Gulf of Gabes
Passarge, Siegfried
 Siegfried Passarge (1866-1958) was a German professor of geography, who had Paul Borchardt as one of his students. When Borchardt proposed that Atlantis had been situated in the chotts of northeast Africa, Passarge investigated the theory but was not completely convinced. mainly because he was unable to identify the cause of the rupture between the chotts and the Gulf of Gabes. Despite this, he was not prepared to completely exclude the possibility that an ancient civilisation had existed in southern Tunisia
Siegfried Passarge (1866-1958) was a German professor of geography, who had Paul Borchardt as one of his students. When Borchardt proposed that Atlantis had been situated in the chotts of northeast Africa, Passarge investigated the theory but was not completely convinced. mainly because he was unable to identify the cause of the rupture between the chotts and the Gulf of Gabes. Despite this, he was not prepared to completely exclude the possibility that an ancient civilisation had existed in southern Tunisia
Passarge was a rabid anti-semite and was among the signatories of “the commitment of the professors at German universities and colleges to Adolf Hitler and the Nazi state”(a). It would appear unlikely that Passarge was aware of Borchardt’s Jewish ancestry!
Pillars of Herakles
Pillars of Heracles, when Googled, will offer nearly 100,000 results, with Wikipedia and Britannica usually heading the list.
Wikipedia says “The Pillars of Hercules was the phrase that was applied in Antiquity to the promontories that flank the entrance to the Strait of Gibraltar. The northern Pillar, Calpe Mons, is the Rock of Gibraltar. A corresponding North African peak not being predominant, the identity of the southern Pillar, Abila Mons, has been disputed throughout history, with the two most likely candidates being Monte Hacho in Ceuta and Jebel Musa in Morocco.”
Britannica says “Pillars of Heracles, also called Pillars of Hercules, two promontories at the eastern end of the Strait of Gibraltar. The northern pillar is the Rock of Gibraltar at Gibraltar, and the southern pillar has been identified as one of two peaks: Jebel Moussa (Musa), in Morocco, or Mount Hacho (held by Spain), near the city of Ceuta (the Spanish exclave on the Moroccan coast).”
Although these two popular sources substantially agree with each other, the concurrence is misleading. In fact, various aspects of the Pillars have been the subject of controversy for a very, very long time.
CONFUSION
The Pillars of Heracles (PoH) according to conventional wisdom were always situated somewhere in the vicinity of the Strait of Gibraltar. However, the truth is rather different. The question of the location of the Pillars has led to confusion and controversy for millennia. A flavour of this was contained in William Smith’s still highly-regarded Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography [1719] of 1854, which lists many of the locations proposed by ancient authors. One short paragraph in it encapsulates the confusion that has existed in the past and still does, although seldom highlighted, today – ” But when the ancient writers began to investigate the matter more closely, they were greatly divided in opinion as to where the Pillars were to be sought, what they were, and why they were called by the name of Hercules.”(w)
When I began my study of the Pillars, it became obvious very early on that the subject was more complicated than usually presented. Frankly, I never expected to end up as bewildered as I did. First of all, I find that some of the ancient writers have not only referred to two pillars but even three(x) and four of them.
HERAKLES
That was bad enough, but when I was then confronted with a multiplicity of mythical heroes named Herakles, numbering three (Diodorus), four (Servius), six Cicero, seven (Herodotus)(ap(z), and a prize-winning forty-four by Varro, I was even more perplexed.
Ariadna Arriaza published a paper about the multiplicity of Herakles’ in ancient texts, particularly Herodotus(z), who offered at least seven! William Smith’s Dictionary noted that “Herodotus tells us that the original Heracles hailed from Egypt and says that according to the Egyptian tradition, Heracles was one of twelve deities descended from the original eight gods who created the universe (2.43-5). Diodorus claimed that when Osiris went to accomplish his labors he left the government of Egypt in the hands of this primordial Heracles. Remarkably, Pausanias, Tacitus, and Macrobius all confirm that Heracles hailed from Egypt [1729.401]”
John K. Lundwall noted the profusion of Herakles’ [1747] and also refers to the Phoenician Herakles – Melqart and its possible influence on the development of the Greek myth. He concluded that ” Heracles was not invented by the Greeks. He was inherited by the Greeks. Half of his labors descend from Mycenaean or Minoan times, implicating a Heracles-like figure with a series of labors in the days before Greece was founded. Gilgamesh is a Near Eastern Heracles.”
Apart from the Canaanite Melqart(ak) and the biblical Samson, Herakles was also associated with Briareus or Cronos. Aelian, in his Varia Historia 5.3, noted that “Aristotle affirms that those Pillars which are now called of Hercules, were first called the Pillars of Briareus.”
Herodotus visited the temple of Heracles in Tyre with two pillars, one of gold and the other emerald. According to the priests there, it had stood for two thousand three hundred years or from approximately 2700 BC. Another suggestion has been that the ‘Pillars Heracles’ was a Greek rendering of the Egyptian ‘Pillars of Osiris’.(t)
So not only do we have a number of Heracles but also a variety of names for them.
THE NATURE OF THE PILLARS
My confusion was further compounded by the term stelai used by Plato to describe the Pillars, which is the Greek word for stone or wooden slabs used as boundary or commemorative markers, not a reference to supportive columns. I must emphasise that Plato referred to stelai, not mountains.
Rhys Carpenter favoured the idea that the term when applied to the Strait of Gibraltar was used with the sense of boundary markers, indicating ”the limits of the Inner Sea that, for the Greeks, was the navigable world” [221.156]. It is reasonable to suggest that as the Greeks became more expansionist with their trade and colonisation, new limits were set as they moved incrementally westward along with the appellation of the ‘Pillars of Hercules’.
One advocate of this idea, Thorwald C. Franke maintains that the westward shift of the ‘Pillars’ from the Strait of Messina towards Gibraltar occurred a century before Solon. He expanded on this at the 2008 Atlantis Conference [0750.170] and in his 2006 book on Herodotus [0300].
Eberhard Zangger noted [483.109] that in a 1927 article, Richard Hennig “investigated the root of the term ‘the Pillars of Heracles’ and concluded that it was not initially applied to the Straits of Gibraltar but to another locality at the end of the Greek sphere of influence.”
Further difficulties were provided by early authors describing the Pillars as mountains, statues, islands or promontories! Egerton Sykes was convinced that the Pillars had been two menhirs, 30ft tall that had stood on top of the Rock of Gibraltar(u)! In this regard, it is interesting that Jürgen Spanuth dismissed those who have identified the red and white cliffs of Heligoland as the Pillars of Heracles, decrying the idea as a fallacy [015.100]. He explained that “Natural rock formations were not what was originally meant by the Pillars of Heracles. Those at the Straits of Gibraltar were not, as one so often reads, the rocks to the north and south of the Straits, but two man-made pillars which stood before the temple of Heracles at Gades (present-day Cádiz) about 100 km north of the Straits.” Spanuth also denied that the Straits of Gibraltar were ever closed [p248].
Some of the earliest references to the Pillars of Heracles come from Pindar, who seems to have used the term as a metaphor for the limits of human capabilities, be it in sport or more usually, geographical boundaries. So as the Greeks gradually extended the range of their maritime capabilities, new boundaries were established and designated as the new Pillars of Heracles. If there had been a Metaxa Book of Records at that time it would have frequently updated the location of the ‘Pillars’.
Totally unrelated to Atlantis is the natural formation on Antigua known as the so-called Pillars of Hercules(bd).
PHOENICIAN PILLARS
Gades was originally named Gadir (walled city) and is thought to have been founded by the Phoenicians around 1100 BC and Carthage circa 814 BC, although there are question marks around both dates.(ao)
Strabo wrote; “Concerning the foundation of Gades, the Gaditanians report that a certain oracle commanded the Tyrians to found a colony by the Pillars of Hercules. Those who were sent out for the purpose of exploring, when they had arrived at the strait by Calpe, imagined that the capes which form the strait were the boundaries of the habitable earth, as well as of the expedition of Hercules, and consequently, they were what the oracle termed the Pillars. They landed on the inside of the straits, at a place where the city of the Exitani now stands. Here they offered sacrifices, which however not being favourable, they returned. After a time others were sent, who advanced about 1500 stadia beyond the strait, to an island consecrated to Hercules, and lying opposite to Onoba, a city of Iberia: considering that here were the Pillars, they sacrificed to the god, but the sacrifices being again unfavourable, they returned home. In the third voyage, they reached Gades and founded the temple in the eastern part of the island, and the city in the west. (3.5.5.) If this story has any historical basis, the first Phoenician visits to the vicinity of Gibraltar must have taken place before 1100 BC.
Heracles is the Greek counterpart of the Phoenician god Melqart, who was the principal god of the Phoenician city of Tyre. Melqart was brought to the most successful Tyrian colony, Carthage and subsequently further west, where at least three temples dedicated to Melqart have been identified in ancient Spain, Gades, Ebusus, and Carthago Nova. Across the Strait in Morocco, the ancient Phoenician city of Lixus also had a temple dedicated to Melqart.
Pairs of free-standing columns were important in Phoenician temples and are also to be found in Egyptian temples, as well as being part of Solomon’s temple (built by Phoenician craftsmen). Consequently, the pillars of Melqart temple in Gades are considered by some to be the origin of the reference to the Pillars of Melqart and later of Heracles (by the Greeks) and Hercules (by the Romans) as applied to the Strait of Gibraltar.
Greek colonisation by individual city-states got underway early in the first millennium BC. This expansion of trade and territory took place gradually during the eighth, seventh and sixth centuries BC. The online Ancient History Encyclopedia website noted that “One of the most important consequences of this process, in broad terms, was that the movement of goods, people, art, and ideas in this period spread the Greek way of life far and wide to Spain, France, Italy, the Adriatic, the Black Sea, and North Africa. In total then, the Greeks established some 500 colonies which involved up to 60,000 Greek citizen colonists, so that by 500 BCE these new territories would eventually account for 40% of all Greeks in the Hellenic World.”(aq)
While the AHE offers an excellent overview of Greek colonisation, a valuable and more detailed study is also available online(ar), namely, The Expansion of the Greek World, Eighth to Sixth Centuries B.C. [1752], edited by Boardman & Hammond.
