Los Millares
2200 BC *
2200 BC is frequently referred to as a time of great social and political upheaval in the Mediterranean and what used to be called the Near East. It is also considered to mark the beginning of the Bronze Age in Central Europe(h).
Helmut Tributsch suggested that the island of Gavrinis near Carnac in Brittany had been the capital of this Atlantean civilisation(d). He dated the destruction of Atlantis to 2200 BC.
The Bronze Age in the Mediterranean region saw two periods of great political turbulence, the first, around 2200 BC and the second a millennium later, generally known as the Bronze Age Collapse.
In 2001 Professor Fekri Hassan, from University College London, studied ancient reports that so many people had died from hunger in southern Egypt that people had resorted to cannibalism. Hassan found evidence of extreme weather conditions around 2200 BC both in Egypt and further afield from a study of cores from ancient lakes(c).
According to some commentators, the Los Millares culture also ended around the same time. W. Sheppard Baird in a paper on the Sea Peoples maintains that the Los Millares culture lasted until 2200 BC and was succeeded by the Argaric named after the el Argar site.
The Oera Linda Book puts the destruction of Atlantis circa 2200 BC(f).
Two of Gavin Menzies‘ specific claims are that transoceanic travel began 100,000 years ago and that the Chinese regularly began visiting America from 2200 BC!
Dr Anton Mifsud has used the reign of King Ninus of Assyria as an anchor for his preferred date for the destruction of Atlantis, in Malta, of around 2200 BC. He points out [209] that Eumelos of Cyrene dated the demise of Plato’s island to the reign of Ninus and links this with the calculation of the Roman historian Aemilius Sura (2nd cent. BC) who placed the reign of Ninus around 2192 BC. Several other authorities attribute similar dates to his reign as recorded by John Jackson in volume one of his 1752 Chronological Antiquities [1555.251].
The collapse of the Egyptian Old Kingdom also took place around 2200 BC.
A 2022 paper(g) by Huw S. Groucutt et al. has investigated the coincidence of the ending of the Temple Building Period in Malta with the so-called 4.2 ka Event, thought by many to be the result of climate change. However, this would need to coincide with a severe seismic or tectonic event on Malta in order to support Mifsud’s theory of a Maltese Atlantis.
Timo Niroma (? – 2009) from Helsinki in Finland had an extensive website(e) in which he discussed various worldwide catastrophes including two main events around 2200 BC and 3100 BC.
In 2001, Tom Slattery published a paper(a) regarding the Comet Hale-Bopp which had been discovered 1n 1995. He speculated that it may have been seen much earlier in 2213 BC and that a fragment of it may have struck the Earth with dire consequences and may have been the trigger for the widespread collapse of civilisations around 2200! While comets are traditionally considered to be harbingers of doom, they certainly were in this instance when “thirty-nine members of the Heaven’s Gate cult committed mass suicide in March 1997 with the intention of teleporting to a spaceship which they believed was flying behind the comet.”(b)
(a) http://www.mgr.org/comet3.html
(b) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comet_Hale–Bopp
(c) BBC News | SCI/TECH | Disaster that struck the ancients
(f) https://earth-history.com/europe/book-the-oera-linda-book/1173-oera-intro
(g) (PDF) The 4.2 ka Event and the End of the Maltese “Temple Period” (researchgate.net)
(h) https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article/file?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0139705&type=printable
Fernandez, Sandra
Sandra Fernandez is a Spanish researcher who has opted for Almería in southeast Spain as the location of Atlantis. She identifies the plain south of the Sierra de Alhamilla as the plain referred to by Plato. Her website has a number of blogs devoted to Atlantis(a). Unfortunately, the site is in Spanish and I find that Google translator does not give a clear translation. Fernandez sees the Los Millares culture centred north west of Almería as preceding the Atlanteans.
I note that at the eastern end of the Gulf of Almería there is Cabo de Gata, while inland to the west of the plain lies Gádor, both of which might be variations of Gades!
(a) https://atlantesdehoy.wordpress.com/2015/08/06/hola-mundo/
Aldamiz, Luis
Luis Aldamiz (aka Maju) is an independent Basque researcher who has  concluded that the Atlantean Empire was at the centre of the VNSP (Vila Nova de São Pedro) culture in ancient Portugal(a)(b). Its capital Zambujal was situated near the modern city of Torres Vedras, just north of Lisbon. He bases his idea on a number of topographical and historical parallels between the VNSP region and Plato’s description of Atlantis(c).
concluded that the Atlantean Empire was at the centre of the VNSP (Vila Nova de São Pedro) culture in ancient Portugal(a)(b). Its capital Zambujal was situated near the modern city of Torres Vedras, just north of Lisbon. He bases his idea on a number of topographical and historical parallels between the VNSP region and Plato’s description of Atlantis(c).
In order to have Plato’s account of the Atlantean War conform to his location theory, he suggests that the Mycenaean Greeks fought alongside the El Argar people in southeast Spain against VNSP Atlanteans! The evidence for such a military alliance is at best tenuous or more likely, purely speculative.
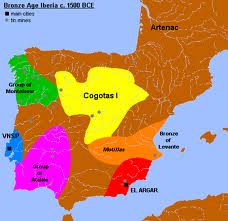 However, the idea is not as farfetched as it might seem when combined with the views of W.Sheppard Baird who claims that Minoans had been the colonisers of Los Millares in Andalusia as early as 4000 BC. In due course, the culture of Los Millares was superseded by that of El Argar. This begs the question as whether the Mycenaeans who had succeeded the Minoans on Crete also replaced them in their Andalusian colonies!
However, the idea is not as farfetched as it might seem when combined with the views of W.Sheppard Baird who claims that Minoans had been the colonisers of Los Millares in Andalusia as early as 4000 BC. In due course, the culture of Los Millares was superseded by that of El Argar. This begs the question as whether the Mycenaeans who had succeeded the Minoans on Crete also replaced them in their Andalusian colonies!
Nevertheless, no matter how interesting the theories of Aldamiz and Baird may be, they have still to explain Plato’s claim that the Atlanteans ‘controlled’ Europe as far as Tyrhennia, along with part of North Africa, before their eastward invasion! Furthermore, the part that Egypt played in their alliance with Athens in the war with Atlantis is totally ignored by them.
