Knossos
Minoan Hypothesis
The Minoan Hypothesis proposes an Eastern Mediterranean origin for Plato’s Atlantis centred on the island of Thera and/or Crete. The term ‘Minoan’ was coined by the renowned archaeologist Sir Arthur Evans after the mythic King Minos. (Sir Arthur was the son of another well-known British archaeologist, Sir John Evans). Evans thought that the Minoans had originated in Northern Egypt and came to Crete as refugees. However, recent genetic studies seem to indicate a European ancestry!
It is claimed(a) that Minoan influence extended as far as the Iberian Peninsula as early as 3000 BC and is reflected thereby what is now known as the Los Millares Culture. Minoan artefacts have also been found in the North Sea, but it is not certain if they were brought there by Minoans themselves or by middlemen. The German ethnologist, Hans Peter Duerr, has a paper on these discoveries on the Academia.edu website(e). He claims that the Minoans reached the British Isles as well as the Frisian Islands where he found artefacts with some Linear A inscriptions near the site of the old German trading town of Rungholt, destroyed by a flood in 1362(f).
The advanced shipbuilding techniques of the Minoans are claimed to have been unmatched for around 3,500 years until the 1950s (l).
The Hypothesis had its origin in 1872 when Louis Guillaume Figuier was the first to suggest [0296] a link between the Theran explosion and Plato’s Atlantis. The 1883 devastating eruption of Krakatoa inspired Auguste Nicaise, in an 1885 lecture(c) in Paris, to cite the destruction of Thera as an example of a civilisation being destroyed by a natural catastrophe, but without reference to Atlantis.
The Minoan Hypothesis proposes that the 2nd millennium BC eruption(s) of Thera brought about the destruction of Atlantis. K.T. Frost and James Baikie, in 1909 and 1910 respectively, outlined a case for identifying the Minoans with the Atlanteans, decades before the extent of the massive 2nd millennium BC Theran eruption was fully appreciated by modern science. In 1917, Edwin Balch added further support to the Hypothesis [151].
As early as April 1909, media speculation was already linking the discoveries on Crete with Atlantis(h), despite Jowett’s highly sceptical opinion.
Supporters of a Minoan Atlantis suggest that when Plato wrote of Atlantis being greater than Libya and Asia he had mistranscribed meison (between) as meizon (greater), which arguably would make sense from an Egyptian perspective as Crete is between Libya and Asia, although it is more difficult to apply this interpretation to Thera which is further north and would be more correctly described as being between Athens and Asia. Thorwald C. Franke has now offered a more rational explanation for this disputed phrase when he pointed out [0750.173] that “for Egyptians, the world of their ‘traditional’ enemies was divided in two: To the west, there were the Libyans, to the east there were the Asians. If an Egyptian scribe wanted to say, that an enemy was more dangerous than the ‘usual’ enemies, which was the case with the Sea Peoples’ invasion, then he would have most probably said, that this enemy was “more powerful than Libya and Asia put together”.
It has been ‘received wisdom’ that the Minoans were a peace-loving people, however, Dr Barry Molloy of Sheffield University has now shown that the exact opposite was true(d) and that “building on recent developments in the study of warfare in prehistoric societies, Molloy’s research reveals that war was, in fact, a defining characteristic of the Minoan society, and that warrior identity was one of the dominant expressions of male identity.”
In 1939, Spyridon Marinatos published, in Antiquity, his opinion that the eruption of Thera had led to the demise of the Minoan civilisation. However, the editors forbade him to make any reference to Atlantis. In 1951, Wilhelm Brandenstein published a Minoan Atlantis theory, echoing many of Frost’s and Marinatos’ ideas, but giving little credit to either.
However, Colin MacDonald, an archaeologist at the British School in Athens, believes that “Thira’s eruption did not directly affect Knossos. No volcanic-induced earthquake or tsunami struck the palace which, in any case, is 100 meters above sea level.” The Sept. 2019 report in Haaretz suggests it’s very possible the Minoans were taken over by another civilization and may have been attacked by the Mycenaeans, the first people to speak the Greek language and they flourished between 1650 B.C. and 1200 B.C. Archaeologists believe that the Minoan and Mycenaean civilisations gradually merged, with the Mycenaeans becoming dominant, leading to the shift in the language and writing system used in ancient Crete.