LOCATION, ACCORDING TO CLASSICAL AUTHORS
Classical writers frequently refer to the ‘Pillars’ without being in any way specific regarding their location. It always seemed to me that when the Greeks began their Mediterranean trade expansion and colonisation outside the Aegean, apart from the Pentapolis of Cyrenaica in the far south and some possible trading posts in the Levant, they did so exploiting the northern shores of the Mediterranean. Understandably, they would have taken the shortest route from the Greek mainland to the heel of Italy and later on to Sicily. As this development progressed, new limits were set, and in time, exceeded. I suggest that these limits were each in turn designated the ‘Pillars of Heracles’ as they expanded further. I speculate that Capo Colonna (Cape of the Column) in Calabria(as), in South Italy, may have been one of those early boundaries. Interestingly, 18th-century maps display up to five islands near the cape, which are no longer shown on charts(at). This appeared on respected atlases as late as 1860. According to Armin Wolf, these were originally added to maps by Ortelius, inspired by some earlier cartographers and the comments of Pseudo-Skylax and Pliny(au)!
Homer did not use the term Pillars of Heracles, although he does refer to the Pillars of Atlas (Odysseus 1.51-4).
Hecataeus (550-476 BC), according to Oliver D. Smith in a 2019 paper(y), placed the PoH at Mastia, which is thought to be Cartagena in southeastern Spain. This identification is principally based on the early 20th-century studies of Adolf Schulten.
Scylax of Caryanda (late 6th & early 5th cent. BC) describes in his Periplus(a), a guide to the Mediterranean, that the Maltese Islands lay to the east of the Pillars of Heracles. This would place the archipelago east of the Gulf of Gabes, which is compatible with the opinions of Hofmann and Sarantitis. Anton Mifsud argues that had the Pillars been located at Gibraltar, the islands to the east would have been the Balearics, which was certainly true for the ancient Greek shore-hugging mariners.
Pindar (518-438 BC) would appear to have considered that the phrase ‘Pillars of Herakles’ was a metaphor for the limits of physical prowess as well-established Greek geographical knowledge (Olympian 3.43-45), a boundary that was never static for long. In 1778, Jean-Silvain Bailly was certain that the Pillars of Hercules were just “a name that denotes limits or boundaries.” [0926.2.293] More recently Professor Dag Øistein Endsjø, at the University of Oslo in Norway, has endorsed the idea that the ancient Greeks used the ‘Pillars of Heracles’ as a metaphor to express the limits of human endeavour(d) and quotes the classicist, James S. Romm in support(e). In a sentence, the Pillars advanced along with extended geographical certainty.
When the Greek expansion westward in the Mediterranean began to gather pace, no location remained long enough as the new limit of Greek influence to enable it to acquire any permanent recognition as the metaphorical Pillars of Herakles. However, when they reached the western end of the Mediterranean and were blocked by the Phoenicians, this region offered the final resting place of the ‘Pillars’, which retains the title today.
Isocrates (436-338 BC) was an ancient Greek rhetorician and a contemporary of Plato. He wrote of Herakles setting up Pillars near Troy as a boundary marker, following the Trojan War (To Philip 5.112)(bi)(bj).
Aristotle (385-322 BC) Aristotle wrote(g) that “outside the pillars of Heracles the sea is shallow owing to the mud, but calm, for it lies in a hollow.” This is not a description of the Atlantic that we know, which is not shallow, calm or lying in a hollow and which he refers to as a ‘sea’ not an ‘ocean’.
Eratosthenes (276-194 BC) was thought by many to have been responsible for the fixing of the PoH at Gibraltar. In fact, in the early days of the compilation of Atlantipedia, I wrote that “no writer prior to Eratosthenes had referred to the Pillars of Heracles being located at Gibraltar.” This was wrong and was the result of a combination of hastily quoting Sergio Frau(al) and badly paraphrasing a passage from George Sarantitis’ book – “How, from the times of Ephorus (405 BC), Plato and Aristotle and until Eratosthenes (276 BC) and Strabo (63 BC), did the Pillars ‘migrate’ to Gibraltar?”(m)
Pseudo-Scymnus (c.140 BC) placed the Pillars at Mainake(y) thought to be modern Malaga. However, Spanuth cites from the same source a reference to a ‘Northern Pillar’ in the land of the Frisians, as support for his North Sea Atlantis!
Also in the Atlantic, there have been some speculative attempts to link the basaltic pillars at the Giant’s Causeway in Northern Ireland and its counterpart across the sea in Scotland’s Isle of Staffa with the PoH.
Strabo (64 BC-23 AD), a Greek historian and geographer, noted that “close to the Pillars there are two isles, one of which they call Hera’s Island; moreover, there are some who call also these isles the Pillars.” (Bk.3, Chap.5) The two isles referred to as near the Pillars have never been identified; as there are no islands in or near the Strait at Gibraltar, but there are in the Sea of Marmara near the Bosporus, another location candidate!
He also records that Alexander the Great built an altar and ‘Pillars of Heracles’ at the eastern limit of his Empire.
Pliny the Elder (23/24-79 AD) noted that in Sogdiana in modern Uzbekistan there was reputed to be an altar and ‘Pillars of Heracles’.
Reginald Fessenden opted for the Caucasus noting “The fact that Nebuchadnezzar, after reaching them in his northern expedition, next went to the north shore of the Black Sea and to Thrace; and that Hercules, coming back from the pillars with the cattle of Geryon, traversed the north shore of the Black Sea (see Megasthenes, quoted by Strabo and Herodotus, 4.8), puzzled the ancient geographers because they thought that the Pillars were at the straits of Gibraltar. And because they had overlooked the fact that the Phoenicians of Sidon had known that the Pillars had been lost and that the Phoenicians had sent out four expeditions to look for them but had reached no conclusion from these expeditions except that the straits of Gibraltar were not the true Pillars of Hercules. See Strabo, 2.5.
Of course, the fact that the true Pillars of Hercules were in the north Caucasus isthmus explains why both Nebuchadnezzar and Hercules, after leaving the Pillars, came next to the shores of the Black Sea.” (w)
Tacitus (55-120 AD), the renowned Latin historian, in his Germania (chap.34), clearly states that it was believed that the Pillars of Hercules were located near the Rhine in the territory of the Frisians. So the Romans either thought that the ‘Pillars’ were not situated at Gibraltar or could exist at more than one location at the same time. In Atlantisforschung, the late Bernhard Beier, quoting Günther Nesselrath, suggests that I have overstated the value of the Tacitus reference(bg).
I contend that although there is no doubt that the term ‘Pillars of Herakles’ was eventually applied to the Gibraltar region, it was also applied to a few stops as the Greeks stuttered their way there from the Aegean along the Mediterranean. Ronald H. Fritze, an ardent Atlantis sceptic, noted in his Invented Knowledge [709.23] ” While at various times the geography of the ancient Greeks applied the name of Pillars of Hercules to other locations in the Aegean region, in this case, Plato is quite explicit that he means the Pillars of Hercules that are now known as the Straits of Gibraltar.” So if it can be accepted that the PoH was applied to several locations in the Aegean by the Greeks, why not also to other places as they gradually expanded westward?
MODERN LOCATION THEORIES
From the 19th century onwards, locations for the Pillars were proposed which stretched the length of the Mediterranean and beyond.
Perhaps the first ‘modern’ writer to propose the Eastern Mediterranean as the location for the ‘Pillars’ was a Russian, Avraam Norov (1795-1869). He considered them to have been shrines, drawing on both Greek and Arabic sources that could be investigated further.
Some also believed that other ‘Pillars of Heracles’ existed in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea region. This is possible because, until the 1st millennium BC, the Greeks were, generally speaking, restricted to those areas. It would appear that for the ancient Greeks, the Pillars of Heracles marked straits or promontories at the limits of their known world. These boundaries were gradually extended further and further as their maritime capabilities improved. and probably led to the decline in the usage of the title at former boundaries, eventually leaving us with only the Strait of Gibraltar to carry the name.
In the Late Bronze Age, the Bosporus in the east and probably the Strait of Sicily in the west confined the Greeks. It was only shortly before Solon’s trip to Egypt that the Greek colony of Massalia (modern Marseilles) was founded and so, at last, the western limit of the Mediterranean was brought within easier regular reach of Greek ships, but Massalia was still nearly 2,000 km, by sea, from Gades (Cadiz). Later their furthest trading post was probably at Mainake (Malaga), beyond which was Phoenician territory and it was 100 km from Gibraltar and 200km from Cadiz.
The idea that geographical designations can radically change their location over time is illustrated by the name (H)esperia, which means ‘evening land’ or as we might say ‘land of the setting sun’, was originally used by Greeks to indicate Italy and later employed by Roman writers as a reference to Spain. It could be argued that the Greek use of this appellation could be an indication that when introduced, they were not too sure what lay beyond Italy!
Fundamentalist Atlantology, as proclaimed by the ‘prophet’ Ignatius Donnelly in the 19th century, will accept no explanation other than that Plato was referring to ‘Pillars’ near Gibraltar‘. Certainly, it is reasonable to conclude that Plato may have been referring to the Strait of Gibraltar, but it is also evident that this was not the only location with that designation in ancient times. Consequently, if any of the alternatives mentioned above enable the construction of a new credible Atlantis location hypothesis, then it deserves careful rational consideration.
Even today, the debate continues, highlighted by modern classical scholars, such as Duane W. Roller (1946- ) in Through the Pillars of Herakles [1483.203], in which he states that “The exact location of the Pillars of Herakles was long a matter of dispute. Although they may seem obvious today as the two large mountains at the western end of the Mediterranean, Gibraltar and Jebel Mousa, such was not the case in antiquity, and understanding of the region changed as topographical knowledge increased. At some early date, Homer’s mythical and unlocated Pillars of Atlas (Od. 1.51-4) became associated with the wanderer Herakles, but as the western end of the Mediterranean became better understood in the latter seventh century BC, uncertainty increased rather than decreased. Herodotus, who mentioned the Pillars several times, placed them east of Gadeira and Tartessos (4.8, 152), which could mean anywhere in the 50-kilometer-long strait (the modern Strait of Gibraltar) that runs east to the opening of the Mediterranean, through rugged topography with several promontories that could be identified as the Pillars, although especially prominent are Gibraltar and Jebel Mousa (the Kalpe and Abilyx of Strabo) at the eastern end. The early prominence of Gadeira caused some (such as Pindar) to place them in that area, or at points east thereof, such as Tarifa or Cape Trafalgar: the sources seem uncertain as to whether height or prominence was the defining criterion.”
