a) Argonautica Book IV ii 1230
(c) https://www.academia.edu/36855091/Atlantis_Once_Lost_Now_Found?auto=download*
Usai, Antonio
Antonio Usai (1957- ) was born in Assemini, 12 km northwest of Cagliari, the capital of Sardinia. Having a passion for ancient  history, he has written a number of papers(a) locating the Pillars of Heracles within the Mediterranean. An English translation of The Pillars of Hercules in Aristotle’s Ecumene is now available on the excellent Academia.edu website as well as a 67-page booklet[0980]. Included in his work is a critique(b) of Sergio Frau’s book[302].
history, he has written a number of papers(a) locating the Pillars of Heracles within the Mediterranean. An English translation of The Pillars of Hercules in Aristotle’s Ecumene is now available on the excellent Academia.edu website as well as a 67-page booklet[0980]. Included in his work is a critique(b) of Sergio Frau’s book[302].
Usai followed a reading of Frau’s book with a study of the works of Herodotus, Aristotle, Polybius and Strabo among others. He was drawn to the story of Hanno’s voyage, where Hanno is described as leaving Carthage, turning east, then passing through the ‘Pillars’ and following the coast south towards Syrtis Minor, which is described as being on their right.>However, the previous passage tells us that he first turned west, which is all rather confusing!<
According to Usai, this would only make sense if the Pillars had been situated between the east coast of Tunisia and the islands of Kerkennah. Furthermore, Usai contends that part of Hanno’s report of his voyage was a hoax!
Finally, after devoting most of his essays to identifying the original Pillars at Kerkennah,>in my opinion he weakened his credibility when he concluded his work by identifying Greenland as the location of Atlantis, contradicting Plato’s text, in which the Pillars are described as close to Atlantis.
For some reason, Usai incorrectly describes Greenland as being surrounded by a continent. It is not; to the west is a large Canadian island, there is nothing to the north, east or south and the nearest continental territory is 500 km away to the southwest.
Additionally, he must explain why or how the few people living on Greenland would attack Athens so many thousands of kilometers away.<
A number of translations of the Periplus (Sea Voyage Guide) of Hanno are available on the internet(c)(d).
(a) https://www.archeomedia.net/wp-content/uploads/2009/12/Le_colonne_dErcole_nellecumene_di_Aristotele.pdf (Italian)
https://www.academia.edu/6910165/The_Pillars_of_Hercules_in_Aristotles_Ecumene (English)
(b) See: https://atlantipedia.ie/samples/archive-2352/
(c) https://archive.org/details/cu31924031441847 (Schoff translation)
(d) http://www.jasoncolavito.com/periplus-of-hanno.html (Colavito translation)
Gabés, Gulf of
Gulf of Gabés on the eastern coast of Tunisia was formerly known as Syrtis Minor. Today is contains the Tunisian oil reserves and has the distinction of having one of the few significant tidal ranges (max. 8 feet) in the Mediterranean, which exposes extensive sandbanks at low tides(b).
Inland from the Gulf are the salt marshes or chotts that originally constituted an inland sea, possibly Lake Tritonis, connected with the Mediterranean but due to a seismic upheaval a ridge was created separating them from the outer sea. A comparable event was the 2011 Fukushima earthquake which moved the seafloor 16 meters vertically and 50 metres laterally(a).
In the 19th century François Roudaire proposed the cutting of a channel from the Gulf of Gabés to the chotts, recreating the former inland sea(c).
His plan was supported by Ferdinand de Lesseps (1805-1894), who developed the Suez Canal. However, when Roudaire surveyed the chott nearest the sea, Chott el-Djerid, he discovered that it was in fact lying significantly above sea level. This forced him to revise the scale of the plan, which in turn began the erosion of support for the project, which was eventually abandoned.
It is interesting that the idea of creating a vast inland sea in the Sahara has been been raised again(d) in the context of the current climate change, which, if unchecked, will raise sea levels dramatically. The objective of this new inland sea would be to partly offset this sea level rise.
Férréol Butavand was one of the first to locate Atlantis in the Gulf of Gabés[205]. In 1929 Dr. Paul Borchardt, the German geographer, claimed to have located Atlantis between the chotts and the Gulf. Dr. Anton Mifsud has drawn attention[209] to the writings of the Greek author, Palefatus of Paros, who stated (cap. 32) that the Columns of Heracles were located close to the island of Kerkenna at the western end of Syrtis Minor.
Alberto Arecchi has built on the earlier work of Butavand and places Atlantis firmly in the Gulf(e) when sea levels were much lower as a result of an isthmus separating Eastern from Western Mediterranean.
