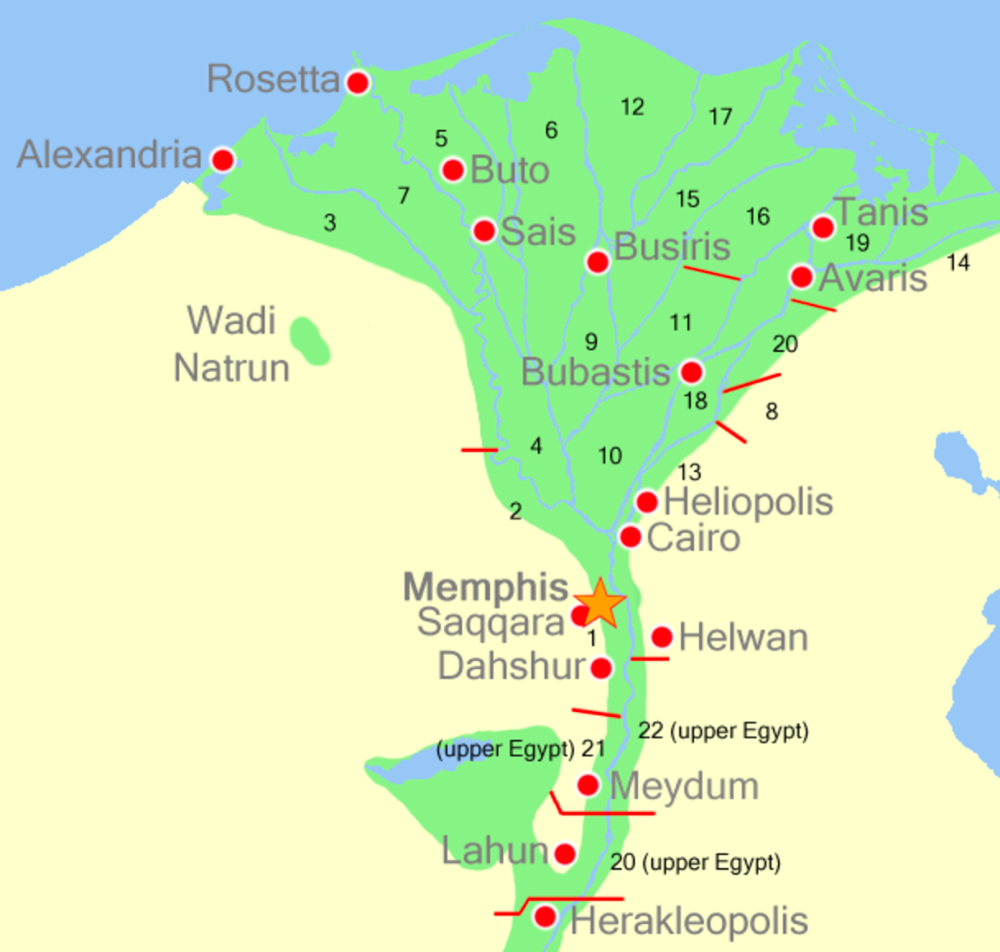
Avaris
Ratti, Diego *
 Diego Ratti is a financial consultant by profession and the author of two related books, Wall Street Watchman [1390] and The Sky Watching Trader [1391]. However, his love of astronomy, archaeology and Lampedusa came together in the development of his website(b). On this small island of Lampedusa in the Strait of Sicily a ‘Stonehenge’ has been identified by Ratti and described in a well-illustrated paper and booklet(c).
Diego Ratti is a financial consultant by profession and the author of two related books, Wall Street Watchman [1390] and The Sky Watching Trader [1391]. However, his love of astronomy, archaeology and Lampedusa came together in the development of his website(b). On this small island of Lampedusa in the Strait of Sicily a ‘Stonehenge’ has been identified by Ratti and described in a well-illustrated paper and booklet(c).
In 2015, he published, in Italian, a book on the prehistory of Lampedusa, La preistoria di Lampedusa [1392].
In a 2016 paper(i) he identified the remains of a prehistoric village on the island as providing “evidence for a late fifth millenium BC colonisation of Lampedusa island by people from Sicily, chronologically around the same time of the Malta early colonisation.” A year later he published another paper(j), La Preistoria di Lampedusa: nuove ipotesi ed interrogativi (The Prehistory of Lampedusa; New Hypotheses and Questions), unfortunately also in Italian only.
Around the same time, Ratti also discovered a “prehistoric underwater place of worship” off the eastern coast of the island(d), and later published a video of the site(e), describing it as a temple similar in layout to some of the Maltese temples.
In March 2021, Ratti published Atletenu [1821], in which he places Atlantis in Egypt, with its capital located at Avaris, better known as the capital of the Hyksos. He identifies Atlas as “Shamshi-Shu I: the Amorite Prince of Ugarit who in 1646 BC led a coalition of Foreign Kings to conquer Egypt starting the XV Dynasty of the ‘Hyksos'”. The book is carefully constructed and well-illustrated, but has no index.
He questions a number of the English translations of the Greek text, offering his own where he deemed it appropriate. One such instance concerns ‘meizon‘, normally translated as ‘greater’ in Tim. 24e & Crit.108e, which Ratti insists should be read as between Libya and Asia, which Avaris clearly is. I pressed Ratti on this interpretation and, after further study, he responded with a more detailed explanation for his conclusion(g). This is best read in conjunction with the book.
However, although he appears to match a number of Plato’s details with the Nile Delta, there was not enough to convince me. Where are the mountains described by Plato with a series of superlatives? Tim 25a-b, describes Atlantean territory as including part of southern Italy, so where is the evidence for the Hyksos occupying any part of Italy? Where is the evidence that Athens fought with the Hyksos?
However, I must acknowledge the extensive amount of research that has gone into this book, which is available as a Kindle or paperback, excerpts from which can be read online(f)(h). It is certainly worth a look.
(b) http://www.megalithic-lampedusa.com/ (link broken)
(c) https://www.scribd.com/doc/64143595/lampedusa-stonehenge
(d) https://www.academia.edu/27713754/Lampedusa_possible_underwater_prehistoric_place_of_worship (link broken)
(e) lampedusa underwater temple – Search (bing.com)
(f) About | Atletenu (archive.org)
(g) More on Atlantis between Asia and Libya (archive.org)
(h) https://www.academia.edu/45672470/Atletenu_Atlantis_Avaris_and_the_Hyksos (link broken)
(i) https://www.academia.edu/27700957/Lampedusa_prehistoric_village_of_Tabaccara_coast?email_work_card=view-paper&li=0 (Link broken) *
(j) https://www.academia.edu/36387354/La_Preistoria_di_Lampedusa_nuove_ipotesi_ed_interrogativi
Meizon
Meizon is given the sole meaning of ‘greater’ in the respected Greek Lexicon of Liddell & Scott. Furthermore, in Bury’s translation of sections 20e -26a of Timaeus there are eleven instances of Plato using megas (great) meizon (greater) or megistos (greatest). In all cases, great or greatest is employed except just one, 24e, which uses the comparative meizon, which Bury translated as ‘larger’! J.Warren Wells concluded that Bury’s translation in this single instance is inconsistent with his other treatments of the word and it does not fit comfortably with the context[787.85]. This inconsistency is difficult to accept, so although meizon can have a secondary meaning of ‘larger’ it is quite reasonable to assume that the primary meaning of ‘greater’ was intended.