Several alternative locations have been identified as being referred to in ancient times as the Pillars of Heracles. Robert Schoch [0454.87] writes “This distinctive name, taken from the most powerful hero of Greek mythology, was given to a number of ancient sites known in modern times by quite different appellations. The Greeks, however, used the name Pillars of Heracles to mark other sites besides Gibraltar, some outside the Mediterranean – namely, the Canary Islands in the Atlantic and the Strait of Kerch dividing the Black Sea from the Sea of Azov – and even more inside – specifically, the Strait of Bonifacio between Corsica and Sardinia, the Strait of Messina between mainland Italy and Sicily, the Greek Peleponnese, the mountainous coast of Tunisia, and the Nile Delta.” Unfortunately, Schoch offers no references.
Even Nikolai Zhirov, a proponent of an Atlantic Atlantis, accepted that they were other locations considered to have been designated Pillars of Herakles, both within and beyond Gibraltar, as shown on a map of half a century ago in his well-regarded book [458.86]. He lists, Gibraltar, Gulf of Gabes, Kerch Strait, the Moroccan coast, the Nile Delta and the Peleponnese, but like Schoch, fails to provide references.
We also find that Arthur C. Clarke suggested that there was evidence that the early Greeks did not originally refer to the Strait of Gibraltar as the Pillars of Heracles. Clarke also failed to cite his sources but expressed a personal preference for the Strait of Messina.
WITHIN THE MEDITERRANEAN
I shall begin my review of PoH locations at the eastern end of the Mediterranean in Lebanon
TYRE
J. P. Rambling has placed the ‘Pillars’ on Insula Herculis, now a small sunken island immediately south of Phoenician Tyre(k).
BOSPORUS
Eberhard Zangger [0483] cited the work of Servius(aa) in which he wrote (“Columnas Herculis legimus et in Ponto et in Hispania”) translated by Zangger as “through the Columns of Herakles we go within the Black Sea as well as in Spain”.
A German site(ab) by Willy Dorn offers a comparable translation – “Durch die Säulen des Herakles fahren wir im Schwarzen Meer wie auch in Spanien”) “We drive through the pillars of Heracles in the Black Sea as well as in Spain”
Similarly, a Spanish author, Paulino Zamarro, wrote(ac) – (“pues sabemos de Columnas de Hércules tanto en el Ponto como en Hispania”) which translates as “for we know of Columns of Hercules both in the Ponto and hispania”.
Nicolae Densusianu offered “according to what we read, the Pillars of Hercules exist both in the Pontos region, and also in Hispania.”(ad)
The Stockton University website(ae), similarly offers “We read of pillars of Hercules both in the Black Sea and in Spain”
Whichever translation is used, it confirms that at least two locations were concurrently referred to as the ‘Pillars of Heracles’.
Werner E. Friedrich has also argued [695] in favour of Pillars at the Bosporus, citing Euctemon of Athens (c.440 BC) who described the Pillars as two islands near the entrance to the strait having characteristics comparable to Prince’s Islands in the Sea of Marmara. Friedrich quotes Ephorus identifying two islands as the Pillars, just as Strabo did (see above), although there are no islands in the Strait of Gibraltar apart from the uninhabitable islet of Perejil off the coast of Morocco. Edwin Bjorkman noted [181.62] that “the insignificant little islet of Perijil” was the chosen location of Calypso’s home by Victor Berard.
Christian & Siegfried Schoppe, in support of their Black Sea location for Atlantis, maintain that the Pillars were situated at the Bosporus and not Gibraltar. They contend “the maintained misinterpretation results from the fact that Herakles went to Iberia. At late Hellenistic and at Roman times Iberia was Spain. However, this leads to inconsistencies: After putting up the Pillars (supposed at Gibraltar) Herakles put together a fleet to go to Iberia – he was still there!” This makes no sense, however, as the Schoppes pointed out that in the distant past ‘Iberia’ related to the land of an ethnic group to the east of the Black Sea.
George K. Weller has added his support to the concept of the Pillars being situated at the Bosporus, in his brief paper on Atlantis(ba). On the other side of the Black Sea, the Strait of Kerch leading to the Sea of Azov was favoured by Alexandre Moreau de Jonnes as the site of the Pillars(bc).
TROY
Isocrates, mentioned above, recorded that following the Trojan War, Herakles set up Pillars as boundary markers near Troy – “while they with the combined strength of Hellas found it difficult to take Troy after a siege which lasted ten years, he (Heracles), on the other hand, in less than as many days, and with a small expedition, easily took the city by storm. After this, he put to death to a man all the princes of the tribes who dwelt along the shores of both continents; and these he could never have destroyed had he not first conquered their armies. When he had done these things, he set up the Pillars of Heracles, as they are called, to be a trophy of victory over the barbarians, a monument to his own valor and the perils he had surmounted, and to mark the bounds of the territory of the Hellenes.”(ax).
DANUBE
Moving eastward and inland from the Black Sea, we have a strong case presented for the Danube as the home of its own Pillars. The Danube was known to the ancient Greeks as the Istros as well as Okeanos Potamos. The lower reaches of the river have ancient and deep-rooted cultural links with Hercules that are still very obvious today.
In Romania, just north of Orsova on a tributary of the Danube lies Baile Herculane, sometimes called Hercules’ City, which has seen human habitation since the Paleolithic era. There is a legend that a weary Hercules stopped in the valley to bathe and rest. During the Roman occupation, the local Herculaneum Spa was known all over the Empire.
Pindar confirms the visit of Hercules to the Danube (Estrus)(ag).
Even as early as the 1st century BC, local coinage displayed images of Hercules(af).
Just over a century ago, Nicolae Densusianu finished his monumental work Ancient Dacia(ah), which included fifteen pages(j) of the most comprehensive and fully referenced defence of any PoH location proposed, namely, the Iron Gates gorge on the Danube in ancient Dacia – modern Romania.
Alexandra Furdui, is a Romanian architect, who now lives in Australia. In her book entitled Island: Myth…Reality …or Both? [1598], she posits Atlantis as a large island in the antediluvian freshwater Black Sea ruled by the Titans of Greek mythology, some of whom later started another civilisation in the lower Danube, where she claims the Pillars of Herakles were situated, probably the result of being influenced by the earlier work of Nicolae Densusianu.
Densusianu’s offering has been reinforced recently by Antonije Shkokljev & Slave Nikolovski–Katin who have recorded [1742] a version of the ‘Labours of Hercules’ that took place in the land of the Hyperboreans and its Danube River(ai). Other more recent writers have also specified the Iron Gates as the location of the PoH.
A paper presented at the 2008 Atlantis Conference by Ticleanu, Constantin & Nicolescu [0750.375] has the ‘Pillars’ at the Iron Gates but places Atlantis a little further west on what is now the Pannonian Plain. In 2020, Veljko Milkovi? proposed the same locations for the ‘Pillars’ and Atlantis(ay).
Similarly, an anonymous commentator, ‘Sherlock’, referencing Pindar (Olympian 3) also places the Pillars at the confluence of the Seva and Danube rivers near today’s Belgrade(s).
AEGEAN
Back in the Mediterranean, Capes Maleas and Matapan (Tainaron) in the Peloponnese are the two most southerly points of mainland Greece. They have been proposed by Galanopoulos & Bacon [0263] as the Pillars of Heracles when the early Greeks were initially confined to the Aegean Sea and the two promontories were the western limits of their maritime knowledge at that time. They argue that it is possible that the ‘Pillars of Hercules’ are not the Straits of Gibraltar.
“This has been the subject of some interesting conjectures. Nearly all the labours of Hercules were performed in the Peloponnese. The last and hardest of those which Eurytheus imposed on the hero was to descend to Hades and bring back its three-headed dog guardian, Cerberus. According to the most general version Hercules entered Hades through the abyss at Cape Taenarun (the modern Cape Matapan), the western cape of the Gulf of Laconia. The eastern cape of this gulf is Cape Maleas, a dangerous promontory, notorious for its rough seas.
Pausanias records that on either side of this windswept promontory were temples, that on the west dedicated to Poseidon, that on the east to Apollo. It is perhaps therefore not extravagant to suggest that the Pillars of Hercules referred to are the promontories of Taenarum and Maleas; and it is perhaps significant that the twin brother of Atlas was allotted the extremity of Atlantis closest to the Pillars of Hercules. The relevant passage in the Critias (114A-B) states:
‘And the name of his younger twin-brother, who had for his portion the extremity of the island near the pillars of Hercules up to the part of the country now called Gadeira after the name of that region, was Eumelus in Greek, but in the native tongue Gadeirus — which fact may have given its title to the country.’
Since the region had been named after the second son of Poseidon, whose Greek name was Eumelus, its Greek title must likewise have been Eumelus, a name which brings to mind the most westerly of the Cyclades, Melos, which is in fact not far from the notorious Cape Maleas. The name Eumelus was in use in the Cyclades; and the ancient inscription (‘Eumelus an excellent danger’) was found on a rock on the island of Thera.
In general, it can be argued from a number of points in Plato’s narrative that placing ‘the Pillars of Hercules’ at the south of the Peloponnese makes sense, while identifying them with the Straits of Gibraltar does not [p.97].”
James Mavor [265] supported Galanopoulos’ proposed location for the Pillars.
Rodney Castleden [225.6] also defended this view, noting that “before the sixth century BC several mountains on the edges of mainland Greece were seen as supports for the sky. Among others, the two southward-pointing headlands on each side of the Gulf of Laconia were Pillars of Heracles.” Other commentators have seen this identification of the Pillars as ratification of the Minoan Hypothesis(p). Caleb Howells is one of the most recent to endorse the Gulf of Laconia as the site of the Pillars(bm).
Paulino Zamarro has mapped 13 locations(f) identified as Pillars by classical authors and expands on this further in his book [0024]. He identified Pori, a rocky islet north of the Greek island of Antikythera, as the location of the Pillars.