(b) https://www.geocities.ws/luis_aldamiz/Atlantis/Atlantis.html
Los Millares
Los Millares is the name given to a culture situated in Andalusia, Spain which flourished during the Copper Age and lasted until around 1800 BC before the introduction of bronze. It was discovered at the end of the 19th century and excavation continues today. The step pyramid of Monte d’Accoddi on Sardinia has been compared to the Los Millares architecture. It is also claimed that Los Millares along with other Iberian sites were Minoan colonies(a) dating from the late 4th millennium BC. Inevitably, some commentators have tried to suggest a link with Atlantis based on the existence there of a series of three concentric battlements.
>Helmut Tributsch was one such advocate of Los Millares as Atlantis, who outlines his reasons in an article(e) on the Atlantisforschung website.<
However, Los Millares fails to match Plato’s description on a number of counts; it’s not an island, it’s not submerged, it had no writing, etc. It might be worth mentioning that Los Millares as the location of Atlantis does not fit with the assumption that the Pillars of Heracles were situated at Gibraltar as Los Millares is not ‘beyond’ the Pillars.
Sheppard Baird in a paper on the Sea Peoples(b) maintains that the Los Millares culture lasted until 2200 BC and was succeeded by the Argaric named after the el Argar site. He also claims the Argaric watchtowers known as ‘motillas’ inspired the development of the ‘nuraghi’ on Sardinia.
In a 2022 article on the Ancient Origins website by historian Natalia Klimczak she offers her view of the importance that copper played in the success of the Los Millares civilisation(a).
Additional information is to be found on the ancient-wlsdom.com website(c).
(a) https://www.minoanatlantis.com/Minoan_Spain.php
(b) http://www.minoanatlantis.com/Origin_Sea_Peoples.php
Minoan Hypothesis *
The Minoan Hypothesis proposes an Eastern Mediterranean origin for Plato’s Atlantis centred on the island of Thera and/or Crete. The term ‘Minoan’ was coined by the renowned archaeologist Sir Arthur Evans after the mythic King Minos. (Sir Arthur was the son of another well-known British archaeologist, Sir John Evans). Evans thought that the Minoans had originated in Northern Egypt and came to Crete as refugees. However, recent genetic studies seem to indicate a European ancestry!
It is claimed(a) that Minoan influence extended as far as the Iberian Peninsula as early as 3000 BC and is reflected thereby what is now known as the Los Millares Culture. Minoan artefacts have also been found in the North Sea, but it is not certain if they were brought there by Minoans themselves or by middlemen. The German ethnologist, Hans Peter Duerr, has a paper on these discoveries on the Academia.edu website(e). He claims that the Minoans reached the British Isles as well as the Frisian Islands where he found artefacts with some Linear A inscriptions near the site of the old German trading town of Rungholt, destroyed by a flood in 1362(f).
The advanced shipbuilding techniques of the Minoans are claimed to have been unmatched for around 3,500 years until the 1950s (l).
The Hypothesis had its origin in 1872 when Louis Guillaume Figuier was the first to suggest [0296] a link between the Theran explosion and Plato’s Atlantis. The 1883 devastating eruption of Krakatoa inspired Auguste Nicaise, in an 1885 lecture(c) in Paris, to cite the destruction of Thera as an example of a civilisation being destroyed by a natural catastrophe, but without reference to Atlantis.
The Minoan Hypothesis proposes that the 2nd millennium BC eruption(s) of Thera brought about the destruction of Atlantis. K.T. Frost and James Baikie, in 1909 and 1910 respectively, outlined a case for identifying the Minoans with the Atlanteans, decades before the extent of the massive 2nd millennium BC Theran eruption was fully appreciated by modern science. In 1917, Edwin Balch added further support to the Hypothesis [151].
As early as April 1909, media speculation was already linking the discoveries on Crete with Atlantis(h), despite Jowett’s highly sceptical opinion.
Supporters of a Minoan Atlantis suggest that when Plato wrote of Atlantis being greater than Libya and Asia he had mistranscribed meison (between) as meizon (greater), which arguably would make sense from an Egyptian perspective as Crete is between Libya and Asia, although it is more difficult to apply this interpretation to Thera which is further north and would be more correctly described as being between Athens and Asia. Thorwald C. Franke has now offered a more rational explanation for this disputed phrase when he pointed out [0750.173] that “for Egyptians, the world of their ‘traditional’ enemies was divided in two: To the west, there were the Libyans, to the east there were the Asians. If an Egyptian scribe wanted to say, that an enemy was more dangerous than the ‘usual’ enemies, which was the case with the Sea Peoples’ invasion, then he would have most probably said, that this enemy was “more powerful than Libya and Asia put together”.
It has been ‘received wisdom’ that the Minoans were a peace-loving people, however, Dr Barry Molloy of Sheffield University has now shown that the exact opposite was true(d) and that “building on recent developments in the study of warfare in prehistoric societies, Molloy’s research reveals that war was, in fact, a defining characteristic of the Minoan society, and that warrior identity was one of the dominant expressions of male identity.”
In 1939, Spyridon Marinatos published, in Antiquity, his opinion that the eruption of Thera had led to the demise of the Minoan civilisation. However, the editors forbade him to make any reference to Atlantis. In 1951, Wilhelm Brandenstein published a Minoan Atlantis theory, echoing many of Frost’s and Marinatos’ ideas, but giving little credit to either.
However, Colin MacDonald, an archaeologist at the British School in Athens, believes that “Thira’s eruption did not directly affect Knossos. No volcanic-induced earthquake or tsunami struck the palace which, in any case, is 100 meters above sea level.” The Sept. 2019 report in Haaretz suggests it’s very possible the Minoans were taken over by another civilization and may have been attacked by the Mycenaeans, the first people to speak the Greek language and they flourished between 1650 B.C. and 1200 B.C. Archaeologists believe that the Minoan and Mycenaean civilisations gradually merged, with the Mycenaeans becoming dominant, leading to the shift in the language and writing system used in ancient Crete.
The greatest proponents of the Minoan Hypothesis were arguably A.G. Galanopoulos and Edward Bacon. Others, such as J.V. Luce and James Mavor were impressed by their arguments and even Jacques Cousteau, who unsuccessfully explored the seas around Santorini, while Richard Mooney, the ‘ancient aliens’ writer, thought [0842] that the Minoan theory offered a credible solution to the Atlantis mystery. More recently Elias Stergakos has proposed in an overpriced 68-page book [1035], that Atlantis was an alliance of Aegean islands that included the Minoans.
Moses Finley, the respected classical scholar, wrote a number of critical reviews of books published by prominent supporters of the Minoan Hypothesis, namely Luce(aa), Mavor(y)(z) as well as Galanopoulos & Bacon(aa)(ab). Some responded on the same forum, The New York Review of Books.