The greatest proponents of the Minoan Hypothesis were arguably A.G. Galanopoulos and Edward Bacon. Others, such as J.V. Luce and James Mavor were impressed by their arguments and even Jacques Cousteau, who unsuccessfully explored the seas around Santorini, while Richard Mooney, the ‘ancient aliens’ writer, thought [0842] that the Minoan theory offered a credible solution to the Atlantis mystery. More recently Elias Stergakos has proposed in an overpriced 68-page book [1035], that Atlantis was an alliance of Aegean islands that included the Minoans.
Moses Finley, the respected classical scholar, wrote a number of critical reviews of books published by prominent supporters of the Minoan Hypothesis, namely Luce(aa), Mavor(y)(z) as well as Galanopoulos & Bacon(aa)(ab). Some responded on the same forum, The New York Review of Books.
Andrew Collins is also opposed to the Minoan Hypothesis, principally because “we also know today that while the Thera eruption devastated the Aegean and caused tsunami waves that destroyed cities as far south as the eastern Mediterranean, it did not wipe out the Minoan civilization of Crete. This continued to exist for several generations after the catastrophe and was succeeded by the later Mycenaean peoples of mainland Greece. For these reasons alone, Plato’s Atlantic island could not be Crete, Thera, or any other place in the Aegean. Nor can it be found on the Turkish mainland at the time of Thera’s eruption as suggested by at least two authors (James and Zangger) in recent years(ad).“
Alain Moreau has expressed strong opposition to the Minoan Hypothesis in a rather caustic article(i), probably because it conflicts with his support for an Atlantic location for Atlantis. In more measured tones, Ronnie Watt has also dismissed a Minoan Atlantis, concluding that “Plato’s Atlantis happened to become like the Minoan civilisation on Theros rather than to be the Minoan civilisation on Theros.” In 2001, Frank Joseph wrote a dismissive critique of the Minoan Hypothesis referring to Thera as an “insignificant Greek island”.(x)
Further opposition to the Minoan Hypothesis came from R. Cedric Leonard, who has listed 18 objections(q) to the identification of the Minoans with Atlantis, keeping in mind that Leonard is an advocate of the Atlantic location for Plato’s Island.
Atlantisforschung has highlighted Spanuth’s opposition to the Minoan Hypothesis in a discussion paper on its website. I have published here a translation of a short excerpt from Die Atlanter that shows his disdain for the idea of an Aegean Atlantis.
“Neither Thera nor Crete lay in the ‘Atlantic Sea’, but in the Aegean Sea, which is expressly mentioned in Crit. 111a and contrasted with the Atlantic Sea. Neither of the islands lay at the mouth of great rivers, nor did they “sink into the sea and disappear from sight.” ( Tim. 25d) The Aegean Sea never became “impassable and unsearchable because of the very shallow mud”. Neither Solon nor Plato could have said of the Aegean Sea that it was ‘still impassable and unsearchable’ or that ‘even today……….an impenetrable and muddy shoal’ ‘blocks the way to the opposite sea (Crit.108e). Both had often sailed the Aegean Sea and their contemporaries would have laughed at them for telling such follies.” (ac)
Lee R. Kerr is the author of Griffin Quest – Investigating Atlantis [0807], in which he sought support for the Minoan Hypothesis. Griffins (Griffons, Gryphons) were mythical beasts in a class of creatures that included sphinxes. Kerr produced two further equally unconvincing books [1104][1675], all based on his pre-supposed link between Griffins and Atlantis or as he puts it “whatever the Griffins mythological meaning, the Griffin also appears to tie Santorini to Crete, to Avaris, to Plato, and thus to Atlantis, more than any other single symbol.” All of which ignores the fact that Plato never referred to a Sphinx or a Griffin!
The hypothesis remains one of the most popular ideas with the general public, although it conflicts with many elements in Plato’s story. A few examples of these are, where were the Pillars of Heracles? How could Crete/Thera support an army of one million men? Where were the elephants? There is no evidence that Crete had walled cities such as Plato described. The Minoan ships were relatively light and did not require the huge harbours described in the Atlantis story. Plato describes the Atlanteans as invading from their western base (Tim.25b & Crit.114c); Crete/Santorini is not west of either Egypt or Athens
Gavin Menzies attempted to become the standard-bearer for the Minoan Hypothesis. In The Lost Empire of Atlantis [0780], he argues for a vast Minoan Empire that spread throughout the Mediterranean and even discovered America [p.245]. He goes further and claims that they were the exploiters of the vast Michigan copper reserves, which they floated down the Mississippi for processing before exporting it to feed the needs of the Mediterranean Bronze industry. He also accepts Hans Peter Duerr’s evidence that the Minoans visited Germany, regularly [p.207].
