Syracuse
Syracuse
Syracuse in Sicily has been suggested as the model for Plato’s Atlantis by Gunnar Rudberg among others. However, it was not the only location proposed as the inspiration for his lost city, with Ecbatana, Dwarka, Helike and Pavlopetri being leading contenders. Nevertheless, in 1917, Gunnar Rudberg the celebrated Swedish classicist published a detailed study of the possible association of Syracuse with Atlantis. This was only available in Swedish until 2012 when Thorwald C. Franke had an English translation(a) of Rudberg’s interesting monograph published [881].
This ancient city was built in a natural harbour with a large island, Ortygia, in it. A causeway bridged a strait between the island and the mainland. There was a wall around Ortygia and its central citadel. The mainland part of the city was also walled.
Syracuse was founded around 743 BC by Archia, a Corinthian and over succeeding centuries developed into a major Mediterranean power, defeating the Carthaginians in 480 BC. In 413 BC the Athenian navy, one of the largest ever, was destroyed by the Syracusans. This happened when Plato was just a teenager and no doubt it would have left a lasting impression on him.
After the death of Socrates, Plato travelled throughout the Eastern Mediterranean. While in Syracuse, he was highly critical of the morality of the city and in doing so he angered its ruler Dionysius I. This resulted in his being sold as a slave but fortunately, his owner freed him. He then returned home to found his famous Academy. However, in later life, as his fame spread, Plato was enticed back to Syracuse to tutor the new ruler, Dionysius II.
To what extent his Sicilian experiences have influenced his writings is impossible to say. The idea that Plato was inspired by the layout of Syracuse to produce a more embellished and schematic version of it in his description of Atlantis is plausible, but no more than that.
What is virtually certain is that Syracuse was not a port before the deglaciation following the last Ice Age as it would have been too far inland due to lower sea levels.
(a) Book: Atlantis and Syracuse – Plato on Sicily – by Gunnar Rudberg – Atlantis-Scout *
Sweden *
Sweden was claimed to be the location of Atlantis by Olaus (Olaf) Rudbeck in the 17th century. Before him another Swede, Johannes Bureus, expressed similar views. His friend Carl Lundius supported Rudbeck’s theories, but received none of the acclaim.
In the 18th century Carl Friedrich Baër was happy to follow a fashion, which placed Atlantis in the Holy Land. I am not aware of any major Swedish contribution to Atlantology in the 19th century. However, the following century saw a number of Swedish researchers make valuable contributions to the subject.
The discovery of the Mid Atlantic Ridge led René Malaise and Hans Pettersson to suggest the Azores as remnants of Atlantis, an idea still popular today. Around the same time Gunnar Rudberg proposed that Syracuse in Sicily had inspired some of Plato’s description of Atlantis. Arvid Högbom advocated the North Sea as the location of Atlantis in 1915, long before Jürgen Spanuth. In the same region Nils Bergquist opted for the Dogger Bank as has Ulf Erlingsson.
More recently, we seem to have come full circle as Bertil Falk has revived some of Rudbeck’s ideas(a) and a short illustrated 2007 paper (updated 2015)(b) by Robert Fritzius also added some additional modern support. However, for something quite different we have Carl Festin promoting a Mediterranean location.
Nils-Axel Mörner and Bob Lind, two controversial researchers, have proposed, in a number of papers, that a Bronze Age trading centre existed in southeast Sweden, which had links with the Mycenaeans, Minoans and Phoenicians in the Mediterranean. They suggest that ancient references to Hyperborea may have been generated by this trade. However, although they do not associate Hyperborea with the story of Atlantis, they delivered their theories in papers presented to the Atlantis Conferences of 2008 [750.685] and 2011(c). They also touch on a number of other peripheral subjects including Cygnus, archaeoastronomy and amber. Similar views on early Baltic trade with the Mediterranean have been expressed elsewhere(d).
