Antonis Kontaratos
Poverty Point
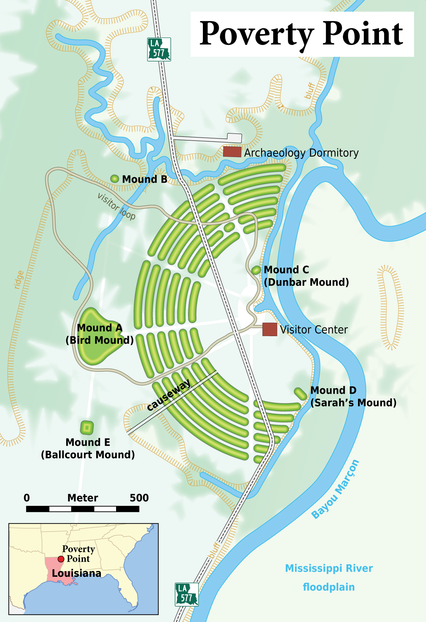
Poverty Point is an ancient site in north-eastern Louisiana with remarkable concentric ridges reminiscent of Plato’s description of Atlantis. Poverty Point is claimed as the remains of the oldest city in North America having been dated to around 1600 BC. Estimates have put the population of the city at 5-15,000 people at its greatest with two major influxes around 1600 and 1000 BC. It appears to have been suddenly abandoned and eventually covered with debris until it was discovered in 1950, when it was spotted from the air.
“The site is composed of some six C-shaped concentric ridges with each ring separated by a gulley. The ridges are all half circles. While the ridges range from 0.3 feet to 6 feet, they would have been much higher in the past as they have worn down over the many years. Much of the geometric design is hard to make out today on the ground, the scale and geometric design of the site only became apparent after aerial photographs were taken.“(e)
The purpose of the site is unknown, although various theories are put forward on a regular basis, one of which is that it was used as the world’s largest solstice marker(b)!
Frank Joseph suggests a definite link with the Atlanteans, claiming [0104.229] that “the site is fundamentally a mirror-image of Plato’s description of Atlantis, an identification reaffirmed by sudden cultural florescence at Poverty Point in 1200 BC, just when Atlantis was finally destroyed, and some of its survivors sought refuge in what is now America.”
The late Professor Antonis Kontaratos went further when he presented three papers [750.237] to the 2008 Atlantis Conference in Athens in which he expressed strong support for the American Hypothesis and that Poverty Point had been the capital of Plato’s Atlantis.
Gavin Menzies claimed [780.290] that Poverty Point was actually where the Minoans processed copper brought down the Mississippi from Michigan before transporting it back to the Mediterranean to feed the Bronze industries there! J.S. Wakefield expressed similar ideas, in great detail, in a 2015 article(d).
 It has also been suggested that the mounds of prehistoric Louisiana, including those at Poverty Point, were constructed as a protection against seasonal flooding!
It has also been suggested that the mounds of prehistoric Louisiana, including those at Poverty Point, were constructed as a protection against seasonal flooding!
Poverty Point has now been designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site of which there are less than 1,000 worldwide and only 24 in the United States (2019)(f). It also has an official website(h).
The results of a study of Mound A, published in the January 2013 edition of Geoarchaeology, have revealed that the structure was built in 90 days or less(a).
An extensive paper from 1996 by Jon L. Gibson is available online(c).
Dr Diana Greenlee of the University of Louisiana Monroe and station archaeologist at Poverty Point was involved in recent research that shows Poverty Point to be more complex than previously believed. Thanks to a 2019 Preservation Technology and Training Grant from the National Park Service, ULM and Minnesota State University Moorhead were able to use radar to send electromagnetic pulses into the earth, helping shed light on what lies below and between the mounds and ridges. What they discovered was a new ridge hidden underground and more information about the creation of the site(g).
Work continues at the site.
(b) https://www.messagetoeagle.com/is-the-poverty-point-octagon-worlds-largest-ancient-solstice-marker/
(c) Louisiana Archaeology Poverty Point Anthropological Study Series (archive.org)
(e) The History Of Poverty Point: One Of America’s Oldest Archeological Sites (thetravel.com)
(f) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_World_Heritage_Sites_in_the_United_States
(h) https://www.povertypoint.us/ *
Plutarchus, Mestrius
Mestrius Plutarchus (c. 46 – 119 AD), more generally known as Plutarch, was a Greek biographer and historian who produced  an impressive 227 works. His most important being Parallel Lives(a).
an impressive 227 works. His most important being Parallel Lives(a).
Although he wrote of Atlantis as if a historical fact, he does imply that Plato embellished the basic story and in the same passage, laments the fact that Plato died before finishing Critias. Plutarch also recorded that Solon learned the story of Atlantis from Psenophis of Heliopolis and Sonchis of Sais (Solon 26.1). These additional details have clearly added to the credibility of Plato’s narrative.
>“Plato, ambitious to elaborate and adorn the subject of the lost Atlantis, as if it were the soil of a fair estate unoccupied, but appropriately his by virtue of some kinship with Solon, began the work by laying out great porches, enclosures, and courtyards, such as no story, tale, or poesy ever had before. But he was late in beginning and ended his life before his work. Therefore the greater our delight in what he actually wrote, the greater our distress in view of what he left undone. For as the Olympieium in the city of Athens, so the tale of the lost Atlantis in the wisdom of Plato is the only one among many beautiful works to remain unfinished.” (Solon 32.1-2)<
He also mentions Saturnia as being around five days sailing west of Britain and added that westwards from that island, there were the three islands to where proud and warlike men used to come from the continent beyond the islands, in order to offer sacrifice to the gods of the ocean. Commentators have seen this as a possible reference to Atlantis or even America.