Andrew Collins is also opposed to the Minoan Hypothesis, principally because “we also know today that while the Thera eruption devastated the Aegean and caused tsunami waves that destroyed cities as far south as the eastern Mediterranean, it did not wipe out the Minoan civilization of Crete. This continued to exist for several generations after the catastrophe and was succeeded by the later Mycenaean peoples of mainland Greece. For these reasons alone, Plato’s Atlantic island could not be Crete, Thera, or any other place in the Aegean. Nor can it be found on the Turkish mainland at the time of Thera’s eruption as suggested by at least two authors (James and Zangger) in recent years(ad).“
Alain Moreau has expressed strong opposition to the Minoan Hypothesis in a rather caustic article(i), probably because it conflicts with his support for an Atlantic location for Atlantis. In more measured tones, Ronnie Watt has also dismissed a Minoan Atlantis, concluding that “Plato’s Atlantis happened to become like the Minoan civilisation on Theros rather than to be the Minoan civilisation on Theros.” In 2001, Frank Joseph wrote a dismissive critique of the Minoan Hypothesis referring to Thera as an “insignificant Greek island”.(x)
Further opposition to the Minoan Hypothesis came from R. Cedric Leonard, who has listed 18 objections(q) to the identification of the Minoans with Atlantis, keeping in mind that Leonard is an advocate of the Atlantic location for Plato’s Island.
Atlantisforschung has highlighted Spanuth’s opposition to the Minoan Hypothesis in a discussion paper on its website. I have published here a translation of a short excerpt from Die Atlanter that shows his disdain for the idea of an Aegean Atlantis.
“Neither Thera nor Crete lay in the ‘Atlantic Sea’, but in the Aegean Sea, which is expressly mentioned in Crit. 111a and contrasted with the Atlantic Sea. Neither of the islands lay at the mouth of great rivers, nor did they “sink into the sea and disappear from sight.” ( Tim. 25d) The Aegean Sea never became “impassable and unsearchable because of the very shallow mud”. Neither Solon nor Plato could have said of the Aegean Sea that it was ‘still impassable and unsearchable’ or that ‘even today……….an impenetrable and muddy shoal’ ‘blocks the way to the opposite sea (Crit.108e). Both had often sailed the Aegean Sea and their contemporaries would have laughed at them for telling such follies.” (ac)
Lee R. Kerr is the author of Griffin Quest – Investigating Atlantis [0807], in which he sought support for the Minoan Hypothesis. Griffins (Griffons, Gryphons) were mythical beasts in a class of creatures that included sphinxes. Kerr produced two further equally unconvincing books [1104][1675], all based on his pre-supposed link between Griffins and Atlantis or as he puts it “whatever the Griffins mythological meaning, the Griffin also appears to tie Santorini to Crete, to Avaris, to Plato, and thus to Atlantis, more than any other single symbol.” All of which ignores the fact that Plato never referred to a Sphinx or a Griffin!
The hypothesis remains one of the most popular ideas with the general public, although it conflicts with many elements in Plato’s story. A few examples of these are, where were the Pillars of Heracles? How could Crete/Thera support an army of one million men? Where were the elephants? There is no evidence that Crete had walled cities such as Plato described. The Minoan ships were relatively light and did not require the huge harbours described in the Atlantis story. Plato describes the Atlanteans as invading from their western base (Tim.25b & Crit.114c); Crete/Santorini is not west of either Egypt or Athens
Gavin Menzies attempted to become the standard-bearer for the Minoan Hypothesis. In The Lost Empire of Atlantis [0780], he argues for a vast Minoan Empire that spread throughout the Mediterranean and even discovered America [p.245]. He goes further and claims that they were the exploiters of the vast Michigan copper reserves, which they floated down the Mississippi for processing before exporting it to feed the needs of the Mediterranean Bronze industry. He also accepts Hans Peter Duerr’s evidence that the Minoans visited Germany, regularly [p.207].
Tassos Kafantaris has also linked the Minoans with the exploitation of the Michigan copper, in his paper, Minoan Colonies in America?(k) He claims to expand on the work of Menzies, Mariolakos and Kontaratos. Another Greek Professor, Minas Tsikritsis, also supports the idea of ancient Greek contact with America. However, I think it is more likely that the Minoans obtained their copper from Cyprus, whose name, after all, comes from the Greek word for copper.
Oliver D. Smith has charted the rise and decline in support for the Minoan Hypothesis in a 2020 paper entitled Atlantis and the Minoans(u).
Frank Joseph has criticised [0802.144] the promotion of the Minoan Hypothesis by Greek archaeologists as an expression of nationalism rather than genuine scientific enquiry. This seems to ignore the fact that Figuier was French, Frost, Baikie and Bacon were British, Luce was Irish and Mavor was American. Furthermore, as a former leading American Nazi, I find it ironic that Joseph, a former American Nazi leader, is preaching about the shortcomings of nationalism.
While the suggestion of an American connection may seem far-fetched, it would seem mundane when compared with a serious attempt to link the Minoans with the Japanese, based on a study(o) of the possible language expressed by the Linear A script. Gretchen Leonhardt(r) also sought a solution in the East, offering a proto-Japanese origin for the script, a theory refuted by Yurii Mosenkis(s), who promotes Minoan Linear A as proto-Greek. Mosenkis has published several papers on the Academia.edu website relating to Linear A(t). However, writing was not the only cultural similarity claimed to link the Minoans and the Japanese offered by Leonhardt.
Furthermore, Crete has quite clearly not sunk beneath the waves. Henry Eichner commented, most tellingly, that if Plato’s Atlantis was a reference to Crete, why did he not just say so? After all, in regional terms, ‘it was just down the road’. The late Philip Coppens was also strongly opposed to the Minoan Hypothesis.(g)
Eberhard Zangger, who favours Troy as Atlantis, disagrees strongly [0484] with the idea that the Theran explosion was responsible for the 1500 BC collapse of the ‘New Palace’ civilisation.
Excavations on Thera have revealed very few bodies resulting from the 2nd millennium BC eruptions there. The understandable conclusion was that pre-eruption rumblings gave most of the inhabitants time to escape. Later, Therans founded a colony in Cyrene in North Africa, where you would expect that tales of the devastation would have been included in their folklore. However, Eumelos of Cyrene, originally a Theran, opted for the region of Malta as the remnants of Atlantis. How could he have been unaware of the famous history of his family’s homeland?
A 2008 documentary, Sinking Atlantis, looked at the demise of the Minoan civilisation(b). James Thomas has published an extensive study of the Bronze Age, with particular reference to the Sea Peoples and the Minoans(j).
