Giuseppe Mura
Mura, Giuseppe
Giuseppe Mura (1943- ) is an enthusiastic supporter of the idea of a Sardinian Atlantis, following in the footsteps of Giovanni Lilliu. In 2009, he published Sardegna: l’isola felice di Nausicàa [1570] in which he expanded on his ideas.
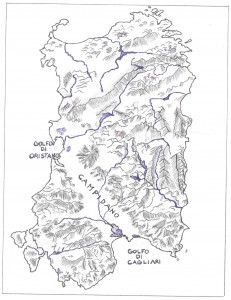
Specifically, he identifies the Gulf of Cagliari as the location of the Pillars of Heracles(a) and outlines in detail how the Plain of Campidano to the north and the region generally conforms to Plato’s description of the city of Atlantis.
>In 2018, Mura published, also in Italian, Tartesso in Sardegna [2068], the full title of which translates as Tartessos in Sardinia: Reasons, circumstances and methods used by ancient historians and geographers to remove Tartessos (the Tarshish of the Bible) from Caralis and place it in Spanish Andalusia. Caralis is an old name for Cagliari, the Sardinian capital.<
(a) https://pierluigimontalbano.blogspot.com/2017/07/archeologia-atlantide-in-sardegna-fu-il.html
Tartessos
Tartessos or Tartessus is generally accepted to have existed along the valley of the Guadalquivir River where the rich deposits of copper and silver led to the development of a powerful native civilisation, which traded with the Phoenicians, who had colonies along the south coast of Spain(k).
A continuing debate is whether Tartessos was developed by a pre-Phoenician indigenous society or was a joint venture by locals along with the Phoenicians.(o) One of the few modern English-language books about Tartessos was written by Sebastian Celestino & Carolina López-Ruiz and entitled Tartessos and the Phoenicians in Iberia [1900].
A 2022 BBC article offers some additional up-to-date developments in the studies of Tartessos(v).
It is assumed by most commentators that Tartessos was identical to the wealthy city of Tarshish that is mentioned in the Bible. There have been persistent attempts over the past century to link Tartessos with Atlantis. The last king of Tartessia, in what is now Southern Spain, is noted by Herodotus to have been Arganthonios, who is claimed to have ruled from 630 BC until 550 BC. Similarly, Ephorus a 4th century BC historian describes Tartessos as ‘a very prosperous market.’ However, if these dates are only approximately true, then Atlantis cannot be identified with Tartessos as they nearly coincide with the lifetime of Solon, who received the story of Atlantis as being very ancient.
However, the suggested linkage of Tartessos with Atlantis is disputed by some Spanish researchers, such as Mario Mas Fenollar [1802] and Ester Rodríguez González(n). Mas Fennolar has claimed that at least a thousand years separated the two. Arysio dos Santos frequently claimed that Atlantis was Tartessos throughout his Atlantis and the Pillars of Hercules [1378].
The existence of a ‘Tartessian’ empire is receiving gradual acceptance. Strabo writes of their system of canals running from the Guadalquivir River and a culture that had written records dating back 6,000 years. Their alphabet was slightly different to the ‘Iberian’. The Carthaginians were said to have been captured by Tartessos after the reign of Arganthonios and after that, contact with Tartessos seems to have ended abruptly!
The exact location of this city is not known apart from being near the mouth of the Guadalquivir River in Andalusia. The Guadalquivir was known as Baetis by the Romans and Tartessos to the Greeks. The present-day Gulf of Cadiz was known as Tartessius Sinus (Gulf of Tartessus) in Roman times. Cadiz is accepted to be a corruption of Gades that in turn is believed to have been named after Gaderius. This idea was proposed as early as 1634 by Rodrigo Caro (image left), the Spanish historian and poet, in his Antigüedades y principado de la Ilustrísima ciudad de Sevilla, now available as a free ebook(i).
In 1849, the German researcher Gustav Moritz Redslob (1804-1882) carried out a study of everything available relating to Tartessos and concluded that the lost city had been the town of Tortosa on the River Ebro situated near Tarragona in Catalonia. The idea seems to have received little support until recently, when Carles Camp published a paper supporting this contention(w). It was written in Valenciano, which is related to Catalan and can be translated with Google Translate using the latter option.
A few years ago, Richard Cassaro endeavoured to link the megalithic walls of old Tarragona with the mythical one-eyed Cyclops and for good measure suggest a link with Atlantis(l). Concerning the giants, the images of doorways posted by Cassaro are too low to comfortably accommodate giants! Cassaro has previously made the same claim about megalithic structures in Italy(m)
The German archaeologist Adolf Schulten spent many years searching unsuccessfully for Tartessos, in the region of the Guadalquivir. He believed that Tartessos had been founded by Lydians in 1150 BC, which became the centre of an ancient culture that was Atlantis or at least one of its colonies. Schulten also noted that Tartessos disappeared from historical records around 500 BC, which is after Solon’s visit to Egypt and so could not have been Atlantis.