In recent years, particularly since Felice Vinci proposed a Baltic setting for Homer’s epics narratives The Illiad & The Odyssey there has been increased interest in Plutarch’s texts. Remarkably, the great majority of these commentators are Greek and all claim that early Greeks crossed the Atlantic, with some minor differences in details. All (Liritzis, Kontaratos, Koutlis, Mariolakos and Tsikritsis) cite Plutarch. One could be forgiven for thinking that there was a concerted attempt to wrest the claim of discovering America away from Columbus as well as the Vikings, Irish, Basques as well as the Welsh. However, Emilio Spedicato, an Italian, also supports the idea of Greek ancestors travelling to America and quotes Plutarch in support of the idea.
(b) When Does Plato’s Atlantis Stop Being Plato’s Atlantis? | Atlantis FYI *
Minoan Hypothesis
The Minoan Hypothesis proposes an Eastern Mediterranean origin for Plato’s Atlantis centred on the island of Thera and/or Crete. The term ‘Minoan’ was coined by the renowned archaeologist Sir Arthur Evans after the mythic King Minos. (Sir Arthur was the son of another well-known British archaeologist, Sir John Evans). Evans thought that the Minoans had originated in Northern Egypt and came to Crete as refugees. However, recent genetic studies seem to indicate a European ancestry!
It is claimed(a) that Minoan influence extended as far as the Iberian Peninsula as early as 3000 BC and is reflected thereby what is now known as the Los Millares Culture. Minoan artefacts have also been found in the North Sea, but it is not certain if they were brought there by Minoans themselves or by middlemen. The German ethnologist, Hans Peter Duerr, has a paper on these discoveries on the Academia.edu website(e). He claims that the Minoans reached the British Isles as well as the Frisian Islands where he found artefacts with some Linear A inscriptions near the site of the old German trading town of Rungholt, destroyed by a flood in 1362(f).
The advanced shipbuilding techniques of the Minoans are claimed to have been unmatched for around 3,500 years until the 1950s (l).
The Hypothesis had its origin in 1872 when Louis Guillaume Figuier was the first to suggest [0296] a link between the Theran explosion and Plato’s Atlantis. The 1883 devastating eruption of Krakatoa inspired Auguste Nicaise, in an 1885 lecture(c) in Paris, to cite the destruction of Thera as an example of a civilisation being destroyed by a natural catastrophe, but without reference to Atlantis.
The Minoan Hypothesis proposes that the 2nd millennium BC eruption(s) of Thera brought about the destruction of Atlantis. K.T. Frost and James Baikie, in 1909 and 1910 respectively, outlined a case for identifying the Minoans with the Atlanteans, decades before the extent of the massive 2nd millennium BC Theran eruption was fully appreciated by modern science. In 1917, Edwin Balch added further support to the Hypothesis [151].
As early as April 1909, media speculation was already linking the discoveries on Crete with Atlantis(h), despite Jowett’s highly sceptical opinion.
Supporters of a Minoan Atlantis suggest that when Plato wrote of Atlantis being greater than Libya and Asia he had mistranscribed meison (between) as meizon (greater), which arguably would make sense from an Egyptian perspective as Crete is between Libya and Asia, although it is more difficult to apply this interpretation to Thera which is further north and would be more correctly described as being between Athens and Asia. Thorwald C. Franke has now offered a more rational explanation for this disputed phrase when he pointed out [0750.173] that “for Egyptians, the world of their ‘traditional’ enemies was divided in two: To the west, there were the Libyans, to the east there were the Asians. If an Egyptian scribe wanted to say, that an enemy was more dangerous than the ‘usual’ enemies, which was the case with the Sea Peoples’ invasion, then he would have most probably said, that this enemy was “more powerful than Libya and Asia put together”.
It has been ‘received wisdom’ that the Minoans were a peace-loving people, however, Dr Barry Molloy of Sheffield University has now shown that the exact opposite was true(d) and that “building on recent developments in the study of warfare in prehistoric societies, Molloy’s research reveals that war was, in fact, a defining characteristic of the Minoan society, and that warrior identity was one of the dominant expressions of male identity.”
In 1939, Spyridon Marinatos published, in Antiquity, his opinion that the eruption of Thera had led to the demise of the Minoan civilisation. However, the editors forbade him to make any reference to Atlantis. In 1951, Wilhelm Brandenstein published a Minoan Atlantis theory, echoing many of Frost’s and Marinatos’ ideas, but giving little credit to either.
However, Colin MacDonald, an archaeologist at the British School in Athens, believes that “Thira’s eruption did not directly affect Knossos. No volcanic-induced earthquake or tsunami struck the palace which, in any case, is 100 meters above sea level.” The Sept. 2019 report in Haaretz suggests it’s very possible the Minoans were taken over by another civilization and may have been attacked by the Mycenaeans, the first people to speak the Greek language and they flourished between 1650 B.C. and 1200 B.C. Archaeologists believe that the Minoan and Mycenaean civilisations gradually merged, with the Mycenaeans becoming dominant, leading to the shift in the language and writing system used in ancient Crete.
The greatest proponents of the Minoan Hypothesis were arguably A.G. Galanopoulos and Edward Bacon. Others, such as J.V. Luce and James Mavor were impressed by their arguments and even Jacques Cousteau, who unsuccessfully explored the seas around Santorini, while Richard Mooney, the ‘ancient aliens’ writer, thought [0842] that the Minoan theory offered a credible solution to the Atlantis mystery. More recently Elias Stergakos has proposed in an overpriced 68-page book [1035], that Atlantis was an alliance of Aegean islands that included the Minoans.
Moses Finley, the respected classical scholar, wrote a number of critical reviews of books published by prominent supporters of the Minoan Hypothesis, namely Luce(aa), Mavor(y)(z) as well as Galanopoulos & Bacon(aa)(ab). Some responded on the same forum, The New York Review of Books.