George Sarantitis delivered three papers to the 2008 Atlantis Conference also locating the Pillars of Heracles in the Gulf of Gabés, which led to the ‘Atlantic Sea in modern Tunisia and Algeria, south of the Atlas Mountains and the site of Atlantis.
>In 2021, Alan Mattingly published Plato’s Atlantis and the Sea Peoples [1948] as a Kindle ebook. In my opinion, this is one of the better Atlantis books of recent years, offering a more forensic look at Plato’s Atlantis texts. He has noted that a “Close reading of Herodotus also locates a feature he calls the Pillars of Herakles, other than the more famous ones at the Straits of Gibraltar, at some point in the Little Syrtis before Carthage is reached; in this case, they were almost certainly at Meninx on the island of Djerba.” [Loc.885]<
(a) https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/japan-earthquake-moves-seafloor/
(b) https://www.britannica.com/place/Gulf-of-Gabes
(c) https://bigthink.com/strange-maps/617-the-sahara-sea-a-french-mirage-in-north-africa
(d) Emancipatory Oceanic Macro-engineering Richard B. Cathcart (See Archive 5079)
Adriatic Sea *
The Adriatic Sea was mainly dry land during the last Ice Age until it was inundated between 8500-6000 BC. The last decade has seen a number of sites in  the Adriatic region nominated as possible locations for Atlantis. A sunken town near Zadar would appear to be the latest candidate(d).
the Adriatic region nominated as possible locations for Atlantis. A sunken town near Zadar would appear to be the latest candidate(d).
Fatih Hodzic, a Slovenian writer, has offered of a new theory(a), which places Atlantis in the southern Adriatic Basin. He contends that the destruction of Atlantis was a consequence of an asteroid impact, recorded in Greek mythology as Phaëton, impacting in either the Ionian or the Tyrrhenian Sea just west of Sicily.
Recently, Alessio Toscano has suggested that the Pillars of Heracles were situated at the Strait of Otranto and that Plato’s ‘Atlantic’ was in fact the Adriatic Sea(c).
The Italian side of the Adriatic has also had claims made of an association with Atlantis such as with Valbruna. Daniela Bortoluzzi has written a lengthy article suggesting a possible link between Atlantis and Venice(h). More detailed is the claim by Morven Robertson that Atlantis had been situated between Padua and Ferrara, not far from Venice.
Mljet is a Croatian island close to Dubrovnik and believed by some to be Homer’s Ogygia, which in turn has been identified as Atlantis. This same island offers a competing claim to be the place where St. Paul was shipwrecked on his way to Rome, rather than Malta. At the risk of offending my Maltese friends, I consider the Mljet claim to have some considerable merit. Apart from anything else, at that time ships, for reasons of safety, preferred to stay close to shore, which suggests that to use the Strait of Otranto would provide the shortest open sea journey available, after that the Strait of Messina would bring them straight up the Italian coast to Rome! I find it hard to understand how at any point on that route that a storm could have threatened to carry them to Syrtis Minor (Southern Tunisia) which was about 400 miles at the nearest point.
Dubrovnik was recently claimed to have a number of pyramids in its vicinity by Pero Metkovic as well as the location of Atlantis. His rather rambling blog(g) offers no evidence apart from over-imaginative speculation.
Another claim is that satellite imagery has revealed a network of lines near Durrés, west of Tirana in Albania, which are the remnants of Plato’s Atlantean canals. The co-ordinates are 41.08-41.02 N and 19.23 E. A blogsite(b) is also home to a number of articles adding support for this Durrés theory.
Andi Zineli, in a now defunct website, advocated an Albanian solution to the mystery of Atlantis. He employed the Oera Linda Book to support his theory.
While the above suggestions are interesting, they are not convincing. Does it not seem strange that had Atlantis been located in the Adriatic, next door to Greece, that the Greeks in general and Plato in particular would have been unaware of it?
The Adriatic was also the backdrop to Homer’s Odyssey according to a new book[1396] by Zlatko Mandzuka, himself a native of the region. Even more radical is the claim that Troy itself had been located in Bosnia-Herzegovina or adjacent Croatia, the former by Roberto Salinas Price in 1985[1544], while more recently the latter is promoted by Vedran Sinožic[1543].
When the sunken ruins of a city, dated to around 1500 BC were discovered in 2015, near Croatia’s oldest city, Zadar, it generated the usual flurry of Atlantis speculation.
There was a media report(f) in early 2017 in which Mark Kempf claimed to have discovered the remains of Atlantis 30 miles off the coast of Croatia. Kempf is a treasure hunter and hopes that the discovery by him and his team will yield a fortune. I consider this report to be somewhat dubious.
