Strait of Gibraltar
Lelewel, Joachim Ignacy

Joachim Ignacy Lelewel (1786-1861) was a Polish historian, geographer and political activist.
He published a number of multi-volume historical works. Regarding Atlantis, he also published a map(a) in 1831[1760] which located Plato’s Island in the Atlantic directly west of the Strait of Gibraltar. While the map only shows lines of latitude, its longitudinal orientation is rather askew. Although it includes a distorted Britain it completely omits Ireland!
However, Lelewel considered Atlantis to be an invention inspired by the ancient stories of the Isles of the Blessed.
Pytheas
Pytheas was a 3rd century BC navigator from the Greek colony of Massalia (Marseilles) and is best known for his voyage in the North Atlantic, possibly around 240 BC. His trip took in the British Isles and as he ventured further North and claimed to have reached Thule.
>Gregory Douglas Wear, in his study of early excursions by Mediterranean peoples into the North Atlantic concluded that with the current state of archaeological and historical research, it is nothing less than impossible to verify with certainty, whether Greeks, Phoenicians, Carthaginians or any other pre-Pythean Mediterranean dweller actually set foot on the British Isles, northern France, or anywhere else in north-western Europe north of Galicia(c).<
Thule has generated volumes of debate regarding its location. Pytheas described Thule as lying six days’ sail to the north of Britain. Iceland, Norway(a) and the Faroes along with the Scottish Shetland and Orkney Islands have all been proposed as Pytheas’ Thule.
Søren Tillisch, a Danish archaeologist, accepts that the identification of the Faeroes as the Thule of Pytheas is reasonable, but he still thinks that the Estonian island of Saaremaa in the Baltic is also a feasible candidate(b).
Rhys Carpenter devoted an interesting chapter of his Beyond the Pillars of Hercules[221] in which he suggested that Pytheas’ voyage was undertaken with commercial objectives in mind, but on that level it was unsuccessful. However, as a voyage of discovery, it was an unparalleled achievement, earning for Pytheas Carpenter’s accolade of ”antiquity’s Greatest Explorer”.
Carpenter favours the idea that the term, ‘Pillars of Hercules’, when applied to the Strait of Gibraltar was used with the sense of boundary markers, indicating ”the limits of the Inner Sea that, for the Greeks, was the navigable world.”[p156]
(a) (99+) (PDF) Pytheas of Massalia’s Route of Travel | Cameron McPhail – Academia.edu
(b) (99+) (DOC) Pytheas of Massalia and the Baltic lecturewpictures | Søren Tillisch – Academia.edu
Landbridges
Landbridges, in biogeography, are described by Wikipedia as “an isthmus or wider land connection between otherwise separate areas, over which animals and plants are able to cross and colonize new lands. A land bridge can be created by marine regression, in which sea levels fall, exposing shallow, previously submerged sections of continental shelf; or when new land is created by plate tectonics; or occasionally when the sea floor rises due to post-glacial rebound after an ice age.”
In the distant past, landbridges are believed to have played a critical part in early human migration. Similarly, 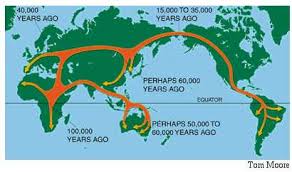 landbridges, both real and speculative are important components in many Atlantis theories. There is no doubt that the ending of the last Ice Age and the consequent rising sea levels led to the creation of islands where continuous land has previously existed. The separation of Ireland and Britain from each other and from mainland Europe is just one example, the latter leading to a number of writers identifying ‘Doggerland‘, which lay between Britain and Denmark as the home of Atlantis.
landbridges, both real and speculative are important components in many Atlantis theories. There is no doubt that the ending of the last Ice Age and the consequent rising sea levels led to the creation of islands where continuous land has previously existed. The separation of Ireland and Britain from each other and from mainland Europe is just one example, the latter leading to a number of writers identifying ‘Doggerland‘, which lay between Britain and Denmark as the home of Atlantis.
>The two most discussed landbridges were at the Bering Strait, where it is thought that it provided the gateway for humans to enter the Americas from Asia and an Atlantic landbridge, which was proposed as early as the 17th century when Francois Placet, a French abbot, who, in 1668, wrote “The break up of large and small world’s, as being demonstrated that America was connected before the flood with the other parts of the world.” A Scientific American article relates how “He argued that the two continents were once connected by the lost continent of “Atlantis” and the flood of the bible separated them.” (d)<
Later by John B. Newman in 1849 [488.8], who wrote that “in former times an island of enormous dimensions, named Atlantis, stretched from the north-western coast of Africa across the Atlantic ocean and that over this continental tract both man and beast migrated westward.“
>Charles Frédéric Martins was a French botanist and geologist who was so intrigued by the similarity of geology as well as plant species on the Azores, Spain and Ireland that he suggested in his 1866 book, Du Spitzberg Au Sahara [1440],that these were physically linked in the distant past and that they may have been part of Atlantis(c).
Martins also said, in the Revue des Deux Mondes for March 1, 1867, “Now, hydrography, geology, and botany agree in teaching us that the Azores, the Canaries, and Madeira are the remains of a great continent which formerly united Europe to North America.”<
The Atlantic landbridge idea became quite popular by the end of the 19th and beginning of the 20th centuries and even as late as the 1970s when espoused by Rene Malaise(a), but is now completely abandoned. Ignatius Donnelly referred to such a landbridge as a ‘connecting plateau’ linking Europe, Africa and America that allowed plants and animals to cross in both directions.
Although there was only one suggestion that the Bering Strait was in any way connected with Plato’s Atlantis, several commentators identified an Atlantic landbridge as the ideal location for Plato’s Atlantis, particularly as he placed it in the Atlantic Sea. However, this should not be confused with the Atlantic Ocean, a word that had an entirely different meaning for the ancient Greeks.