In the 1990s, art historian and museum educator, Roger Dell, presented an illustrated lecture on the art and religion of the Minoans titled Art and Religion of the Minoans: Europe’s first civilization”, which offered a new dimension to our understanding of their culture(p). In this hour-long video, he also touches on the subject of Atlantis and the Minoans.
More extreme is the theory of L. M. Dumizulu, who offers an Afrocentric view of Atlantis. He claims that Thera was part of Atlantis and that the Minoans were black!(m)
In 2019, Nick Austin attempted [1661] to add further support to the idea of Atlantis on Crete, but, in my opinion, he failed. The following year, Sean Welsh also tried to revive the Minoan Hypothesis in his book Apocalypse [1874], placing the Atlantean capital on Santorini, which was destroyed when the island erupted around 1600 BC. He further claims that the ensuing tsunami led to the biblical story of the Deluge.
Evan Hadingham published a paper(v) in 2008 in which he discussed the possibility that the Minoan civilisation was wiped out by the tsunami generated by the eruption(s) of Thera. Then, seven years later he produced a second paper(w) exonerating the tsunami based on new evidence or lack of it.
In April 2023, an attempt was made to breathe some new life into the Minoan Hypothesis in an article(ae) on the Greek Reporter website. This unconvincing piece claims “Plato describes in detail the Temple of Poseidon on Atlantis, which appears to be identical to the Palace of Knossos on the island of Crete.” The writer, Caleb Howells, has conveniently overlooked that Atlantis was submerged creating dangerous shoals and remained a maritime hazard even up to Plato’s day (Timaeus 25d). The Knossos Palace is on a hill and offers no evidence of ever having been submerged. Try again.
The same reporter did try again with another unconvincing piece supporting the Minoan Hypothesis, also on the Greek Reporter site, in October 2023(af). This time, he moved the focus of his claim to Santorini where he now placed the Palace of Poseidon relocating it from Crete! I suppose he will eventually make his mind up. Nevertheless, Howells revisited the subject of the Palace of Poseidon just a few weeks later, once again identifying it as the Palace of Knossos – “Plato’s account of the lost civilization of Atlantis includes a description of a marvelous temple of god Poseidon. It was said to have been in the center of Atlantis, so it was a very prominent part. However, in most investigations into the origin of Atlantis, this detailed temple description is ignored. In fact, an analysis of Plato’s details indicates that the Temple of Poseidon on Atlantis was actually identical to the Palace of Knossos on the island of Crete, Greece.” (ag)
Most Atlantis theories manage to link their their chosen site with some of the descriptive details provided by Plato. The Minoan Hypothesis is no exception, so understandably Howells has highlighted the similarities, while ignoring disparities. The Minoans were primarily concerned with trading, not territorial expansion. When did they engage in a war with Athens or threaten Egypt? If Howells can answer that he may have something relevant to build upon!
For a useful backdrop to the Minoan civilisation I suggest that readers have a look at a fully illustrated 2019 lecture by Dr. Gregory Mumford of the University of Alabama at Birmingham. In it he give a broad overview of the Eastern Mediterranean, with a particular emphasis on the Aegean Sea, during the Middle- Late Bronze Age (2000-1200 BC). (ah)
(a) http://www.minoanatlantis.com/Minoan_Spain.php
(b) http://video.pbs.org/video/1204753806/
(c) http://fr.wikisource.org/wiki/Les_Terres_disparues
(d) http://www.sci-news.com/archaeology/article00826.html
(e) See: Archive 3928
(f) http://dienekes.blogspot.ie/2008/08/minoans-in-germany.html
(g) https://web.archive.org/web/20180128190713/http://philipcoppens.com/lectures.php (June 3, 2011)
(j) https://medium.com/the-bronze-age
(k) GREECE AND WORLD: Minoan colonies in America? *
(m) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QqTQeF2gLpg
(o) Archive 3930 | (atlantipedia.ie)
(p) https://vimeo.com/205582944 Video
(q) https://web.archive.org/web/20170113234434/http://www.atlantisquest.com/Minoan.html
(r) https://konosos.net/2011/12/12/similarities-between-the-minoan-and-the-japanese-cultures/
(t) https://www.academia.edu/31443689/Researchers_of_Greek_Linear_A
(u) https://www.academia.edu/43892310/Atlantis_and_the_Minoans
(v) Did a Tsunami Wipe Out a Cradle of Western Civilization? | Discover Magazine
(w) https://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/article/megatsunami-may-wiped-europes-first-great-civilization/
(x) Atlantis Rising magazine #27 http://pdfarchive.info/index.php?pages/At
(y) Wayback Machine (archive.org)
(z) https://www.nybooks.com/articles/1969/12/04/back-to-atlantis-again/
(aa) Back to Atlantis | by M.I. Finley | The New York Review of Books (archive.org)
(ab) The End of Atlantis | by A.G. Galanopoulos | The New York Review of Books (archive.org)
(ac) Jürgen Spanuth über ‘Atlantis in der Ägäis’ – Atlantisforschung.de
(ad) Kreta oder Thera als Atlantis? – Atlantisforschung.de (atlantisforschung-de.translate.goog)
(ae) Was Atlantis’ Temple of Poseidon the Palace of Knossos in Crete? (greekreporter.com)
(af) Was Atlantis a Minoan Civilization on Santorini Island? (greekreporter.com)
(ag) https://greekreporter.com/2023/12/01/atlantis-temple-poseidon-palace-knossos-crete/
Dating Atlantis *
Dating Atlantis is one of the most contentious difficulties faced by Atlantology. The critical problem is to identify the time of the Atlantean War and that of the later destruction of Atlantis itself; two events possibly separated by a period not recorded by Plato. This entry is primarily concerned with the date of the war. However, it should be pointed out that Plato also reveals that the Atlantis story has a very long history before the war, back to a time when ships and sailing did not yet exist (Crit.113e), so it is understandable when Plato filled that historical gap with mythological characters, namely five sets of twins sired by Poseidon. Of course, Poseidon being a sea god did not require a boat to get to the island of Atlantis! Plato also informs us that the twins and their descendants lived on the island for ‘many generations’ and extended their rule over many other islands in the sea (Crit.114c).
There are roughly three schools of thought regarding this important detail. The first group persists in accepting at face value Plato’s reference to a period of 9,000 solar years having elapsed since the War with Atlantis up to the time of Solon’s visit around 550 BC. The second group is convinced that the 9,000 refers to periods other than solar years, such as lunar cycles or seasons. The third group seeks to identify the time of Atlantis by linking it to other known historical events.