Jürgen Spanuth addressed this problem in Atlantis-The Mystery Unravelled [017.109] noting that “In other parts of the Atlantis report misunderstandings easily arose. Plato asserts that Atlantis was ‘larger’, ‘more extensive’ (meizon),than Libya and Asia Minor. The Greek word ‘meizon’ can mean both ‘larger in size’ and ‘more powerful.’ As the size of the Atlantean kingdom is given between two hundred and three hundred miles, whereas Asia Minor is considerably bigger, in this context the word ‘meizon’ should be translated not by ‘larger in size’ but by ‘more powerful’, which corresponds much better to the actual facts.”
In 2006, on a now-defunct website of his, Wells noted that “Greater can mean larger, but this meaning is by no means the only possible meaning here; his overall usage of the word may show he meant greater in some other way.”
It is also worth considering that Alexander the Great, (Aléxandros ho Mégas) was so-called, not because of his physical size, apparently, he was short of stature, but because he was a powerful leader.
The word has entered Atlantis debates in relation to its use in Timaeus 24e ’, where Plato describes Atlantis as ‘greater’ than Libya and Asia together and until recently has been most frequently interpreted to mean greater ‘in size’, an idea that I previously endorsed. However, some researchers have suggested that he intended to mean greater ‘in power’.
Other commentators do not seem to be fully aware that ‘Libya’ and ‘Asia’ had completely different meanings at the time of Plato. ‘Libya’ referred to part or all of North Africa, west of Egypt, while ‘Asia’ was sometimes applied to Lydia, a small kingdom in what is today Turkey. Incidentally, Plato’s statement also demonstrates that Atlantis could not have existed in either of these territories as ‘a part cannot be greater than the whole.’
A more radical, but less credible, interpretation of Plato’s use of ‘meizon’ came from the historian P.B.S. Andrews suggested that the quotation has been the result of a misreading of Solon’s notes. He maintained that the text should be read as ’midway between Libya and Asia’ since in the original Greek there is only a difference on one letter between the words for midway (meson) and larger than (meizon). This suggestion was supported by the classical scholar J.V. Luce and more recently on Marilyn Luongo‘s website(a), which is now closed.
Luongo attempted to link Mesopotamia with Atlantis, beginning with locating the ‘Pillars of Heracles‘ at the Strait of Hormuz and then using the highly controversial interpretation of ‘meizon‘ meaning ‘between’ rather than ‘greater’ she proceeded to argue that Mesopotamia is ‘between’ Asia and Libya and therefore is the home of Atlantis! She cited a paper by Andreea Haktanir to justify this interpretation of meizon(a).
This interpretation is quite interesting, particularly if the Lydian explanation of ‘Asia’ mentioned above is correct. Viewed from either Athens or Egypt we find that Crete is located ‘midway’ between Lydia and Libya.
Jacques R. Pauwels also supported Andrews’ controversial interpretation of Plato’s text (Tim.24d-e) in his 2010 book Beneath the Dust of Time [1656]. Therefore, he believes that the text should have described Atlantis as being between Libya and Asia rather than greater than Libya and Asia combined, arguably pointing to the Minoan Hypothesis.
As there are hundreds of islands ‘between’ Libya and Asia in the Aegean, this interpretation is very imprecise and useless as a geographical pointer.
In 2021, Diego Ratti, proposed in his new book Atletenu [1821], an Egyptian location for Atlantis, centred on the Hyksos capital, Avaris. In that context, he found it expedient to interpret ‘meizon’ in Tim. 24e & Crit.108e as meaning between Libya and Asia, which Avaris clearly is. I pressed Ratti on this interpretation and, after further study, he responded with a more detailed explanation for his conclusion(d). This is best read in conjunction with the book.
>>Some years ago, the late R. Cedric Leonard offered the following contribution to the meizon debate:
In Plato’s time (4th century B.C.) he would have written in large (all-capitals), continuous (no spaces between words), Athenian characters. The old Greek word meson would look like MESON in the Athenian script of Plato’s time. But mezon would look like MEION – the ancient Z closely resembled our modern capital letter I – the difference between the S and Z in the large Athenian script is obvious. (The Greek Z resembling our Roman Z is modern and does not apply to the older Attic scripts.)
But even in the later minuscule script the s and z in no wise resemble each other. A minuscule z (zeta) looks like ? while a medial s (sigma) looks like ? (absolutely nothing alike). The final backbreaker is that Plato included the same comparison in his Critias (108), in which his copyists would have to have made an identical mistake in that work as well. The odds are against the same identical mistake occuring in two separate works.(e) (see link for actual characters)<<
In relation to all this, Felice Vinci has explained that ancient mariners measured territory by the length of its coastal perimeter, a method that was in use up to the time of Columbus. This would imply that the island of Atlantis was relatively modest in extent – I would speculate somewhere between the size of Cyprus and Sardinia. An area of such an extent has never been known to have been destroyed by an earthquake.
Until the 21st century, it was thought by many that meizon must have referred to the physical size of Atlantis rather than its military power. However, having read a paper[750.173] delivered by Thorwald C. Franke at the 2008 Atlantis Conference, I was persuaded otherwise. His explanation is that “for Egyptians, the world of their ‘traditional’ enemies was divided in two: To the west, there were the Libyans, to the east there were the Asians. If an Egyptian scribe wanted to say, that an enemy was more dangerous than the ‘usual’ enemies, which was the case with the Sea Peoples’ invasion, then he would have most probably said, that this enemy was ‘more powerful than Libya and Asia put together’”.
This is a far more elegant and credible explanation than any reference to physical size, which forced researchers to seek lost continental-sized land masses and apparently justified the negativity of sceptics. Furthermore, it reinforces the Egyptian origin of the Atlantis story, demolishing any claim that Plato concocted the whole tale. If it had been invented by Plato he would probably have compared Atlantis to enemy territories nearer to home, such as the Persians.
This interpretation of meizon has now been ‘adopted’ by Frank Joseph in The Destruction of Atlantis[102.82], but without giving any due credit to Franke(b). No surprise there.!
(b) https://lost-origins.com/atlantis-no-lost-continent/ (offline Jan. 2018) See: Archive 2349
(c) https://web.archive.org/web/20070212101539/https://greekatlantis.com/
(d) More on Atlantis between Asia and Libya (archive.org)
(e) https://web.archive.org/web/20170113130726/http://www.atlantisquest.com/Plato.html *
Sahara Desert
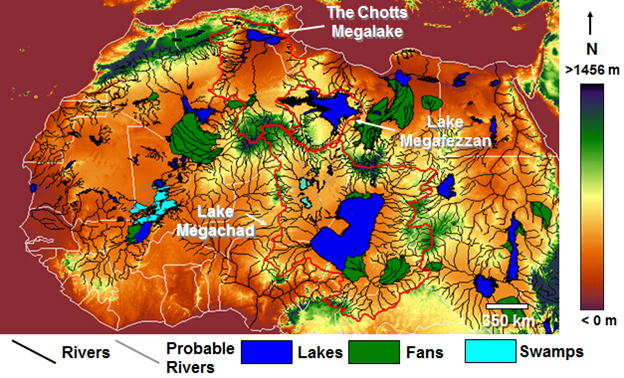
The Sahara Desert and in particular its northern regions have attracted its share of attention from Atlantis investigators. However unlikely it may appear as a possible location for Atlantis it must be kept in mind that the Sahara of prehistory was very different from what we see today. Not only was it wetter at various periods in the past, but also there is clear evidence for the existence of a large inland sea extending across the borders of modern Algeria and Tunisia. This evidence is in the form of the chotts or salt flats in both countries. This proposed sea is considered by some to have been the Lake Tritonis referred to by classical writers. It is suggested that some form of tectonic/seismic activity, common in the region, was responsible for isolating this body of seawater from the Mediterranean and eventually turning it into the salt flats we see today.