The idea was initially put forward in order to explain the floral and faunal similarities shared by the Old World and the New World of the Americas. The hypothetical Atlantic landbridges or a series of steppingstone islands. also offered possible routes for the peopling of the Americas by Europeans and/or Africans. It was not long before the discovery of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge(b) seemed to confirm this idea. Then it was suggested that Atlantis existed on this landbridge, which was destroyed by rising sea levels after the last Ice Age, leaving just the Azores, Madeira and a few other islands as remnants.
A number of landbridges have been proposed for the Mediterranean and linked to a variety of Atlantis theories, the most notable being proposed for the straits of Gibraltar, Sicily, Messina and Bonifacio. Although it is evident that landbridges existed at most of these locations, to associate them with any particular Atlantis theory requires that the date of their existence is compatible with Plato’s narrative.
Less popular theories have been constructed involving landbridges in locations, such as the Caribbean and Indonesia.
(a) Atlantis, Vol.27, No.1, Jan-Feb 1974.
(b) From the Contracting Earth to early Supercontinents – Scientific American Blog Network
Italy
Italy seems to have an uncertain etymology; Thucydides claims that Italos, the Sicilian king gave his name to Italy, while more recently Emilio Spedicato(h) considers that ”the best derivation we believe to be the one proposed by the Italian nuclear engineer Felice Vinci (1998), in his monograph claiming a Baltic setting for the Homeric epic: he derives Italia from the rare Greek word aithalia, meaning the smoking one.” This is thought to be a reference to Italy’s many volcanoes.
Italy today is comprised of territory south of the Alps on mainland Europe including a very large boot-shaped peninsula, plus Sicily, Sardinia and some smaller island groups, which along with the French island of Corsica virtually enclose the Tyrrhenian Sea.
The earliest proposal that Italy could be linked with Atlantis came from Angelo Mazzoldi in 1840 when he claimed that before Etruria, Italy had been home to Atlantis and dated its demise to 1986 BC. Mazzoldi expressed a form of hyperdiffusion that had his Italian Atlantis as the mother culture which seeded the great civilisations of the eastern Mediterranean region(b).
Some of Mazzoldi’s views regarding ancient Italy were expanded on by later scholars such as Camillo Ravioli, Ciro Nispi-Landi, Evelino Leonardi, Costantine Cattoi, Guido DiNardo and Giuseppe Brex. Ravioli sought to associate the Maltese island of Gozo with his proposed Atlantis in Italy.
The Italian region of Lazio, which includes Rome, has had a number of very ancient structures proposed as Atlantean; Monte Circeo (Leonardi) and Arpino(a) (Cassaro). Another aspect of Italian prehistory is the story of Tirrenide, which was described as a westward extension of the Italian landmass into the Tyrrhenian Sea during the last Ice Age, with a land bridge to a conjoined Sardinia and Corsica. At the same time, there were land links to Sicily and Malta, which were all destroyed as deglaciation took place and sea levels rose.
 It is surprising that so few researchers have commented on Italy’s part in Plato’s Atlantis narrative considering that he twice, without any ambiguity, informs us that the Atlantean domain extended as far as Tyrrhenia (modern Tuscany).
It is surprising that so few researchers have commented on Italy’s part in Plato’s Atlantis narrative considering that he twice, without any ambiguity, informs us that the Atlantean domain extended as far as Tyrrhenia (modern Tuscany).
Crit.114c. So all these, themselves and their descendants dwelt for many generations bearing rule over many other islands throughout the sea and holding sway besides, as was previously stated, over the Mediterranean peoples as far as Egypt and Tuscany. Tim.25a/b. Now in this island of Atlantis there existed a confederation of kings, of great and marvellous power, which held sway over all the island, and over many other islands also and parts of the continent; and, moreover, of the lands here within the Straits they ruled over Libya as far as Egypt, and over Europe as far as Tuscany. (Bury)
The quotation from Timaeus is most interesting because of its reference to a ‘continent’. Some have understandably but incorrectly claimed that this is a reference to America or Antarctica, when quite clearly it refers to southern Italy as part of the continent of Europe. Moreover, Herodotus is quite clear (4.42) that the ancient Greeks knew of only three continents, Europe, Asia and Libya.
Philo of Alexandria (20 BC-50 AD) in his On the Eternity of the World(g) wrote “Are you ignorant of the celebrated account which is given of that most sacred Sicilian strait, which in old times joined Sicily to the continent of Italy?” (v.139).>The name ‘Italy’ was normally used until the third century BC to describe just the southern part of the peninsula(e).<Some commentators think that Philo was quoting Theophrastus, Aristotle’s successor. This would push the custom of referring to Italy as a ‘continent’ back near to the time of Plato. More recently, Armin Wolf, the German historian, when writing about Scheria relates(f) that “Even today, when people from Sicily go to Calabria (southern Italy) they say they are going to the ‘continente’.” This continuing usage is further confirmed by a current travel site(d) and by author, Robert Fox[1168.141]. I suggest that Plato used the term in a similar fashion and can be seen as offering the most rational explanation for the use of the word ‘continent’ in Timaeus 25a.
When you consider that close to Italy are located the large islands of Sicily, Sardinia and Corsica, as well as smaller archipelagos such as the Egadi, Lipari and Maltese groups, the idea of Atlantis in the Central Mediterranean can be seen as highly compatible with Plato’s description.
If we accept that Plato stated unambiguously that the domain of Atlantis included at least part of southern Italy and also declared that Atlantis attacked from beyond the Pillars of Heracles, then this appellation could not be applied at that time to any location in the vicinity of the Strait of Gibraltar but must have been further east, probably not too far from Atlantean Italy. This matches earlier alternative locations recorded by classical writers who placed the ‘Pillars’ at the straits of Messina or Sicily. I personally favour Messina, unless there is stronger evidence that some of the islands in or near the Strait of Sicily such as the Maltese or Pelagian Islands or Pantelleria were home to the ‘Pillars’.