While these groups offered some level of evidence, however flimsy, to support their claims, some individuals have placed Atlantis up to millions of years in the past based on nothing more than their fertile imaginations or delusions. Arguably the best-known was Edgar Cayce, but purveyors of such daft ideas are still lurking among us!(m)
Rene Malaise writing in Egerton Sykes‘ Atlantis journal (#108, January/February 1967, Vol. 20 No. 1) challenged the idea that Plato’s 9,000 years was a reference to years of 12 months. Atlantisforschung has now republished the article in German and I have added an English translation below(s).
Desmond Lee has commented[0435] that “the Greeks, both philosophers and others…….seem to have been curiously lacking in their sense of time-dimension.”
[1.0] 9550 BC is factually correct
This view has a slowly dwindling number of supporters among serious investigators. Massimo Rapisarda is one such promoter, who has offered his reasons for accepting this early date(p). To support this idea proponents usually cite a wide range of evidence to suggest the existence of advanced cultures in the 10th millennium BC. Matters such as an earlier than conventionally accepted date for the Sphinx, early proto-alphabets a la Glozel or the apparently anomalous structures such as the Lixus foundations or the controversial Baalbek megaliths have all been recruited to support an early date for Atlantis, many, if not all, have their dates hotly disputed. Apart from the contentious dates, there is NOTHING to definitively link any of them with Plato’s Atlantis.
In common with most nations, the Egyptians competitively promoted the great antiquity of their own origins. Herodotus reports that while in Egypt he was told of a succession of kings extending over 17,000 years. The priests of Memphis told him firmly that 341 kings and a similar number of high priests had until then, ruled their country. (Herodotus, Book II, 142). ), of course, there is not a shred of archaeological evidence to support such a claim. Even an average reign of 20 years would give a total of nearly 7000 years whereas a more improbable 26-year average would be required to span the necessary 9000 years.
It is therefore obvious that the 17,000 years related to Herodotus is not credible raising a question regarding the trustworthiness of the 9000 years told to Solon.
In The Laws Plato refers to Egyptian art going back 10,000 years, seemingly, indicating consistency in his belief in the great antiquity of civilisation and fully compatible with his date for Atlantis. However, I have discovered that in Plato’s time ‘ten thousand’ was frequently used simply to express a large but indefinite number.
A Bible study site tells us that “The use of definite numerical expressions in an indefinite sense, that is, as round numbers, which is met with in many languages, seems to have been very prevalent in Western Asia from early times to the present day.”(h)
The acceptance of Plato’s 9,000 years as literally correct defies both commonsense and archaeological evidence, which demonstrates that neither Athens nor a structured Egypt existed at such an early period. The onus is on those, who accept the prima facie date of 9,600 BC, to explain how Atlantis attacked a non-existent Athens and/or Egypt.
A major difficulty in accepting Plato’s 9,000 years at face value is that it conflicts with our current knowledge of ancient seafaring. Professor Seán McGrail (1928-2021) wrote in his monumental work, Boats of the World “There is no direct evidence for water transport until the Mesolithic even in the most favoured regions, and it is not until the Bronze Age that vessels other than logboats are known” [1949.10]. Wikipedia’s list of ancient boats supports this view(r). For those that adhere to a 10th millennium BC date for the Atlantean War with Athens, this lack of naval evidence to support such an early date undermines the idea. An invasion fleet of canoes travelling from beyond the Pillars of Herakles to attack Athens or Egypt seems rather unlikely!
Even more incongruous is Plato’s description of horse baths (Crit.117b), a facility that was highly unlikely around 9600 BC, when you consider that this is probably millennia before the domestication of horses.
In a 2021 article(h) concerning 10,000 BC, Thorwald C. Franke offered the following opinion; “Many scientists seem to live quite comfortably with Graham Hancock and similar authors speculating about 10,000 BC because these hypotheses are so nonsensical that they do not interfere with real science. Sometimes you have the impression that many scientists even prefer such misleading popular errors over more informed hypotheses because they would make the audience ask more serious questions and then the questions could not be dismissed so easily anymore. But this is only an impression. In truth, scientists shy away from the effort to overcome these popular errors. It is much easier to stay silent and to ignore them.”
Alexandros Angelis wrote(q) of how he is “always suspicious of coincidence. Whenever I hear this word, an alarm sets off in my head. In my book ‘Our Unknown Ancient Past: Thoughts and Reflections on the Unexplained Mysteries of Prehistory’ I state that it cannot be a coincidence that Plato’s date of Atlantis’ destruction (9.600 BC) is spot on, coinciding with the abrupt end of the Younger Dryas (9.600 BC).”
When I first encountered this ‘coincidence’ I was also suspicious. However, as I investigated further I realised that all of Plato’s large numbers seemed to be inflated by what was arguably a common factor – another coincidence? I have devoted an entire chapter in Joining the Dots to this problem.
Angelis considers the ‘rapid’ gradual melting of the ice at the end of the Younger Dryas as the cause of Atlantis’ submergence, which might have been true except that Plato tells us that the catastrophe took place over a day and a night and that the event was triggered by an earthquake. Angelis seems unaware that isostatic rebound is a very slow process of readjustment involving centuries and sometimes thousands of years and even when glaciers melt rapidly, sea levels, because of the vastness of our oceans, rise slowly.
[2.0] 9000 refers to units of time other than solar years
Advocates of this view, understandably point out, that the Atlantis described in such detail by Plato belongs to the Bronze Age and could not have existed at an earlier date. It is worth noting that the technology is coincidental with the most advanced known to Plato and his audience. For those who argue that mankind has been destroyed on one or more occasions and has had to start again from scratch, it is not credible that if this was the case, the culture and technology described by Plato as existing in 9500 BC is precisely what he would have experienced himself. There is nothing in the Atlantis texts to connect it with a pre-Bronze Age society, nor is there anything to suggest any technology or cultural advance beyond that of the 4th century BC. Plato’s tale tells of the existence of at least three major nations before the destruction of Atlantis: Egypt, Athens and Atlantis itself. There is no archaeological evidence to indicate anything other than Neolithic cultures existing in Egypt or Athens around 9500 BC. The currently accepted date for the beginning of Egyptian civilisation is circa 3100 BC and also for the existence of a primitive culture around Athens at about the same time. This would parallel the time of the Western European megalithic builders.