(a) https://www.vof.se/folkvett/ar-1993/nr-4/platons-atlantis-diktning-som-tagits-pa-allvar/ (Swedish)
(b) See: https://web.archive.org/web/20100807201746/https://www.datasync.com/~rsf1/vel/atlantis.htm
(c) https://web.archive.org/web/20230926080904/https://file.scirp.org/Html/1-1140054_59543.htm *
Schmeck, Alfred E. *
 Alfred E. Schmeck (1934-2003) is a retired German engineer who proposed in a short (80-page) 2003 book[542] that Atlantis was merely an expression of Plato’s conception of a Utopian state. He contended that Syracuse in Sicily provided the geographical inspiration for the story.
Alfred E. Schmeck (1934-2003) is a retired German engineer who proposed in a short (80-page) 2003 book[542] that Atlantis was merely an expression of Plato’s conception of a Utopian state. He contended that Syracuse in Sicily provided the geographical inspiration for the story.
Thorwald C. Franke has written a critique(a) of Schmeck’s theory.
(a) Schmeck: Atlantis – Platons Idealstaat – Mysteria3000 (archive.org) * (German)
Rudberg, Gunnar
Gunnar Rudberg (1880-1954) was a Swedish professor of classical philology  at the University of Kristiania. He is one of a number of writers who have identified ancient Syracuse in Sicily as the inspiration for Plato’s city of Atlantis[531]. His paper has been translated for the first time into English by Cecelia Murphy, the project being edited and funded by the German researcher Thorwald C. Franke[881]. The original was published in Swedish over a century ago in 1917.
at the University of Kristiania. He is one of a number of writers who have identified ancient Syracuse in Sicily as the inspiration for Plato’s city of Atlantis[531]. His paper has been translated for the first time into English by Cecelia Murphy, the project being edited and funded by the German researcher Thorwald C. Franke[881]. The original was published in Swedish over a century ago in 1917.
Rudberg begins his work with a review and refutation of the more popular Atlantis theories of his day. As this paper was published less than 40 years after Donnelly’s seminal work, Atlantis: The Antediluvian World[021], was written, much of the material will appear dated, particularly as many of today’s better known theories were still many years in the future.
Rudberg moves on to outline his own view that Plato, who had first-hand experience of Sicily, “when developing his portrayal of Atlantis, had the Dionysian’s Syracuse in mind” but added “I do not claim that this is an exhaustive explanation”.
In spite of the date of the original monograph, this English translation is a valuable addition, to the Atlantis literature of the early 20th century, in that language.
Franke has reported that the German magazine Focus, published an article on Rudberg’s views(a) in October 2013. More recently, Franke’s book has been reviewed by Anna Afonasina, a lecturer in philosophy at Novosibirsk State University(b) in Siberia.
(b) Review: Gunnar Rudberg, Atlantis and Syracuse, by Anna S. Afonasina (atlantis-scout.de)
Concentric Rings *
The Concentric Rings or other architectural features extracted by artists from Plato’s description of the capital of Atlantis have 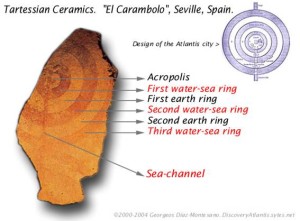 continually fascinated students of the story and many have attempted to link them with similar ancient features found elsewhere in the world as evidence of a widespread culture. Stonehenge, Old Owstrey, Carthage and Syracuse have all been suggested, but such comparisons have never been convincing. Diaz-Montexano has recently published(a) an image of a fragment of pottery found near Seville in Spain that shows concentric circles and insists that it is a symbol of Atlantis. Ulf Erlingsson has made a similar claim regarding some concentric circles carved on a stone basin found at Newgrange in Ireland.
continually fascinated students of the story and many have attempted to link them with similar ancient features found elsewhere in the world as evidence of a widespread culture. Stonehenge, Old Owstrey, Carthage and Syracuse have all been suggested, but such comparisons have never been convincing. Diaz-Montexano has recently published(a) an image of a fragment of pottery found near Seville in Spain that shows concentric circles and insists that it is a symbol of Atlantis. Ulf Erlingsson has made a similar claim regarding some concentric circles carved on a stone basin found at Newgrange in Ireland.
Less well-known are the concentric stone circles that are to be found on the island of Lampedusa in the Strait of Sicily(b).