(a) http://www.richardcassaro.com/hidden-italy-the-forbidden-cyclopean-ruins-of-giants-from-atlantis
(b) Archive 2509P (Eng) Archive 2943 (Ital)
(c) Archive 2946
(d) Four Ways to Do Sicily – Articles – Departures (archive.org)
(e) https://profilbaru.com/article/Name_of_Italy *
(f) Wayback Machine (archive.org)
(g) http://www.earlychristianwritings.com/yonge/book35.html
(h) http://2010-q-conference.com/ophir/ophir-27-10-09.pdf
Abrams, Dennis
 Dennis Abrams (1960- ) lives in Texas and is the author of a number of biographies of mainly 20th century personalities. He has also written (The Lost World of) Atlantis[1160] which is intended for younger readers. Understandably, it gives an overview of current theories and according to the publisher’s blurb the author locates Atlantis near the Strait of Gibraltar.
Dennis Abrams (1960- ) lives in Texas and is the author of a number of biographies of mainly 20th century personalities. He has also written (The Lost World of) Atlantis[1160] which is intended for younger readers. Understandably, it gives an overview of current theories and according to the publisher’s blurb the author locates Atlantis near the Strait of Gibraltar.
Smith, Oliver D. *
Oliver D. Smith studied Classics at Roehampton University and is currently studying archaeology at the Oxford Learning College. In May 2013, he published his BA disserta tion, entitled Atlantis as Sesklo, as an ebook(i).
tion, entitled Atlantis as Sesklo, as an ebook(i).
Smith devoted the initial part of his paper to a review of the interpretation of the Atlantis story by euhemerists since the time of Plato. Having briefly, and I might say dismissively, dealt with some modern theories, and then began to unveil a new hypothesis. Firstly, he proceeded to ignore archaeological opinion and support the early date for the existence of Atlantis. He also argued that Atlantis was destroyed by the flood that occurred during the reign of the Pelasgian king Ogyges.
Smith daringly suggested that the inspiration for the Atlantean capital was Sesklo, an ancient site situated north of Athens near modern Volos.
Although Smith has obviously researched his subject, I cannot agree with his conclusion, which I consider somewhat speculative. Apart from taking issue with the early date for Atlantis, Plato described the Atlantean attack as coming from the west, not the north. Furthermore, Sesklo is certainly not submerged and the site is too small to match Plato’s description of the city.
He also contended that the claim by Plato that Atlantis was ‘greater than Libya and Asia combined’ was in fact a reference to the extreme age of Atlantis!(c)
On March 14th, 2014, Smith announced(b) that “I have now closed my blog, and removed my research to work on a new project which will take many years (I will be working on a proper book covering the literary genre and origin of Atlantis). Personally, I think the Atlantis community has too many location hypotheses and not enough material put out exploring Plato’s dialogues, etc, and Atlantis in general in detail.” He expanded on this in a later article.(f)
Nevertheless, Smith did return to the Atlantis question in May 2016 and declared his belief that Plato’s account was complete fiction!(d) Readers may be interested in reading other blogs by Smith as they touch on other matters that relate to Atlantis studies such as the Pillars of Heracles(j) and the etymology of ‘Atlantis’. Smith identifies four locations in southern Iberia that have been designated as locations of the ‘Pillars’. He names them as Mastia, Mainake, Strait of Gibraltar, and Cádiz.
In 2020 he published a paper attacking the Minoan Hypothesis and continuing his assault on what he claims is Plato’s fictional account of Atlantis.(g)
Perhaps more relevant to an assessment of Smith’s reliability is a review of his, meandering, tortured intellectual journey to date(e).
In January 2022, Smith, who is unhappy with Hisarlik as the location of Troy and dissatisfied with alternatives proposed by others has now proposed a Bronze Age site, Yenibademli Höyük, on the Aegean island of Imbros(h). His paper was published in the Athens Journal of History (AJH).
>In early 2023, Smith published a paper on the Researchgate website, in which he sought to identify the inspiration behind what he prefers to describe as Plato’s fictional Atlantis. This he now believes to have been the ancient Arcadian kingdom of Atlantos centred on the town of Methydrium, which is situated near modernday Methydrio(k).<
(c) The Size of Atlantis: A New Interpretation (link broken)
(d) Archive 3062 | (atlantipedia.ie)
(e) Oliver D. Smith – Encyclopedia Dramatica (archive.org) (link broken) See: Archive 3195
(f) http://shimajournal.org/issues/v10n2/d.-Smith-Shima-v10n2.pdf & Wayback Machine (archive.org) *
(g) (6) (PDF) Atlantis and the Minoans | Oliver D Smith – Academia.edu
(h) https://athensjournals.gr/history/2022-8-1-4-Smith.pdf
(i) https://atlantipedia.ie/samples/archive-3062/
(j) https://www.academia.edu/39947152/In_Search_of_the_Pillars_of_Heracles
(k) (PDF) Arcadian Atlantis and Plato’s Pseudomythology (researchgate.net)
Nicholls, Melville
 Melville Nicholls is a senior research scientist at the University of Colorado where he studies atmospheric science, mainly relating to hurricanes. In May 2013, he published Children of the Sea God[944] as a Kindle ebook. One of his main contentions is that Atlantis existed during the early Bronze Age at the time of the Bell Beaker culture, >which he claims originated in Portugal around 2800 BC.<
Melville Nicholls is a senior research scientist at the University of Colorado where he studies atmospheric science, mainly relating to hurricanes. In May 2013, he published Children of the Sea God[944] as a Kindle ebook. One of his main contentions is that Atlantis existed during the early Bronze Age at the time of the Bell Beaker culture, >which he claims originated in Portugal around 2800 BC.<
He also contends that Britain was the large island of Atlantis described by Plato. However he also proposes that the main port city of Atlantis, with the concentric rings of land and water was situated in southwest Spain near Gibraltar. He proposes that this port was destroyed by an event such as a tsunami.