Andrew Collins is also opposed to the Minoan Hypothesis, principally because “we also know today that while the Thera eruption devastated the Aegean and caused tsunami waves that destroyed cities as far south as the eastern Mediterranean, it did not wipe out the Minoan civilization of Crete. This continued to exist for several generations after the catastrophe and was succeeded by the later Mycenaean peoples of mainland Greece. For these reasons alone, Plato’s Atlantic island could not be Crete, Thera, or any other place in the Aegean. Nor can it be found on the Turkish mainland at the time of Thera’s eruption as suggested by at least two authors (James and Zangger) in recent years(ad).“
Alain Moreau has expressed strong opposition to the Minoan Hypothesis in a rather caustic article(i), probably because it conflicts with his support for an Atlantic location for Atlantis. In more measured tones, Ronnie Watt has also dismissed a Minoan Atlantis, concluding that “Plato’s Atlantis happened to become like the Minoan civilisation on Theros rather than to be the Minoan civilisation on Theros.” In 2001, Frank Joseph wrote a dismissive critique of the Minoan Hypothesis referring to Thera as an “insignificant Greek island”.(x)
Further opposition to the Minoan Hypothesis came from R. Cedric Leonard, who has listed 18 objections(q) to the identification of the Minoans with Atlantis, keeping in mind that Leonard is an advocate of the Atlantic location for Plato’s Island.
Atlantisforschung has highlighted Spanuth’s opposition to the Minoan Hypothesis in a discussion paper on its website. I have published here a translation of a short excerpt from Die Atlanter that shows his disdain for the idea of an Aegean Atlantis.
“Neither Thera nor Crete lay in the ‘Atlantic Sea’, but in the Aegean Sea, which is expressly mentioned in Crit. 111a and contrasted with the Atlantic Sea. Neither of the islands lay at the mouth of great rivers, nor did they “sink into the sea and disappear from sight.” ( Tim. 25d) The Aegean Sea never became “impassable and unsearchable because of the very shallow mud”. Neither Solon nor Plato could have said of the Aegean Sea that it was ‘still impassable and unsearchable’ or that ‘even today……….an impenetrable and muddy shoal’ ‘blocks the way to the opposite sea (Crit.108e). Both had often sailed the Aegean Sea and their contemporaries would have laughed at them for telling such follies.” (ac)
Lee R. Kerr is the author of Griffin Quest – Investigating Atlantis [0807], in which he sought support for the Minoan Hypothesis. Griffins (Griffons, Gryphons) were mythical beasts in a class of creatures that included sphinxes. Kerr produced two further equally unconvincing books [1104][1675], all based on his pre-supposed link between Griffins and Atlantis or as he puts it “whatever the Griffins mythological meaning, the Griffin also appears to tie Santorini to Crete, to Avaris, to Plato, and thus to Atlantis, more than any other single symbol.” All of which ignores the fact that Plato never referred to a Sphinx or a Griffin!
The hypothesis remains one of the most popular ideas with the general public, although it conflicts with many elements in Plato’s story. A few examples of these are, where were the Pillars of Heracles? How could Crete/Thera support an army of one million men? Where were the elephants? There is no evidence that Crete had walled cities such as Plato described. The Minoan ships were relatively light and did not require the huge harbours described in the Atlantis story. Plato describes the Atlanteans as invading from their western base (Tim.25b & Crit.114c); Crete/Santorini is not west of either Egypt or Athens
Gavin Menzies attempted to become the standard-bearer for the Minoan Hypothesis. In The Lost Empire of Atlantis [0780], he argues for a vast Minoan Empire that spread throughout the Mediterranean and even discovered America [p.245]. He goes further and claims that they were the exploiters of the vast Michigan copper reserves, which they floated down the Mississippi for processing before exporting it to feed the needs of the Mediterranean Bronze industry. He also accepts Hans Peter Duerr’s evidence that the Minoans visited Germany, regularly [p.207].
Tassos Kafantaris has also linked the Minoans with the exploitation of the Michigan copper, in his paper, Minoan Colonies in America?(k) He claims to expand on the work of Menzies, Mariolakos and Kontaratos. Another Greek Professor, Minas Tsikritsis, also supports the idea of ancient Greek contact with America. However, I think it is more likely that the Minoans obtained their copper from Cyprus, whose name, after all, comes from the Greek word for copper.
Oliver D. Smith has charted the rise and decline in support for the Minoan Hypothesis in a 2020 paper entitled Atlantis and the Minoans(u).
Frank Joseph has criticised [0802.144] the promotion of the Minoan Hypothesis by Greek archaeologists as an expression of nationalism rather than genuine scientific enquiry. This seems to ignore the fact that Figuier was French, Frost, Baikie and Bacon were British, Luce was Irish and Mavor was American. Furthermore, as a former leading American Nazi, I find it ironic that Joseph, a former American Nazi leader, is preaching about the shortcomings of nationalism.
While the suggestion of an American connection may seem far-fetched, it would seem mundane when compared with a serious attempt to link the Minoans with the Japanese, based on a study(o) of the possible language expressed by the Linear A script. Gretchen Leonhardt(r) also sought a solution in the East, offering a proto-Japanese origin for the script, a theory refuted by Yurii Mosenkis(s), who promotes Minoan Linear A as proto-Greek. Mosenkis has published several papers on the Academia.edu website relating to Linear A(t). However, writing was not the only cultural similarity claimed to link the Minoans and the Japanese offered by Leonhardt.
Furthermore, Crete has quite clearly not sunk beneath the waves. Henry Eichner commented, most tellingly, that if Plato’s Atlantis was a reference to Crete, why did he not just say so? After all, in regional terms, ‘it was just down the road’. The late Philip Coppens was also strongly opposed to the Minoan Hypothesis.(g)
Eberhard Zangger, who favours Troy as Atlantis, disagrees strongly [0484] with the idea that the Theran explosion was responsible for the 1500 BC collapse of the ‘New Palace’ civilisation.