Izabol Apulia, better known as ‘Map Mistress’ placed the Pillars on Rhodes(be).
EGYPT
In Volume No. 4 of the 1897 Science Review Journal, Alexander Karnoschitsky placed the Pillars of Heracles near Sais in Egypt and located Atlantis in the eastern Mediterranean(bb).
More recently two writers, R. McQuillen and Hossam Aboulfotouh have independently suggested the vicinity of Canopus situated in the west of the Nile Delta as the location of the ‘Pillars’. Luana Monte, a supporter of the Minoan Hypothesis has also proposed [0485] a location at the mouth of the Nile Delta where the recently rediscovered sunken city of Herakleoin was situated. This identification appears to have been made in order to keep the Minoan Empire west of the ‘Pillars’.
STRAIT of OTRANTO
Moving on, we find that Alessio Toscano has suggested that the Pillars were situated at the Strait of Otranto and that Plato’s ‘Atlantic’ was in fact the Adriatic Sea!
The Arcus-Atlantis website had the following titbit to offer(bl) – “From a very early period in their exploration of the seas around their homeland, the ancient Greeks appear to have assigned twin pillars to locations regarding as marking the furthest possible point of exploration. Perhaps the earliest of these, which are described in the De Mirabilibus Auscultatonibus, a work ascribed (wrongly) to Aristotle, were to be found in the northernmost reaches of the Adriatic Sea, either at the mouth of the River Po or just south of Istria.“
The STRAIT of MESSINA is a strong contender as a location of the PoH in the Central Mediterranean. For years I have struggled with the idea that the Atlanteans had attacked from beyond the Pillars located at Gibraltar since Plato tells us that they already had control of northern Africa and southern Italy along with several islands. To me, this could only make sense if the Pillars were situated some distance east of Gibraltar.
I recently recalled that Thorwald C. Franke had arrived at the same conclusion in a paper delivered to the 2008 Atlantis Conference held in Athens [750], where he noted that “On the one hand Atlantis is said to have ruled in Italy and Northern Africa before it invaded the region ‘within the straits’. On the other hand, Atlantis wanted to subdue ‘at a blow…..the whole region within the straits.’ How could Atlantis subdue ‘at a blow’ the ‘whole’ region ‘within the straits’ after Atlantis already had conquered the whole western Mediterranean sea”
“This is easily explained if we localise the Atlantis straits at the straits of Messina and consider the sea ‘within the straits’ to be the eastern Mediterranean sea only.”
I have discovered that in the Strait of Messina there had been a pillar erected north of the ancient city of Rhegium (Reggio Calabria), apparently marking what had been, at that time, the closest point to Sicily. Little is known about the early history of the pillar or even its precise location(av).
Some commentators had suggested the Strait of Sicily, but I find it strange that what we call today the Strait of Sicily is 90 miles wide. Now the definition of ‘strait’ is a narrow passage of water connecting two large bodies of water. How 90 miles can be described as ‘narrow’ eludes me. Is it possible that we are dealing with a case of mistaken identity and that the ‘Strait of Sicily’, when referred to in ancient times, was in fact the Strait of Messina, which is narrow? Keeping in mind that Philo of Alexandria (20 BC-50 AD) in his On the Eternity of the World(aj) wrote “Are you ignorant of the celebrated account which is given of that most sacred Sicilian strait, which in old times joined Sicily to the continent of Italy?” So. understandably, the Strait of Messina is a ‘prime suspect’.
On the other hand, the Strait of Messina was one of the locations known as the site of the ‘Pillars’ and considering that mariners at that time preferred to stay close to the coast, I would opt for the Strait of Messina rather than the more frequently proposed Strait of Sicily. In a 1959 article(r) entitled Atlantis – A New Theory, Arthur R. Weir investigates the story of Scylla & Charybdis and is happy to accept that it refers to features in the Strait of Messina. In commenting on the Pillars he notes it is “quite clear that while to a Roman of the time of Julius Caesar the ‘Pillars of Heracles’ meant the Straits of Gibraltar, to a Greek of six centuries or more earlier they meant the Straits of Messina, and this immediately suggests a very different location for Atlantis.” Weir goes on to suggest a location, south of Sardinia and east of the Balearics.?
SICILY
Federico Bardanzellu locates the Pillars on the island of Motya off the west coast of Sicily(h), a view that is hotly disputed. This would suggest that Atlantis was located west of there, which would bring you to Sardinia – 200 miles away. However, the Pillars were described as being close to Atlantis, which makes this suggestion improbable.
Sergio Frau in his book, Le Colonne d’Ercole: Un’inchiesta [0302], insists that the Pillars were in fact located in the Strait of Sicily. He sees this location as agreeing with the writings of Homer and Hesiod. He discusses in detail the reference by Herodotus to an island to the west of the Pillars, suggesting that the word ‘ocean’ had a different meaning than today and pointing out that elsewhere Herodotus refers to Sardinia as the largest island in the world. Following this lead, Frau concluded that Atlantis was located in Sardinia.
Louis Godart, an Italian archaeologist of Belgian extraction, has offered a number of points that support Frau’s location(bh), including one particular comment – “First of all, in the lists in our possession, there is no place name that can refer, with a minimum degree of credibility, to a toponym located west of the Strait of Sicily.” I think that this should be investigated further as Godart offers no references and the implications, if verified, are far-reaching.
SARDINIA
 Sardinia has considerable support as the location of Atlantis. This idea appears to have had addition support from Professor Giorgio Saba who has identified Carloforte on the island of San Pietro off the southwest coast of Sardinia as the site of the Pillars of Heracles, known locally as the ‘Faraglione Antiche Columns’.
Sardinia has considerable support as the location of Atlantis. This idea appears to have had addition support from Professor Giorgio Saba who has identified Carloforte on the island of San Pietro off the southwest coast of Sardinia as the site of the Pillars of Heracles, known locally as the ‘Faraglione Antiche Columns’.
STRAIT of BONIFACIO
The Strait of Bonifacio is the name of the 11km stretch of water that lies between Sardinia and Corsica. As mentioned above, Robert Schoch included this strait in a list of locations that he believes were formerly designated by the Greeks as ‘Pillars of Heracles’, alas, all without references. Paolo Valente Poddighe who nominated Sardinia and Corsica as Atlantis 40 years ago, also situated the ‘Pillars’ at Bonifacio.
MALTA
As Felice Vinci mentioned earlier, according to Aristotle, the Pillars of Heracles were also known by the earlier name of ‘Pillars of Briareus’ (Aelian Var. Hist.5.3). Plutarch places Briareus near Ogygia, from which we can assume that the Pillars of Heracles are close to Ogygia [019.270]. Since Malta is identified by some as Ogygia, it is not unreasonable, to conclude that the Pillars were probably in the region of the Maltese Islands.
Anton Mifsud has now revised his opinion regarding the Pillars and in a December 2017 illustrated article(o) he identified the Maltese promontory of Ras ir-Raheb near Rabat, with its two enormous limestone columns as the Pillars of Herakles. This headland had originally been topped by a Temple of Herakles, confirmed by archaeologist, Professor Nicholas Vella. A 2020 article about the Minoans offered additional support for this location(v).
STRAIT OF SICILY
Robert J. Tuttle is the author of The Fourth Source [1148], in which he touched on the subject of Atlantis, takes issue with the translations of Plato’s text by Bury and Lee, who refer to the ‘Atlantic Ocean’, which he claims should read as the ‘Sea of Atlantis’ and locates the ‘Pillars of Herakles’ somewhere between Tunisia, Sicily and the ‘toe of Italy’.
Pier Paolo Saba also placed the PoH between Sicily and Tunisia.
Rosario Vieni has suggested that the Symplegades, at the Bosporus, encountered by Homer’s Argonauts were precursors of the Pillars of Heracles, although Vieni settled on the Strait of Sicily as their location [1177] before Sergio Frau adopted the same location. However, there is little doubt that during the last two centuries, BC ‘the Pillars’ referred almost exclusively to the Strait of Gibraltar.
Delisle de Sales placed the ‘Pillars’ not too far away at the Gulf of Tunis, the gateway to Carthage.
GULF OF GABES
As mentioned above Scylax of Caryanda described in his Periplus(a) that the Maltese Islands lay to the east of the Pillars of Heracles, which would place the archipelago east of the Gulf of Gabes. Antonio Usai, in a critique of Frau’s book Usai, opted for the Pillars having been between the east coast of Tunisia and the islands of Kerkennah in the Gulf of Gabes [0980]. George Sarantitis presented a paper to the 2008 Atlantis Conference in which he also argued that the Pillars had been situated in the Gulf of Gabes [750.403]. He cites Strabo among others to highlight the multiplicity of locations that have been attributed to Pillars in ancient times.
Ulrich Hofmann combines the Periplus of Scylax with the writings of Herodotus to build a credible argument for placing Atlantis in North Africa in Lake Tritonis, now occupied by the chotts of modern Algeria and Tunisia. Consequently, Hofmann places the Pillars in the Gulf of Gabés. Hofmann also argues that the Pillars were part of Atlantis rather than separate from it.
 I must not forget Paul Borchardt who advocated Tunisia as the location of Atlantis. In a map drawn by him (see left), he placed the Pillars (Columnae Herculis) at the Gulf of Gabes(bf).
I must not forget Paul Borchardt who advocated Tunisia as the location of Atlantis. In a map drawn by him (see left), he placed the Pillars (Columnae Herculis) at the Gulf of Gabes(bf).
Alan Mattingly strongly supports the Gulf of Gabes as at least one location for the ‘Pillars’. I have taken the liberty of quoting his comments in full from his very interesting Kindle book Plato’s Atlantis and the Sea Peoples: A Review of Context and Evidence [1948].