Richard Hennig in the 1920s also supported the idea of Tartessos being Atlantis and situated in southern Spain. However, according to Atlantisforschung he later changed his opinion opting to adopt Spanuth’s Helgoland location instead(x).
Otto Jessen, a German geographer, also believed that there had been a connection between Atlantis and Tartessos. Jean Gattefosse was convinced that the Pillars of Heracles were at Tartessos, which he identifies as modern Seville. However, Mrs E. M. Whishaw, who studied in the area for 25 years at the beginning of the 20th century, believed that Tartessos was just a colony of Atlantis. The discovery of a ‘sun temple’ 8 meters under the streets of Seville led Mrs Whishaw to surmise[053] that Tartessos may be buried under that city. Edwin Björkman wrote a short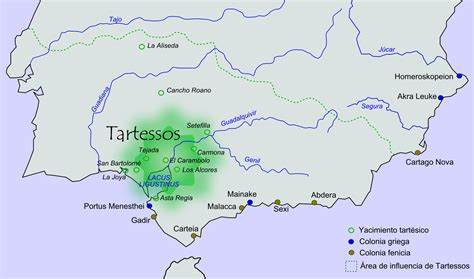 book, The Search for Atlantis[181] in which he identified Atlantis with Tartessos and also Homer’s Scheria.
book, The Search for Atlantis[181] in which he identified Atlantis with Tartessos and also Homer’s Scheria.
Steven A. Arts, the author of Mystery Airships in the Sky, also penned an article for Atlantis Rising in which he suggests that the Tarshish of the Old Testament is a reference to Tartessos and by extension to Atlantis(r)!
More recently Karl Jürgen Hepke has written at length, on his website(a), about Tartessos. Dr Rainer W. Kühne, following the work of another German, Werner Wickboldt, had an article[429] published in Antiquity that highlighted satellite images of the Guadalquivir valley that he has identified as a possible location for Atlantis. Kühne published an article(b) outlining his reasons for identifying Tartessos as the model for Plato’s Atlantis.
Although there is a consensus that Tartessos was located in Iberia, there have been some refinements of the idea. One of these is the opinion of Peter Daughtrey, expressed in his book, Atlantis and the Silver City[0893] in which he proposes that Tartessos was a state which extended from Gibraltar around the coast to include what is today Cadiz and on into Portugal’s Algarve having Silves as its ancient capital.
It was reported(c) in January 2010 that researchers were investigating the site in the Doñana National Park, at the mouth of the Guadalquivir, identified by Dr Rainer Kühne as Atlantis in a 2011 paper(s). In the same year, Professor Richard Freund of the University of Hartford garnered a lot of publicity when he visited the site and expressed the view that it was the location of Tartessos which he equates with Atlantis. The Jerusalem Post in seeking to give more balance to the discussion quoted archaeology professor Aren Maeir who commented that “Richard Freund is known as someone who makes ‘sensational’ finds. I would say that I am exceptionally skeptical about the thing, but I wouldn’t discount it 100% until I see the details, which haven’t been published as far as I know.”(u)
A minority view is that Tarshish is related to Tarxien (Tarshin) in Malta, which, however, is located some miles inland with no connection to the sea. Another unusual theory is offered by Luana Monte, who has opted for Thera as Tartessos. She bases this view on a rather convoluted etymology(e) which morphed its original name of Therasia into Therasios, which in Semitic languages having no vowels would read as ‘t.r.s.s’ and can be equated with Tarshish in the Bible, which in turn is generally accepted to refer to Tartessos.
Giorgio Valdés favours a Sardinian location for Tartessos(f), an idea endorsed later by Giuseppe Mura in his 2018 book, published in Italian, Tartesso in Sardegna [2068], the full title of which translates as Tartessos in Sardinia: Reasons, circumstances and methods used by ancient historians and geographers to remove Tartessos (the Tarshish of the Bible) from Caralis and place it in Spanish Andalusia. Caralis is an old name for Cagliari, the Sardinian capital.
Andis Kaulins has claimed that further south, in the same region, Carthage was possibly built on the remains of Tartessos, near the Pillars of Heracles(j).
A more radical idea was put forward in 2012 by the Spanish researcher, José Angel Hernández, who proposed(g)(h) that the Tarshish of the Bible was to be found in the coastal region of the Indus Valley, but that Tartessos was a colony of the Indus city of Lhotal and had been situated on both sides of the Strait of Gibraltar!
A recent novel by C.E. Albertson[130] uses the idea of an Atlantean Tartessos as a backdrop to the plot.