Tassos Kafantaris has also linked the Minoans with the exploitation of the Michigan copper, in his paper, Minoan Colonies in America?(k) He claims to expand on the work of Menzies, Mariolakos and Kontaratos. Another Greek Professor, Minas Tsikritsis, also supports the idea of ancient Greek contact with America. However, I think it is more likely that the Minoans obtained their copper from Cyprus, whose name, after all, comes from the Greek word for copper.
Oliver D. Smith has charted the rise and decline in support for the Minoan Hypothesis in a 2020 paper entitled Atlantis and the Minoans(u).
Frank Joseph has criticised [0802.144] the promotion of the Minoan Hypothesis by Greek archaeologists as an expression of nationalism rather than genuine scientific enquiry. This seems to ignore the fact that Figuier was French, Frost, Baikie and Bacon were British, Luce was Irish and Mavor was American. Furthermore, as a former leading American Nazi, I find it ironic that Joseph, a former American Nazi leader, is preaching about the shortcomings of nationalism.
While the suggestion of an American connection may seem far-fetched, it would seem mundane when compared with a serious attempt to link the Minoans with the Japanese, based on a study(o) of the possible language expressed by the Linear A script. Gretchen Leonhardt(r) also sought a solution in the East, offering a proto-Japanese origin for the script, a theory refuted by Yurii Mosenkis(s), who promotes Minoan Linear A as proto-Greek. Mosenkis has published several papers on the Academia.edu website relating to Linear A(t). However, writing was not the only cultural similarity claimed to link the Minoans and the Japanese offered by Leonhardt.
Furthermore, Crete has quite clearly not sunk beneath the waves. Henry Eichner commented, most tellingly, that if Plato’s Atlantis was a reference to Crete, why did he not just say so? After all, in regional terms, ‘it was just down the road’. The late Philip Coppens was also strongly opposed to the Minoan Hypothesis.(g)
Eberhard Zangger, who favours Troy as Atlantis, disagrees strongly [0484] with the idea that the Theran explosion was responsible for the 1500 BC collapse of the ‘New Palace’ civilisation.
Excavations on Thera have revealed very few bodies resulting from the 2nd millennium BC eruptions there. The understandable conclusion was that pre-eruption rumblings gave most of the inhabitants time to escape. Later, Therans founded a colony in Cyrene in North Africa, where you would expect that tales of the devastation would have been included in their folklore. However, Eumelos of Cyrene, originally a Theran, opted for the region of Malta as the remnants of Atlantis. How could he have been unaware of the famous history of his family’s homeland?
A 2008 documentary, Sinking Atlantis, looked at the demise of the Minoan civilisation(b). James Thomas has published an extensive study of the Bronze Age, with particular reference to the Sea Peoples and the Minoans(j).
In the 1990s, art historian and museum educator, Roger Dell, presented an illustrated lecture on the art and religion of the Minoans titled Art and Religion of the Minoans: Europe’s first civilization”, which offered a new dimension to our understanding of their culture(p). In this hour-long video, he also touches on the subject of Atlantis and the Minoans.
More extreme is the theory of L. M. Dumizulu, who offers an Afrocentric view of Atlantis. He claims that Thera was part of Atlantis and that the Minoans were black!(m)
In 2019, Nick Austin attempted [1661] to add further support to the idea of Atlantis on Crete, but, in my opinion, he failed.>>His book is now available online(ai) along with a related paper(aj).<<
The following year, Sean Welsh also tried to revive the Minoan Hypothesis in his book Apocalypse [1874], placing the Atlantean capital on Santorini, which was destroyed when the island erupted around 1600 BC. He further claims that the ensuing tsunami led to the biblical story of the Deluge.
Evan Hadingham published a paper(v) in 2008 in which he discussed the possibility that the Minoan civilisation was wiped out by the tsunami generated by the eruption(s) of Thera. Then, seven years later he produced a second paper(w) exonerating the tsunami based on new evidence or lack of it.
In April 2023, an attempt was made to breathe some new life into the Minoan Hypothesis in an article(ae) on the Greek Reporter website. This unconvincing piece claims “Plato describes in detail the Temple of Poseidon on Atlantis, which appears to be identical to the Palace of Knossos on the island of Crete.” The writer, Caleb Howells, has conveniently overlooked that Atlantis was submerged creating dangerous shoals and remained a maritime hazard even up to Plato’s day (Timaeus 25d). The Knossos Palace is on a hill and offers no evidence of ever having been submerged. Try again.