“Further, Herodotus strongly implies that the Pillars of Herakles that he is talking about are located near to Gabes in the Little Syrtis. ‘I have now mentioned all the pastoral tribes along the Libyan coast. Up country further to the south lies the region where wild beasts are found, and beyond that there is a great belt of sand stretching from Thebes in Egypt to the Pillars of Herakles. (Book IV.181) Thus far I am able to give you the names of the tribes who inhabit the sand belt, but beyond this point my knowledge fails. I can affirm, however; that the belt continues to the Pillars of Herakles’ and beyond…’ (Book IV.185) Since Herodotus’ tribal descriptions do not go west of Carthage these statements suggest that the Pillars of Herakles he is referring to lie somewhere within the Gulf of Sirte. I would note that there is a sand belt that indeed extends from Egypt through Libya to southern Tunisia and Algeria, although not in one unbroken mass. It does not however go further west than the ouadi Rhir, there are separate sand seas to the south-west in Mauretania and Mali, but it should be noted that there is no great sand belt in the vicinity or anywhere near the Straits of Gibraltar. Since Herodotus is professing no knowledge of what lies beyond the Atlantes or beyond Carthage along the North African Coast the implication would be that the Pillars are to the East of these points (along the coast south and east of Carthage). Since the sand belt touches the coast last near Gabes, the further implication is that the Pillars were in this vicinity.”
GIBRALTAR
There is no doubt that the region of Gibraltar was considered, at least by the Greeks, to be home to the Pillars from the middle of the first millennium BC. However, although sought by Phoenicians, Greeks and Romans, they were never found. I am forced to contend that they were principally metaphorical.
Oliver D. Smith investigated the matter of the ‘Pillars’ and concluded that there were four locations in southern Iberia nominated as home to the Pillars and named them as Mastia, Mainake, Strait of Gibraltar and Cádiz(az).
In 1916, Konrad Miller, the German historian, who published a number of old maps offered one that purported to show the ‘Pillars’ just west of Gibraltar. What is unusual about this is that it is depicted on an island!(m)
There is one interesting comment by the late Steven Sora [395.6] that may have a bearing on the location of the Pillars of Heracles, where, citing Ernle Bradford [1011], he claimed that at the time when Homer wrote, around 775 BC, the Greeks had barely ventured as far as Italy. To me, this would appear to suggest that at that time it is improbable that the ‘Pillars’ were identified by the Greeks with Gibraltar, but more likely to have been somewhere in the Central Mediterranean. Nevertheless, Sora opted for the Gibraltar location [p217]!
BEYOND GIBRALTAR
A more distant location was proposed by Chechelnitsky who placed the ‘Pillars’ at the Bering Strait between the Chukchi and Seward peninsulas in Russia and the USA respectively.
Arguably the most unusual suggestion this year has come from Marco Goti in his book, The Island of Plato [1430] in which he identified the ‘Pillars’ in the Atlantic, being the basalt columns of the Giant’s Causeway in Northern Ireland in the west and their counterpart in Scotland’s Isle of Staffa in the east! However, this idea is not original, having been first mooted nearly seventy years ago by W.C. Beaumont(n). Alberto Majrani is a recent advocate of this interpretation(bk).
The Cyclopean Islands off the east coast of Sicily near Mt. Etna and referred to by Homer in his Odyssey are also known for their basaltic columns.
Olof Rudbeck‘s chosen location was further east in the Baltic at the Øresund Strait between Sweden and Denmark.
Ogygia has also been identified with one of the Faroe Islands in the North Atlantic by Felice Vinci [019.3], who then proposed that the Pillars of Heracles had also been located in that archipelago. John Larsen has made similar suggestions.
Exotic locations such as Chott-el-Jerid in Tunisia, Bab-el-Mandeb(b) at the mouth of the Red Sea, the Strait of Hormuz(i) at the entrance to the Persian Gulf and even the Palk Strait between Sri Lanka and India have all been suggested at some stage as the ‘Pillars’.
George H. Cooper offered [0236] an even more outrageous solution when he wrote that the megaliths of Stonehenge in England were the original Pillars of Heracles.
In 2018, David L. Hildebrandt published Atlantis–The Awakening [1602], in which he endeavoured to do just that with a mass of material that he claims supports the idea of Atlantis in Britain and Stonehenge as the remnants of the Temple of Poseidon. He suggests that the five trilithons represent the five sets of male twins, an idea voiced by Jürgen Spanuth and more recently by Dieter Braasch.
The late Arysio dos Santos [0320] claimed that “there was only one real pair of pillars: the ones that flank Sunda Strait in Indonesia”, in keeping with his Indonesian location for Atlantis. However, he does offer a map showing [p.130] nine sites designated by ancient authorities (but without references) as having been locations of ‘Pillars’, reinforcing the idea that the term was not exclusively applied to just one site. Santos’ map was based on the work of José Imbelloni.
ATLANTIS AND THE PILLARS OF HERACLES
The assumed location of the Pillars of Heracles, at the time of Solon, often plays a critical part in the formulation of the many Atlantis theories on offer today. Even the authors of theories that have placed Plato’s island civilisation in such diverse locations as Antarctica, the North Sea or the South China Sea, have felt obliged to include an explanation for the nature and location of the ’Pillars’ within the framework of their particular hypothesis.
There is one location clue in Plato’s text (Tim.24e) that is often overlooked, namely, that the island of Atlantis was situated close to the Pillars of Heracles. Although it can be argued that Plato’s island was immediately before or beyond the Pillars, the text seems to clearly imply proximity. This was pointed out by W.K.C. Guthrie in volume V of A History of Greek Philosophy [0946.245] and independently endorsed by Joseph Warren Wells in The Book on Atlantis [0783].
Sometimes, in ancient Greek literature, this phrase PoH refers to the strait between Sicily and the southern tip of Italy (a place which the Greeks did know well, having established colonies in Sicily and Southern Italy). An indication of the level of confusion that existed in early geography and cartography is the fact that some ancient maps & texts mark the Mediterranean region west of the Strait of Sicily as ‘the Atlantic Ocean‘ and even state that Tyrrhenia is in the ‘Atlantic’!
Finally, my own conclusion regarding the location of the ‘Pillars’ is that a careful reading of Plato’s text shows clearly that they were located in the Central Region of the Mediterranean. I base this view on Critias 108 which states that the Atlantean war was between those that lived outside the Pillars of Heracles and those that lived within them and (ii) Critias 114 which declares that Atlantis held sway over the Western Mediterranean as far as Tyrrhenia in the north and up to the borders of Egypt in the south. Consequently, we can safely assume that the west of Tyrrhenia and Egypt was beyond the Pillars of Heracles. Depending on the exact location of the ancient borders of Tyrrhenia and Egypt, the Pillars were probably situated somewhere in the vicinity of the Strait of Sicily.
This interpretation opens up the possibility of Malta, Sicily or even Sardinia as prime candidates for the location of Atlantis, with the ‘Pillars’ probably being at the Strait of Messina between Sicily and mainland Italy. My principal reason is that a strait is defined as “a naturally formed, narrow, typically navigable waterway that connects two larger bodies of water.” The Strait of Sicily is 145 km wide and cannot be realistically considered a strait. Similarly, it can be argued that at 13 km in width, the Strait of Gibraltar cannot be described as ‘narrow’! On the other hand, the Strait of Messina, which at its narrowest is 3.1 km wide, fits the bill perfectly. Andis Kaulins is similarly inclined to favour the Central Mediterranean, also with the Strait of Messina as his prime candidate(q).
What is clear from all of the above is that the term Pillars of Heracles was, without doubt, applied to a variety of locations but Plato’s reference might relate to Gibraltar although equally strong if not stronger cases can be made for other sites at earlier dates. It is also plausible that at some point it also became a metaphor for any geographical limit.
CONCLUSION
Leaving aside the multiplicity of Herakles’ noted above, it is clear that the Herakles associated with Pillars was a mythological figure and when taken together with the fact that the ancient writers could not agree on the exact location or the nature of the Pillars and combined with the failure of both the Phoenicians and later the Romans to find them, it is reasonable to conclude that there were no physical Pillars of Herakles at Gibraltar.
It should be obvious that if the ancient mariners, Greeks, Phoenicians and Romans, despite centuries of searching, were unable to definitively identify the location of the Pillars, making my suggestion, that they were not physical but metaphorical, more credible.
Furthermore, the Gibraltar region together with all the other locations proposed for the Pillars of Herakles, none are known to have possessed the stelai described by Plato.
The PoH are described by Plato in terms implying proximity to Atlantis. He also described Atlantis as being beyond the Pillars of Herakles or westward of them. Furthermore, without any ambiguity, Plato identified central Mediterranean territory in southern Italy and northern Africa together with a number of the many islands there, as the Atlantean domain. Consequently, we must look to somewhere not too far east of those lands for the location of the Pillars. My personal choice is the Strait of Messina, one of the proposed locations named the Pillars on their journey westward in step with the expansion of Greek trade and colonisation.
As explained elsewhere, ancient empires or alliances only expanded by invading contiguous territory or attacking by sea, land that is within ‘easy reach’. From Gibraltar to Athens is over 2,500 km, which would make an attack over that distance totally irrational, whereas an invasion launched from southern Italy across the Strait of Otranto to mainland Greece is quite credible.
However, my view now is that generally, most references to Pillars of Herakles noted above used the term metaphorically to indicate an unspecified geographical limitation.
TRIVIA
Apart from any connection with Atlantis, it has been suggested that the vertical lines in the US dollar $ign (and by extension on the Bitcoin logo) represent the Pillars of Heracles!(l)
A more ‘out of this world’ suggestion(c) is that the ‘Pillars’ were actually two bright stars in the western sky at the end of the last Age of Libra around 12,500 BC.
(a) http://www2.le.ac.uk/departments/archaeology/people/shipley/pseudo-skylax
(b) http://www.grahamhancock.com/underworld/DrSunilAtlantis.php
(c) http://dailygrail.com/blogs/Charles-Pope/2011/8/Atlantis-Above-and-Below-Part-3
(d) https://web.archive.org/web/20020603011136/http://www.gunnzone.org:80/constructs/endsjo.htm
(f) La localización de la Atlántida (archive.org)
(g) .ii.html”http://classics.mit.edu?Aristotle/meteorology.2.ii.html
(h) https://web.archive.org/web/20200403114225/http://www.museodeidolmen.it/popomare.html
(i) https://web.archive.org/web/20200220020342/http://www.middle-east.mavericsa.co.za/history.html (over halfway down the page)
(j) https://shebtiw.wordpress.com/the-sea/the-pillars-of-hercules/
(k) http://redefiningatlantis.blogspot.ie/search/label/Heracles
(l) http://www.pravda-tv.com/2016/07/atlantis-die-dollar-note-und-die-saeulen-des-herakles/
(m) http://gibraltar-intro.blogspot.ie/2015/10/bc-pillars-of-hercules-if-ordinary.html
(n) https://www.theflatearthsociety.org/library/pamphlets/Is%20Britain%20the%20Lost%20Atlantis.pdf
(p) https://stillcurrent.wordpress.com/2016/04/05/atlantis-maybe-not-so-lost/
(q) https://web.archive.org/web/20200130221548/http://www.lexiline.com/lexiline/lexi60.htm
(r) https://drive.google.com/file/d/10JTH401O_ew1fs8uhXR9C5IjNDvqnmft/view Science Fantasy #35 1969
(s) https://sherlockfindsatlantis.wordpress.com/
(t) (Atlantean) Research, Vol 1 No.2, July/August , 1948
(u) Atlantis, Vol.29, No.2, March 76.