It is noteworthy that researchers who support a 9,600 BC date for the war between Atlantis and Athens cannot explain how this took place millennia before there was any structured society in Greece or Egypt.
It may be worth noting the comments of Israel Finkelstein and Neil Silberman who have argued[280] for a 7thcentury BC date for the final draft of the Exodus narrative rather than during the 2nd millennium BC as suggested by the text. “In much the same way that European illuminated manuscripts of the Middle Ages depicted Jerusalem as a European city with turrets and battlements to heighten its direct impact on contemporary readers” (p68). Similarly, it is possible that Plato added architectural and technological details of his day to a more ancient tale of a lost civilisation to make a more powerful impression on his audience.
According to Bury’s translation, Plato mentions (Crit. 119e) that iron was used for utensils and weapons in Atlantis and so forcing us to look to a date later than 2000 BC for its destruction. Olaf Rudbeck drew attention to this reference around 1700.
[2.1]
Diaz-Montexano claims that the ‘9000 years’ in Critias has been mistranslated. He refers to the earliest versions of Critias that are available and insists that the texts permit a translation of either ‘9 times in a 1000 years’ or ‘1009’, the first being the more rational! Frank Joseph has also used this 1009 number, quoting private correspondence from Kenneth Caroli, in his 2015 regurgitation[1074] of Atlantis and 2012. Diaz-Montexano has also drawn attention to the commentary on Timaeus by Proclus, writing in the 5th century AD, where he treats Plato’s use of 9000 as having symbolic rather than literal meaning. It should also be kept in mind that many cultures, ancient and modern use specific numbers to indicate indefinite values(e). In a more recent paper, Diaz-Montexano concluded that “we can place their military and colonizing expansion towards the end of 3.500 BC, at the earliest, and the end of their civilization (with Atlantis sinking) between 2.700 and 1.700 BC.”(o)
[2.2] In June 2017, a forum on the Historum.com website included the following possible explanation for the Atlantean dates:
“ The date 8000 is given as a fraction of 8 since the Greeks commonly used fractional notation. Plato wrote in 400 BC and Solon obtained the account in 570 BC.
No Egyptian Annals ever went back 9000 or even 8000 years. The furthest back the Egyptian annals went at the time of Herodotus was to 3050 BC to the reign of Menes the first Pharaoh who Herodotus knew about. Therefore it is obvious that the number of years has been given as a fraction which was extremely common in Greek numerology.
Thus the war between Atlantis and Athens occurred in 9000/8 + 570 = 1695 BC (+/-63 years) which is pretty close to the date of the war between the Titans and the Gods c.1685-1675 BC. The entire story of Atlantis runs concurrent to the time of the Thera Eruption. You even have 10 kings ruling the land equivalent to the 12 Titans.”
The Bible too denotes years as fractions, i.e. seasons, equinoxes/solstices etc. That is why you have biblical patriarchs that lived 800 and 900 years old. The ages to Noah are all counted in Lunar months.”(i)
While I’m aware that the Egyptians also had a different way of dealing with fractions, I really cannot fully understand any of the suggestions made above.
[2.3] 900, not 9000 years
To address these apparent dating problems, some have suggested that the stated 9000 years, which allegedly elapsed since the catastrophe, are the result of incorrect transcription by someone along what is a very long chain of transmission and that hundreds have somehow been confused with thousands and that the correct figure should be 900 years. Another suggestion is that the Egyptian hieroglyphics for ‘hundred’ and ‘thousand’ are easily confused. This explanation does not hold water, as there is little room for confusion between these hieroglyphics as illustrated below. This idea has been adopted by Don Ingram and incorporated into his Atlantis hypothesis.
Immanuel Velikovsky also endorsed the idea of a tenfold discrepancy in Plato’s date for the time of Atlantis in Worlds in Collision [037.152].
However, 900 years earlier than Solon would place the conflict with the Atlanteans during the XVIIIth Dynasty and would have been well recorded. More recently Diaz-Montexano put forward the idea that the Egyptian words for ‘100’ and ‘1000’ when spoken sounded similar leading to Solon’s error. This idea has now been taken up by James Nienhuis and in greater detail by R. McQuillen(a).
Another explanation offered by James W. Mavor Jnr. is that the original Egyptian story emanated from Crete where it may have been 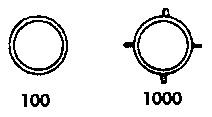 written in either the Linear A or Linear B script where the symbols for 100 and 1000 are quite similar. In both scripts, the symbol for 100 is a circle whereas the symbol for 1000 is a circle with four equally spaced small spikes or excrescences projecting outward.
written in either the Linear A or Linear B script where the symbols for 100 and 1000 are quite similar. In both scripts, the symbol for 100 is a circle whereas the symbol for 1000 is a circle with four equally spaced small spikes or excrescences projecting outward.
Nevertheless, the most potent argument against the ‘factor ten’ solution is that if the priests did not intend to suggest that Egypt was founded 8000 years before Solon’s visit but had meant 800 years, it would place the establishment of Egypt at around 1450 BC, which is clearly at variance with undisputed archaeological evidence. However, I contend that they were referring to the establishment of Sais as a centre of importance, not the foundation of the entire nation of Egypt.
In Joining the Dots, I supported the ‘factor ten’ explanation but did so because all of Plato’s large numbers relating as they do to dimensions, manpower and time invariably appear to be exaggerations, but become far more credible when reduced by a factor of ten. Supporters of Plato’s 9,000 years as factual seem to ignore all the other numbers that also appear to be seriously inflated!
[2.4] 9000 months not years
The earliest suggestion that I have found which implied that the age of Atlantis noted by Plato referred to months rather than solar years comes from the early fourteenth century.
Thorwald C. Franke has drawn attention to Thomas Bradwardine‘s rejection of Plato’s, or more correctly the Egyptian priest’s, apparent claim of a very early date for Atlantis [1255.242]. It seems that he found such a date conflicted with biblical chronology. In the end, he proposed that Plato’s ‘years’ were lunar cycles. Similarly, Pierre d’Ailly (1350-1420), a French theologian who became cardinal, arrived at the same conclusion for similar reasons.
Around two and a half centuries later in 1572 Pedro Sarmiento de Gamboa suggested the application of lunar ‘years’ rather than solar years to Plato’s figures. Augustin Zárate expressed the same view in 1577, quoting Eudoxus in support of it.
In the 18th century, Cornelius De Pauw also believed that Plato’s 9000 ‘years’ was a reference to lunar cycles.