While all these features have been proposed individually as characteristics of Atlantis, Nicholls brings them together in a comprehensive theory, but not without indulging in a liberal amount of speculation.
He devotes a considerable amount of space attempting to link Stonehenge with the Atlanteans. While I was not won over by Nicholl’s book, it is worth a read and might best be studied along with Donald Ingram’s book, The Unlost Island[665].
The idea of ‘two’ Atlantises was probably first promoted by Lewis Spence and more recently by Karl Jürgen Hepke. In fact, were there not ten Atlantises?
In November 2013, Nicholls published a second ebook, The Real and Imaginary Atlantis[945], in which he revisits his theory of a British/Spanish Atlantis and its relationship to the Bell Beaker People. In conclusion, he seems to reluctantly write that “I still come down in favor of the theory that Plato invented the story as the one most likely to be correct.”
Hanno, The Voyage of *
The Voyage of Hanno, the Carthaginian navigator, was undertaken around 500 BC. The general consensus is that his journey took him through the Strait of Gibraltar and along part of the west coast of Africa. A record, or periplus, of the voyage was inscribed on tablets and displayed in the Temple of Baal at Carthage. Richard Hennig 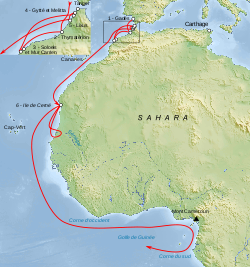 speculated that the contents of the periplus were copied by the Greek historian, Polybius, after the Romans captured Carthage. It did not surface again until the 10th century when a copy, in Greek, was discovered (Codex Heildelbergensis 398) and was not widely published until the 16th century.
speculated that the contents of the periplus were copied by the Greek historian, Polybius, after the Romans captured Carthage. It did not surface again until the 10th century when a copy, in Greek, was discovered (Codex Heildelbergensis 398) and was not widely published until the 16th century.
The 1797 English translation of the periplus by Thomas Falconer along with the original Greek text can be downloaded or read online(h).
Edmund Marsden Goldsmid (1849-?) published a translation of A Treatise On Foreign Languages and Unknown Islands[1348] by Peter Albinus. In footnotes on page 39 he describes Hanno’s periplus as ‘apocryphal’. A number of other commentators(c)(d) have also cast doubts on the authenticity of the Hanno text.
Three years after Ignatius Donnelly published Atlantis, Lord Arundell of Wardour published The Secret of Plato’s Atlantis[0648] intended as a rebuttal of Donnelly’s groundbreaking book. The ‘secret’ referred to in the title is that Plato’s Atlantis story is based on the account we have of the Voyage of Hanno.
Nicolai Zhirov speculated that Hanno may have witnessed ‘the destruction of the southern remnants of Atlantis’, based on some of his descriptions.
Rhys Carpenter dedicated nearly twenty pages to the matter of Hanno commented that ”The modern literature about his (Hanno’s) voyage is unexpectedly large. But it is so filled with disagreement that to summarize it with any thoroughness would be to annul its effectiveness, as the variant opinions would cancel each other out”[221.86]. Carpenter included what he describes as ‘a retranslation of a translation’ of the text.
Further discussion of the text and topography encountered by Hanno can be read in a paper[1483] by Duane W. Roller.
What I find interesting is that so much attention was given to Hanno’s voyage as if it was unique and not what you would expect if Atlantic travel was as commonplace at that time, as many ‘alternative’ history writers claim.
However, even more questionable, is the description of Hanno sailing off “with a fleet of sixty fifty-oared ships, and a large number of men and women to the number of thirty thousand, and with wheat and other provisions.” The problem with this is that the 50-oared ships would have been penteconters, which had limited room for much more than the oarsmen. If we include the crew, an additional 450 persons per ship would have been impossible, in fact, it is unlikely that even the provisions for 500 hundred people could have been accommodated!
Lionel Casson, the author of The Ancient Mariners[1193] commented that “if the whole expedition had been put aboard sixty penteconters, the ships would have quietly settled on the harbour bottom instead of leaving Carthage: a penteconter barely had room to carry a few days’ provisions for its crew, to say nothing of a load of passengers with all the equipment they needed to start a life in a colony.“
The American writer, William H. Russeth, commented(f) on the various interpretations of Hanno’s route, noting that “It is hard for modern scholars to figure out exactly where Hanno travelled, because descriptions changed with each version of the original document and place names change as different cultures exert their influence over the various regions. Even Pliny the Elder, the famous Roman Historian, complained of writers committing errors and adding their own descriptions concerning Hanno’s journey, a bit ironic considering that Romans levelled the temple of Ba’al losing the famous plaque forever.”
George Sarantitis has a more radical interpretation of the Voyage of Hanno, proposing that instead of taking a route along the North African coast and then out into the Atlantic, he proposes that Hanno travelled inland along waterways that no longer exist(e). A 2013 report in New Scientist magazine(n) revealed that 100,000 years ago the Sahara had been home to three large rivers that flowed northward, which probably provided migration routes for our ancestors. Furthermore, if these rivers lasted into the African Humid Period they may be interpreted as support for Sarantitis’ contention regarding Hanno!
He insists that the location of the Pillars of Heracles, as referred to in the narrative, matches the Gulf of Gabes [1470].
The most recent commentary on Hanno’s voyage is on offer by Antonio Usai in his 2014 book, The Pillars of Hercules in Aristotle’s Ecumene[980]. He also has a controversial view of Hanno’s account, claiming that in the “second part, Hanno makes up everything because he does not want to continue that voyage.” (p.24) However, the main objective of Usai’s essays is to demonstrate that the Pillars of Hercules were originally situated in the Central Mediterranean between eastern Tunisia and its Kerkennah Islands.