>Nevertheless, although it cannot be directly linked to Atlantis, I feel obliged to add a May 2023 report that a “prehistoric road was discovered under layers of sea mud at the sunken Neolithic site of Soline, and helped connect the Hvar settlement to the now-isolated island of Kor?ula in Croatia(i). The ‘road’ has been dated to around 5000 BC.<
(a) http://en.atlantida.spletnestrani.com/atlantida/
(b) http://atlantisinalbania.blogspot.com/2008/07/name-and-location.html
(c) http://templeofapollobelenus.blogspot.ie/
(d) https://www.reddit.com/r/worldnews/comments/3u7rce/archeologists_in_croatia_announced_their/
(f) https://empirenews.net/lost-city-of-atlantis-uncovered-in-mediterranean-sea/
(i) 7,000-Year-Old Ancient Road Found Buried Underneath the Mediterranean Sea! | Weather.com
Shoals of Mud
A Shoal of mud is stated by Plato (Tim.25d) to mark the location of where Atlantis ‘settled’. He described these shallows in the present tense, clearly implying that they were still a maritime hindrance even in Plato’s day.
Three of the most popular translations clearly indicate this:
….the sea in those parts is impassable and impenetrable because there is a shoal of mud in the way; and this was caused by the subsidence of the island.
…..the ocean at that spot has now become impassable and unsearchable, being blocked up by the shoal of mud which the island created as it settled down.”
…..the sea in that area is to this day impassible to navigation, which is hindered by mud just below the surface, the remains of the sunken island.
Wikipedia has noted(h) that “during the early first century, the Hellenistic Jewish philosopher Philo wrote about the destruction of Atlantis in his On the Eternity of the World, xxvi. 141, in a longer passage allegedly citing Aristotle’s successor Theophrastus.
‘ And the island of Atalantes [translator’s spelling; original: “????????”] which was greater than Africa and Asia, as Plato says in the Timaeus, in one day and night was overwhelmed beneath the sea in consequence of an extraordinary earthquake and inundation and suddenly disappeared, becoming sea, not indeed navigable, but full of gulfs and eddies’.”
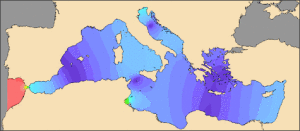
Since it is probable that Atlantis was destroyed around a thousand years or more before Solon’s Egyptian sojourn, to have continued as a hazard for such a period suggests a location that was little affected by currents or tides. The latter would seem to offer support for a Mediterranean Atlantis as that sea enjoys negligible tidal changes, as can be seen from the chart below. The darkest shade of blue indicates the areas of minimal tidal effect.
 If Plato was correct in stating that Atlantis was submerged in a single day and that it was still close to the water’s surface in his own day, its destruction must have taken place a relatively short time before since the slowly rising sea levels would eventually have deepened the waters covering the remains of Atlantis to the point where they would not pose any danger to shipping. The triremes of Plato’s time had an estimated draught of about a metre so the shallows must have had a depth that was less than that.
If Plato was correct in stating that Atlantis was submerged in a single day and that it was still close to the water’s surface in his own day, its destruction must have taken place a relatively short time before since the slowly rising sea levels would eventually have deepened the waters covering the remains of Atlantis to the point where they would not pose any danger to shipping. The triremes of Plato’s time had an estimated draught of about a metre so the shallows must have had a depth that was less than that.
The reference to mud shoals resulting from an earthquake brings to mind the possibility of liquefaction. This is perhaps what happened to the two submerged ancient cities close to modern Alexandria. Their remains lie nine metres under the surface of the Mediterranean.
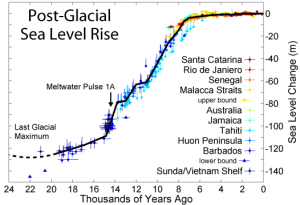 Our knowledge of sea-level changes over the past two and a half millennia should enable us to roughly estimate all possible locations in the Mediterranean where the depth of water of any submerged remains would have been a metre or less in the time of Plato.
Our knowledge of sea-level changes over the past two and a half millennia should enable us to roughly estimate all possible locations in the Mediterranean where the depth of water of any submerged remains would have been a metre or less in the time of Plato.
Some supporters of a Black Sea Atlantis have suggested the shallow Strait of Kerch between Crimea and Russia as the location of Plato’s ‘shoals’(e) .
The tidal map above offers two areas west of Athens and Egypt that do appear to be credible location regions, namely, (1) from the Balearic Islands, south to North Africa and (2), a more credible straddling the Strait of Sicily. This region offers additional features, making it much more compatible with Plato’s account.
By contrast, just over a hundred miles south of that Strait, lies the Gulf of Gabés, which boasts the greatest tidal range (max 8 ft) within the Mediterranean.