An even more extensive inland sea, further south, was proposed by Ali Bey el Abbassi and based on his theory a map was published in 1802 which can be viewed online(c).
More recently, Riaan Booysen has published an illustrated paper on the ancient inland Saharan seas as indicated on the 16th-century maps of Mercator and Ortelius(i). King’s College London runs The Sahara Megalakes Project which studies the Megalakes and the Saharan Palaeoclimate record(m).>>The largest of these was possibly Lake Chad which at its most extensive is estimated to have been greater than the combined Great Lakes of North America.<<
 A 2013 report in New Scientist magazine(d) revealed that 100,000 years ago the Sahara had been home to three large rivers that flowed northward, which probably provided migration routes for our ancestors. Depending on how long the African Humid Period lasted, this article may be read in conjunction with George Sarantitis‘ theory regarding the Voyage of Hanno that he claims took place in the interior of Africa.
A 2013 report in New Scientist magazine(d) revealed that 100,000 years ago the Sahara had been home to three large rivers that flowed northward, which probably provided migration routes for our ancestors. Depending on how long the African Humid Period lasted, this article may be read in conjunction with George Sarantitis‘ theory regarding the Voyage of Hanno that he claims took place in the interior of Africa.
Other studies(h) have shown the previous existence of a huge river system in the Western Sahara, which flowed into the Atlantic on the Mauritanian coast.
An article in the Sept. 2008 edition of National Geographic pointed out that the Saharan climate has been similar for the past 70,000 years except for a period beginning 12,000 years ago when a number of factors combined to alter this fact. A northerly shift by seasonal monsoons brought additional rain to an area the size of the contiguous USA. This period of a greener Sahara lasted until around 4,500 years ago.
More recent studies claim that “there’s geologic evidence from ocean sediments that these orbitally-paced Green Sahara events occur as far back as the Miocene epoch (23 million to 5 million years ago), including during periods when atmospheric carbon dioxide was similar to and possibly higher than today’s levels. So, a future Green Sahara event is still highly likely in the distant future.” (p)
>>However, in the Sept. 2024 edition of National Geographic an article Peter Gwin notes that “the Sahara hasn’t always been a desert. In fact, it transforms from desert to lush savanna about every 21,000 years. A quirk in Earth’s planetary mechanics periodically causes its axis to tilt slightly, increasing the amount of radiation directed to the Northern Hemisphere, which in turns pulls Africa’s seasonal rains northward.”<<
Henri Lhote contributed an article to Reader’s Digest‘s, The World’s Last Mysteries [1083], regarding the ‘green’ Sahara that existed prior to 2500 BC. Two German climatologists Rudolph Kuper and Stefan Kröpelin have estimated that this last greening of the Sahara began around 8500 BC and ended sometime between 3500 BC and 1500 BC(r)(u) .
A team from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Research led by Professor Martin Claussen published a number of papers in the late 1990s following their production of a successful computer simulation of prehistorical North Africa(v). According to a report on the climateark website (now offline), one of their conclusions was “that the change to desert climate in the Sahara was triggered by changes in the Earth’s orbit and the tilt of Earth’s axis.”
Some, such as Kröpelin, have suggested a connection between the latest aridification of the Sahara and the migration of settlers to the Nile Valley(w), where, coincidentally, the ancient Egypt we know about was founded around 3100 BC.
Others have endeavoured to link the last drying of the Sahara with the destruction of Atlantis!
More recently, human activity has been blamed as a major contributory factor for the desertification of the Sahara region less than 10,000 years ago.(n)
Related to the above is a recent study of sediments off the west coast of Africa, which resulted in the discovery of what was “primarily a new “beat,” in which the Sahara vacillated between wet and dry climates every 20,000 years, in sync with the region’s monsoon activity and the periodic tilting of the Earth.” (o)
In Mauritania, a huge natural feature known as the Richat Structure has been claimed as the remnant of Atlantis by George Sarantitis [1470] as well as by Alexander & Rosen and others. >>However, Ulf Richter has pointed out that it is too wide (35km), too elevated (400metres) and too far from the sea (500km) to be seriously considered as the location of Atlantis. Apart from which, a scientific study of the Structure reveals it to be a natural feature(x).<<
In 1868, it was proposed by D.A. Godron, the French botanist, that the Sahara was the location of Atlantis. In 2003, the non-existent archaeologist Dr.Carla Sage announced that she was hoping to lead an international expedition to the Sahara in search of Atlantis. Her contention was that “Atlantis was the capital of a vast North African empire with ports on the Gulf of Sidra”. This report is now confirmed to have been a hoax! I am indebted to Stel Pavlou for uncovering the origin of this story(e).
The idea of an African Atlantis was highlighted in 2021 with the publication of Atletenu [1821], in which the author, Diego Ratti, identified the Hyksos as Atlanteans with their capital at Avaris in the eastern Nile Delta. At the other end of North Africa, the chotts of Tunisia and Algeria were nominated by Holden Zhang as the location of Atlantis in a YouTube clip(q).
Gary Gilligan, the well-known catastrophist, wrote a thought-provoking article(k) on the origin of the Saharan sands, which he claims are extraterrestrial in origin and expands on the idea in his 2016 book Extraterrestrial Sands [1365]. A March 2024 report(t). on the BBC website has revealed that a particular type of sand dune has now been dated. They are known as ‘star’ or ‘pyramid’ dunes – “are named after their distinctive shapes and reach hundreds of metres in height.” They are found in Africa, Asia and North America, as well as on Mars – but experts had never before been able to put a date on when they were formed. Now scientists have discovered that a dune called Lala Lallia in Morocco formed 13,000 years ago.”
David Mattingly, an archaeologist at Leicester University has found that an ancient people known as the Garamantes had an extensive civilisation in the Sahara(l). He has evidence of at least three cities and twenty other settlements. The Garamantes reached their peak around 100 BC and then gradually diminished in influence as fossil water supplies reduced until in the 7th century AD they were subjected to Islamic domination. Some researchers such as Frank Joseph have identified the Garamantes as being linked with the Sea Peoples. Bob Idjennaden has published short but informative Kindle books about both the Garamantes [1194] and the Sea Peoples [1195], without a suggestion of any connection between the two.
A 2017 article on the Popular Archaeology website told us that “New research investigating the transition of the Sahara from a lush, green landscape 10,000 years ago to the arid conditions found today, suggests that humans may have played an active role in its desertification.” (n).
The discovery of megalithic structures discovered at Nabta Playa (Nabta Lake) in the Egyptian Sahara has provided evidence for the existence of a sophisticated society in that area around 5000 BC. In the same region, near the Dakhleh Oasis, archaeologists have produced data that supports the idea that pre-Pharaonic Egypt had Desert Origins rather than being an importation from Mesopotamia or elsewhere(a).
Nabta Playa is not unique, in fact, the largest megalithic ellipse in the world is to be found at Mzorah, 27 km from Lixus in Morocco(b). It appears that the construction methods employed at both Mezorah and Nabta Playa are both similar to that used in the British Isles. An even more impressive site is Adam’s Calendar in South Africa which has been claimed as 75,000-250,000 years old.
West of Cairo near the border with Libya is the Siwa Oasis, where it has now been demonstrated that “it is in fact home to one of Ancient Egypt’s astounding solar-calendar technologies– the solar equinox alignment between the Timasirayn Temple and the Temple of Amun Oracle in Aghurmi.”(j).