Excavations on Thera have revealed very few bodies resulting from the 2nd millennium BC eruptions there. The understandable conclusion was that pre-eruption rumblings gave most of the inhabitants time to escape. Later, Therans founded a colony in Cyrene in North Africa, where you would expect that tales of the devastation would have been included in their folklore. However, Eumelos of Cyrene, originally a Theran, opted for the region of Malta as the remnants of Atlantis. How could he have been unaware of the famous history of his family’s homeland?
A 2008 documentary, Sinking Atlantis, looked at the demise of the Minoan civilisation(b). James Thomas has published an extensive study of the Bronze Age, with particular reference to the Sea Peoples and the Minoans(j).
In the 1990s, art historian and museum educator, Roger Dell, presented an illustrated lecture on the art and religion of the Minoans titled Art and Religion of the Minoans: Europe’s first civilization”, which offered a new dimension to our understanding of their culture(p). In this hour-long video, he also touches on the subject of Atlantis and the Minoans.
More extreme is the theory of L. M. Dumizulu, who offers an Afrocentric view of Atlantis. He claims that Thera was part of Atlantis and that the Minoans were black!(m)
In 2019, Nick Austin attempted [1661] to add further support to the idea of Atlantis on Crete, but, in my opinion, he failed.>>His book is now available online(ai) along with a related paper(aj).<<
The following year, Sean Welsh also tried to revive the Minoan Hypothesis in his book Apocalypse [1874], placing the Atlantean capital on Santorini, which was destroyed when the island erupted around 1600 BC. He further claims that the ensuing tsunami led to the biblical story of the Deluge.
Evan Hadingham published a paper(v) in 2008 in which he discussed the possibility that the Minoan civilisation was wiped out by the tsunami generated by the eruption(s) of Thera. Then, seven years later he produced a second paper(w) exonerating the tsunami based on new evidence or lack of it.
In April 2023, an attempt was made to breathe some new life into the Minoan Hypothesis in an article(ae) on the Greek Reporter website. This unconvincing piece claims “Plato describes in detail the Temple of Poseidon on Atlantis, which appears to be identical to the Palace of Knossos on the island of Crete.” The writer, Caleb Howells, has conveniently overlooked that Atlantis was submerged creating dangerous shoals and remained a maritime hazard even up to Plato’s day (Timaeus 25d). The Knossos Palace is on a hill and offers no evidence of ever having been submerged. Try again.
The same reporter did try again with another unconvincing piece supporting the Minoan Hypothesis, also on the Greek Reporter site, in October 2023(af). This time, he moved the focus of his claim to Santorini where he now placed the Palace of Poseidon relocating it from Crete! I suppose he will eventually make his mind up. Nevertheless, Howells revisited the subject of the Palace of Poseidon just a few weeks later, once again identifying it as the Palace of Knossos – “Plato’s account of the lost civilization of Atlantis includes a description of a marvelous temple of god Poseidon. It was said to have been in the center of Atlantis, so it was a very prominent part. However, in most investigations into the origin of Atlantis, this detailed temple description is ignored. In fact, an analysis of Plato’s details indicates that the Temple of Poseidon on Atlantis was actually identical to the Palace of Knossos on the island of Crete, Greece.” (ag)
Most Atlantis theories manage to link their their chosen site with some of the descriptive details provided by Plato. The Minoan Hypothesis is no exception, so understandably Howells has highlighted the similarities, while ignoring disparities. The Minoans were primarily concerned with trading, not territorial expansion. When did they engage in a war with Athens or threaten Egypt? If Howells can answer that he may have something relevant to build upon!
For a useful backdrop to the Minoan civilisation I suggest that readers have a look at a fully illustrated 2019 lecture by Dr. Gregory Mumford of the University of Alabama at Birmingham. In it he give a broad overview of the Eastern Mediterranean, with a particular emphasis on the Aegean Sea, during the Middle- Late Bronze Age (2000-1200 BC). (ah)
(a) http://www.minoanatlantis.com/Minoan_Spain.php
(b) http://video.pbs.org/video/1204753806/ (Link broken)
(c) http://fr.wikisource.org/wiki/Les_Terres_disparues
(d) http://www.sci-news.com/archaeology/article00826.html
(e) See: Archive 3928
(f) http://dienekes.blogspot.ie/2008/08/minoans-in-germany.html
(g) https://web.archive.org/web/20180128190713/http://philipcoppens.com/lectures.php (June 3, 2011)
(j) https://medium.com/the-bronze-age
(k) GREECE AND WORLD: Minoan colonies in America?
(m) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QqTQeF2gLpg
(o) Archive 3930 | (atlantipedia.ie)
(p) https://vimeo.com/205582944 Video
(q) https://web.archive.org/web/20170113234434/http://www.atlantisquest.com/Minoan.html
(r) https://konosos.net/2011/12/12/similarities-between-the-minoan-and-the-japanese-cultures/
(t) https://www.academia.edu/31443689/Researchers_of_Greek_Linear_A
(u) https://www.academia.edu/43892310/Atlantis_and_the_Minoans
(v) Did a Tsunami Wipe Out a Cradle of Western Civilization? | Discover Magazine
(w) https://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/article/megatsunami-may-wiped-europes-first-great-civilization/
(x) Atlantis Rising magazine #27 http://pdfarchive.info/index.php?pages/At
(y) Wayback Machine (archive.org)
(z) https://www.nybooks.com/articles/1969/12/04/back-to-atlantis-again/
(aa) Back to Atlantis | by M.I. Finley | The New York Review of Books (archive.org)
(ab) The End of Atlantis | by A.G. Galanopoulos | The New York Review of Books (archive.org)
(ac) Jürgen Spanuth über ‘Atlantis in der Ägäis’ – Atlantisforschung.de
(ad) Kreta oder Thera als Atlantis? – Atlantisforschung.de (atlantisforschung-de.translate.goog)
(ae) Was Atlantis’ Temple of Poseidon the Palace of Knossos in Crete? (greekreporter.com)
(af) Was Atlantis a Minoan Civilization on Santorini Island? (greekreporter.com)
(ag) https://greekreporter.com/2023/12/01/atlantis-temple-poseidon-palace-knossos-crete/
(ai) https://www.academia.edu/44267221/Atlantis_the_evidence?email_work_card=view-paper *
(aj) (99+) Atlantis the evidence | Nick Austin – Academia.edu *
Linforth, Ivan (L)
Ivan Linforth (1879-1976) was a renowned American Hellenist scholar, who was Professor of Greek Studies at the University of California. In his Solon the Athenian[045] he controversially expressed the view that Plato himself brought the Atlantis story back to Athens and that the introduction of Solon into the provenance of the tale was “a literary device”.