The Gulf of Gabes formerly known as Syrtis Minor and the larger Gulf of Sidra to the east, previously known as Syrtis Major, was greatly feared by ancient mariners and continue to be very dangerous today because of the shifting sandbanks created by tides in the area.
There are two principal ancient texts that possibly support the gulfs of Syrtis as the location of Plato’s ‘shoal’. The first is from Apollonius of Rhodes who was a 3rd-century BC librarian at Alexandria. In his Argonautica (Bk IV ii 1228-1250)(a) he unequivocally speaks of the dangerous shoals in the Gulf of Syrtis. The second source is the Acts of the Apostles (Acts 27 13-18) written three centuries later, which describes how St. Paul on his way to Rome was blown off course and feared that they would run aground on “Syrtis sands.” However, good fortune was with them and after fourteen days they landed on Malta. The Maltese claim regarding St. Paul is rivalled by that of the Croatian island of Mljet as well Argostoli on the Greek island of Cephalonia. Even more radical is the convincing evidence offered by Kenneth Humphreys to demonstrate that the Pauline story is an invention(b).
Both the Strait of Sicily and the Gulf of Gabes have been included in a number of Atlantis theories. The Strait and the Gulf were seen as part of a larger landmass that included Sicily according to Butavand, Arecchi and Sarantitis who named the Gulf of Gabes as the location of the Pillars of Heracles. Many commentators such as Frau, Rapisarda and Lilliu have designated the Strait of Sicily as the ‘Pillars’, while in the centre of the Strait we have Malta with its own Atlantis claims.
Zhirov[458.25] tried to explain away the ‘shoals’ as just pumice stone, frequently found in large quantities after volcanic eruptions. However, Plato records an earthquake, not an eruption and Zhirov did not explain how the pumice stone was still a hazard many hundreds of years after the event. Although pumice can float for years, it will eventually sink(c). It was reported that pumice rafts associated with the 1883 eruption of Krakatoa were found floating up to 20 years after that event. Zhirov’s theory does not hold water (no pun intended) apart from which, Atlantis was destroyed as a result of an earthquake. not a volcanic eruption and I think that the shoals described by Plato were more likely to have been created by liquefaction and could not have endured for centuries.
Nevertheless, a lengthy 2020 paper(d) by Ulrich Johann offers additional information about pumice and in a surprising conclusion proposes that it was pumice rafts that inspired Plato’s reference to shoals!
Andrew Collins in an effort to justify his Cuban location for Atlantis needed to find Plato’s ‘shoals of mud’ in the Atlantic and for me, in what seems to have been an act of desperation he decided that the Sargasso Sea fitted the bill [072.42]. Similarly, Emilio Spedicato in support of a Hispaniola Atlantis also opted for the Sargasso. However, neither Collins or Spedicato were the first to make this suggestion. Chedomille Mijatovich (1842-1932), a Serbian politician, economist and historian was one of the first in modern times to suggest that the Sargasso Sea may have been the maritime hazard described by Plato as a ‘shoal of mud’, which resulted from the submergence of Atlantis. However, neither explains how anyone can mistake seaweed for mud!
The late Andis Kaulins believed that Atlantis did exist and considered two possible regions for its location; the Minoan island of Thera or some part of the North Sea that was submerged at the end of the last Ice Age when the sea levels rose dramatically. Kaulins noted that part of the North Sea is known locally as ‘Wattenmeer’ or Sea of Mud’ reminiscent of Plato’s description of the region where Atlantis was submerged, after that event.
An even more absurd suggestion came from the American scholar William Arthur Heidel (1868-1941), who denied the reality of Atlantis and wrote a critical paper [0374] on the subject (republished July 2013(g)). He claimed that an expeditionary naval force sent by Darius in 515 BC under Scylax of Caryanda to explore the Indus River, eventually encountered waters too shallow for his ships, and that this was the inspiration behind Plato’s tale of unnavigable seas. Heidel further claimed that Plato’s battle between Atlantis and Athens is a distorted account of the war of invasion between the Persians and the peoples of the Indus Valley (Now Pakistan)!
(a) https://www.sacred-texts.com/cla/argo/argo53.htm
(b) The Curious Yarn of Paul’s “Shipwreck” (archive.org) *
(c) https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2017/05/170523144110.htm
(e) Index (atlantis-today.com)
(f) https://www.abovetopsecret.com/forum/thread61382/pg1
(g) A Suggestion concerning Plato’s Atlantis on JSTOR (archive.org)
(h) Atlantis – Wikipedia_?s=books&ie=UTF&qid=1376067567&sr=-