The same reporter did try again with another unconvincing piece supporting the Minoan Hypothesis, also on the Greek Reporter site, in October 2023(af). This time, he moved the focus of his claim to Santorini where he now placed the Palace of Poseidon relocating it from Crete! I suppose he will eventually make his mind up. Nevertheless, Howells revisited the subject of the Palace of Poseidon just a few weeks later, once again identifying it as the Palace of Knossos – “Plato’s account of the lost civilization of Atlantis includes a description of a marvelous temple of god Poseidon. It was said to have been in the center of Atlantis, so it was a very prominent part. However, in most investigations into the origin of Atlantis, this detailed temple description is ignored. In fact, an analysis of Plato’s details indicates that the Temple of Poseidon on Atlantis was actually identical to the Palace of Knossos on the island of Crete, Greece.” (ag)
Most Atlantis theories manage to link their their chosen site with some of the descriptive details provided by Plato. The Minoan Hypothesis is no exception, so understandably Howells has highlighted the similarities, while ignoring disparities. The Minoans were primarily concerned with trading, not territorial expansion. When did they engage in a war with Athens or threaten Egypt? If Howells can answer that he may have something relevant to build upon!
For a useful backdrop to the Minoan civilisation I suggest that readers have a look at a fully illustrated 2019 lecture by Dr. Gregory Mumford of the University of Alabama at Birmingham. In it he give a broad overview of the Eastern Mediterranean, with a particular emphasis on the Aegean Sea, during the Middle- Late Bronze Age (2000-1200 BC). (ah)
(a) http://www.minoanatlantis.com/Minoan_Spain.php
(b) http://video.pbs.org/video/1204753806/ (Link broken)
(c) http://fr.wikisource.org/wiki/Les_Terres_disparues
(d) http://www.sci-news.com/archaeology/article00826.html
(e) See: Archive 3928
(f) http://dienekes.blogspot.ie/2008/08/minoans-in-germany.html
(g) https://web.archive.org/web/20180128190713/http://philipcoppens.com/lectures.php (June 3, 2011)
(j) https://medium.com/the-bronze-age
(k) GREECE AND WORLD: Minoan colonies in America?
(m) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QqTQeF2gLpg
(o) Archive 3930 | (atlantipedia.ie)
(p) https://vimeo.com/205582944 Video
(q) https://web.archive.org/web/20170113234434/http://www.atlantisquest.com/Minoan.html
(r) https://konosos.net/2011/12/12/similarities-between-the-minoan-and-the-japanese-cultures/
(t) https://www.academia.edu/31443689/Researchers_of_Greek_Linear_A
(u) https://www.academia.edu/43892310/Atlantis_and_the_Minoans
(v) Did a Tsunami Wipe Out a Cradle of Western Civilization? | Discover Magazine
(w) https://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/article/megatsunami-may-wiped-europes-first-great-civilization/
(x) Atlantis Rising magazine #27 http://pdfarchive.info/index.php?pages/At
(y) Wayback Machine (archive.org)
(z) https://www.nybooks.com/articles/1969/12/04/back-to-atlantis-again/
(aa) Back to Atlantis | by M.I. Finley | The New York Review of Books (archive.org)
(ab) The End of Atlantis | by A.G. Galanopoulos | The New York Review of Books (archive.org)
(ac) Jürgen Spanuth über ‘Atlantis in der Ägäis’ – Atlantisforschung.de
(ad) Kreta oder Thera als Atlantis? – Atlantisforschung.de (atlantisforschung-de.translate.goog)
(ae) Was Atlantis’ Temple of Poseidon the Palace of Knossos in Crete? (greekreporter.com)
(af) Was Atlantis a Minoan Civilization on Santorini Island? (greekreporter.com)