To me, this seems highly improbable, as it would require Plato to lie and then implicate the highly regarded Solon in the same untruth. Then, for good measure, claim that his own family was complicit in transmitting this account from Solon to him. If this is the best that a scholar could come up with, I despair. Plato wrote Timaeus and Critias in his old age, not a time when a highly respected person normally resorts to lying.
Compounding this is the fact that the late Antonis Kontaratos identified an unprecedented twenty-two instances in the Atlantis narrative where Plato, directly or indirectly, claims the story to be true.
Atlantis Conference – 2005
The Atlantis Conference – 2005 was addressed by a wide range of speakers who hold many conflicting theories regarding the truth behind Plato’s story. It was held on the Aegean island of Melos, which Dr. Galanopoulos suggested had been named after Eumelos, the brother of Atlas, king of Atlantis.
The conference concluded with agreement on a list of 24 criteria, which any proposed site must meet to qualify as a site where Atlantis could have existed:
1. The Metropolis of Atlantis should have been located where an island used to be and where parts of it may still exist.
2. The Metropolis of Atlantis should have had a most distinct geomorphology composed of alternating concentric rings of land and water.
3. The Atlantis should have been located outside the Pillars of Hercules.
4. The Metropolis of Atlantis was greater than Libya and Anatolia and Middle East and Sinai (combined).
5. Atlantis must have sheltered a literate population with metallurgical and navigational skills.
6. The Metropolis of Atlantis should have been routinely reachable from Athens by sea.
7. At the time, Atlantis should have been at war with Athens.
8. The Metropolis of Athens must have suffered a devastating physical destruction of unprecedented proportions.
9. The Metropolis of Atlantis should have sunk entirely or partly below the water.
10. The Metropolis of Atlantis was destroyed 9000 Egyptian years before the 6th century B.C.
11. The part of Atlantis was 50 stadia (7.5 km) from the city.
12. Atlantis had a high population density, enough to support a large army (10,000 chariots, 1,200 ships, 1,200,000 hoplites)
13. The region of Atlantis involved the sacrifice of bulls.
14. The destruction of Atlantis was accompanied by an earthquake.
15. After the destruction of Atlantis, the passage of ships was blocked.
16. Elephants were present in Atlantis.
17. No physically or geologically impossible processes were involved in the destruction of Atlantis.
18. Hot and cold springs, with mineral deposits, were present in Atlantis.
19. Atlantis lay on a coastal plain 2000 x 3000 stadia surrounded by mountains falling into the sea.
20. Atlantis controlled other states of the period.
21. Winds in Atlantis came from the north (only in Northern hemisphere)
22. The rocks in Atlantis were of various colours: black, white, and red.
23. There were canals for irrigation in Atlantis.
24. Every 5th and 6th year, they sacrificed bulls.
While it is interesting that a majority of the gathering supported a list of this nature, many of the individual points will be considered highly contentious by a number of investigators. For my part I see the principal flaw with the list is that it is built on the assumption that all of what Plato wrote is factual and not mythological and does not contain any errors or embellishments.
Jim Allen is also unhappy with aspects of this list and has expanded it by a further 26 criteria giving us a round 50 identification elements(a). Allen then applies this list to 24 Atlantis theories and surprise, surprise, all theories fail except his Andean theory. This expanded list includes all the original flaws plus new ones introduced to bolster Allen’s Bolivian theory.
This 2005 Conference is also notable for the contribution of Antonis Kontaratos, who used the occasion to list the twenty-two instances, both directly and indirectly, where Plato points to the Atlantis story as true.
The proceedings of the conference were subsequently published, in English, in a substantial and valuable volume, edited by Stavros Papamarinopoulos, entitled The Atlantis Hypothesis: Searching for a Lost Land[0629].
>(a) https://web.archive.org/web/20170724234247/http://www.atlantisbolivia.org/beyond24points.htm<
America *
America as the home of Atlantis took off as an idea shortly after its discovery (or perhaps more correctly, rediscovery) by Columbus. Initially, reports sent back to Europe designated America as ‘Paradise’ 
until its identification as Atlantis quickly took hold. John Dee in the time of Elizabeth I was convinced that the newly discovered Americas were in fact, Atlantis, an idea endorsed by Francis Bacon. The first time that America was so named on a map was on the 1507(c) Waldseemüller map, sometimes referred to as “America’s birth certificate.” A rare copy of this map was recently found in Germany(e).
Nevertheless, from the early 1600’s dissenting voices were raised, such as those of José de Acosta, and Michel de Montaigne.
As late as 1700, a map of the world by Edward Wells was published in Oxford that highlights the paucity of information regarding the Americas at that time. However, in this instance the accompanying text notes that “this continent with the adjoining islands is generally supposed to have been anciently unknown though there are not wanting some, who will have even the continent itself to be no other than the Insula Atlantis of the ancients.”
For over five centuries a variety of commentators have associated Atlantis with America and many of its ancient cultures together with a range of location theories that stretch from Maine through the Caribbean and Central America to Argentina.