A 1912 English translation of the text can be read online(a), as well as a modern English translation by Jason Colavito(k).
Another Carthaginian voyager, Himilco, is also thought to have travelled northward in the Atlantic and possibly reached Ireland, referred to as ‘isola sacra’. Unfortunately, his account is no longer available(g).
The controversial epigrapher Barry Fell went so far as to propose that Hanno visited America, citing the Bourne Stone as evidence!(m)*
The livius.org website offers three articles(i) on the text, history and credibility of the surviving periplus together with a commentary.
Another excellent overview of the document is available on the World History Encyclopedia website.(l)
(a) https://web.archive.org/web/20040615213109/https://www.jate.u-szeged.hu/~gnovak/f99htHanno.htm
(c) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hanno_the_Navigator
(d) https://annoyzview.wordpress.com/2012/04/
(e) https://platoproject.gr/voyage-hanno-Carthaginian/
(f) https://www.goodreads.com/author/show/1033187.William_H_Russeth/blog?page=2 *
(g) https://gatesofnineveh.wordpress.com/2011/12/13/high-north-carthaginian-exploration-of-ireland/
(j) BSMQgoYSQYFJ90bRJIhQ&hl=mt&ei=–tuSfNEIaqnAOo_NjHBA&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=&ved=CBgQ https://archive.org/details/cu31924031441847
(l) Hanno: Carthaginian Explorer – World History Encyclopedia
(n) NewScientist.com, 16 September 2013, https://tinyurl.com/mg9vcoz
Homer
Homer (c. 8th cent. BC) is generally accepted as the author of the Iliad and the Odyssey, regarded as the two greatest epic poems of ancient Greece. A recent study of the Greek used by Homer has enabled scientists from the University of Reading to confirm that the language used is compatible with that used in the 8th century BC, in fact dating it to around 762 BC(i).
Nevertheless, there are questions raised regarding the authorship of the ‘Homeric’ epics. For example, Andreas Pääbo is certain that the Odyssey and the Iliad came from two different authors(ar).
Even more extreme was the opinion of the ancient geographer, Eratosthenes who was a persistent critic of Homer, whom he considered to be a fantasist. Strabo reported what the geographer said in the late 3rd century BC: “You will find the scene of Odysseus’ wanderings when you find the cobbler who sewed up the bag of winds”(av).
Manolis Manoledakis, a professor of Classical Archaeology, in a paper(as) on the Academia website “examines an aspect of the broader issue of the geography of the Odyssey, the primary stimulus being the references of the poem to places that could be associated with the Black Sea, namely the Aeaea and the entrance to the Underworld. As we shall see, while these particular places are indeed relevant to the Black Sea region, they do not belong to the context of a specific journey with specific halts in a specific geographical sequence. The Odyssey is a synthesis of many different episodes, and there is no point in trying to trace a complete geographical course for Odysseus’ voyage.”
It should also be noted that over 130 quotations from the Illiad and Odyssey have been identified in Plato’s writings(s). George Edwin Howes (1865-1942), an American classicist, produced a dissertation[1458]+ on Homeric quotations in Plato and Aristotle.
Almost nothing is known of Homer’s life. He has been variously described as mad, blind and even mythical. Andrew Dalby, the English linguist, has gone so far as to claim[0591] that the author of the two famed epics was a woman! While in 1897 Samuel Butler, the novelist, was even more specific when he proposed that Homer was a Sicilian woman(j).
For centuries it was assumed that the content of these Homeric poems was the product of his imagination, just as the historical reality of Homer himself has been questioned. In 1795, F.A. Wolf, a German academic declared that ‘Homer’ was just a collective name applied to various  poets whose works were finally combined into their present form in the 6th century BC. Wolf’s ideas sparked furious argument among Greek scholars that still resonates today. Now (2015), historian, Adam Nicholson has claimed that the author ‘Homer’ should not be thought of as a person but instead as a ‘culture’(o).
poets whose works were finally combined into their present form in the 6th century BC. Wolf’s ideas sparked furious argument among Greek scholars that still resonates today. Now (2015), historian, Adam Nicholson has claimed that the author ‘Homer’ should not be thought of as a person but instead as a ‘culture’(o).
In a 2021 review of Victor Davis Hanson’s Who Killed Homer? [1854], Adam Kirsch outlines how “Milman Perry proved that the Iliad and the Odyssey were not written by a lone genius(ah). They were originally not written at all, but through fieldwork in Yugoslavia, Perry (1902-1935) demonstrated how the Homeric epics were the result of traditional bardic storytelling. Wikipedia describes Perry as “an American Classicist whose theories on the origin of Homer’s works have revolutionized Homeric studies to such a fundamental degree that he has been described as the ‘Darwin of Homeric studies’.”
Ed Whelan, an Irish classical scholar, published a brief paper in 2021 that endorsed the Homeric ‘multiple authors’ theory(ap).
An anonymous author offered “Although there has been a great deal of controversy about the question of whether Homer alone wrote the two famous poems, much of the evidence points towards Homer being the author due to the consistent style of writing. Also, some analysts argue that Homer may have written one of the poems but not the other since both differ greatly in style. In contrast, the reason other analysts state for this difference is that Iliad was written in his youth while Odyssey was created during Homer’s years of age.” (aq).
The identification of the site at Hissarlik in modern Turkey as Troy by Heinrich Schliemann led to a complete re-appraisal of Homer’s work and, of course, further controversy. Homer’s Iliad is the story of the Trojan War and it has been suggested that in fact, he had compressed three or more Trojan wars into one narrative. What is not generally known is that there are also ancient non-Homeric accounts of the Trojan War(q).