I think we can expect further exciting discoveries in the Sahara leading to a clearer picture of the prehistoric cultures of the region and what connections there are, if any, with Plato’s Atlantis. In the meanwhile in the Eastern Egyptian Desert, Douglas Brewer, a professor of archaeology at the University of Illinois, has discovered over 1,000 examples of rock art, including numerous depictions of boats although the sites, so far undisclosed, are remote from water.
Even more remarkable is the report(e) of March 2015 that a survey of the Messak Settafet escarpment in the central Sahara revealed that there were enough discarded stone tools in the region “to build more than one Great Pyramid for every square kilometre of land on the continent”! Coincidentally, around the same time, it was reported that over a thousand stone tools had been found in the Northern Utah Desert(g). What the Utah discovery lacked in quantity was made up for in quality with the finding of the largest known Haskett point spearhead, measuring around nine inches in length.
(a) Saudi Aramco World (2006, Vol. 57, No.5 p.2-11)
(c) https://web.archive.org/web/20201019061756/http://catalog.afriterra.org/zoomMap.cmd?number=1036
(d) NewScientist.com, 16 September 2013, https://tinyurl.com/mg9vcoz
(e) https://books.google.com/books?id=GvMDAAAAMBAJ&pg=PA46&dq=dr.+carla+sage+archaeologist&hl=en&sa=X&ei=GSENVKiaO9W0yASJgoIY&ved=0CCYQ6AEwAA#v=onepage&q=dr.%20carla%20sage%20archaeologist&f=false
(f) https://www.cam.ac.uk/research/news/saharan-carpet-of-tools-is-the-earliest-known-man-made-landscape
(i) 7. The lakes in the middle of the Sahara desert – Page 8 (archive.org)
(l) See: Archive 3268
(n) https://popular-archaeology.com/issue/winter-2017/article/did-humans-create-the-sahara-desert
(o) https://phys.org/news/2019-01-sahara-swung-lush-conditions-years.html#jCp
(p) https://www.livescience.com/will-sahara-desert-turn-green.html
(q) Revive Eden 3 Convincing Atlantis – YouTube
(r) https://www.smithsonianmag.com/history/uncovering-secrets-of-the-sphinx-5053442/
(s) https://las.illinois.edu/news/2006-09-01/oasis-art-egyptian-desert
(t) Star dune: Scientists solve mystery behind Earth’s largest desert sands – BBC News
(u) Shift From Savannah to Sahara Was Gradual, Research Suggests – The New York Times (nytimes.com)
(x) Eye Of The Sahara or Richat Structure » Geology Science *
McQuillen, R(ich) *
R(ich) McQuillen is an American investigator who has cogently argued for an Egyptian location for Atlantis. He has diligently gathered an impressive array of evidence from classical writers including Hellanicus, Solinus and Aeschylus to support his view and arranged the morass that is Greek mythology to construct a credible timeframe for the Atlantis narrative.
However, McQuillen is not the first to locate Atlantis in or near Egypt, in fact, the earliest I have found is in the late 19th century by A.N. Karnozhitsky, while the most recent was published by Diego Ratti in 2021.
McQuillen places the Pillars of Heracles at Canopus, which was formerly in the Western Nile delta but is now submerged about 6.5 km from the coast in the Bay of Aboukir. He is also of the opinion that the Egyptians used lunar ‘years’ rather than solar years bringing the backdrop to the Atlantis story into the 2nd millennium BC. However, he now seems to favour the ‘factor ten’ interpretation of Plato’s date.
McQuillen locates Atlantis at Pharos, which was near modern Alexandria. His website(a) is well worth a visit.
Extensive underwater excavations in the region have been undertaken in recent years by Franck Goddio and his team with remarkable results (b).
It is also worth noting that the late Ulf Richter reasoned that a river delta was the most likely topographical setting for Atlantis (c).
In March 2022 McQuillen added six papers(d-i) expanding on background details employed in his interpretation of the Atlantis story. All six are available on the Academia.edu website.
In 2020, McQuillen published A Simple Chronology of Greek Mythology(k) adding a further paper(j) in 2022 that offered a radical reappraisal of Biblical chronology that included the following.
1 People have been questioning Standard Biblical Chronology (the literal times), for 2000 years, and yet this still persists in modern Biblical Archaeology
2 I have thrown out the early dates entirely and introduced a different paradigm to try to find some of these elusive characters. This paper talks about the Pre-Noachian Kings, like Cainan, and links him to the real-world Syrian Hyksos King Khyan, and finds archaeological evidence of the existence of other Hyksos Kings.
3 It links the flood of Noah to the flood of Ahmose and Atrahasis, and shows it to be a real flood caused by Santorini.
4 It finds Jacob at the same time as the Israel stele of Merneptah. It finds Joseph as the Semitic Pharoah Siptah, whose mother has the same name as Jacob’s second wife. It finds Moses around the time of the Smallpox plague in Egypt (ranging from Ramses 4 to 9)(1182?1136BC).
In his paper ‘Perfecting Plato’ McQuillen is critical of some available translations available to us, of passages in Plato’s Atlantis texts. In his summary of the paper “There are a bunch of controversial passages within the Timaeus. This has led to 50k books on the topic with a bunch of different interpretations of the same passages. These stem from mistranslations, intentional mistakes, wild speculation, etc… The purpose of this paper is to identify and correct the mistakes and add additional insight. The Timaeus is long and in most parts well-translated and irrelevant, so I’m selecting only interesting passages, where I can add insight. I’m using the Bury Translation, with a little bit of Calcidius thrown in.
Plato’s myth has been described as a fable and a description of an idealized society. Instead, it was intended as a story about 18th dynasty Egypt, and its interactions with the Haunebu (Aegaens). The past is often romanticized and idealized in the history books; History is written by the winners.” He then proceeded to comment on a number of specific passages in Timaeus(h).
In 2024, McQuillen published a new paper(l) focused on the work of Manetho. “This paper explores other Egyptan Sources to verify the veracity of Plato’s tale; specifically, intends a lot of the peculiarites in Plato’s text, that also exist in Manetho’s writngs. Plato says this tale comes from Solon in the days of Amasis; there are, in fact, Egyptan elements within this tale which were not invented by Plato, and can be confirmed to also exist in the Egyptan writngs from Manetho and others. Manetho specifically does menton 9000 years, and a war, and a flood, and a city, similar to Plato.”
In this more recent paper, he identifies Avaris as the City of Atlantis although as you can see above he previously(2007) named Pharos, near Alexandria. In the same paper he also identifies the Atlantean Gadir with Rhakotis, an ancient city near Alexandria.
In 2020, McQuillen published the first draft of A Simple Chronology of Greek Mythology, in which he was inspired by Herodotus to develop his own methodology and applied it to the histories of Athens, Crete and Egypt(m). He concluded “I have attempted to create a mythological timeframe for a majority of the Greek Mythological Kings in Greece. These timeframes have been tied to real world events like Troy. They have been synchronized with known timeframes of Egyptian Pharaohs. I list the kings of 20 different ancient cities and attempted to synchronize their history. I have created a framework to compare likes with likes and show when and where one might expect to find these names in Archaeology.”