In 1969 two commercial pilots, Robert Brush and Trigg Adams photographed a series of large concentric circles in about three feet of water off the coast of Andros in the Bahamas. Estimates of the diameter of the circles range from 100 to 1,000 feet. Apparently, these rings are now covered by sand. It is hard to understand how such a feature in such very shallow water cannot be physically located and inspected. Richard Wingate in his book [0059] estimated the diameter at 1,000 yards. However, the rings described by Wingate were apparently on land, among Andros’ many swamps.
A recent (2023) report has drawn attention to the ancient rock art found on Kenya’s Mfangano Island where a number of concentric circles estimated as 4,000 years old can be seen(q).
Two papers presented to the 2005 Atlantis Conference on Melos describe how an asteroid impact could produce similar concentric rings, which, if located close to a coast, could be converted easily to a series of canals for seagoing vessels. The authors, Filippos Tsikalas, V.V. Shuvavlov and Stavros Papamarinopoulos gave examples of such multi-ringed concentric morphology resulting from asteroid impacts. Not only does their suggestion provide a rational explanation for the shape of the canals but would also explain the apparent over-engineering of those waterways.
At the same conference, the late Ulf Richter presented his idea [629.451], which included the suggestion that the concentric rings around the centre of the Atlantis capital had a natural origin. Richter has proposed that the Atlantis rings were the result of the erosion of an elevated salt dome that had exposed alternating rings of hard and soft rock that could be adapted to provide the waterways described by Plato.
Georgeos Diaz-Montexano has suggested that the ancient city under modern Jaen in Andalusia, Spain had a concentric layout similar to Plato’s description of Atlantis. In August 2016 archaeologists from the University of Tübingen revealed the discovery(i) of a Copper Age, Bell Beaker People site 50km east of Valencina near Seville, where the complex included a series of concentric earthwork circles.
A very impressive example of man-made concentric stone circles, known in Arabic as Rujm el-Hiri and in Hebrew as Gilgal Refaim(a), is to be found on the Golan Heights, now part of Israeli-occupied Syria. It consists of four concentric walls with an outer diameter of 160metres. It has been dated to 3000-2700 BC and is reputed to have been built by giants! Mercifully, nobody has claimed any connection with Atlantis. That is until 2018 when Ryan Pitterson made just such a claim in his book, Judgement of the Nephilim[1620].
Jim Allen in his latest book, Atlantis and the Persian Empire[877], devotes a well-illustrated chapter to a discussion of a number of ‘circular cities’ that existed in ancient Persia and which some commentators claim were the inspiration for Plato’s description of the city of Atlantis. These include the old city of Firuzabad which was divided into 20 sectors by radial spokes as well as Ecbatana and Susa, both noted by Herodotus to have had concentric walls. Understandably, Allen, who promotes the idea of Atlantis in the Andes, has pointed out that many sites on the Altiplano have hilltops surrounded by concentric walls. However, as he seems to realise that to definitively link any of these locations with Plato’s Atlantis a large dollop of speculation was required.
Rodney Castleden compared the layout of Syracuse in Sicily with Plato’s Atlantis noting that the main city “had seen a revolution in its defensive works, with the building of unparalleled lengths of circuit walls punctuated by numerous bastions and towers, displaying the city-state’s power and wealth. The three major districts of the city, Ortygia, Achradina and Tycha, were surrounded by three separate circuit walls; Ortygia itself had three concentric walls, a double wall around the edge and an inner citadel”.[225.179]
Dale Drinnon has an interesting article(d) on the ‘rondels’ of the central Danubian region, which number about 200. Some of these Neolithic features have a lot in common with Plato’s description of the port city of Atlantis. The ubiquity of circular archaeological structures at that time is now quite clear, but they do not demonstrate any relationship with Atlantis.
The late Marcello Cosci based his Atlantis location on his interpretation of aerial images of circular features on Sherbro Island, but as far as I can ascertain this idea has gained little traction.
One of the most remarkable natural examples of concentric features is to be found in modern Mauritania and is known as the Richat Structure or Guelb er Richat. It is such a striking example that it is not surprising that some researchers have tried to link it with Atlantis. Robert deMelo and Jose D.C. Hernandez(o) are two advocates along with George S. Alexander & Natalis Rosen who were struck by the similarity of the Richat feature with Plato’s description and decided to investigate on the ground. Instability in the region prevented this until late 2008 when they visited the site, gathering material for a movie. The film was then finalised and published on their then newly established website in 2010(l), where the one hour video in support of their thesis can be freely downloaded(m).