A relatively recent claim associating Tartessos with Atlantis came from Simcha Jacobovici in a promotional interview(p) for the 2017 National Geographic documentary, Atlantis Rising. In it, Jacobovici was joined by James Cameron as producer, but unfortunately, the documentary did not produce anything of any real substance despite a lot of pre-broadcast hype.
There is an extensive website(d) dealing with all aspects of Tartessos, including the full text of Schulten’s book on the city. Although this site is in Spanish, it is worthwhile using your Google translator to read an English version.
“Today, researchers consider Tartessos to be the Western Mediterranean’s first historical civilization. Now, at an excavation in Extremadura—a region of Spain that borders Portugal, just north of Seville—a new understanding of how that civilization may have ended is emerging from the orange and yellow soil. But the site, Casas del Turuñuelo, is also uncovering new questions.”(q) First surveyed in 2014 it was in late 2021, a report emerged of exciting excavations there that may have a bearing on the demise of Tartessos. Work is currently on hold because of a dispute with landowners, with only a quarter of the site uncovered. The project director is Sebastian Celestino Perez. The Atlas Obscura website offers further background and details of discoveries at the site(t).
(a) http://web.archive.org/web/20170716221143/http://www.tolos.de/History%20E.htm
(b) Meine Homepage (archive.org)
(d) TARTESSOS.INFO: LA IBERIA BEREBER (archive.org)
(e) http://xmx.forumcommunity.net/?t=948627&st=105
(f) http://gianfrancopintore.blogspot.ie/2010/09/atlantide-e-tartesso-tra-mito-e-realta.html
(g) http://joseangelh.wordpress.com/category/mito-y-religion/
(h) http://joseangelh.wordpress.com/category/arqueologia-e-historia/
(j) Pillars of Heracles – Alternative Location (archive.org)
(k) Archive 3283 | (atlantipedia.ie)
(n) (PDF) Tarteso vs la Atlántida: un debate que trasciende al mito (researchgate.net)
(o) (PDF) Definiendo Tarteso: indígenas y fenicios (researchgate.net)
(p) Lost City of Atlantis And Its Incredible Connection to Jewish Temple (israel365news.com)
(q) The Ancient People Who Burned Their Culture to the Ground – Atlas Obscura
(r) Atlantis Rising magazine #36 http://pdfarchive.info/index.php?pages/At
(t) https://www.atlasobscura.com/articles/tartessos-casas-del-turunuelo
(u) https://www.jpost.com/jewish-world/jewish-news/the-deepest-jewish-encampment
(v) https://www.bbc.com/travel/article/20220727-the-iberian-civilisation-that-vanished
(w) https://www.inh.cat/articles/La-localitzacio-de-Tartessos-es-desconeguda.-Pot-ser-Tartessos-Tortosa- *
(x) Richard Hennig – Atlantisforschung.de (atlantisforschung-de.translate.goog) *
Identity of the Atlanteans *
The Identity of the Atlanteans has produced a range of speculative suggestions nearly as extensive as that of the proposed locations for Plato’s lost island. However, it is highly probable that we already know who the Atlanteans were, but under a different name.
The list below includes some of the more popular suggestions and as such is not necessarily exhaustive. While researchers have proposed particular locations for Atlantis, not all have identified an archaeologically identified culture to go with their chosen location. The problem is that most of the places suggested have endured successive invasions over the millennia by different peoples.
It would seem therefore that the most fruitful approach to solving the problem of identifying the Atlanteans would be to first focus on trying to determine the date of the demise of Atlantis. This should reduce the number of possible candidates, making it easier to identify the Atlanteans.
A final point to consider is that the historical Atlanteans were a military alliance, and as such may have included more than one or none of those listed here. The mythological Atlanteans, who included the five sets of male twins and their successors would be expected to share a common culture, whereas military coalitions are frequently more disparate.
Basques: William Lewy d’Abartiague, Edward Taylor Fletcher
Berbers: Alberto Arecchi, Alf Bajocco, Ulrich Hofmann, Jacques Gossart, Ibn Khaldun
British: William Comyns Beaumont, E. J. de Meester, Donald Ingram, George H. Cooper, Anthony Roberts, Paul Dunbavin.
Cro-Magnons: R. Cedric Leonard, Theosophists, Georges Poisson, Robert B. Stacy-Judd, Kurt Bilau, Louis Charpentier
Etruscans: Richard W. Welch, Frank Joseph *
Guanches: B. L. Bogaevsky, Bory de Saint Vincent, Boris F. Dobrynin, Eugène Pégot-Ogier
Irish: Ulf Erlingsson, George H. Cooper, John Whitehurst, Thomas Dietrich, Padraig A. Ó Síocháin, Lewis Spence,
Maltese: Anton Mifsud, Francis Xavier Aloisio, Kevin Falzon, Bibischok, Joseph Bosco, David Calvert-Orange, Giorgio Grongnet de Vasse, Albert Nikas, Joseph S. Ellul, Francis Galea, Tammam Kisrawi, Charles Savona-Ventura, Hubert Zeitlmair.