(ag) https://greekreporter.com/2023/12/01/atlantis-temple-poseidon-palace-knossos-crete/
(ai) https://www.academia.edu/44267221/Atlantis_the_evidence?email_work_card=view-paper *
(aj) (99+) Atlantis the evidence | Nick Austin – Academia.edu *
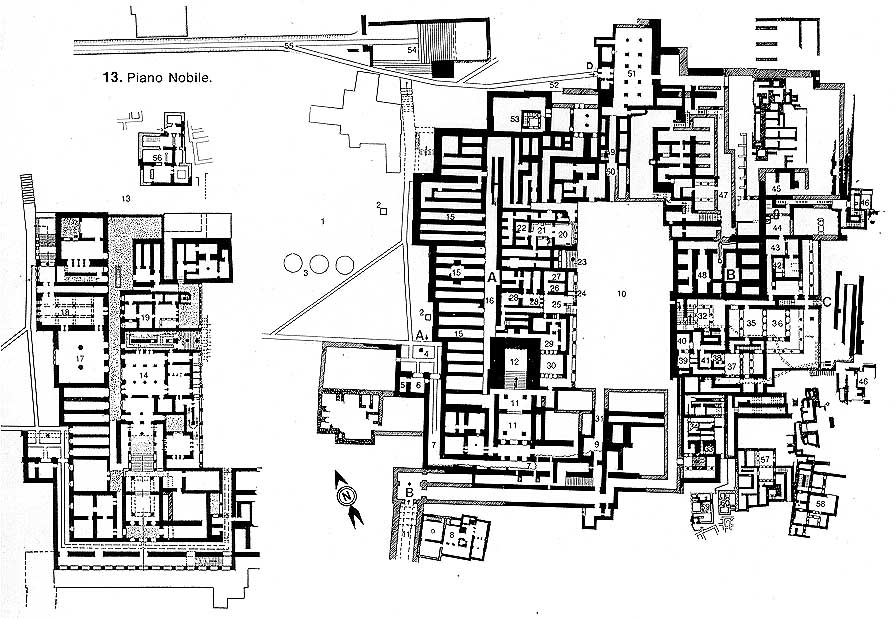
Knossos (m)
Knossos was one of a number of cities found on Crete that were not fortified, leading to the suggestion that their construction was carried out during a period of peace. This is in sharp contrast with the defensive design of the Atlantean capital and the warlike attitude of the latter-day Atlanteans as reported by Plato. This single fact somewhat undermines the identification of Minoan Crete with Atlantis.
2016 brought reports(a)(b) that Knossos was three times the size previously thought by archaeologists and had thrived into the Iron Age.
Crete
Crete was until recently thought to have been first settled around 7000 BC. However, excavations at nine sites in 2008 and 2009 have revealed double-edged hand axes dated to “at least” 130,000 years ago. This discovery has suggested(a) that Stone Age man had developed seafaring abilities.
>There is something of a consensus that Crete was known as Keftiu to the ancient Egyptians. Some others have been in favour of identifying Keftiu with Cyprus, among whom, Immanuel Velikovsky argued(e) that if Cyprus was not Caphtor, then it is the only island of any importance in the Eastern Mediterranean not mentioned in the Bible [039.210]. Caphtor/Keftiu: A New Investigation [1052] by John Strange also supports this identification with Cyprus.<
Sir Arthur Evans, knighted for his archaeological finds on Crete, excavated at Knossos from 1900-1905 leading to the discovery of the famous ‘palace’ there. Evans saw Knossos as an administrative centre although it had no defensive features, which might be expected. In the 1970’s Hans Georg Wunderlich (1928-1974) following the views of Oswald Spengler, proposed in The Secret of Crete[826] , that the ‘palace’ was in fact a mortuary temple. This idea has more recently been considered by the late Philip Coppens(c).
As early as 1910 the Rev. James Baikie suggested Crete as the location of Atlantis. A year earlier K.T. Frost outlined parallels between Atlantis and the Minoan empire. In the 1920’s Joseph McCabe a former Catholic priest was also convinced that Crete was the location of Atlantis. More decades were to pass before Dr Angelos Galanopoulos developed the idea further[0263][0264]. There has been doubt that the decline of the Minoan civilisation in the 2nd millennium BC was linked with Theran explosion. Nevertheless, Bacon and Galanopoulos admit that a Minoan explanation for the Atlantis story ‘is correct in all points’ except date, dimensions and location of ‘Pillars’! Many commentators have added reasons to support the Minoan Hypothesis.
 James Mavor records[265] how a stone was discovered on Thera with the name Eumelos inscribed on it in archaic Greek. However, it would be unwise to read too much into a single isolated object.
James Mavor records[265] how a stone was discovered on Thera with the name Eumelos inscribed on it in archaic Greek. However, it would be unwise to read too much into a single isolated object.
J. V. Luce lists a number of interesting similarities between Crete and Plato’s description of Atlantis[120].
*Atlantis was the way to other islands. This is an accurate description of Crete as the gateway to the Cyclades and Greece.
*The palace of the Atlanteans is on a low hill 50 stadia inland and near to a fertile plain is a good description of Knossos.
*The description of the land fits perfectly with the southern coast of Crete.