(a) http://gizacalc.freehostia.com/Atlantis.html
(b) Franck Goddio: Homepage (archive.org)
(c) Archive 6142 | (atlantipedia.ie)
(d) https://www.academia.edu/43493561/A_Simple_Chronology_of_Greek_Mythology_First_Draft
(e) https://www.academia.edu/69049558/Dissecting_Diodorus_The_Legend_of_Myrina_and_Orus
(f) https://www.academia.edu/76436465/Finding_a_God_Phaethon_King_Tut_and_the_Amarna_Period
(g) https://www.academia.edu/76548637/Defining_Danaus_and_Egyptus
(h) https://www.academia.edu/76880053/Perfecting_Plato_A_colorful_commentary_on_the_Timaeus
(i) (DOC) Perfecting Plato: A colorful commentary on the Critias – Part 1 (archive.org)
(j) (99+) A Simple Chronology for Biblical Archaeology | Rich McQuillen – Academia.edu
(k) https://www.academia.edu/43493561/A_Simple_Chronology_of_Greek_Mythology_-First_Draft
(m) (99+) A Simple Chronology of Greek Mythology -First Draft | Rich McQuillen – Academia.edu *
Lampedusa
Lampedusa is the principal island of the Pelagian (Pelagie) archipelago off the coa st of Tunisia, between the African mainland and Malta, and is controlled by Italy.
st of Tunisia, between the African mainland and Malta, and is controlled by Italy.
Anton Mifsud and his co-authors offer evidence[209] that Atlantis was actually a large island that joined Malta to Lampedusa and contends that the famous archaeological sites on Malta are just remnants of the Atlantean civilisation. However, as can be seen from bathymetric maps, if Malta was joined to Lampedusa it may also have been connected with what is modern Tunisia, completing the Sicilian land bridge. The implications of this claim are that if true, it is quite probable that there was also a Gibraltar Dam and that during the last Ice Age, the Mediterranean was reduced to a number of relatively small freshwater lakes.
A website(a) published by Diego Ratti has now highlighted that tiny Lampedusa has an interesting collection of megalithic remains including a feature that has been  dubbed the ‘Lampedusa Stonehenge’.A 39-page booklet, by Ratti, which describes this feature in greater detail can now be downloaded(b). Ratti is a financial consultant by profession and the author of two books, Wall Street Watchman and The Skywatching Trader. However, his love of astronomy, archaeology and Lampedusa came together in the development of his website.
dubbed the ‘Lampedusa Stonehenge’.A 39-page booklet, by Ratti, which describes this feature in greater detail can now be downloaded(b). Ratti is a financial consultant by profession and the author of two books, Wall Street Watchman and The Skywatching Trader. However, his love of astronomy, archaeology and Lampedusa came together in the development of his website.
In 2015 he published, in Italian, a book on the prehistory of Lampedusa, La preistoria di Lampedusa. In 2016 Ratti also discovered a “prehistoric underwater place of worship” off the eastern coast of the island(c), which he describes as a temple similar in layout to those found on Malta(d).
In the Introduction to a 2016 paper describing a prehistoric village on Lampedusa he wrote “A prehistoric hut with Stentinello pottery found in Cala Pisana provided evidence for a late fifth millennium BC colonisation of Lampedusa island by people from Sicily, chronologically around the same time of the Malta early colonisation.”
In 2021, Ratti, controversially proposed in his new book Atletenu [1821], an Egyptian location for Atlantis, centred on the Hyksos capital, Avaris.>Around the same time he had some of his earlier postings removed from the internet!<
(a) https://web.archive.org/web/20181128232114/https://www.megalithic-lampedusa.com/
(b) lampedusa-stonehenge (archive.org) *
(e) About | Atletenu (archive.org)
(f) (99+) Lampedusa: prehistoric village of Tabaccara coast | Diego Ratti – Academia.edu
Avaris
Avaris (Tell el Dab’a) located in the Nile Delta, was the capital of the Hyksos rulers of northern Egypt during the second millennium BC. Recent excavations have unearthed Minoan-style frescoes, including bull leaping. At least one commemtator has remarked on the similarity of this ‘island’ city to Plato’s Atlantis (The Jerusalem Post, July 12th 2006).
Manfred Bietak (1940- ) the celebrated Austrian archaeologist spent many years excavating at two sites in the Nile Delta and identified Tell El-Dab’a as the location of Avaris, the capital of the Hyksos period; and Piramesse, which was the capital of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt(b). In 1991 he delivered an illustrated lecture at the British Museum on his most recent discoveries in Egypt(c).
In 2021, Diego Ratti published Atletenu(a), in which he identified the Hyksos as Atlanteans and situated their capital as Avaris! He claims to have matched Plato’s description of the city of Atlantis with the Egyptian location. I identified a number of discrepancies and was not convinced.
>In a recent (2024) paper(e), R(ich) McQuillen also identified Avaris as the City of Atlantis although you can see that he previously (2007) named Pharos, near Alexandria as Atlantis(d). In that earlier paper he also identified the Atlantean Gadir with Rhakotis, an ancient city near Alexandria.<
Also See: Meizon
(a) About | Atletenu (archive.org)
(b) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Manfred_Bietak
(c) (99+) Avaris: Capital of the Hyksos | Manfred Bietak – Academia.edu
(d) http://gizacalc.freehostia.com/Atlantis.html (See Summary) *
(e) (99+) Manifestin with Manetho: Finding commonality from Plato’s Atlantis and Egyptian Sources | Rich McQuillen – Academia.edu *
*
Atlas
Atlas was the first king of Atlantis and was the son of Poseidon according to the story of Atlantis from Plato. However, in traditional , Atlas was the son of the Titan, Iapetus, often identified with the biblical Japheth, and the nymph Clymene. This apparent contradiction can be explained by the fact that the name Atlas is applied to more than one figure in Greek legends.
, Atlas was the son of the Titan, Iapetus, often identified with the biblical Japheth, and the nymph Clymene. This apparent contradiction can be explained by the fact that the name Atlas is applied to more than one figure in Greek legends.
Atlas is usually portrayed kneeling with the world on his shoulders. However, the earliest known statue of Atlas, the 2nd century Farnese Atlas(c), which is a Roman copy of an older Greek statue, has the sky is represented as a sphere with a map of the stars and constellations known to the Ancient Greeks, which they represented as objects, animals and mythological creatures and characters. 16th century cartographers assumed that the globe represented the Earth, not the sky and since then it has been depicted accordingly.
Edwin Björkman noted the opinion that the name Atlas does not have a Greek root but is generally thought to have a Semitic origin. He also suggested the possibility that the name may have been derived from one of the Greek words for sea, thalassa.
However, Peter James points out[047.190] the name has a clear etymology in the Greek root ‘tlaô’ which can mean ‘to bear’, ‘to endure’ or ‘to dare’.>Tantalis, the capital of ancient Lydia, was apparently named after the legendary King Tantalus, its first king, who shared remarkable similarities with Atlas, the first king of Atlantis; they were both Titans, supported the heavens and had mountains named after them(f).<
Atlas has also been identified with both the Egyptian god Shu and the biblical Enoch, the latter being a more controversial concept. Lewis Spence went further and identified the Meso-American deity, Quetzalcoatl, with Atlas!
A somewhat more conventional view was offered by Thorwald Franke who has written a convincing paper(a) identifying Atlas with king Italos of the Sicels, who gave their name to Sicily and were one of the earliest groups to inhabit the island.
A more radical view has been put forward by Brit-Am writer John R.Salverda, who claims that the biblical Adam is the Atlas of Plato’s Atlantis narrative. A similar theory was proposed by Roger M. Pearlman in a 2018 booklet [1596]. In this small, difficult to read, book the author suggests, a linkage between the destruction of Sodom & Gomorrah and Atlantis, places Atlantis in the Jordan Valley and equates Abraham with Atlas – “ If Atlas as described in Plato’s work was based on a historic figure, Abraham alone meets key criteria.”In a more recent paper(d), Pearlman also suggested that Göbekli Tepe was founded by Noah (Noach) and his sons!