(v) https://www.argophilia.com/news/was-the-end-of-the-minoans-the-will-of-the-gods/227053/ (near the end of page)
(w) http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/hopper/text?doc=Perseus:text:1999.04.0064:entry=herculis-columnae-geo
(x) http://dlib.nyu.edu/awdl/isaw/isaw-papers/5/
(y) https://www.researchgate.net/publication/334683935_In_Search_of_the_Pillars_of_Heracles
(z) (Microsoft Word – Numéro complet.docx) (univ-lille.fr)
(aa) Servius on Vergil’s Aeneid 11.262.1
(ab) Atlantis – a lost paradise? – On the coasts of light (archive.org) (German)
(ac) La localización de la Atlántida (archive.org)
(ae) https://www.stockton.edu/hellenic-studies/documents/chs-summaries/culley94.pdf
(af) http://www.wildwinds.com/coins/celtic/danube/i.html
(ag) Pindar, Olympian 3.25
(ai) https://www.academia.edu/30587794/_Cradle_of_the_Aegean_Culture_by_Antonije_Shkokljev_and_Slave_Nikolovski_Katin?email_work_card=view-paper (Chap. 16)
(aj) https://web.archive.org/web/20200726123301/http:/www.earlychristianwritings.com/yonge/book35.html, v139
(ak) https://en.wikisource.org/wiki/The_Anabasis_of_Alexander/Book_II/Chapter_XVI
(al) https://www.chasingtheunexpected.com/sardinia-land-of-mystery-part-2-atlantis-lost-civilization/
(am) Plato’s Atlantis (Decoding the most famous myth) English translation of ‘The Apocalypse of a Myth’, 2017
(an) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Claudius_Aelianus#Varia_Historia
(ao) https://archive.aramcoworld.com/issue/199203/pillars.of.hercules.sea.of.darkness.htm
(ap) II, 42.44 {4747}
(aq) https://www.ancient.eu/Greek_Colonization/
(as) https://www.atlasobscura.com/places/capo-colonna
(at) https://nl.pinterest.com/pin/734438651719489108/
(au) See: Note 5 Armin Wolf’s Wayback Machine (archive.org)
(av) https://it.wikipedia.org/wiki/Colonna_Reggina
(aw) http://www.radiocom.net/Deluge/Deluge7-10.htm
(ax) Isocrates. To Philip 5.112
(ay) Pannonian Atlantis by Veljko Milkovi? | VEMIRC
(az) https://www.academia.edu/39947152/In_Search_of_the_Pillars_of_Heracles
(bb) Alexander Nikolajewitsch Karnoschitsky – Atlantisforschung.de
(bc) Alexandre Moreau de Jonnès – Atlantisforschung.de
(bd) https://www.islandroutes.com/caribbean-tours/antigua/9284/pillars-of-hercules-hiking-adventure
(be) http://pseudoastro.wordpress.com/2009/02/01/planet-x-and-2012-the-pole-shift-geographic-spin-axis-explained-and-debunked/ (Comment March 9, 2009, about halfway down the page)
(bf) Paul Borchardt: Atlantis in Tunisia – Atlantisforschung.de (atlantisforschung-de.translate.goog)
(bh) The Archaeologist / Louis Go
(bi) https://greekreporter.com/2023/05/25/pillars-hercules-greek-mythology/
(bk) https://ilionboken.w ordpress.com/insight-articles/guest-article-where-were-the-pillars-of-hercules/
(bl) Where exactly is Atlantis? (archive.org) (p.3)
(bm) What Are the Pillars of Hercules Mentioned in Greek Mythology? – GreekReporter.com
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Rogers, Charles A.
Charles A. Rogers is the author of a fully illustrated paper(a) in which he locates the city of Atlantis on the Tunisian River Triton, which led from Chott el Jerid (formerly Lake Tritonis?) to the Gulf of Gabes. He dates the demise of Atlantis to 1404 BC based on a possible connection with a close encounter with Phäeton, which in turn he identifies as what was later to be known as Halley’s Comet. He also combines all this with the eruption of Thera that generated a tsunami, which ran across the Mediterranean to the Gulf of Gabes and destroyed the city of Atlantis and in Egypt wiped out the Pharoah and his men during the biblical Exodus. There seems to be too many coincidences required here.
With regard to the location of Atlantis, the satellite imagery used by Rogers is, in my view, not very convincing and although I am sympathetic to the existence of Atlantis in that region, I think only investigation on the ground will offer real evidence.
(a) https://www.academia.edu/36855091/Atlantis_Once_Lost_Now_Found
Late Bronze Age Collapse
Late Bronze Age Collapse of civilisations in the Eastern Mediterranean in the second half of the 2nd millennium BC has been variously attributed to earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and severe climate change. It is extremely unlikely that all these occurred around the same time through coincidence. Unfortunately, it is not clear to what extent these events were interrelated. As I see it, political upheavals do not lead to earthquakes, volcanic eruptions or drought and so can be safely viewed as an effect rather than a cause. Similarly, climate change is just as unlikely to have caused eruptions or seismic activity and so can also be classified as an effect. Consequently, we are left with earthquakes and volcanoes as the prime suspects for the catastrophic turmoil that took place in the Middle East between the 15th and 12th centuries BC. Nevertheless, August 2013 saw further evidence published that also blamed climate change for the demise of Bronze Age civilisations in the region.
In 2022, a fourth possible cause emerged from a genetic research project -disease. The two disease carriers in question were the bacteria Salmonella enterica, which causes typhoid fever, and the infamous Yersinia pestis, the bacteria responsible for the Black Death plague that decimated the population of medieval Europe. These are two of the deadliest microbes human beings have ever encountered, and their presence could have easily triggered significant heavy population loss and rampant social upheaval in ancient societies(d).
Robert Drews[865] dismisses any suggestion that Greece suffered a critical drought around 1200 BC, citing the absence of any supporting reference by Homer or Hesiod as evidence. He proposes that “the transition from chariot to infantry warfare as the primary cause of the Great Kingdoms’ downfall.”
Diodorus Siculus describes a great seismic upheaval in 1250 BC which caused radical topographical changes from the Gulf of Gabes to the Atlantic. (181.16)
This extended period of chaos began around 1450 BC when the eruptions on Thera took place. These caused the well-documented devastation in the region including the ending of the Minoan civilisation and probably the Exodus of the Bible and the Plagues of Egypt as well. According to the Parian Marble, the Flood of Deucalion probably took place around the same time.
Professor Stavros Papamarinopoulos has written of the ‘seismic storm’ that beset the Eastern Mediterranean between 1225 and 1175 BC(a). Similar ideas have been expressed by Amos Nur & Eric H.Cline(b)(c). The invasion of the Sea Peoples recorded by the Egyptians, and parts of Plato’s Atlantis story all appear to have taken place around this same period. Plato refers to a spring on the Athenian acropolis (Crit.112d) that was destroyed during an earthquake. Rainer Kühne notes that this spring only existed for about 25 years but was rediscovered by the Swedish archaeologist, Oscar Broneer, who excavated there from 1959 to 1967. The destruction of the spring and barracks, by an earthquake, was confirmed as having occurring at the end of the 12th century BC. Tony Petrangelo published two interesting, if overlapping, articles in 2020 in which he discussed Broneer’s work on the Acropolis(e)(f).
>A recent review of two books on subject in the journal Antiquity begins with the following preamble;
“The collapse c.1200 BC’ in the Aegean and eastern Mediterranean—which saw the end of the Mycenaean kingdoms, the Hittite state and its empire and the kingdom of Ugarit—has intrigued archaeologists for decades. As Jesse Millek points out in (his book) Destruction and its impact, the idea of a swathe of near-synchronous destructions across the eastern Mediterranean is central to the narrative of the Late Bronze Age collapse: “destruction stands as the physical manifestation of the end of the Bronze Age” (p.6). Yet whether there was a single collapse marked by a widespread destruction horizon is up for debate.” (g)<
(b) https://academia.edu/355163/2001_Nur_and_Cline_Archaeology_Odyssey_Earthquake_Storms_article (this is a shorter version of (c) below)
(e) https://atlantis.fyi/blog/platos-fountain-on-the-athens-acropolis
(f) A General Program of Defense | Atlantis FYI
(g) Getting closer to the Late Bronze Age collapse in the Aegean and eastern Mediterranean, c. 1200 BC | Antiquity | Cambridge Core*
Rhelissia *
Rhelissia is a small settlement in the Kebili region of Tunisia on the south east edge of Chott el Jerid(a). It is situated at the mouth of what was considered the old River Tritonis, which once flowed into the Gulf of Gabes. Albert Herrmann identified it as the location of Atlantis based on his interpretation of Plato’s text. He was particularly impressed by the traces of ancient irrigation works in the vicinity, which were on a scale and of a style which Herrmann considered beyond the capabilities of the local inhabitants of his time.
(a) Rhelissia Driving Directions and Map in Kebili (archive.org) *
Hanno, The Voyage of *
The Voyage of Hanno, the Carthaginian navigator, was undertaken around 500 BC. The general consensus is that his journey took him through the Strait of Gibraltar and along part of the west coast of Africa. A record, or periplus, of the voyage was inscribed on tablets and displayed in the Temple of Baal at Carthage. Richard Hennig 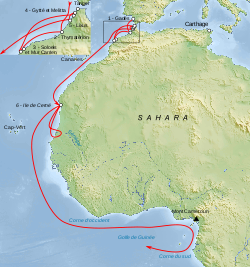 speculated that the contents of the periplus were copied by the Greek historian, Polybius, after the Romans captured Carthage. It did not surface again until the 10th century when a copy, in Greek, was discovered (Codex Heildelbergensis 398) and was not widely published until the 16th century.
speculated that the contents of the periplus were copied by the Greek historian, Polybius, after the Romans captured Carthage. It did not surface again until the 10th century when a copy, in Greek, was discovered (Codex Heildelbergensis 398) and was not widely published until the 16th century.