Although most proponents of an American Atlantis, particularly following the continent’s discovery, did not specify a location but were happy to consider the Americas in their entirety as Plato’s lost land. In 2019, Reinoud de Jonge published a paper declaring that from 2500-1200 BC America had been an Egyptian colony. He expanded on this in 2912(l), when he claimed that the American colonies, North and South had supplied the copper and tin for the Bronze Age of the Mediterranean. For good measure, he threw in a wildly speculative translation of the Phaistos Disk to support these contentions.
Over time attention was more focused on Mesoamerica and the northern region of South America, where the impressive remains of the Maya and Incas led many to consider them to be Atlantean.
North America received minimal attention until the 19th century when an 1873 newspaper report(i) claimed that there was support from unnamed scientists for locating remnants of Atlantis in the Adirondacks and some of the mountains of Maine! More recently Dennis Brooks has advocated Tampa Bay, Florida, while John Saxer supports Tarpon Springs, also in Florida as Atlantean. To confuse matters further, Mary Sutherland locates Atlantis in the Appalachian Mountains of Kentucky and for good measure suggests that King Solomon’s mines are to be found in the same region!
For example, the discovery of the remains of the remarkable cultures of Mesoamerica generated speculation on the possibility of an Atlantean connection there. This view gained further support with the publication of Ignatius Donnelly’s groundbreaking work on Atlantis.
Some have seen an Atlantic location for Atlantis as a conduit between the culture of ancient Egypt and that of Meso-America(d).
Half a century ago Nicolai Zhirov claimed that Plato had knowledge of America [458.22] indicated by his statement that Atlantis was in a sea with a continent encompassing it. He thought that this was the earliest record of a continent beyond the Atlantic.
However, Plato also said that Atlantis was surrounded ‘on all sides’ by this continent, which is not compatible with the Azores, advocated by Zhirov as the location of Plato’s sunken island. In an effort to strengthen this claim Zhirov also claims that there is evidence that King Sargon of Akkad travelled to America in the middle of the third millennium BC, an idea that has gained little traction.
The idea of Sumerians in America was promoted by A.H. Verrill and his wife Ruth, who claimed [838] that King Sargon travelled to Peru, where he was known as Viracocha. The Verrills support their contention with a range of cultural, linguistic and architectural similarities between the Sumerians and the Peruvians.
More recently, Andrew Collins has promoted the idea of Atlantis in the Caribbean, specifically Cuba. Followers of Edgar Cayce are still expecting the Bahamas to yield evidence of Plato’s island. Gene Matlock supports the idea of a Mexican location with an Indian connection, while Duane McCullough opts for Guatemala. Ivar Zapp and George Erikson have also chosen Central America for investigation. Further south Jim Allen has argued strongly for Atlantis having been located on the Altiplano of Bolivia. A website entitled American Atlantis Research from Edward Alexander , now offline, was rather weak on content and irritatingly referred to the ‘Andies’.
Although much of what has been written about an American location for Atlantis is the result of serious research, it all falls far short of convincing me that the Atlantis of which Plato wrote is to be found there. No evidence has been produced to even hint that any American culture had control of the Mediterranean as far Tyrrhenia in the north and Libya in the south. No remains or carvings of triremes or chariots have been found in the Americas. How could an ancient civilisation from America launch an attack across the Atlantic and at the furthest end of the Mediterranean 9,000 or even 900 years before Solon? An even more important question is, why would they bother? There is no evidence of either motive, means or opportunity for an attack from that direction.
A number of Plato’s descriptions of Atlantis would seem to rule out America as its location.
(a) As mentioned above, the ‘opposite continent’ referred to by Plato (Timaeus 25a) is described as encompassing the sea in which Atlantis lay. America cannot be described as enclosing the Atlantic. Around 550 AD, Procopius noted that when viewed from the southern side of the Strait of Gibraltar “the whole continent opposite this was named Europe”(m) (not America)!
(b) The Greeks only knew of three continents, Europe, Asia and Libya. Armin Wolf, the German historian, when writing about Scheria relates(f) that “Even today, when people from Sicily go to Calabria (southern Italy) they say they are going to the “continente.” I suggest that Plato used the term in a similar fashion and was quite possibly referring to that same part of Italy which later became known as ‘Magna Graecia’. Robert Fox in The Inner Sea[1168.141] confirms that this long-standing usage of ‘continent’ refers to Italy.
(c) Herodotus described Sardinia as “the biggest island in the world” (Hist.6.2). In fact Sicily is marginally larger but as islands were measured in those days (Felice Vinci) [019] by the length of their coastal perimeter Herodotus was correct. Consequently, it can be argued that since Cuba and Hispaniola are much more extensive than Sardinia, the Greeks had no knowledge of the Caribbean.
(d) Plato makes frequent references to horses in Atlantis. The city itself had a track for horseracing (Critias 117c). The Atlanteans had thousands of chariots (Critias 119a). The Atlanteans even had horse baths (Critias 117b). All these references make no sense if Plato was describing an American Atlantis as there were no horses there for over 12,000 years, when they died out, until brought back by the Spaniards millennia later. Furthermore, it makes even less sense if you subscribe to the early date (9600 BC) for Atlantis as it is thousands of years before we have any evidence for the domestication of the horse, anywhere.
A recent study of worldwide DNA patterns suggests that “no more than 70 people inhabited North America 14,000 years ago.”(b) But a more important claim has been offered by Professors Jennifer Raff and Deborah Bolnick who have co-authored a paper offering evidence(j) that the genetic data only supports a migration from Siberia to America. This certainly runs counter to any suggestion of transatlantic migration from Europe.In 1900,
Peter de Roo put forward the idea that the ancient Greeks had knowledge of America, despite the fact that Herodotus clearly said that only three continents were known to them [Histories 4.42]. A 2013 book, L’America dimenticata [1060], by Italian physicist and philologist Lucio Russo, also claims that the ancient Greeks had knowledge of America and it was gradually forgotten because of mistakes made by Ptolemy including a 15-degree error for the latitude of the Canaries(g).