Kenneth Wood and his wife Florence have built on the research of his mother-in-law, the late Edna Leigh, and produced Homer’s Secret Iliad[391], a book that attempts to prove that the Iliad was written as an aide-memoire for a wide range of astronomical data.
Allied to, but not directly comparable with, is the astronomical information identified in the Bible by the likes of E. W. Maunder (1851-1928)[1137].
Guy Gervis has adopted some of their work and, in a lengthy article, specifies a date of around 2300 BC for the events described in the Iliad and Odyssey, based on an analysis of this astronomical data(n). Harald A.T. Reiche held similar views which followed some of the ideas expressed in Hamlet’s Mill[0524] by Santillana & Dechend who were colleagues of Reiche at M.I.T. They also claimed that “myths were vehicles for memorising and transmitting certain kinds of astronomical and cosmological information.”
Much has been written about the historicity of Homer’s epic accounts, including a good overview on Wikipedia(ab). Many have concluded that Homer did use real events, even if they were frequently dressed in mythological clothing compatible with the literary conventions of his day. I consider Plato to have treated the story of Atlantis similarly.
A recent study of solar eclipses recorded in Odyssey using data from NASA has confirmed that Odysseus returned to Ithaca on the 25th of October 1207 BC(r).
Scholars have generally supported the idea that Homer’s works have a Mediterranean backdrop with regular attempts to reconcile his geography with modern locations, such as the claim in 2005 by Robert Brittlestone, a British investigator to have located the site of Ithaca, the homeland of Odysseus, on the Greek island of Cephalonia. This popular idea should be put alongside the views of Zlatko Mandzuka who maintains[1396] that all the locations mentioned in the Odyssey can be identified in the Adriatic.
Kazmer Ujvarosy of San Francisco State University, has noted that there are 22 different places currently on offer as the location of Ithaca(ax).
Nevertheless, there has been a growing body of opinion that insists that this Mediterranean identification is impossible. A range of alternative regions has been proposed(f) as the setting for the epics, which extend from Portugal as far northward as the Baltic.
In his Odyssey (VII: 80), Homer wrote about the island of Scheria in the western sea. His description of the island has been compared with Plato’s description of Atlantis and has led to the theory that they refer to the same place. There is little doubt that both the detailed geography and climatic descriptions that are provided by Homer cannot be easily reconciled with that of the Mediterranean. Consequently, the Odyssey has had many interpretations, ranging from Tim Severin’s conclusion[392] that it refers entirely to the Eastern Mediterranean to Iman Wilkens’ book, Where Troy Once Stood[610], which has the voyage include the west coast of Africa, then across to the West Indies and following the Gulf Stream returns to Troy which he locates in Britain.
Location is not a problem exclusive to the writings of Plato. Wilkins’s claims are a reflection of similar ideas expressed by Théophile Cailleux[393] in the 19th century. Gilbert Pillot has also argued for voyages of Ulysses having taken him into the North Atlantic [742]. A Spanish review of Pillot’s book is available(ag). In 1973, Ernst Gideon (? – 1975) wrote in a similar vein in Homerus Zanger der Kelten, reprinted later as Troje Lag in Engelan[1643].
It is worth noting that Bernard Jones in The Discovery of Troy[1638] has recently moved Troy to Britain, probably in the vicinity of Cambridge, a location also preferred by Wilkens! Like many others, he argues that Homer’s Iliad and Odyssey were not set in the Mediterranean as so many of the details that he provides are incompatible with the characteristics of that sea. However, Jones has gone further and claimed that there are details in Virgil’s Aeneid, which are equally inconsistent with the Mediterranean [p.6-10], requiring a new location! Jones’ book has been reviewed on the Hall of Maat website(at) as well as by Jason Colavito(au).
An interesting overview of the various attempts to transfer the Odyssey from the Mediterranean to Northern Europe is available(w). Damien Mackey has also endorsed the idea of a Northern European backdrop to Homer’s Odyssey(aa).
Another researcher who places most of Odysseus’ travels in the eastern Atlantic is Gerard. W.J. Janssen of Leiden University on the academia.edu website(v). In a series of six papers(ai-an), he systematically reviews Homer’s geography, identifying locations referred to by him with places in the Atlantic. He compares his identifications with other commentators including Iman Wilkens and Théophile Cailleux. His website, with an English translation, offers additional information, including the suggestion(ao) that Homer’s Laestrygonians were to be found in Cuba, an interpretation also offered by Cailleux and Wilkens. They also claim that Odysseus’ Caribbean trip included a visit to Saba, a Dutch possession, which is identified as the Aeolian Isle!
The idea of an Atlantic backdrop to the Homeric epics will not go away. The Dutch researcher, N.R. De Graaf(ae). continues to write extensively on his Homeros Explorations website(ad)(x) regarding many of the specifics in Homer’s accounts. He has proposed Lanzarote in the Canaries as the location of Scheria, which concurs with the views of Wilkens and Janssen. Other specifics are that Ithaca was near Cadiz and that Sparta was Cordoba, while the ancient city of Carmona on the plains of Andalucia are, for De Graaf, Mycenae!(af)
E.J. de Meester also argued(ac) for the British Isles as the location of many of Homer’s references. It struck me as quite remarkable that the level of debate regarding the date, source and geographical details of Homer’s works is rather similar to the controversy surrounding Plato’s Atlantis in Timaeus and Critias. The late Edo Nyland was another researcher who had also opted for a Scottish backdrop to the Odyssey and had recently published his views[394].
Felice Vinci also supports[019] a Northern European background to the Iliad and Odyssey. However, in Vinci’s case, Scandinavia, and in particular the Baltic Sea, is identified as the location for the adventures in Homer’s classic. An English language synopsis of his book is available on the Internet. The persuasiveness of Vinci’s argument has recently renewed interest in the idea of a Baltic Atlantis. The assumption is that if Troy could be located in the Baltic, so might Atlantis. Vinci’s views are comparable with those of J. Rendel Harris expressed in a lecture delivered in 1924(p) in which he claims that “we are entitled to take Homer and his Odysseus out of the Mediterranean or the Black Sea, and to allow them excursions into Northern latitudes.”