The 1797 English translation of the periplus by Thomas Falconer along with the original Greek text can be downloaded or read online(h).
Edmund Marsden Goldsmid (1849-?) published a translation of A Treatise On Foreign Languages and Unknown Islands[1348] by Peter Albinus. In footnotes on page 39 he describes Hanno’s periplus as ‘apocryphal’. A number of other commentators(c)(d) have also cast doubts on the authenticity of the Hanno text.
Three years after Ignatius Donnelly published Atlantis, Lord Arundell of Wardour published The Secret of Plato’s Atlantis[0648] intended as a rebuttal of Donnelly’s groundbreaking book. The ‘secret’ referred to in the title is that Plato’s Atlantis story is based on the account we have of the Voyage of Hanno.
Nicolai Zhirov speculated that Hanno may have witnessed ‘the destruction of the southern remnants of Atlantis’, based on some of his descriptions.
Rhys Carpenter dedicated nearly twenty pages to the matter of Hanno commented that ”The modern literature about his (Hanno’s) voyage is unexpectedly large. But it is so filled with disagreement that to summarize it with any thoroughness would be to annul its effectiveness, as the variant opinions would cancel each other out”[221.86]. Carpenter included what he describes as ‘a retranslation of a translation’ of the text.
Further discussion of the text and topography encountered by Hanno can be read in a paper[1483] by Duane W. Roller.
What I find interesting is that so much attention was given to Hanno’s voyage as if it was unique and not what you would expect if Atlantic travel was as commonplace at that time, as many ‘alternative’ history writers claim.
However, even more questionable, is the description of Hanno sailing off “with a fleet of sixty fifty-oared ships, and a large number of men and women to the number of thirty thousand, and with wheat and other provisions.” The problem with this is that the 50-oared ships would have been penteconters, which had limited room for much more than the oarsmen. If we include the crew, an additional 450 persons per ship would have been impossible, in fact, it is unlikely that even the provisions for 500 hundred people could have been accommodated!
Lionel Casson, the author of The Ancient Mariners[1193] commented that “if the whole expedition had been put aboard sixty penteconters, the ships would have quietly settled on the harbour bottom instead of leaving Carthage: a penteconter barely had room to carry a few days’ provisions for its crew, to say nothing of a load of passengers with all the equipment they needed to start a life in a colony.“
The American writer, William H. Russeth, commented(f) on the various interpretations of Hanno’s route, noting that “It is hard for modern scholars to figure out exactly where Hanno travelled, because descriptions changed with each version of the original document and place names change as different cultures exert their influence over the various regions. Even Pliny the Elder, the famous Roman Historian, complained of writers committing errors and adding their own descriptions concerning Hanno’s journey, a bit ironic considering that Romans levelled the temple of Ba’al losing the famous plaque forever.”
George Sarantitis has a more radical interpretation of the Voyage of Hanno, proposing that instead of taking a route along the North African coast and then out into the Atlantic, he proposes that Hanno travelled inland along waterways that no longer exist(e). A 2013 report in New Scientist magazine(n) revealed that 100,000 years ago the Sahara had been home to three large rivers that flowed northward, which probably provided migration routes for our ancestors. Furthermore, if these rivers lasted into the African Humid Period they may be interpreted as support for Sarantitis’ contention regarding Hanno!
He insists that the location of the Pillars of Heracles, as referred to in the narrative, matches the Gulf of Gabes [1470].
The most recent commentary on Hanno’s voyage is on offer by Antonio Usai in his 2014 book, The Pillars of Hercules in Aristotle’s Ecumene[980]. He also has a controversial view of Hanno’s account, claiming that in the “second part, Hanno makes up everything because he does not want to continue that voyage.” (p.24) However, the main objective of Usai’s essays is to demonstrate that the Pillars of Hercules were originally situated in the Central Mediterranean between eastern Tunisia and its Kerkennah Islands.
A 1912 English translation of the text can be read online(a), as well as a modern English translation by Jason Colavito(k).
Another Carthaginian voyager, Himilco, is also thought to have travelled northward in the Atlantic and possibly reached Ireland, referred to as ‘isola sacra’. Unfortunately, his account is no longer available(g).
The controversial epigrapher Barry Fell went so far as to propose that Hanno visited America, citing the Bourne Stone as evidence!(m)*
The livius.org website offers three articles(i) on the text, history and credibility of the surviving periplus together with a commentary.
Another excellent overview of the document is available on the World History Encyclopedia website.(l)
(a) https://web.archive.org/web/20040615213109/https://www.jate.u-szeged.hu/~gnovak/f99htHanno.htm
(c) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hanno_the_Navigator
(d) https://annoyzview.wordpress.com/2012/04/
(e) https://platoproject.gr/voyage-hanno-Carthaginian/
(f) https://www.goodreads.com/author/show/1033187.William_H_Russeth/blog?page=2 *
(g) https://gatesofnineveh.wordpress.com/2011/12/13/high-north-carthaginian-exploration-of-ireland/
(j) BSMQgoYSQYFJ90bRJIhQ&hl=mt&ei=–tuSfNEIaqnAOo_NjHBA&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct=result&resnum=&ved=CBgQ https://archive.org/details/cu31924031441847
(l) Hanno: Carthaginian Explorer – World History Encyclopedia
(n) NewScientist.com, 16 September 2013, https://tinyurl.com/mg9vcoz
Syrtis
Syrtis was the name given by the Romans to two gulfs off the North African coast; Syrtis Major which is now known as the Gulf of Sidra off Libya and Syrtis Minor, known today as the Gulf of Gabes in Tunisian waters. They are both shallow sandy gulfs that have been feared from ancient times by mariners. In the Acts of the Apostles (Acts 27.13-18) it is described how St. Paul on his way to Rome was blown off course and feared that they would run aground on ‘Syrtis sands.’
However, they were shipwrecked on Malta or as some claim on Mljet in the Adriatic.
The earliest modern reference to these gulfs that I can find in connection with Atlantis was by Nicolas Fréret in the 18th century when he proposed that Atlantis may have been situated in Syrtis Major. Giorgio Grongnet de Vasse expressed a similar view around the same time. Since then there has been little support for the idea until recent times when Winfried Huf designated Syrtis Major as one of his five divisions of the Atlantean Empire.
However, the region around the Gulf of Gabes has been more persistently associated with aspects of the Atlantis story. Inland from Gabes are the chotts, which were at one time connected to the Mediterranean and considered to have been part of the legendary Lake Tritonis, sometimes suggested as the actual location of Atlantis.
In the Gulf itself, Apollonius of Rhodes placed the Pillars of Herakles(a) , while Anton Mifsud has drawn attention[0209] to the writings of the Greek author, Palefatus of Paros, who stated (c. 32) that the Columns of Heracles were located close to the island of Kerkennah at the western end of Syrtis Minor. Lucanus, the Latin poet, located the Strait of Heracles in Syrtis Minor. Mifsud has pointed out that this reference has been omitted from modern translations of Lucanus’ work!
Férréol Butavand was one of the first modern commentators to locate Atlantis in the Gulf of Gabés[0205]. In 1929 Dr. Paul Borchardt, the German geographer, claimed to have located Atlantis between the chotts and the Gulf, while more recently Alberto Arecchi placed Atlantis in the Gulf when sea levels were lower(b) . George Sarantitis places the ‘Pillars’ near Gabes and Atlantis itself inland, further west in Mauritania, south of the Atlas Mountains. Antonio Usai also places the ‘Pillars’ in the Gulf of Gabes.
In 2018, Charles A. Rogers published a paper(c) on the academia.edu website in which he identified Tunisia as Atlantis with it capital located at the mouth of the Triton River on the Gulf of Gabes. He favours Plato’s 9.000 ‘years’ to have been lunar cycles, bringing the destruction of Atlantis into the middle of the second millennium BC and coinciding with the eruption of Thera which created a tsunami that ran across the Mediterranean destroying the city with the run-up and its subsequent backwash. This partly agrees with my conclusions in Joining the Dots!
Also See: Gulf of Gabes and Tunisia
(a) Argonautica Book IV ii 1230
(c) https://www.academia.edu/36855091/Atlantis_Once_Lost_Now_Found?auto=download*
Sarantitis, George
George Sarantitis (1954- ) was born in Athens and is by profession an electronics  engineer. He is also a serious student of Ancient Greek history and literature whose research(a) enabled him to present three papers to the 2008 Atlantis Conference. These included a revised translation of many of the keywords and phrases in Plato’s Atlantis texts. He quotes Strabo’s Geographica (3.5.5.20) to demonstrate the multiplicity of locations on offer for the Pillars of Heracles. He places Atlantis in North Africa at the Richat Structure, with the Pillars of Heracles situated in the Gulf of Gabes which formerly led to an inland sea where the chotts of Tunisia and Algeria are today, as well as a number of other lakes and rivers in what is now the Sahara.
engineer. He is also a serious student of Ancient Greek history and literature whose research(a) enabled him to present three papers to the 2008 Atlantis Conference. These included a revised translation of many of the keywords and phrases in Plato’s Atlantis texts. He quotes Strabo’s Geographica (3.5.5.20) to demonstrate the multiplicity of locations on offer for the Pillars of Heracles. He places Atlantis in North Africa at the Richat Structure, with the Pillars of Heracles situated in the Gulf of Gabes which formerly led to an inland sea where the chotts of Tunisia and Algeria are today, as well as a number of other lakes and rivers in what is now the Sahara.