In 2008, George Sarantitis put forward the idea that the Richat Structure was the location of Atlantis, supporting his contention with an intensive reappraisal of the translation of Plato’s text(n). He developed this further in his Greek language 2010 book, The Apocalypse of a Myth[1470] with an English translation currently in preparation.
However, Ulf Richter has pointed out that Richat is too wide (35 km), too elevated (400metres) and too far from the sea (500 km) to be seriously considered as the location of Atlantis.
A dissertation by Oliver D.Smith has suggested(e) the ancient site of Sesklo in Greece as the location of Atlantis, citing its circularity as an important reason for the identification. However, there are no concentric walls, the site is too small and most importantly, it’s not submerged. Smith later decided that the Atlantis story was a fabrication!(p)
Brad Yoon has claimed that concentric circles are proof of the existence of Atlantis, an idea totally rejected by Jason Colavito(j).
In March 2015, the UK’s MailOnline published a generously illustrated article(g) concerning a number of sites with unexplained concentric circles in China’s Gobi Desert. The article also notes some 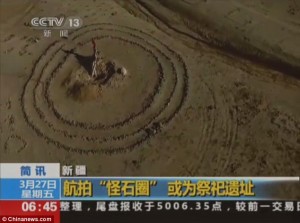 superficial similarities with Stonehenge. I will not be surprised if a member of the lunatic fringe concocts an Atlantis theory based on these images. (see right)
superficial similarities with Stonehenge. I will not be surprised if a member of the lunatic fringe concocts an Atlantis theory based on these images. (see right)
Paolo Marini has written Atlantide:Nel cerchio di Stonehenge la chiave dell’enigma (Atlantis: The Circle is the Key to the enigma of Stonehenge) [0713]. The subtitle refers to his contention that the concentric circles of Atlantis are reflected in the layout of Stonehenge!
In 2011 Shoji Yoshinori offered the suggestion that Stonehenge was a 1/24th scale model of Atlantis(f). He includes a fascinating image in the pdf.
This obsession with concentricity has now extended to the interpretation of ancient Scandinavian armoury in particular items such as the Herzsprung Shield(c).
For my part, I wish to question Plato’s description of the layout of Atlantis’ capital city with its vast and perfectly engineered concentric alternating bands of land and sea. This is highly improbable as the layout of cities is invariably determined by the natural topography of the land available to it(h). Plato is describing a city designed by and for a god and his wife and as such his audience would expect it to be perfect and Plato did not let them down. I am therefore suggesting that those passages have been concocted within the parameters of ‘artistic licence’ and should be treated as part of the mythological strand in the narrative, in the same way, that we view the ‘reality’ of Clieto’s five sets of male twins or even the physical existence of Poseidon himself.
Furthermore, Plato was a follower of Pythagoras, who taught that nothing exists without a centre, around which it revolves(k). A concept which may have inspired him to include it in his description of Poseidon’s Atlantis.
(b) Megalithic Lampedusa (archive.org)
(c) https://www.parzifal-ev.de/index.php?id=20
(d) See: Archive 3595
(e) https://atlantipedia.ie/samples/archive-3062/
(f) https://www.pipi.jp/~exa/kodai/kaimei/stonehenge_is_small_atrantis_eng.pdf
(i) First Bell Beaker earthwork enclosure found in Spain | ScienceDaily (archive.org) *
(j) https://www.jasoncolavito.com/blog/rings-of-power-do-concentric-circles-prove-atlantis-real
(k) Pythagoras and the Mystery of Numbers (archive.org)
(l) Visiting Atlantis | Gateway to a lost world (archive.org)
(m) https://web.archive.org/web/20171022134926/https://visitingatlantis.com/Movie.html
(n) https://platoproject.gr/system-wheels/ https://platoproject.gr/page13.html (offline Nov.2015)
(o) https://blog.world-mysteries.com/science/a-celestial-impact-and-atlantis/ (item 11)
(p) https://shimajournal.org/issues/v10n2/d.-Smith-Shima-v10n2.pdf
Architecture of Atlantis
The Architecture of Atlantis is described in such detail, that you can almost feel the ’buzz’ of a large maritime capital. We are left with the feeling that it is either the creation of a skilled writer or the report of an observant eyewitness. Once again, I am inclined to see it as an amalgam of both. Quite possibly the description is based on one of the models that have been suggested by some writers, such as Troy, Syracuse, Carthage or even Athens. In fact, elements from all these can be seen in Plato’s Atlantis.