Then there are others, such as Émile Mir Chaouat and Jürgen Hepke who also subscribe to the view that the 9000 ‘years’ recorded by Plato referred to months rather than solar years, as the early Egyptians extensively used a lunar calendar and continued to use it throughout their long history, particularly for determining the dates of religious festivals and since Solon received the Atlantis story from Egyptian priests it would be understandable if they used lunar ‘years’ in their conversations. Eudoxus of Cnidos (c.400 BC- c. 350 BC), a mathematician and astronomer, who spent a year in Egypt, declared, “The Egyptians reckon a month as a year”. Diodorus Siculus (1st cent. BC) echoes this statement. (see Richard A. Parker[682]) and Manetho (3rd cent.BC) (Aegyptiaca[1373.40])
Olof Rudbeck also proposed that Plato misunderstood the Greek priesthood’s use of lunar cycles rather than solar years to calculate time. This in turn led him to date the Atlantean War to 1350 BC.
Robert Argod wrote [065.254] “This story, which was supposedly related to Solon by Egyptian priests, speaks of 8,000 years, which are certainly in fact moons – for this was how the Egyptians counted. This dates the story reasonably accurately to the 13th century BC, at the memorable period of the battles between Rameses II and Rameses III against the Sea Peoples.” A coincidence?
This use of months rather than years would give us a total of just 750 years before Solon’s visit and so would place the Atlantis catastrophe around 1300 BC, nearly coinciding with the eruption of Thera and the collapse of the Minoan civilisation.
A similar explanation has been offered by J.Q. Jacobs to rationalise the incredible time spans found in ancient Indian literature, who suggested that numbers referred to days rather than years(b).
Stefan Bittner seemed to date the Atlantean War in 1644 BC using a combination of treating Plato’s years as months and reducing the same years by a factor of ten!
Even more bizarre is the suggestion from Patrick Dolciani that Plato’s 9000 ‘years’ were in fact periods of 73 days because it agrees with both the synodical revolution of Venus and our solar year!!
[2.5] 5,000 not 9,000 years
A claim was made on Graham Hancock’s website in 2008(c) that Plato did not write 9,000 but instead wrote 5,000, but that the characters for both were quite similar leading to the misunderstanding. This claim was originally made by Livezeanu Mihai. However, my reading of Greek numerals makes this improbable as 9,000 requires five characters ( one for 5,000 and one for each of the other four thousand), while 5,000 needs just one.
Adrian Bucurescu claims that Plato originally said 5,000, not 9,000 years had elapsed between the Atlantean war and Solon’s visit to Egypt. He bases this claim on the fact that the works of the Greek philosophers were preserved in Arabic translations after the fall of Constantinople and that their numbers ‘5’ and ‘9’ were sufficiently similar to have led to a transcription error!(b) This is difficult to accept as the Arabic character for nine is rather like our ‘9’, while the Arabic five is like our zero!
[3.1] Sometime after 9500 BC.
Jonas Bergman correctly points out that according to the story related by the priests of Sais to Solon, the Egyptian civilisation was founded 1000 years after Athens was first established in 9600 BC. Although this probably just refers to the founding of the city of Sais rather than the early Egyptian state.
Plato describes the original division of the earth between the gods of old, Poseidon got Atlantis and Athena got Greece. The implication is that both were founded at the same time, namely in 9600 BC. Realistically, the 9000-year time span is better treated as an introductory literary cliché such as ‘once upon a time’ or the Irish ‘fado, fado’ (long, long ago). Plato’s text describes the building of Atlantis and informs us that no man could get to the island ‘for ships and voyages were not yet’. Since Atlantis had twelve hundred warships at the time of the conflict with Athens, the war could not have taken place in 9600 BC. The development of seafaring and shipbuilding would have taken considerable time. Bergman concludes that the war with Atlantis took place long after 9600 BC.
Another date was proposed by Otto Muck [098] in 1976 when he maintained that Atlantis had been situated in the Atlantic and was destroyed by an asteroidal impact in 8498 BC and proposed that the same event also created the Carolina Bays!
Felipoff, a Russian refugee living in Algiers presented a paper to the French Academy of Sciences in which he claimed to have astronomically calculated the exact date of the destruction of Atlantis as 7256 BC! Felipoff has been described as an astronomer whose ideas received some attention around the 1930s, apart from which little else is known about him.
[3.2] Peter James as quoted in Francis Hitching’s The World Atlas of Mysteries[307.138] is reported to have accepted the orthodox date of 3100 BC as the start of Egyptian civilisation and considering the priest’s statement that the events outlined took place one thousand years before the creation of Egypt and so added only 500 years to compensate for nationalistic exaggeration and has concluded that 3600 BC is a more realistic date for the destruction of Atlantis.
[3.3] Early in the 20th century, the German scholar Adolf Schulten and the classicist H. Diller from Kiel, both advocated an even more radical date of around 500 BC, having identified the narrative of Plato as paralleling much of the Persian wars (500-449 BC) with the Greeks. This however would be after Solon’s trip to Egypt and have made little sense of Plato’s reference to him.
[3.4] 4015 BC is the precise date offered by Col. Alexander Braghine who credits the destruction of Atlantis to a close encounter with Halley’s Comet on the 7th of June in that year. This is close to the date favoured by de Grazia.
[3.5] 3590-1850 BC has been suggested by the Czech writer Radek Brychta who has developed an ingenious idea based on the fact that the Egyptians who were so dependent on the Nile, divided their year into three seasons related to their river, the flooding, the blossom and the harvest periods. Brychta points out that counting time by seasons rather than solar years was common in the Indus civilisation that occupied part of modern Pakistan. Even today Pakistan has three seasons, cool, hot and wet. Brychta contends that the 9000 ‘years’ related to Solon were in fact seasons and should be read by us as 3000 years which when added to the date of Solon’s Egyptian visit would give an outside date of 3590 BC. If Brychta is correct this 9000-year/season corruption could easily have occurred during the transmission and translation of the story during its journey from the Indus to the Nile valley.
In the 18th century, Samuel Engel also interpreted Plato’s 9,000 years as a reference to seasons of four months each. (See: Axel Hausmann)
[3.6] 3100 BC as a date for the destruction of Atlantis has been proposed by several investigators including, David Furlong, Timo Niroma, and Duncan Steel. Hossam Aboulfotouh has proposed a similar 3070 BC as the date of Atlantis’ demise(f).