Moving further east, the Hittites had an equivalent if not an original version of Atlas in the form of Tantalus. The Hittites in turn may have developed the identity from the Hurrian god Ubelleris. It was this Anatolian figure that led Peter James to his conclusion that Atlantis had been located in Turkey. Tantalus had a son Pelops, whom some consider Phrygian and according to Herodotus the Phrygians were the oldest race on earth.
Diego Ratti claims “that Atlantis was Avaris, capital of the Hyksos Kingdom and that king Atlas was Shamshi-Shu I: the Amorite Prince of Ugarit who in 1646 BC led a coalition of Foreign Kings to conquer Egypt starting the XV Dynasty of the ‘Hyksos’.”(e)
An even more extreme idea has been proposed by Sean Griffin that the yogic concept of ‘Kundalini’ is contained within part of Plato’s Atlantis story(b). Griffin begins his explanation by pointing out that Atlas is the medical term for the 33rd vertebra of the human spine!
(a) https://www.atlantis-scout.de/atlantis_italos.htm
(b) https://www.scribd.com/doc/211332861/Atlantis-and-Kundalini
(c) https://www.dioi.org/ggg.htm
(d) https://www.academia.edu/38664571/Gobekli_Tepe_founded_by_Noah_and_sons
(e) Atletenu | Atletenu (archive.org)
(f) https://www.jstor.org/stable/262536?seq=2#page_scan_tab_contents *
Andrews, P.B.S.
P.B.S. Andrews is an English historian who has been involved in a variety of controversial subjects including the dating of Pride and Prejudice, the Piltdown Hoax(a) and the location of Ithaca. In 1967 in a short article[056] in the journal Greece and Rome, he expressed the view the 2nd millennium BC explosion of Thera had inspired the Atlantis story. In addition, he suggested that Plato’s declaration that the island of Atlantis was larger than Libya and Asia combined, was the result of either a scribal error or a misreading of Solon’s notes. The alteration of a single letter would have rendered the translation as noting the island being located ‘between’ Libya and Asia. This explanation is somewhat suspect as the majority of Atlantis candidates, such as the Atlantic could not be described in those terms. In fact, the only place that is exactly between Libya and Asia is Egypt!
However, Andrews’ idea never gained any great support and in recent years the explanation offered by Thorwald C. Franke is that the Egyptian priest was describing the military power of Atlantis being greater than the combined might of Egypt’s traditional enemies, the Libyans and the Asians. This interpretation is more compatible with the Greek word used for ‘greater’, meizon.
>Nevertheless, in 2021 Diego Ratti in his book, Atletenu [1821] questioned a number of the English translations of the Greek text, offering his own where he deemed it appropriate. One such instance concerns ‘meizon‘, normally translated as ‘greater’ in Tim. 24e & Crit.108e, which Ratti, like Andrews, insists should be read as between Libya and Asia, where Avaris clearly is!<
(a) https://www.clarku.edu/~piltdown/map_prim_suspects/DAWSON/Dawson_Prosecution/historyislies.html
Hyksos
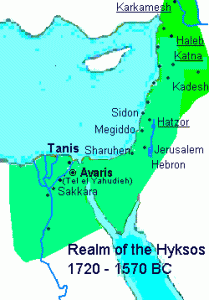 The Hyksos is the name applied to two dynasties of foreign kings who ruled Egypt around 1650-1530 BC(a). Gerard Gertoux suggests three dynasties reigning from circa 1750- 1530!(l) They are generally accepted to have been Semitic people, from an unknown land, who invaded Egypt around 1710 BC. They ruled for over a hundred years until defeated by the Egyptian Pharaoh Amasis I.
The Hyksos is the name applied to two dynasties of foreign kings who ruled Egypt around 1650-1530 BC(a). Gerard Gertoux suggests three dynasties reigning from circa 1750- 1530!(l) They are generally accepted to have been Semitic people, from an unknown land, who invaded Egypt around 1710 BC. They ruled for over a hundred years until defeated by the Egyptian Pharaoh Amasis I.
Their name was originally taken to mean ‘Shepherd Kings, but more recently, it is accepted that the Egyptian term ‘heqa-khase’ which means ‘rulers of foreign lands’ gives us a simple but credible title of ‘Foreign Kings’. It has been suggested by David J. Gibson (1904-1966) that the modern interpretation indicated that the Hyksos ruled a vast empire and has devoted a book[1507] to justifying this view(g). This empire lay mainly to the east of Egypt with the possible exception of Crete. Gibson identifies the Hyksos with the biblical Edomites!
Walter Baucum summarises his view on the subject as follows, “The Early Hyksos Shepherd Rulers of Egypt were descendants of Shem and identical with Typhon and the Titans, the peoples of Set, and to some degree with the Hebrews. The early Hyksos were to a large degree Israelites but after they left, the Amalekites conquered Egypt and were also referred to as Hyksos”.
This identification of the Hyksos with the biblical Amalakites was supported by Velikovsky, Rohl and Donovan Courville(o). This identification is disputed by Emmet Sweeney [1867], who is generally sympathetic to Velikovsky’s revised chronology, but disagrees with him in this instance. In a recent (2023) paper(r) on the Academia.edu website Donald Keith Mills was highly critical of Velikovsky’s research on the Hyksos and Amalakites in Ages in Chaos.
“Repeatedly, when faced with conflicting accounts of pre-Islamic (and essentially prehistoric) events, Velikovsky selected only those that met his purposes. The damaging aspect of this criticism is the fact that, almost without exception, he did so without discussing the alternatives, without providing reasons for rejecting them, and without even acknowledging their existence.“
There have also been persistent suggestions that there were strong links between the Hyksos and Crete, as referred to both above and below. But the exact nature of the links is unclear and may not be more than you get between nations trading over an extended period. The relevance of such links, if they were ever shown to be political rather than commercial, would take on new significance for supporters of the Minoan Hypothesis. Time will tell.
Peter A. Clayton, an Egyptologist and author of Chronicle of the Pharaohs suspected that the Hyksos had their origins in Crete. E. J. de Meester has suggested links between Crete and the Hyksos, an idea included in an article by Philip Coppens(b). In a similar vein, Diaz-Montexano claims that a study of the names of the Hyksos pharaohs suggests to him that they were proto-Greek or Mycenaeans.
An example of the diversity of opinions regards the origins of the Hyksos is a brief article written by Emilio Spedicato who identifies them with the Scythians. Gunnar Heinsohn (1943- ) is a German professor emeritus at the University of Bremen, who presented a paper entitled ‘Who were the Hyksos’ to the 6th International Congress of Egyptology in 1993, in which he concluded that they were to be identified with the Old-Akkadians(j).
Perhaps even more radical is the suggestion by Riaan Booysen that the Hyksos were the fleeing Israelites in the biblical Exodus story(c). He claims that there were two ‘exoduses’ which coincided with two separate eruptions on Thera. This idea is not as new as it might seem as something similar was proposed by the 1st century AD Jewish historian Josephus(d).
Nick Austin also identifies the Hyksos as Jews [1661.184] but is more generous than Booysen claiming that there were four separate eruptions of Thera. Like many others, he has also associated the biblical Exodus and the Plagues of Egypt with the Theran eruptions.
Ralph Ellis, among others, has endorsed(e)(f) the idea that the biblical Exodus and the historical Expulsion of the Hyksos describe the same event. There are theories, many and varied, regarding the origins and post-Egyptian settlement of the Hyksos.