The canals, bridges, watchtowers, warehouses and the acropolis, as described, would all have been within the experience of Plato or his associates.
H. R. Stahel a professional architect has published a book[560] illustrating the principal features of the city described by Plato.
Mention should be made of the dimensions ascribed by Plato to some of the architectural features of Atlantis, which appear to be exaggerated even for a sophisticated Late Bronze Age city. No matter how wealthy Atlantis may have been, the level of over-engineering suggested by Plato is not credible. However, Ulf Richter has recently provided a rational explanation for the apparently extravagant structures in the city by suggesting that the much shorter Egyptian khet rather than the Greek stade was the unit of measurement originally recorded by Solon.
For the record, I should mention that the earliest prehistoric archictecture was reported in 2012(a) after the remains of 20,000 year-old huts were discovered in Jordan. A decade ago, it was discovered that the Zarqa Valley, also in Jordan, has been inhabited and irrigated for 13,000 years(b), which is is close to the time of Göbekli Tepe!
>(a) https://www.world-archaeology.com/world/asia/jordan/20000-year-old-huts-in-jordan/ <
(b) https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2009/12/091215155956.htm
Allegory
An Allegory is the most common description of Plato’s Atlantis story offered by sceptics, eager to deny any historical value in the narrative. Parallels have been drawn with the Persian wars; Plato’s experiences in Syracuse and even more opaquely by Alan Alford, who proposed that “Atlantis – was an allegory for the myth of the creation of the Universe.”
Rand Flem-Ath quite reasonably argues that the idea of Atlantis as an allegory makes sense only if there is no realistic geographic explanation for Plato’s description of the site of the lost land. Consequently if an interpretation of the story can indicate a credible location and time for the destruction of Atlantis then the allegory theory is considerably weakened.
>>Last year (2023) Nikos Mavrakis from the UK’s University of Birmingham, School of Metallurgy and Materials published a paper(a) offering a new allegorical interpretation of Plato’s Atlantis story. He “argues that Plato’s account can be seen as a reply to the Greeks’ views, partly influenced by Herodotus’s Histories, that the Egyptian civilization was superior to theirs.” Mavrakis infers that Herodotus was in effect an Egyptian propagandist, a view he incorporates in the title of his paper.<<
If the Atlantis mystery is ever finally resolved, I am inclined to think that it will be found that Plato used the actual prehistoric destruction of a powerful civilisation as the core for his story and wrapped it in the details of events closer to his own time presenting the entire account as a morality tale.
Nevertheless, it is interesting that Plato’s ‘ideal state’ of Atlantis is claimed as the inspiration for both Sir Thomas More’s ‘Utopia’ and St. Augustine’s ‘City of God’ among many others.
Franke, Thorwald C.
Thorwald C. Franke was born in 1971 in Konstanz in southwest Germany. He studied computer science at the University of Karlsruhe and now works as a software developer. Since 1999 he has been promoting the idea of Atlantis having been located in Sicily. He has written a paper, which makes the case for identifying Atlas with king Italos of the Sicels, who was one of the first tribes to inhabit Sicily and gave their name to the island.
In October 2010, Franke announced that a part of his theory has some elements in it that require further research(f).
He believes that the war with the Atlanteans was recorded by the Egyptians as the conflict with the Sea Peoples of whom the Sicilians are generally accepted to have been part.
Franke has a well-presented website(a), in English and German, where he cogently outlines his views. He has also written a lengthy, 23-page paper on the need for a classification of Atlantis theories. Even though this item is in German, English readers may find it quite interesting using their browser’s translator. Franke has also compiled an extensive list of Atlantis-related websites(d) that he expanded further in a new format in October 2011.