*There were bulls hunted without weapons, which is characteristic of Minoan Crete.
*The construction of the buildings matches Knossos.
Rodney Castleden[0225] uses statistics to demonstrate that Minoan Crete was closer to Plato’s description of Atlantis than previously thought.
Marjorie Braymer[198] highlights the fact that the Cretan Mesara Plain is oblong in shape and one tenth of the dimensions of the plain mentioned by Plato. A fact that gains in importance if a tenfold exaggeration of the dimensions by Plato is accepted.
J. G. Bennett has gone further and argued strongly for a linkage of the destruction of Minoan civilisation, with the Flood of Deucalion, the Biblical Exodus and the obliteration of Plato’s Atlantis. Bennett quotes Plato’s Laws (705.15), which speaks of a significant migration from Crete, as evidence for a major catastrophe on the island.
In April 2004, a BBC Timewatch programme looked at a possible link between Crete and Atlantis focussing on evidence of ancient tsunami damage on the island that they linked to the eruption of Thera. This idea has been refuted by W. Shepard Baird who offers a pyroclastic surge as a more credible explanation(b). In 2010, the BBC broadcast another documentary supporting the Minoan Hypothesis, although not very convincingly in the opinion of this compiler.
On the other hand, Peter James points out that there is no connection in Greek mythology between Crete and Atlas. Further objections include the fact that no ancient canals have been found on Crete, the island did not sink and the failure of Plato to simply name Crete as the location of his Atlantis, even though it was well-known to the mainland Greeks.
Recently Gavin Menzies has, unsuccessfully, in my view, attempted to breathe new life into the Minoan Hypothesis in The Lost Empire of Atlantis.
An even less impressive effort to support a Minoan Atlantis is a slender work by Lee R. Kerr entitled Griffin Quest – Investigating Atlantis [807], who also published an equally useless sequel, Atlantis of the Minoans and Celts[1104].
(a) https://www.stonepages.com/news/archives/003678.html
(b) https://www.minoanatlantis.com/Sinking_Atlantis_Myth.php
(c) https://www.philipcoppens.com/crete_dead.html (offline Mar. 2018 see Archive 2133)
(d) https://trove.nla.gov.au/ndp/del/article/204059231?searchTerm=Atlantis discovered&searchLimits=
Castleden, Rodney
 Rodney Castleden (1945- ) has been researching prehistory for the past twenty-five years and has written over forty books on such diverse subjects(a) as Stonehenge, Knossos and the Mycenaeans [226] as well as criminology. He is the author of a well-received volume, Atlantis Destroyed [225] in which he advocates the idea that the destruction of Minoan Crete provided the inspiration for Plato’s Atlantis.
Rodney Castleden (1945- ) has been researching prehistory for the past twenty-five years and has written over forty books on such diverse subjects(a) as Stonehenge, Knossos and the Mycenaeans [226] as well as criminology. He is the author of a well-received volume, Atlantis Destroyed [225] in which he advocates the idea that the destruction of Minoan Crete provided the inspiration for Plato’s Atlantis.
His book is also available on the Wayback Machine website(b).
(a) https://www.goodreads.com/author/show/475412.Rodney_Castleden
>(b) https://archive.org/details/atlantisdestroye0000cast_g7v6/page/n5/mode/2up<
Indus Valley
The Indus Valley civilisation is dated to 2600-1900 BC (preceded by the Mehrgarh People) is now referred to as the Harappan civilisation. To date, over a thousand settlements and five cities have been identified, but only 10% have been excavated(v).
The origins of the Indus people has been debated for some time, but a DNA study of four skeletons discovered, some years ago, at Rakhigarhi, in India, may offer some clues. However, three years later (2017) the results have still not been made public(z)(aa)! A September 2019 report in Live Science highlighted the fact that gathering usable DNA from the Indus Valley is extremely difficult as the climate there degrades it rapidly. Attempts to extract DNA from 61 individuals in the cemetery in Rakhigarhi were successful in only one instance. Unfortunately, only limited information was gleaned from this study, namely that “about two-thirds to three-fourths of the ancestry of all modern South Asians come from a population group related to that of this Indus Valley individual.” according to Vagheesh Narasimhan, one of the authors of the report.