>In March 2024 an undated paper on the Academia website written under the pseudonym of ‘The Mumble’ and titled Mexico City & the Site of Atlantis(s). Its basic contention is that the Olmecs were originally Hyksos, who ruled an empire stretching from America to India! Unfortunately, real evidence is in short supply here to support this wild hypothesis. The paper is full of misquotations and other inaccuracies that are offered throughout.
One glaring error, at the heart of the claim is that Mexico City was city of Atlantis described by Plato. Unfortunately, Plato’s Atlantis was situated close to the sea, while Mexico City is roughly 200 miles from both the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans. Canals led from the city to the sea – where are the 200-mile-long canals in Mexico? Additionally, Mexico City lies at a height of 7,350 feet and could not have been inundated by either ocean. According to Plato, Atlantis disappeared underwater, but Mexico did not! I think it was a good idea for ‘The Mumble’ to write under a pseudonym.<
In July 2020, it was reported that “new research led by Bournemouth University archaeologists supports the theory that the Hyksos, the rulers of the 15th Dynasty of ancient Egypt, were not from a unified place of origin, but Western Asiatics whose ancestors moved into Egypt during the Middle Kingdom lived there for centuries, and then rose to rule the north of Egypt.”(k)
The full facts relating to the Hyksos’ rule are only slowly emerging(m) and I expect that it will be some years before a definitive history can be agreed upon. Just over a year after I wrote this, In March 2021, Diego Ratti published Atletenu, in which he identified the Hyksos as Atlanteans, with their capital situated at Avaris in the eastern Nile Delta(n).
Ratti explains “that the first king of Atlantis called Atlas by Plato was a prince of Ugarit called Shamshi-Shu I who led a coalition of Foreign Kings to conquer Egypt. Plato’s “Critias” mentions the name of the first 10 kings of Atlantis: in “Atletenu” author Diego Ratti explains that the names of these 10 kings provide us with an indication of the origin and ethnicity of the Hyksos.
It was a coalition of 10 foreign Hyksos kings to invade Egypt in 1646 BC: some of them were from Southern Canaan and Northern Sinai while their majority was from Northern Syria and Lebanon. The prevalent ethnicity of the Hyksos coalition was the Amorite one: they had Amorite names, Amorite customs, traditions and religion. The prince of Ugarit leading the coalition of Hyksos was an Amorite.
The legend of Atlantis was the history of the Hyksos: this fascinating thesis is discussed in the book “Atletenu” with supporting archaeological and textual evidence.” (q)
A paper by the distinguished Austrian archaeologist Manfred Bietak entitled Avaris: The Capital of the Hyksos(p) should be read in conjunction with Ratti’s theory.
>Arguably, the most exotic suggestion put forward regarding the Hyksos comes from a Chinese geochemist, Professor Sun Weidong(h)(i) at the University of Science and Technology in Hefei in eastern China stirred up a debate with the suggestion “that the founders of Chinese civilization were not in any sense Chinese but actually migrants from Egypt. He conceived of this connection in the 1990s while performing radiometric dating of ancient Chinese bronzes; to his surprise, their chemical composition more closely resembled those of ancient Egyptian bronzes than native Chinese ores.” Sun specifies these culture bearers as the Hyksos. A paper(t) by Ricardo Lewis on the Academia.edu website offers more details and background information.<
(a) https://web.archive.org/web/20180203181622/https://history-world.org/hyksos.htm
(b) See: Archive 2133
(c) https://riaanbooysen.com/misc/167-book-announcement
(d) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Origins_of_the_Hyksos
(e) https://www.bibleandscience.com/archaeology/exodus.htm
(f) https://lists.ibiblio.org/pipermail/b-hebrew/2000-January/006340.html
(g) See: Archive 3468
(j) https://web.archive.org/web/20111202130828/https://www.egyptologie.be/6IECT_1993_hyksos_heinsohn.htm
(l) https://www.academia.edu/2414447/Dating_the_war_of_the_Hyksos
(m) Did the Hyksos Pull Off a Peaceful Invasion of Egypt? | Ancient Origins (ancient-origins.net)
(n) Book Author | Atletenu (archive.org)
(o) https://en.everybodywiki.com/Donovan_Courville
(p) https://www.academia.edu/10071070/Avaris_Capital_of_the_Hyksos
(q) Hyksos | Atletenu (archive.org)
(r) (99+) VELIKOVSKY AND THE AMALEKITES | Donald Keith Mills – Academia.edu
(s) (99+) Mexico City & the Site of Atlantis | The Mumble – Academia.edu *
(t) Does Chinese Civilization Come From Ancient Egypt? – Foreign Policy *
Egypt *
Egypt occupies the northeastern corner of Africa. However, the ancient Egyptians considered themselves 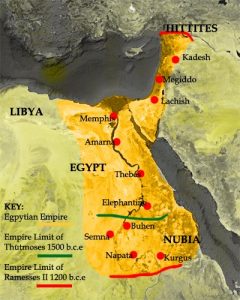 Asian (Tim. 24b). Over its long history, Egypt itself was overrun by a variety of invaders – Hyksos, Kushites, Assyrians, Persians, Greeks and Romans.
Asian (Tim. 24b). Over its long history, Egypt itself was overrun by a variety of invaders – Hyksos, Kushites, Assyrians, Persians, Greeks and Romans.
In practical terms, its territory consisted of a few miles on either side of the Nile together with its large Delta. In an expansionist period in the 2nd millennium BC, Egypt controlled parts of what are now Israel, Lebanon, Syria and Libya.
The exact extent of Egyptian-controlled territory in Libya at the time of Atlantis is unclear. We do know that “In the mid-13th century BC, Marmarica was dominated by an Egyptian fortress chain stretching along the coast as far west as the area around Marsa Matruh; by the early 12th century, Egypt claimed overlordship of Cyrenaican tribes as well. At one point a ruler chosen by Egypt was set up (briefly!) over the combined tribes of Meshwesh, Libu, and Soped.”(r)
A Wikipedia map(q) suggests that Egyptian New Kingdom control stretched at least halfway towards Syrtis Major, which has been proposed by some as the location of Atlantis.
As most are aware the history of Egypt is inextricably linked with that of the Old Testament, leading to the suggestion by some, such as Ahmed Osman(k), that individuals in the Egyptian 18th Dynasty can be identified with some of the Hebrew Patriarchs, most notably Moses and the heretic king Akhenaten. Interestingly, this linkage had been put forward previously by Sigmund Freud!
Charles N. Pope has endorsed Osman’s identification of Moses as Akhenaten in his online book Living in Truth: Archaeology and the Patriarchs(z).
Osman goes further and contends that the main tenets of Christianity developed on the banks of the Nile [1852] and additionally “provides a convincing argument that Jesus himself came out of Egypt.” This is in sharp contrast to those that claim that both Moses and Jesus are completely fictitious characters(l).
Egypt was viewed by the Greeks of Plato’s time as guardians of ancient history and wisdom and consequently was a place of pilgrimage for many of its greatest philosophers, who travelled there to be initiated into the cults of Isis and Osiris. Gustav Parthey (1798-1872), the German antiquarian, researched the education of 40 leading philosophers, writers and politicians of ancient Greece and found that all had studied under Egyptian priests. Clement of Alexandria (150-215 AD) suggested that Plato travelled to Heliopolis and was a disciple of the Egyptian priest Sechnuphis. Other classical writers such as Strabo and Plutarch have confirmed this(i).
Zsofia Frei has published a paper defending the idea that Greek philosophy came from Egypt(s).
Despite this, the Greeks arrogantly referred to all non-Greeks, including the Atlanteans (Crit. 113a) as ‘barbarians’. It is of interest that Athene after whom the Greek capital is named originated in Egypt where she was worshipped as Neith.