However, the idea that the Greeks had an awareness of America persists, with some claiming that they had colonies in Canada. Among these are Lucio Russo, Ioannis Liritzis(n) and Minas Tsikritsis(p). Manolis Koutlis has gone one further and claims that not only were there Greek Colonies in Canada but that Atlantis had been situated in the Gulf of St. Lawrence(o).
The late Professor Antonis Kontaratos placed the capital of Atlantis at Poverty Point in Louisiana or it at least inspired some of Plato’s description since “there is also solid evidence that the Greeks were travelling to America in prehistoric times too and could have witnessed firsthand the impressive earthworks at Poverty Point, information which could have reached Plato independently as a fading legend [0750].” Kontaratos cited Plutarch to support his contention of Greek transatlantic travel in prehistory.
I note that there is a suspiciously disproportionate number of Greeks supporting the idea of pre-Columbian Hellenic visitors to America!
While there is extensive debate regarding the Americas being visited by ancient Greeks (Minoans), Phoenicians and even Sumerians, there seems little doubt that America had been visited by various other peoples prior to Columbus such as Welsh, Vikings or Irish. The case for the latter is strengthened by a 500-year-old report(h) of a long-established Irish colony in North America called Duhare.
America as Atlantis and the source of freemasonry knowledge was recently repackaged in a brief article on the Odyssey website(k) quoting Manly P. Hall who in turn cited Plato and Sir Francis Bacon. It then proceeds to speculate on what lessons the story of this original American Atlantis offers the America of today!
(c) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Waldseem%C3%BCller_map
(d) https://www.africaspeaks.com/reasoning/index.php?topic=5106.0
(f) Wayback Machine (archive.org)
(g) Reconsidering History: Ancient Greeks Discovered America Thousands of Years Ago (archive.org) *
(j) https://phys.org/news/2016-01-genetic-ancient-trans-atlantic-migration-professor.html
(k) https://www.theodysseyonline.com/america-as-atlantis
(l) https://www.academia.edu/3894415/COPPER_AND_TIN_FROM_AMERICA_c.2500-1200_BC_
(m) Vandal Wars 1.1.7
(n) https://www.hakaimagazine.com/news/did-ancient-greeks-sail-to-canada/
Oera Linda Book
The Oera Linda Book, sometimes referred as the Ura-Linda Chronicle, is a highly controversial book from Holland that occasionally is referred to in books and articles relating to Atlantis. It is claimed to be one of the oldest books ever discovered.
The Oera Linda Book came to light in 1867 when Cornelis Over de Linden (1811–1874) handed the manuscript, which he claimed to have inherited from his grandfather, via his aunt, over to Eelco Verwijs (1830–1880), the provincial librarian of Friesland, for translation and publication. Verwijs rejected the manuscript, but in 1871 Jan Gerhardus Ottema (1804–1879), a prominent member of the Frisian Society for History and Culture, published a Dutch translation. Ottema believed it to be written in authentic Old Frisian(r).
While a Dutch translation appeared in 1871, it was not until 1876 that the first English translation of the Oera Linda Book by William R. Sandbach was published by Trubner & Co(k). This was allegedly a translation of a 13th-century Frisian manuscript based on much earlier traditions.
The book tells the story of the destruction of a large landmass in the North Sea known as ‘Atland’ following earthquakes and tidal waves. Atland means Old Land in Frisian. It dates this catastrophe to 2193 BC. However, the current consensus is that the landbridge between the Shetlands Isles and Norway was submerged around 5500 BC and not the date given in the Oera Linda Book.
Nearly seventy years were to pass before the book came under scrutiny again in Britain, when Harold T. Wilkins wrote an article in Egerton Sykes’ first issue of Atlantis magazine, supporting its authenticity. Thirty years later another English writer, Robert Scrutton, wrote two books[117][118] on the Oera Linda Book. These again opened up the controversy regarding the authenticity of the book.
Andrew Collins has written a short paper(g) casting doubt on the authenticity of the book.
Now Anthony Radford presents a new review of the Book and offers the first edition of his book free online (f).
Andi Zeneli, the Albanian researcher, has used the text of the Oera Linda Book in an attempt to support his claim of an Albanian connection with Atlantis. Georg Lohle also follows the Oera Linda Book in suggesting[446] a North Sea location for Atlantis(s)*.
The English text of the book is available on the internet(b)(c) with the original 212 Frisian language pages, which is accessible on a Dutch site(d). A recent (2012) vindication of the OLB is now available online(h).
It is reported(p) that when Heinrich Himmler was given a translation of the OLB by his friend Hermann Wirth he was totally besotted with its contents and it became known as ‘Himmler’s Bible’. However, even within the Nazi party, there were many sceptical voices, which led to much dispute. Finally, “The two opposing camps officially “squared off” during a panel discussion centred on The Oera Linda Book that took place on May 4th 1934 at the aforementioned University of Berlin. The discussion turned into a heated debate, but in the end, The Oera Linda Book was officially declared “a hoax” by the NSDAP, and “Himmler’s Bible” receded once again into obscurity.”
I must mention that the American neo-Nazi National Socialist Movement has taken an interest in the Oera Linda Book(e), promoting it as ‘positive’ reading material!
The late Antonis Kontaratos was favourably disposed to quote the OLB in support of Atlantis, in a paper delivered to the 2005 Atlantis Conference [629.435], although he also noted that “the authenticity of the Oera Linda Book still awaits official approval or disapproval”.
Alewyn J. Raubenheimer has theorised[744] that an asteroid impact created the Burckle Crater in the Indian Ocean which in turn generated a megatsunami recorded in the bible as Noah’s Flood and in the Oera Linda Book as the flooding of Atland in 2193 BC. With regard to Atlantis he states categorically (p.49)“that no attempt is made here to equate Atland with Atlantis although there may be a connection.” His defence of the Oera Linda Book has been hailed by some as an important scholarly contribution(i) while others have endeavoured to discredit the book’s authenticity(j).