His paper for the 2nd Atlantis Conference in Athens in 2008 is available on the Internet(c) in which he expanded on his Sicilian location for Atlantis.
 Franke has also published a book, in German[300] that focussed on Herodotus’ contribution to the Atlantis question(p). In the same paper, he dealt with the true meaning of the word ‘meizon‘ in Timaeus 24e which tells us that Atlantis was ‘greater’ than Asia and Libya combined, which he clarified as actually referring to their combined power rather than size. However, Franke proposed that the Egyptian word ‘wr’, whose primary meaning is ‘big’ and is sometimes used in a metaphorical sense, may have influenced the wording of the Greek text
Franke has also published a book, in German[300] that focussed on Herodotus’ contribution to the Atlantis question(p). In the same paper, he dealt with the true meaning of the word ‘meizon‘ in Timaeus 24e which tells us that Atlantis was ‘greater’ than Asia and Libya combined, which he clarified as actually referring to their combined power rather than size. However, Franke proposed that the Egyptian word ‘wr’, whose primary meaning is ‘big’ and is sometimes used in a metaphorical sense, may have influenced the wording of the Greek text
Then in a more recent (2010) book[706] regarding Aristotle and Atlantis, he disputes the generally perceived view that Aristotle did not accept the existence of Atlantis. He builds his case on an 1816 misinterpretation by a French mathematician, Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre, of a 1587 commentary on Strabo’s Geographica by Isaac Casaubon. Combined with other evidence he has presented a case that removes the only prominent classical writer alleged to have dismissed the existence of Atlantis. In late 2012 Franke published an English translation with the title of Aristotle and Atlantis[880]. Franke’s views regarding Aristotle have been well received and his book is frequently cited, most recently by Dhani Irwanto in his Atlantis: The Lost City is in the Java Sea[1093.110].
Franke has now augmented his book on Aristotle with a YouTube video in English(l) and German(m). This important book can now be read on the Researchgate website.(ae)
2012 also saw the publication, by Franke, of the first English translation of Gunnar Rudberg’s 1917 monograph Atlantis och Syrakusai, now Atlantis and Syracuse[881]. This is a welcome addition to Atlantis literature in English. Students of the Atlantis mystery owe a debt of gratitude to Herr Franke.
In 2006, Franke published a paper outlining Wilhelm Brandenstein’s contribution to Atlantology which in 2013 he published in English(g). This was followed by a translation(h) of his overview of the work of Massimo Pallattino, who had adopted some of Brandenstein’s approaches to the Atlantis question.
On the 30th of May 2013, Franke announced(i) that his Atlantis Newsletter, which until now was only available in German, in future will also be published in English. Today he discusses the antics of extremist Atlantis sceptics and the abuse of Wikipedia. I encourage everyone to register and congratulate Thorwald on this development.
There is also a video clip available of Franke showing his library of Atlantis-related books(e). 2017 has seen Franke produce a number of 30-minute videos, which readers will find informative. They are available in both German and English, (Just Google Plato’s Atlantis – Thorwald C. Franke – YouTube).
Franke has now (July 2013) revamped his website (https://www.atlantis-scout.de/)
More recently, July 2016 saw the publication, in German, of Kritische Geschichte der Meinungen und Hypothesen zu Platons Atlantis[1255] (Critical history of the hypotheses on Plato’s Atlantis). This tome of nearly 600 pages will undoubtedly be a valuable addition to any serious researcher’s library. There is a promotional video, in German, to go with it(j). Hopefully, an English translation of the book will follow. However, Franke does provide an English summary of the book(af). In June 2021, Franke announced the publication of the second edition of this remarkable book, but again, in German only. It is now in two volumes, totalling over 800 pages, which include hundreds of new references(y). Two publications in one week is a record to be proud of.
In June 2018, Franke published a YouTube video in English(r) and German(s) highlighting how Plato’s 9,000 years have been alternatively accepted and then rejected many times over since the time of Plato. Franke proposes that the 9,000 years recorded by Plato were comparable with the accepted age of Egypt in his day, at 11,00 years. However, archaeology has demonstrated that Egypt was only 3,000 years old or less when Plato was alive, suggesting that the 9,000 should be reduced by a comparable amount to arrive at the real-time of Atlantis.