In recent years, the Indus region has received several nominations as the source of the Atlantis story. Dr Ashok Malhotra has identified the submergence of the city of Dwarka as the inspiration for the story, which was then brought to Sumeria and later Egypt 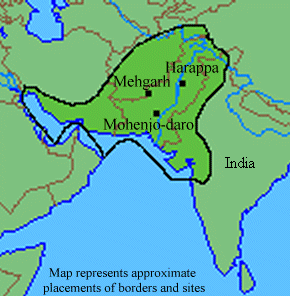 before transmission to Greece.
before transmission to Greece.
However, Radek Brychta has opted[203] for the ancient city of Dholavira as a more likely candidate, while independently Yashwant Koak arrived at the same conclusion and intends to publish soon.
A 2014 blogger offered similar ideas with a paper(n) entitled ‘Atlantis was Indus Valley plateau?’ but then proceeds to describe Indonesia as the hyperdiffusionist source for the great civilisations “such as those of the Egyptians, the Greeks, the Cretans and the Mesopotamians. These also included the Jews, the Phoenicians, and the Aryans, driven away from their ancestral lands in Indonesia and Southeast Asia.”
In Thorwald C. Franke’s Newsletter No.119 he draws attention to a review by Professor Heinz-Günther Nesselrath of a new over-priced book by Erika Daniels-Qasim. Although the book is published in German[1580], Nesselrath’s highly critical review is in English(ac), Nesselrath reveals that this is just another useless attempt to link Plato’s Atlantis with the Indus Valley civilisation. Franke describes it as a ‘sad book’.
Although the ‘ancient alien’ idea has nothing to back it up, the claim that a very ancient nuclear war destroyed the Indus civilisation has had some support(ad). However, Jason Colavito has also debunked the story of the ‘radioactive skeleton’ there(ab). A decade ago (2013) Dale Drinnon also published a blog refuting the ancient atomic war claims(aj).
In 2012, the Spanish researcher, José Angel Hernández, proposed that the Tarshish of the Bible was to be found on the coastal region of the Indus Valley, but that Tartessos was a colony of the Indus city of Lhotal and had been situated on both sides of the Strait of Gibraltar! He also compared the bull cult of Plato’s Atlantis with that of the Indus civilisation(f)(g).
The central Indus city of Mohenjo-Daro was only rediscovered in 1922(m) and a curious more recent discovery there, was that 10% of artefacts found there related to play! Clusters of game pieces suggested the use of communal social centres. Unrelated, but perhaps more relevant to our study is the fact that there is a dearth of weaponry fortifications or evidence of warfare in the Indus culture(d), which is in sharp contrast to the belligerent Atlantean society described by Plato. More details of the city and the Indus culture can be read on the Italian larazzodeltempo.it website(ag)(ah).
A frequently referred to anomaly at Mohenjo-Daro is evidence of vitrification and radioactivity that some have attributed to atomic warfare or attacks by ancient aliens(af). A more balanced view(k)(l) can be found online. A 2015 article on this subject is also worth a look(o). Jason Colavito has unearthed(ab) the origin of this claim, tracing it back to the 1960s and an unreliable Russian writer, Alexander Gorbovsky, compounded by later distortions by ‘fringe investigators.
A 2012 conference on Harappan archaeology saw the origins of that culture pushed back to the 7th millennium BC, contemporary with that of Sumer(j). The same conference saw linguistic connections between the two cultures under discussion. However, despite numerous attempts over the past century the Indus Valley script remains undeciphered(p), although there are regular claims of successful decipherment, 2007(q), 2009(r), 2011(s), 2013(t), to date totalling nearly 100, somewhat reminiscent of the constant flow of Atlantis theories. Now linguists are turning to computer technology to finally solve the problem(x).
A radical theory regarding Mohenjo-Daro has been proposed by an Indian researcher, Jeyakumar Ramasami, in which he claims that the city was a necropolis and not a metropolis. His book on the subject can be downloaded as a free Word file(e). A similar theory was proposed by Hans Georg Wunderlich regarding the Minoan ‘palace’ of Knossos on Crete.
A comprehensive website(a) with many photos and diagrams relating to the Indus Valley civilisation is available. A related article by Patrick Chouinard is also of interest(b).
A recent discovery off the Konkan Coast in the State of Maharashtra in western India has revealed a remarkable structure that is based on sea-level changes that may be 8,000 years old(c). A wall 24 km long, 2.7 metres high and 2.5 metres in width was discovered in just three metres of water. Speculation has centred on the possibility of it being evidence of a completely unknown civilisation that could pre-date that of the Indus Valley. A second site, thought to be pre-Harappan, located in Rakhigarhi village in Haryana’s Hisar district, over 200 km from Chandigarh, is now under investigation.