The late Philip Coppens went as far as to suggest(a) that Greece was an Egyptian colony!
Plato’s text seems to infer that the destruction of Atlantis in 9600 BC was contemporary with Egyptian civilisation, raising archaeological questions regarding the earliest date for the establishment of an organised society in Egypt. Unfortunately, there is not a lot to support this contention. The oldest known art in Egypt was discovered in 2007 when petroglyphs were estimated to be 15,000 years old(u). The earliest culture along the Nile, identified by archaeologists is that of what is known as the Badarian dating to around 4500 BC. They produced basic pottery, and jewellery and used stone tools although they had some knowledge of metals. The Badarians were followed by the Naqada who led on to what we identify as the spectacular ancient Egyptian civilisation. However, in 2007, rock carvings, similar in style to the Lascaux paintings were discovered near the village of Qurta, 650km south of Cairo. The 160 carvings, spread over 1.5km of the rock face, discovered so far, mainly depict wild bulls and have been dated to 13000 BC(h)
September 2013 saw the publication(c)(d) of a more definitive date for the start of the state of Egypt, beginning with the reign of king Aha circa 3100 BC. Before that, early agriculture in Egypt appears to date back to around 5000 BC(t). This eventually led to the establishment of permanent agricultural villages. In time some of these grew into towns and cities eventually leading to Dynastic Egypt. This undermines even more firmly the claims of the Egyptians that their country was founded around 8,600 BC as reported by Plato.
It is not surprising that ancient Egypt has presented us with very many unanswered questions, some of which have been compiled, posted on Wikipedia but subsequently removed(g).
Many writers have remarked how all aspects of ancient Egyptian culture seem to have arrived fully developed, while later dynasties did not surpass some of the achievements of the earlier ones! The conclusion of some is that the fully matured civilisation of the early Egyptians was a legacy from elsewhere.
Sanchuniathon refers to the original kings of Egypt calling them ‘Aleteans’. Albert Slosman claims[551] that survivors from Atlantis had migrated to Egypt. The archaeologist, Marcelle Weissen-Szumianska, in a 1965 book, Origines Atlantiques des Anciens Egyptiens [837], maintained that the pre-pharaonic Egyptians originated in Atlantis, which had been situated in Morocco! Others suggest that Egypt was an Atlantean colony. The idea was brought to a ridiculous level by Augustus Le Plongeon who claimed that Egypt was a Mayan colony!
A more grounded study by Alapan Roy Chowdhury investigates the claim put forward by some researchers that there are remarkable similarities between the cultures of ancient India and Egypt(v-y)*. “Was there a real connection or are these similarities only coincidences?”(j) The tributetohinduism.com website(n) develops this idea further.
Robert Schoch has controversially dated the construction of the Sphinx to between 7000-5000 BC, while the megalithic structures at Nabta Playa suggest a sophisticated culture in that region around 5000 BC. Even if both these early dates are correct they are still over four and a half millennia short of Plato’s date. This most likely explanation is that Plato’s number of 9,000 years before Solon is incorrect as 9000 is too neat and may have been a siglum used to express a large but uncertain number or is an exaggeration just as today we speak of having ‘a million and one things to do’.
In 1897, a Russian scientist, A.N. Karnozhitsky was probably the earliest commentator to propose a close link between Egypt and Atlantis, placing the Pillars of Heracles near Sais and locating Atlantis itself not far from the western mouth of the Nile.
Some years ago, Egypt was again been proposed as the original Atlantis, in a still (June 2021) unpublished book, The Joshua Crossing, by N. R. James. However, 2006 saw a paper presented by Professor Hossam Aboulfotouh of Minia University, Egypt, placed Atlantis in the Nile Delta. The following year R. McQuillen also offered an Egyptian location for Atlantis, placing it at Pharos near Alexandria.
In 2020 Jean-Pierre Pätznick, a French Egyptologist published an article in Pharaon magazine (No 41) about Atlantis and Egypt(o). Thorwald C. Franke has written a critical review of the paper(p).
More recently (March 2021), Diego Ratti, published Atletenu [1821], in which he placed Atlantis in Egypt, with its capital located at Avaris, better known before now as the capital of the Hyksos. He questions a number of the English translations of the Greek text, offering his own where ‘appropriate’. The book is carefully constructed and well-illustrated, but, although he appears to match some of Plato’s Atlantis details with the Nile Delta, there was not enough to convince me.
A novel idea has been put forward by Mary Whispering Wind(b), who bravely offers the idea that the Atlantean province of Egypt was, Colchis, situated on the east coast of the Black Sea! She bases her claim on an interpretation of Herodotus (Book II.104/5) who was commenting on circumcision being only practised by Egyptians, Ethiopians and Colchians, in my mind, stretching what Herodotus said beyond the acceptable.
An even more radical suggestion was made by Reinoud M. de Jong in a 2009 paper(f) where he boldly claimed “that during the whole period of the (Michigan) copper trade, America was part of the Egyptian Empire” and during the Old Kingdom “this huge empire was known as Atlantis”!
One blogger, from California, has gone so far as to suggest that the ‘Egypt’ that Solon visited was on the shores of the Sea of Marmara!(e)
Margaret Bunson’s Encyclopedia of Ancient Egypt [1872]+ is now available online.
Kathryn A. Bard, Professor Emerita of Archaeology and Classical Studies at Boston University is the compiler and editor of The Encyclopedia of the Archaeology of Ancient Egypt [2084], which is available online(aa).
[1872]+(99+) Bunson – Encyclopedia of ancient Egypt | Iffa Hamzah – Academia.edu
(a) See Archive 2136
(b) https://atlantis-today.com/Atlantis_Atlantis_Code.htm
(d) https://ancientfoods.wordpress.com/2013/09/13/egypt-wasnt-built-in-a-day-but-it-did-rise-quickly/
(e) https://www.unexplained-mysteries.com/forum/index.php?showtopic=253407&st=45#entry4895373
(f) https://megalithicresearch.blogspot.com/2009/12/copper-trade-with-old-world-poverty.html
(g) https://www.historyandheadlines.com/list-of-unsolved-problems-in-egyptology/
(i) https://www.vision.org/history-of-ancient-egyptian-city-of-heliopolis-influence-on-modern-culture-41
(j) https://pathoflight15.wordpress.com/author/alapan88/
(k) http://www.domainofman.com/ankhemmaat/contents.html
(l) Jesus Moses were Invented – Bible Dates (archive.org)
(o) (99+) Atlantis and Egypt. In search of the egyptian version of the myth (academia.edu) *
(p) https://www.atlantis-scout.de/atlantis-paetznick.htm
(q) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/New_Kingdom_of_Egypt
(r) https://www.penn.museum/sites/expedition/egyptians-and-libyans-in-the-new-kingdom/
(s) (99+) Egypt and the origins of greek philosophy | Zsofia Frei – Academia.edu
(t) How old is ancient Egypt? | Live Science
(u) http://africascience.blogspot.com/2007/07/egypts-oldest-known-art-identified-is.html
(v) (99+) BHAARATIYAS IN EGYPT | Alapan Roy Chowdhury – Academia.edu
(w) (99+) BHAARATIYAS IN EGYPT (Part-2) | Alapan Roy Chowdhury – Academia.edu
(x) (99+) BHAARATIYAS IN EGYPT (Part-3) | Alapan Roy Chowdhury – Academia.edu
(y) (99+) BHAARATIYAS IN EGYPT (Part-4) | Alapan Roy Chowdhury – Academia.edu
(z) http://www.domainofman.com/book/chap-16.html