In his Newsletter No.90, Franke has highlighted that a small German right-wing group, ‘Pro Deutschland’, has cited on their website the ‘superior civilisation’ of Atlantis in support of their extremist views.
Franke’s Newsletter No. 103 has now provided us with five parallel versions of the Atlantis texts(n), Two English; Jowett & Bury and Two German; Susemihl & Müller as well as a Greek text from the Scottish classicist John Burnet (1863 – 1928)[1492].
Franke’s Newsletter No.104 offers an overview of the difficulties involved in accepting Plato’s writings too literally(o). He gives particular attention to the 9,000 years claimed to have elapsed between the Atlantean War and Solon’s visit to Egypt.
In November 2017, Franke published an uncompromising critique(q) of Stephen P. Kershaw’s recent book, A Brief History of Atlantis[1410].
Franke has now published two new videos(t), in both German and English, in which he reviews a number of Atlantis-related books, both supportive and sceptical. He does so in his usual balanced manner and also exhorts students of Atlantology to learn German to have access to important works only available in that language.
The difficulty of independent researchers getting their work published in academic journals was highlighted by Franke some time ago(a). However, he has had some academic recognition(a) and has modified his view on the function of the academic press vis-á-vis independent writers(a).
>>An interesting paper by Franke entitled The Dark Side of Atlantis Scepticism(aq) was published in 2021, which outlines how scepticism has been used to promote such diverse subjects as false religious and political dogmas.<<
In June 2021, Franke announced the publication of his latest book(x). Platonische Mythen (Platonic Myths)[1858], currently in German only. In May 2022 a favourable review, also in German, of Franke’s book was published on the atlantisforschung.de website(ag). I have archived an English translation in atlantipedia.ie(ah).
The following month, Franke published Newsletter No.175 in which he accuses the Bryn Mawr Classical Review (BMCR) of scientific bias and inconsistency(z). The full Newsletter should be read but in particular his conclusions below.
“Let us sum up what we have: BMCR claims to accept no self-published books, but it did review such a book [mine-AO’C]. BMCR claims that it accepts only peer-reviewed books, but besides the question, of what this exactly means, they do indeed review books that were not peer-reviewed. BMCR claims to accept translations but did not accept the translation of Gunnar Rudberg [Franke’s]. BMCR claims to review bad Atlantis books of a certain intelligence in order to debunk them, but at the same time, they avoided a review of a bad book by an Atlantis sceptical Oxford scholar. They claim to treat every author with respect but failed to do so in my case, and not only once. And the same scholar who admits that his scientific view was impacted (!) by one of my books writes BMCR reviews about other Atlantis books, but my books are not reviewed. Long story short: BMCR acts in an arbitrary way and damages its credibility. They screwed up everything that can be screwed up. And it was not me who lead them up the garden path. They did that all by themselves.”
In Franke’s Newsletter No.158 published in early 2021, he reviewed a lecture, previously unknown to him, given by Heinz-Günther Nesselrath, in Bologna, a few years ago(aa) during which he apparently misrepresented Franke’s Atlantis theories. Shortly afterward Nesselrath issued a rather intemperate reply to Franke’s criticisms.(ab) A further document(ac) from Franke detailed his continuing annoyance with what he perceives as ‘a breach of trust’ on the part of Nesselrath. Now in August 2021, Nesselrath has reignited matters again with a further assault on Franke’s views(ad), many of which I share. In a further postscript dated 20.08.21(ab) Franke fired off a few more salvos. I think it’s time for an armistice?
However, in April 2023, Franke issued his Newsletter No. 212(ao), with the following introduction;
“Professor Heinz-Günther Nesselrath has once again written and published two PDF articles(ak)(al) to defend his Atlantis scepticism against the arguments brought up by me. One is directed against my internet article “The Dark Side of Atlantis Scepticism” from 2021, based on my book about the reception history of Plato’s Atlantis story from 2016/2021. The other one makes the attempt to undermine especially the literary arguments of Wilhelm Brandenstein, which I cultivated and will cultivate even more in my next publication.”