However, a scathing review of Vinci’s book can be found on the Internet(d) and in issue 216 (2006) of Fortean Times written by Marinus Anthony van der Sluijs.
Further support for a Northern European Troy has come from the historian Edward Furlong, a former naval navigation officer, who has advocated for over twenty years that the journey of Odysseus went as far north as Norway>>after visting Ireland and the Scottish Islands.<< His particular views are outlined on the Internet(c).
Other writers, such as the late Henrietta Mertz [0396/7], have suggested that Homer’s epic refers to a trip to North America. Professor Enrico Mattievich Kucich of Lima University is also certain that the ancient Greeks discovered America America[400]. However revolutionary this idea may seem it shows how this particular subject is growing and would probably justify a reference book of its own.
The idea of an Atlantic backdrop to the Homeric epics will not go away. The Dutch researcher, N.R. De Graaf continues to write extensively on his Homeros Explorations website(x) regarding many of the specifics in Homer’s accounts.
In 1973, James Bailey also proposed in his well-received The God-Kings and the Titans[149] that the Odyssey recorded a trans-Atlantic trip. Evidence exists for large-scale mining in the Americas as early as the 5th millennium BC. Bailey maintained that the Europeans imported enormous quantities of copper and tin from Central and South America to feed the demands of the Old World Bronze Age, an idea that was later heavily promoted by Frank Joseph and in great, if overly speculative, detail by Reinoud de Jong(y).
Finally, the Atlantis connection with this entry is that if, as now appears to be at least a possibility, Homer’s Odyssey was about a journey to the North Sea then the possibility of the North Sea setting for the Atlantis story is somewhat reinforced.
A recent book[395] by Steven Sora has developed the Atlantic notion further with the suggestion that not only was Troy located outside the Strait of Gibraltar but that both Homer’s Trojan War and Plato’s Atlantean war are two versions of the same war with the understandable distortions and embellishments that can occur with a narrative, probably involving some degree of oral transmission and then written down hundreds of years after the events concerned.
Ukraine is soon to be added to the growing list of alternative locations for the setting of Homer’s epics with the publication of Homer, The Immanent Biography, a book by A.I. Zolotukhin(g). He claims that Homer was born in Alibant (Mykolayiv, Ukraine) on September 14, 657 BC(t). He follows the views of Karl Ernst von Baer (1792-1876) who believed that most of Odysseus’s travels took place in the Black Sea rather than the Mediterranean. Additionally, he locates Atlantis in the western Crimean area of Evpatoria(l). His 60-page book is available on his website(m).
An interesting paper(e) by the German historian, Armin Wolf, relates how his research over 40 years unearthed 80 theories on the geography of the Odyssey, of which around 30 were accompanied by maps. One of the earliest maps of the travels of Odysseus was produced by Abraham Ortelius in 1597(u), in which the adventures of Odysseus all take place within the Central and Eastern Mediterranean, arguably reflecting the maritime limits of Greek experience at the time of Homer or his sources! Another website(z) by Jonathan S. Burgess, Professor of Classics at the University of Toronto offers further information on this, including some informative bibliographical material.
In 2009, Wolf published, Homers Reise: Auf den Spuren des Odysseus[669] a German-language book that expands on the subject, also locating all the travels of Odysseus within the Central and Eastern Mediterranean.
Wolf’s ideas were enthusiastically adopted by Wolfgang Geisthövel in Homer’s Mediterranean[1578], who also concurs with the opinion of J.V. Luce [1579], who proposed that Homer was “describing fictional events against authentic backgrounds.” This would be comparable to a James Bond movie, which has an invented storyline set in actual exotic locations around the world.
Perhaps the most radical suggestion has come from the Italian writer, Michele Manher, who has proposed(h) that Homer’s Iliad originated in India where elements of it can be identified in the Mahabharata!
In August 2015, a fifteen-hour reading of the Iliad was performed in London.