He posits a number of large inland seas in Africa including a much larger Lake Chad(f). The 2014 May/June edition of Saudi Aramco World has an article(c) on the remnants of the ‘Green Sahara’, during what is known technically as the African Humid Period (9000-3000 BC). Sarantitis also claims that at one stage in the distant past Libya had been a peninsula. In a June 2015 report the University of Royal Holloway in London revealed that the size of Lake Chad was dramatically reduced in just a few hundred years(d). A similar map showing enormous inland North African lakes 13,000 years ago are included in Taylor Hansen’s The Ancient Atlantic [0527.36].
Sarantitis offers details of his theories on his extensively illustrated Plato Project website(a), which I wholeheartedly recommend readers to visit. He includes a rather technical forensic analysis of Plato’s use of myth. Sarantitis also suggests that the ‘unfinished’ Critias is in fact continued at the beginning of Homer’s Odyssey (1.32-34).
Some of Sarantitis’ sections on the Methodology of Mythology will be difficult for non-academic readers, such as myself, to fully comprehend. For me, his proposal that there were two Atlantean Wars, which took place in 9600 BC and 8600 BC(e) is extremely difficult to accept, since those wars were with Athens and Egypt that did not even exist at those dates! I find it difficult to accept this apparent abandonment of commonsense and the science of archaeology.
In 2010, Sarantitis published his theories in The Apocalypse of a Myth in Greek. Now (2017) that work has been translated into English and is currently being prepared for publication with a new title of Plato’s Atlantis: Decoding the Most Famous Myth.
There is now an extensive video clip Q & A session available on Sarantitis’ website(b).
Sarantitis’ theories have been been given additional exposure with a new 2024 Jack Kelley documentary entitled The Atlantis Code that is now available on Amazon and YouTube. The official website for the film includes a number of interviews with Kelley and other commentators(g).
Thorwald C. Franke has highlighted in his newsletter No. 225 one of the fundamental errors in Sarantitis’ theory is his claim that Atlantis as the Richat Structure existed around 10,000 BC. Franke provides a link to an earlier paper debunking this idea(h). I fully concur with Franke and would add that no one has explained how Atlantis in West Africa could attack Athens millennia before it existed. Not only is the suggestion plain silly, but the proposal that 12,000 years ago, when little more than logboats(i) existed, an attack was launched on a non-existent Athens, nearly 4000 km away by land (3000 km by sea) from the ‘Structure’, is pure nonsense.
(a) Plato Project – Timeus & Critias: The ultimate explanation (archive.org)
(b) FAQ’s – Plato Project (archive.org)
(c) https://archive.aramcoworld.com/issue/201403/last.lakes.of.the.green.sahara.htm
(e) Proceedings of the 2008 Atlantis Conference[750.389](editor S.Papamarinopoulos)
(f) https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2015/06/150629162542.htm *
(g) https://www.empirebuilderproductions.com/the-atlantis-puzzle *
(h) https://www.atlantis-scout.de/atlantis-10000-bc-engl.htm *
(i) https://hakaimagazine.com/news/uncovering-culture-bronze-age-logboats/ *
Verne, Jules Gabriel
Jules Gabriel Verne (1828-1905) was a French novelist credited with ‘inventing’ science fiction. It is claimed that his 1870 classic, 20,000 Leagues Under the Sea, in which the lost city of Atlantis is featured, is said to have inspired Ignatius Donnelly to undertake his researches that led to the publication, in 1882, of his own foundational work, Atlantis: The Antediluvian World. It is also suggested that Donnelly’s second catastrophist work, Ragnarok, was also prompted by another of Verne’s novels – Off on a Comet.
The last book published before his death was L’Invasion de la Mer, only recently translated into English as Invasion of the Sea[779]. It was based on an actual suggestion by a French geographer that the chotts of Algeria and Tunisia should be reconnected with the Mediterranean at the Gulf of Gabes. These chotts or salt lakes are reputed to have been the location of the legendary Lake Tritonis and considered by some to have included the port of Atlantis. Alberto Arecchi has proposed that Lake Tritonis was the original ‘Atlantic Sea’.
>In 1863, Verne wrote Paris in the 20th Century which was not published until 1994 (in French), because his publisher thought it too farfetched and might damage his reputation. It was eventually published in English in 1997 [2067]. In this science fiction novel, he offers an astonishing number of technological predictions, such as motor cars, fax machines, computers, electronic music, etc, etc, etc(a).<
Tunisia
Tunisia has now offered evidence of human activity dated to nearly 100,000 years ago(d) at a site near Tozeur, in the southwest of the country, where the Chotts are today.
Alfred Merlin (1876-1965) was head of the Tunisian Antiquities Administration from 1905 to 1920. In 1907 the discovery of ancient artefacts of the old Tunisian port of Mahdia was initially thought by Merlin to be relics from Atlantis. However, following some investigation, the matter seemed to fade from Merlin’s field of interest and apparently never wrote anything on the subject(n).
Tunisia was proposed in the 1920s, by Albert Herrmann, as holding the location of Plato’s Atlantis, at a dried-up saltwater lake known today as Chott el Djerid and was, according to Herrmann, previously called Lake Tritonis.
>>Léonce Joleaud was a French Professor of Geology and Palaeontology. In 1928 he became president of the Geological Society of France(o) and in the same year, he published a paper entitled L’Atlantide envisagée par un Paléontologiste (Atlantis considered by a Paleontologist). He was satisfied that Plato’s island had been located in Southern Tunisia, as did many of his compatriots at that time.<<
Around this same period Dr. Paul Borchardt, a German geologist, also favoured a site near the Gulf of Gabés, off Tunisia, as the location of Atlantis. He informed us that Shott el Jerid had also been known locally as Bahr Atala or Sea of Atlas.
geologist, also favoured a site near the Gulf of Gabés, off Tunisia, as the location of Atlantis. He informed us that Shott el Jerid had also been known locally as Bahr Atala or Sea of Atlas.
Hong-Quan Zhang has a Ph.D. in Fluid Mechanics and lectures at Tulsa University. He is a recent supporter of Atlantis being located in the chotts of Tunisia and Algeria(l). He offers his interpretation of excerpts from the ancient Pyramid Texts in support of his contention(m).
More recently, Alberto Arecchi developed a theory that places Atlantis off the present Tunisian coast with a large inland sea, today’s Chotts, which he identifies as the original ‘Atlantic Sea’, straddling what is now the Tunisian-Algerian border. Arecchi claims that this was nearly entirely emptied into the Mediterranean as a result of seismic or tectonic activity in the distant past.
In 2018, Charles A. Rogers published a paper(f) on the academia.edu website in which he identified Tunisia as Atlantis with its capital located at the mouth of the Triton River on the Gulf of Gabes. He favours Plato’s 9.000 ‘years’ to have been lunar cycles, bringing the destruction of Atlantis into the middle of the second millennium BC and coinciding with the eruption of Thera which created a tsunami that ran across the Mediterranean destroying the city with the run-up and its subsequent backwash. This partly agrees with my conclusions in Joining the Dots!
There is clear evidence(b) that Tunisia had been home to the last wild elephants in the Mediterranean region until the demise of the Roman Empire. Furthermore, North Africa and Tunisia in particular have been considered the breadbasket of imperial Rome supplying much of its wheat and olive oil. In particular the Majardah (Medjerda) River valley has remained to this day the richest grain-producing region of Tunisia(i). Roman Carthage became the second city of the Western Empire. Although the climate has deteriorated somewhat since then, it is still possible to produce two crops a year in the low-lying irrigated plains of Tunisia. Furthermore, around the mountains of northwest Africa, there is an abundance of trees including Aleppo pine forests that cover over 10,000 km2 (h). All these details echo Plato’s description of Atlantis and justify the consideration of Tunisia as being at least part of the Atlantean confederation.
It is worth noting that Mago, was the Carthaginian author of a 28-volume work on the agricultural practices of North Africa. After the destruction of Carthage in 146 BC, his books were brought to Rome, where they were translated from Punic into Latin and Greek and were widely quoted thereafter. Unfortunately, the original texts did not survive, so today we only have a few fragments quoted by later writers. Clearly, Mago’s work was a reflection of a highly developed agricultural society in that region, a description that could also be applied to Plato’s Atlantis!
In 2017, the sunken city of Neapolis was located off the coast of Nabeul, southeast of Tunis. This city was reportedly submerged by a tsunami ”on July 21 in 365 AD that badly damaged Alexandria in Egypt and the Greek island of Crete, as recorded by historian Ammianus Marcellinus.(e)(g)” However, water from a tsunami eventually drains back into the sea, but the demise of Neapolis might be better explained by liquefaction, in the same way, that Herakleion(j), near Alexandria, was destroyed, possibly by the same event. Neapolis and Herakleion are around 1,900 km apart, which suggests an astounding seismic event if both were destroyed at the same time!(e)
In addition to all that, in winter the northern coast of Tunisia is assailed with cold winds from the north bringing snow to the Kroumirie Mountains in the northwest(c).
Interestingly, in summer 2014, a completely new lake was discovered at Gafsa, just north of Shott el Jerid and quickly became a tourist attraction(a), but its existence was rather short-lived.
In November 2021, Aleksa Vu?kovi? published an article on the Ancient Origins website reviewing the current evidence for a Tunisian location for Plato’s Atlantis. Unfortunately, nothing new is offered that you cannot find here(k)!
To be clear, I consider parts of Tunisia to have been an important element in the Atlantean alliance, which according to Plato, also included southern Italy along with some of the Mediterranean islands (Tim.25a-b).
(a) https://www.unexplained-mysteries.com/news/270241/mysterious-lake-appears-in-tunisian-desert
(b) New Scientist. 7 February, 1985
(c) Tunisia Weather & Climate with Ulysses (archive.org)
(d) https://phys.org/news/2016-09-tunisian-year-human-presence.html
(f) https://www.academia.edu/36855091/Atlantis_Once_Lost_Now_Found
(g) Submerged Ancient Roman City Of Neapolis Discovered In Tunisia (archive.org)
(h) Northern Africa: Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia | Ecoregions | WWF (archive.org)
(i) https://www.britannica.com/place/Majardah-valley
(j) Science Notes 2001: The Sunken Cities of Egypt (ucsc.edu)
(l) https://medcraveonline.com/IJH/is-atlantis-related-to-the-green-sahara.html
(m) https://medcraveonline.com/IJH/IJH-06-00301.pdf
(n) Alfred Merlin – Atlantisforschung.de (atlantisforschung-de.translate.goog)