Franke responded with two papers(am)(an) that should be read in their entirety.
Franke’s Newsletter #193 reviews an interview with sceptic Flint Dibble(ai). He followed that in July 2022 (#194) with a critique of an article ‘Not Exactly Atlantis’ by Professor Carolina López-Ruiz that Franke identifies as over-dependent on the arguments of promoters of the ‘invention hypothesis’ particularly those of Pierre Vidal-Naquet and Diskin Clay. Franke then proceeded to offer a list of her many errors(aj).
>In January 2024, Franke published his Newsletter #215(ao) where he references a 2023 Graham Hancock lecture(ap) in which “He just takes the numbers in Plato’s text literally, and on this basis he makes his conclusions and calculations. He never asks the question, not for a second, that Plato’s numbers could be wrong. Wrong in a very typical and understandable way, when looking to the historical context. Because, all the ancient Greeks were wrong about the age of Egypt (where the Atlantis story allegedly, or really, had come from). They thought, Egypt was 10,000 years old, and older. But in fact, Egypt was founded only around 3,000 BC. Therefore, if an ancient Greek text points to an event 9,000 years before its time, of which it got to know from Egypt, this means in fact a time after 3,000 BC.
Once you realize this, the whole narrative of a prehistorical Ice Age civilization melts down to nothing, and a completely different picture of the Atlantis question appears.<
(a) http://www.thorwalds-internetseiten.de
(c) https://www.atlantis-scout.de/atlantis_sicily.htm
(d) https://www.atlantis-scout.de/atlanlinks.htm
(e) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5r2yDLEYfjA
(f) https://www.atlantis-scout.de/index_engl.htm
(g) https://www.atlantis-scout.de/atlantis_brandenstein_engl.htm
(h) https://www.atlantis-scout.de/atlantis_pallottino_engl.htm
(i) https://www.atlantis-scout.de/atlantis_newsl_archive.htm
(j) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y1orj7aqdTo
(k) https://www.atlantis-scout.de/atlantis_newsl_archive.htm
(l) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=inWb6IVNWFQ (English)
(m) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qDG7a09xkZE (German)
(n) https://www.atlantis-scout.de/atlantis-timaeus-critias-synopsis.htm
(o) https://www.atlantis-scout.de/atlantis-historical-critical-engl.htm
(p) https://www.atlantis-scout.de/Franke_Herodotus_Atlantis2008_Proceedings.pdf
(q) https://www.atlantis-scout.de/kershaw-brief-history-atlantis-review-engl.htm
(r) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=F2RlO_vhk8c
(s) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yb-24rxELnc
(u) https://www.atlantis-scout.de/atlantis-academic-journals-engl.htm
(v) https://www.atlantis-scout.de/atlantis-success-engl.htm
(w) https://www.atlantis-scout.de/atlantis_newsl_archive.htm
(x) & (y) https://www.amazon.de/Bücher-Thorwald-C-Franke/s?rh=n:186606,p_27:Thorwald+C.+Franke
(z) The scientific bias of the BMCR review – Atlantis-Scout
(aa) Review of: Heinz-Günther Nesselrath, News from Atlantis? 2017. (atlantis-scout.de) (See first half)
(ab) Review of: Heinz-Günther Nesselrath, News from Atlantis? 2017. (atlantis-scout.de) (See last half)
(ac) Severe breach of trust by Heinz-Günther Nesselrath (atlantis-scout.de)
(af) https://www.atlantis-scout.de/atlantis-geschichte-hypothesen.htm
(ag) Buchbesprechung: Thorwald C. Franke: Platonische Mythen – Atlantisforschung.de
(ah) Archive 7104 | (atlantipedia.ie)
(ai) Atlantis Newsletter Archive – Atlantis-Scout
(aj) Review of: Carolina López-Ruiz, Not Exactly Atlantis – Atlantis-Scout
(ao) https://www.atlantis-scout.de/atlantis_newsl_archive.htm
(ap) Graham Hancock: Beyond Ancient Apocalypse | Presentation @ Logan Hall, London – YouTube
(aq) (99+) The Dark Side of Atlantis Scepticism | Thorwald C. Franke – Academia.edu *