James Nienhuis also accepts the historicity of the OLB(n), but today’s leading proponent of its authenticity is arguably Jan Ott, a Dutch researcher, born in West Friesland, who has released video and audio interviews on YouTube(l)(m) in support of his views. A list of all translations of the OLB can be accessed on his website(o) as well as many other aspects of Oera Linda studies. Ott has been interviewed on Red Ice Radio, a Swedish right-wing broadcaster.
A 2022 critical review of the OLB by an Indian researcher, Bipin Dimri, added support to the more generally accepted view that the OLB is a forgery. He suggests that “Either Cornelis Over de Linden or Eelco Verwijs (or possibly an acquaintance of both men) are the two most likely authors, writing a comedy text to poke fun at an overtly nationalistic audience in the late 19th century. It was likely never to be taken seriously(q).
>The Oera Linda Foundation is a Dutch organisation founded in 2020. Its Dutch/English website(t) aims to support the authenticity of the OLB. This interesting website, includes a forum, a wiki and up-to-date translations of the Book.<
(b) https://archive.org/stream/oeralindabookfr00sandgoog#page/n40/mode/2up
(c) https://www.earth-history.com/Europe/index.htm
(d) https://archive.org/details/oeralindabookfr00ottegoog
(f) https://earth-history.com/Europe/God-king/radford-intro.htm
(g) https://www.andrewcollins.com/page/interactive/northeur.htm
(h) https://www.historum.com/speculative-history/36777-oera-linda-book-7.html
(i) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Talk%3AOera_Linda_Book
(j) https://spiritualitydiscussiongroup.yuku.com/topic/793/The-Oera-Linda-Book (link broken)*
(k) https://www.google.co.uk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=4&ved=0CDgQFjAD&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.forgottenbooks.org%2Fdownload_pdf%2FThe_Oera_Linda_Book_1000847682.pdf&ei=vhw3U9WULZDT7Abd34GIBA&usg=AFQjCNHcQ7T8MwZfRDYovr0BdftweYTKBA&bvm=bv.63808443,d.ZGU
(l) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kflHJpB9f1s
(m) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3CAoZS52CoU
(o) https://fryskednis.blogspot.ie/2017/12/inventory-of-earlier-oera-linda.html
(p) https://joshualightningwarrior.wordpress.com/2018/03/17/the-fryan-question-part-i/
(q) https://www.historicmysteries.com/oera-linda/
(r) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oera_Linda_Book
Shermer, Michael
Michael Shermer (1954- ) is the founding publisher of Skeptic magazine and Skeptic.com. For eighteen years he wrote the ‘skeptic’ column for Scientific American(h).
Suffering as he does from terminal scepticism, Shermer could not resist offering his views on Atlantis(a), which  basically assume that Plato created the myth of Atlantis to support his political philosophy. This idea has been put forward by many sceptics. However, nobody seems to have suggested that while Plato may have been promoting his political philosophy with the Atlantis story, there is absolutely no reason why he could not have been using real historical events to achieve the same result. This explains how the late Professor Antonis Kontaratos was able to point out at the 2005 Atlantis Conference that Plato states directly and indirectly, twenty-two times, in both Timaeus & Critias, that the story of Atlantis is true [629.79].
basically assume that Plato created the myth of Atlantis to support his political philosophy. This idea has been put forward by many sceptics. However, nobody seems to have suggested that while Plato may have been promoting his political philosophy with the Atlantis story, there is absolutely no reason why he could not have been using real historical events to achieve the same result. This explains how the late Professor Antonis Kontaratos was able to point out at the 2005 Atlantis Conference that Plato states directly and indirectly, twenty-two times, in both Timaeus & Critias, that the story of Atlantis is true [629.79].
I should note here the comment of Martin Ebon that “the narrative, unlike the Republic, espouses no particular theory and reads more like historical fact, however confusing, than a myth.”[286.16]
Shermer does accept that Plato mixed history with myth but does not suggest how we might separate the two, instead, he is content to dispose of both baby and bath-water. I consider fatuous, his comment that “Plato’s Atlantean dialogues are essentially an ancient Greek version of Star Wars.” This silly comparison was recently (2018) echoed on an Australian website(d).
Georgeos Diaz-Montexano responded to Shermer’s views with a 2005 article, contentiously entitled Errors, Fallacies and Lies.
Shermer wrote an article(b) for Scientific American (Jan.1.2016) on the subject of ‘Homo Naledi, which generated a highly critical response, noting that “Shermer preferred to speculate without evidence and publish an essay without fact-checking.” Even Shermer nods!
>Some years ago Rod Martin wrote a short but interesting paper grading the arguments of some of the better-known Atlantis sceptics, such as Shermer and Kevin Christopher(i)
In a 2017 article in Scientific American, Shermer offered a highly critical review(f) of Graham Hancock’s Magicians of the Gods.<
However, to give credit where credit is due I must acknowledge that recently (2020) Shermer, among others, has back-pedalled on their previous sustained opposition to the idea of the Younger Dryas Impact Hypothesis(e). The impetus for this volte-face seems to have been provided by James Lawrence Powell, also a former sceptic, and his book, Deadly Voyager [1911].
In June 2023, Shermer published an article in Skeptic magazine attacking Graham Hancock‘s theories in general and the Netflix 2022 eight-part series Ancient Apocalypse(g) in particular.
(a) https://michaelshermer.com/sciam-columns/myth-is-the-message/#more-52
(b) https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/did-this-extinct-human-species-commit-homicide1/
(c) Michael Shermer: Murdering the facts about Homo naledi? – john hawks weblog (archive.org)
(e) In praise of intellectual honesty – The Cosmic Tusk
(f) No, There Wasn’t an Advanced Civilization 12,000 Years Ago – Scientific American
(h) https://michaelshermer.com/sciam-columns/
(i) Mission: Atlantis, by Rod Martin, Jr. — Grading the Skeptics (archive.org) *