[3.7] 2200 BC is the proposed date put forward by Dr Anton Mifsud for the end of Atlantis, located in the vicinity of his native Malta. He arrived at this conclusion after studying the comments of Eumelos of Cyrene who dated the catastrophe to the reign of King Ninus of Assyria. Around the same time, in Egypt, unusually low Nile floods led to the collapse of centralised government and generations of political turmoil(f). According to some commentators(g), the Los Millares culture in Iberia also ended around the same time.
[3.8] Circa 1200 BC is a date favoured by investigators such as Eberhard Zangger [483] and Steven Sora [395] who both identify the Atlantean War with the Trojan War. Frank Joseph is more precise proposing that “it appears, then, that the destruction of Atlantis took place around the first three days of November 1198 BCE. [102.208]. It may be worth noting that this date has also been linked to the suggested close encounter with the Phaëton comet and its destructive effects globally.
[3.9] Stelios Pavlou has taken a different approach, basing his conclusion on a close analysis of the Egyptian King Lists with particular reference to that of Manetho. Pavlou’s paper is well(l) worth studying. In the end, he contends that the time of Atlantis was in or around 4532 BC.
[4.0] More than one Atlantis!
It is not unreasonable to consider Plato’s Atlantis narrative as a literary amalgam of two or more historically based stories or myths. One possibility is that the Egyptian priests related to Solon the tale of the inundation of a powerful and advanced culture in the dim and distant past. Such an event did occur, worldwide, when the Ice Age glaciers melted, resulting, for example, in the eastern Atlantic, the flooding of the North Sea, the Celtic Shelf and dramatically reducing in size of the Canaries and the Azores and creating the British Isles. The entire world was affected by this event so there were also major inundations in the West Indies and the South China Sea. However, events off the coasts of Europe and Africa would be more likely to become part of folklore on this side of the Atlantic.
Over 70 years ago, Daniel Duvillé suggested, that there had been two Atlantises, one in the Atlantic and the other in East Africa.
[5.0] My preference is to treat the use of 9000 by Solon/Plato as an expression of a large but indefinite number or an exaggeration by a factor of ten. At the beginning of my research, I strongly favoured the former, but as I proceeded to investigate other aspects of Plato’s Atlantis story, I realised that virtually all other large numbers used by him also appeared to be inflated by a comparable amount. In seeking a solution to this I found myself drawn to Occam’s Razor, which states that where there are competing theories, the simpler is to be preferred.
It is worth noting that the Egyptian hieratic numerals also stopped with the highest value, expressed by a single character, being 9000. However, having studied the matter more closely I am reluctantly drawn to the ‘factor ten’ theory. This I have written about at some length in Joining the Dots.
The 1st millennium BC saw the introduction and gradual development of new writing and numerical systems by the Greeks. Some claim that the Greeks borrowed the Egyptian numbers(k).
At an early stage, 9000 was the highest number expressed by a single character in Greek, which in time came to be used to denote a large but uncertain value. As the needs of commerce and science demanded ever higher numbers a new character ‘M’ for myriad with a value of 10,000 was introduced. It also was used to indicate a large indefinite number, a practice that continues to this very day. Greek numerical notation was still being developed during Plato’s life.
Today, we use similar expressions such as ‘I have a million things to do’ with no intention of being taken literally, but simply to indicate ‘many’(e). Unfortunately, this interpretation of 9,000 does little to pinpoint the date of the Atlantean war, but it is not unreasonable to attribute a value to it of something above 1,000 and possibly a multiple of it.
Diaz-Montexano has drawn attention to the writings of Proclus, who in his commentary on Timaeus declared the number 9,000 to have had a symbolic value (Timaeus 45b-f).
However, having said that, I am also attracted to the ’factor ten’ theory after a study of other numbers in the Atlantis narrative which all seem to be consistently exaggerated by a similar amount, which seems to be a factor of ten!
Andrew Collins in his Gateway to Atlantis[072.52] wrote “a gross inconsistency has crept into the account, for although Critias affirms that Athens’ aggressor came from ‘without’ the Pillars of Hercules, the actual war is here said to have taken place ‘nine thousand years’ before the date of the dialogue, c.421 BC. This implies a date in the region of 9421 BC, which is not what was stated in the Timaeus. Here 9000 years is the time that has elapsed between the foundation of Athens and Solon’s visit to Sais c. 570 BC. Since Egypt was said to have been founded a full thousand years later, and the ‘aggressor’ rose against both Athens and Egypt, it provides a date post 8570 BC. These widely differing dates leave us with a glaring anomaly that defies explanation. The only obvious solution is to accuse Plato of a certain amount of sloppiness when compiling the text.”
Collins’ suggestion of ‘sloppiness’ is made somewhat redundant if my suggestion that Plato was using 9,000 as a large but indefinite idiomatic value, could be substantiated.
The late Ulf Richter was quite unwilling to accept Plato’s 9,000 years as reliable after a close study of the relevant texts.
Others have produced evidence to suggest that this period in the Earth’s history saw one or more major catastrophic events that may or may not have been interconnected; (i) a collision or near-miss with an extraterrestrial body, (ii) a pole shift, (iii) the melting of the glaciers of the last Ice Age and the consequent raising of sea levels worldwide. This rise provides a credible mechanism that could account for the ’sinking’ of Atlantis.
Mary Settegast, an archaeological researcher, has defended the early date of Atlantis with a remarkable book[545] that delves extensively into Mediterranean and Middle Eastern prehistory and mythologies.
(a) See: https://web.archive.org/web/20181215223457/https://gizacalc.freehostia.com/Atlantis.html
(b) http://www.jqjacobs.net/astro/aryabhata.html
(c) https://www.grahamhancock.com/phorum/read.php?f=1&i=249446&t=249446
(e) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Indefinite_and_fictitious_numbers
(f) Archive 2668 | (atlantipedia.ie)
(g) https://www.minoanatlantis.com/Origin_Sea_Peoples.php
(h) https://www.biblestudytools.com/dictionary/number/
(i) https://historum.com/speculative-history/128055-atlantis-truth-myth-3.html
(j) https://web.archive.org/web/20100708140347/www.fotouh.netfirms.com/Aboulfotouh-Atlantis.htm
(k) https://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/3109806.stm
(m) https://matthewpetti.com/atlantis/
(n) Do you believe in 10,000 BC? – Atlantis-Scout
(p) http://cab.unime.it/journals/index.php/AAPP/article/view/AAPP.932C1/AAPP932C1
(q) https://ourunknownancientpast.blogspot.com/2021/08/plato-atlantis-probability-of.html
(r) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_oldest_surviving_ships
(s) Dating the Atlantis catastrophe – Atlantisforschung.de (atlantisforschung-de.translate.goog)