A 2008 article(i) adds further information about the Indus Valley, which includes a reference to the Neolithic site at Mehrgarh a precursor to the Indus civilisation and dated to 7000 BC, a date that has now been pushed back to 8000 BC according to a paper published(u) in the May 25th, 2016 edition of Nature.
A recent paper(w) has revealed how the Indus people coped with the consequences of climate change when their civilisation was at its height around 2500-1900 BC. Another paper suggests that the demise of the Indus Valley civilisation was the result of climate change caused by changing monsoon patterns. The author, Nishant Malik, assistant professor at the Rochester Institute of Technology’s School of Mathematical Sciences, used mathematical modelling to support his claim(ae).
Until now it was thought that many of the Indus settlements had been dependent on a major Himalayan river, the Ghaggar-Hakra, now dried up. However, recent studies(y) indicate that this river changed course over 8,000 years ago suggesting that “when the Indus people settled the area, there was only an abandoned large river valley occupied by seasonal monsoon river flow instead of a large Himalayan river.” So it seems that, unlike the Egyptian and Mesopotamian civilisations the Indus people did not require a substantial permanent river!
Joanna Gillan published an article giving a potted history of Mohenjo Daro and including a critical review of those, including David Davenport, who have tried to prove that the site was the location of an ancient atomic war. Supporters of this idea have pointed to quotations from the Mahabharata in support of this idea. However, Gillan revealed that “Rather than being entirely fictitious, the passage is composed of a merging together of various unrelated passages scattered throughout the 200,000-verse epic, some of which are also questionable English translations of a questionable French translation of the original Sanskrit. When viewed in their original context, they are a little less convincing”(ak).
Another article on the Ancient Origins website, also by Gillan, in January 2022 reviews the history of Mohenjo Daro and unfortunately highlights that “Although it has survived for five millennia, Mohenjo Daro now faces imminent destruction. While the intense heat of the Indus Valley, monsoon rains, and salt from the underground water table is having damaging effects on the treasured site, it is the visitors that flock in their thousands to the site that are the biggest threat. Adding to the problem is a lack of funding, public indifference, and government neglect. The government even approved a festival being held at the site back in 2014, where tents, lights and stages were hammered into the walls of the delicate ruins.
Mohenjo Daro is already in an incredibly fragile condition. It is estimated that at its current rate of degradation, the World Heritage-listed site could be gone within 20 years(ai).
(b) https://newagearchaeology.weebly.com/the-indus-valley.html
(c) A civilisation as old as Indus valley? (archive.org)
(d) Indus Valley Civilization: The Demise of Utopia (archive.org)
(e) https://archive.org/details/NewInterpretationsOnIndusValleyCivilization
(f) https://joseangelh.wordpress.com/category/mito-y-religion/
(g) https://joseangelh.wordpress.com/category/arqueologia-e-historia/
(i) https://wondersofpakistan.wordpress.com/2009/02/21/mehrgarh-the-lost-civilisation-2/
(j) Archive 2329
(k) Mohenjo Daro – The Thunderbolts Project™ (archive.org) (new link)
(l) See: Archive 3516
(m) https://www.freerepublic.com/focus/chat/2959492/posts
(n) See: Archive 3617
(o) https://dailygrail.com/Hidden-History/2015/2/Mohenjo-Daro-Ancient-Nuclear-Mystery
(p) https://www.nature.com/news/ancient-civilization-cracking-the-indus-script-1.18587
(q) https://www.hindunet.org/hvk/articles/0207/56.html (offline Nov. 2016)
(r) https://www.theguardian.com/science/2009/apr/23/indus-civilisation-language-symbols
(s) https://www.boloji.com/articles/10657/a-new-light-on-the-decipherment-of
(t) Decoding the Ancient Script of the Indus Valley | Archaeology Online *
(z) https://www.quora.com/When-will-Rakhigarhi-excavations-DNA-results-be-published
(ac) https://bmcr.brynmawr.edu/2018/2018.08.23/
(ad) Nuclear War In Ancient Times | War Between Rama Empire and Atlantis? (archive.org)
(ag) Mohenjo-Daro, a Bronze Age metropolis – The Tapestry of Time (larazzodeltempo.it)
(ai) Mohenjo Daro and The Mounds That Hid a Civilization | Ancient Origins (ancient-origins.net)
(aj) Archive 2324 | (atlantipedia.ie)
(ak) Was the Mohenjo Daro ‘Massacre’ Real? | Ancient Origins (ancient-origins.net)