[1458]+ https://archive.org/stream/jstor-310358/310358_djvu.txt
(c) https://www.academia.edu/8167048/WHERE_DID_ODYSSEUS_GO_
(d) https://mythopedia.info/Vinci-review.pdf
(e) https://authorzilla.com/9AbvV/armin-wolf-mapping-homer-39-s-odyssey-research-notebooks.html (link broken)
(f) https://codexceltica.blogspot.com/search?q=atlantis
(g) https://pushkinclub.homerandatlantis.com/english/homer.html
(h) https://www.migration-diffusion.info/article.php?id=100
(i) https://www.insidescience.org/content/geneticists-estimate-publication-date-iliad/946
(j) https://www.sacred-texts.com/cla/aoto/index.htm
(k) https://web.archive.org/web/20180320072706/https://www.nwepexplore.com (see ‘n’)
(l) https://homerandatlantis.com/?lang=en
(m) https://homerandatlantis.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/01/Homer_The_Immanent_biography_pdf2.pdf
(n) https://web.archive.org/web/20180320072706/https://www.nwepexplore.com
(o) https://www.newser.com/story/200859/homer-wasnt-a-person-historian.html
(p) https://www.escholar.manchester.ac.uk/api/datastream?publicationPid=uk-ac-man-scw:1m1163&datastreamId=POST-PEER-REVIEW-PUBLISHERS-DOCUMENT.PDF (link broken)
(q) https://luwianstudies.org/the-homeric-epics/
(r) Scientists provide evidence that Homer´s Odyssey is not fiction (archive.org)
(s) https://plato-dialogues.org/tools/char/homerqot.htm
(t) https://homerandatlantis.com/?p=4938&lang=en
(u) https://kottke.org/19/03/mapping-the-odyssey-isnt-easy
(v) https://www.academia.edu/38535990/ATLANTIC_OGUGIA_AND_KALUPSO?email_work_card=view-paper
(w) https://codexceltica.blogspot.com/2009/10/homers-north-atlantic-odyssey.html
(x) http://www.homeros-explorations.nl/
(y) https://www.academia.edu/3894415/COPPER_AND_TIN_FROM_AMERICA_c.2500-1200_BC_
(z) https://wakeofodysseus.com/
(ab) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Historicity_of_the_Homeric_epics#History
(ac) https://web.archive.org/web/20090907222615/https://home-3.tiscali.nl/~meester7/engodyssey.html
(ad) Homeros Explorations – Homer, facts or fiction? (homeros-explorations.nl)
(ae) https://www.homeros-explorations.nl
(af) Mycenae, rich in gold – Homeros Explorations (homeros-explorations.nl)
(ag) Perijóresis: Odisea (perijoresis.blogspot.com) (Spanish)
(ah) https://www.newyorker.com/magazine/2021/06/14/the-classicist-who-killed-homer
(ai) https://www.academia.edu/40668880/ATLANTIC_GEOGRAPHY_IN_HOMER_I
(aj) https://www.academia.edu/40849368/ATLANTIC_GEOGRAPHY_IN_HOMER_II
(ak) https://www.academia.edu/40982169/ATLANTIC_GEOGRAPHY_IN_HOMER_III
(al) https://www.academia.edu/41200642/ATLANTIC_GEOGRAPHY_IN_HOMER_IV
(am) https://www.academia.edu/41474241/ATLANTIC_GEOGRAPHY_IN_HOMER_PART_V
(an) https://www.academia.edu/41625852/ATLANTIC_GEOGRAPHY_IN_HOMER_PART_VI
(ao) LAISTRUGONIACUBA, LA HAVANA (homerusodyssee.nl)
(ap) The Homeric Question – Who WAS Homer? (bibliotecapleyades.net)
(aq) Homer | Biography, Books and Facts (famousauthors.org)
(ar) (26) The Odyssey’s Northern Origins and a Different Author Than Homer | Andres Pääbo – Academia.edu
(at) http://www.hallofmaat.com/migrations/the-discovery-of-troy-and-its-lost-history/
(av) Strabo 1.2.15
Tyre
Tyre was located in what is modern Lebanon and is considered to have been originally a colony of Sidon. According to  Egyptian records they ruled it during the middle of the second millennium BC, but lost control when their influence in the area declined. Independence brought commercial success that saw Tyre surpass Sidon in wealth and influence and eventually establish its own colonies across the Mediterranean. One of these was Carthage in North Africa, which in time became independent and eventually rivalled the Roman Empire in the west. It also had colonies in Greece and frequently fought with Egypt.
Egyptian records they ruled it during the middle of the second millennium BC, but lost control when their influence in the area declined. Independence brought commercial success that saw Tyre surpass Sidon in wealth and influence and eventually establish its own colonies across the Mediterranean. One of these was Carthage in North Africa, which in time became independent and eventually rivalled the Roman Empire in the west. It also had colonies in Greece and frequently fought with Egypt.
The location of Tyre, on an island with a superb natural harbour and which had great wealth and was supported by its many colonies, has been seen as a mirror of Atlantis. The Old Testament prophecies of Ezekiel, writing around 600 BC, described (26:19, 27: 27-28) the destruction of Tyre in terms that have prompted some to link it with Plato’s description of Atlantis’ demise, written two hundred years later.*The earliest claim that Ezekiel’s Tyrus was a reference to Atlantis was made by Madame Blavatsky in The Secret Doctrine [1495] in 1888.
However, although both J.D. Brady and David Hershiser promote the idea of a linkage between Ezekiel’s Tyrus and Atlantis, they are certain that Tyrus is not the Phoenician city of Tyre. Beyond that, Brady identifies Tyrus/Atlantis with Troy, while Hershiser has placed his Tyrus/Atlantis in the Atlantic just beyond the Strait of Gibraltar(b).
Early in the 20th century Hanns Hörbiger also cited Ezekiel as justification for identifying Tyre as Atlantis.*
Recently, a sunken city has been discovered between Tyre and Sidon and according to its discoverer, Mohammed Sargi, is the 4,000 year old City of Yarmuta referred to in the Tell al-Amarna letters.
Carl Fredrich Baer, the imaginative 18th century writer, proposed a linkage between Tyre and Tyrrhenia. This idea has been 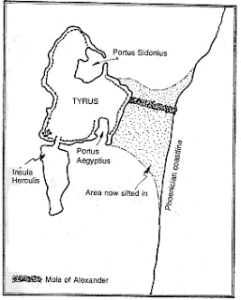 revived recently by the claims of Jaime Manuschevich[468] that the Tyrrhenians were Phoenicians from Tyre. Other supporters of a Tyrrhenian linkage with Tyre are J.D.Brady, Thérêse Ghembaza and most recently Dhani Irwanto. J.S. Gordon also claims[339.241] that Tyre was so named by the Tyrrhenians.
revived recently by the claims of Jaime Manuschevich[468] that the Tyrrhenians were Phoenicians from Tyre. Other supporters of a Tyrrhenian linkage with Tyre are J.D.Brady, Thérêse Ghembaza and most recently Dhani Irwanto. J.S. Gordon also claims[339.241] that Tyre was so named by the Tyrrhenians.
In Greek mythology it is said that Cadmus, son of the Phoenician king Agenor, brought the alphabet to Greece, suggesting a closer connection than generally thought.
J.P. Rambling places the Pillars of Heracles on Insula Herculis, now a sunken island, immediately south of Tyre(a).
(a) https://redefiningatlantis.blogspot.ie/search/label/Heracles
*(b) See: Archive 3395*