Maya: Robert B. Stacy-Judd, Charles Gates Dawes, Colin Wilson, Adrian Gilbert, L. M. Hosea, Augustus le Plongeon, Teobert Maler, Joachim Rittstieg, Lewis Spence, Edward Herbert Thompson, Jean-Frédérick de Waldeck,
Megalith Builders: Lucien Gerardin, Paolo Marini, Sylvain Tristan, Jean Deruelle, Alan Butler, Alfred deGrazia, Helmut Tributsch, Hank Harrison, Walter Schilling, Robert Temple, Manuel Vega
Minoans: K.T. Frost, James Baikie, Walter Leaf, Edwin Balch, Donald A. Mackenzie, Ralph Magoffin, Spyridon Marinatos, Georges Poisson, Wilhelm Brandenstein, A. Galanopoulos, J. G. Bennett, Rhys Carpenter, P.B.S. Andrews, Edward Bacon, Willy Ley, J.V. Luce, James W. Mavor, Henry M. Eichner, Prince Michael of Greece, Nicholas Platon, N.W. Tschoegl, Richard Mooney, Rupert Furneaux, Martin Ebon, Francis Hitching, Charles Pellegrino, Rodney Castleden, Graham Phillips, Jacques Lebeau, Luana Monte, Fredrik Bruins, Gavin Menzies, Lee R. Kerr, Daniel P. Buckley.
Persians: August Hunt, Pierre-André Latreille, William Henry Babcock, Hans Diller.
Phoenicians: Jonas Bergman, Robert Prutz,
Sardinians: Paolo Valente Poddighe, Robert Paul Ishoy, Sergio Frau, Mario Tozzi, Diego Silvio Novo, Antonio Usai, Giuseppe Mura.
Sicilians: Phyllis Young Forsyth, Thorwald C. Franke, Axel Hausmann, Peter Jakubowski, Alfred E. Schmeck, M. Rapisarda,
Swedes: Johannes Bureus, Olaf Rudbeck
Sea Peoples: Wilhelm Christ, Jürgen Spanuth, Spyridon Marinatos, Rainer W. Kühne, John V. Luce, Theodor Gomperz, Herwig Görgemanns , Tony O’Connell, Sean Welsh, Thorwald C. Franke, Werner Wickboldt.
Sardinia *
Sardinia is an autonomous region of Italy and after Sicily is the second largest island in the Mediterranean. Before the end of the last Ice Age, Sardinia had been joined to the European mainland because of the lower sea levels, which provided an easy access route for early settlers. Recent genetic studies revealed that “an exceptionally high proportion of the population is seemingly descended from people who have occupied it since the Neolithic and Bronze Age, between 8,000 and 2,000 years ago.”(al) Known to the Greeks as ‘Hyknusa’, during its long history, Phoenicians, Etruscans, Greeks and Romans have all left their mark on Sardinia. Before that, the megalith builders(j) were active in Sardinia and Corsica. A comprehensive history of Sardinia from the time of Atlantis is available online, in Italian and English(m). There is a tradition that Sardinia got its name from Sardus, son of Hercules(aa).
Sardinia’s important position in the ancient world was suggested by Mark McMenamin, a geologist at Mount Holyoke College in Massachusetts, who announced in Numismatist Magazine in November 1996(ar), that he believed that the Carthaginians produced gold coins, between 350 and 320 BC, depicting small maps of the Mediterranean world with India to the east and America to the west(e). When computer enhancement was applied to the images on some of those coins, he was amazed to note how the strange markings on them resembled maps made by Ptolemy, the Greek astronomer and geographer, who lived around 500 years later. The maps show what appears to emphasise the Mediterranean region, with Sardinia as a dot in the centre. The north coast of Africa appears at the bottom with Europe at the top, above the Phoenician homeland and India. The Strait of Gibraltar lies to the west; after that is the landmass of America. Some sceptics have been convinced of the correctness of McMenamin’s interpretation after seeing the enlarged images.
However, in 2000, McMenamin was obliged to confirm that the coins in question were fakes(as) as revealed in his book, Phoenicians, Fakes and Barry Fell [1738].
It has been suggested(p) that the ancient city (2000-1400 BC) of Nora, just south of today’s Pula, was thriving long before the arrival of the Phoenicians in the 8th cent. BC. It appears that contact between Sardinia and its trading partners suddenly ceased around 1400 BC, until the arrival of the Phoenicians. Phoenician inscriptions, one dated to the 11th century BC, were been found at Nora(q) in 1773. These inscriptions refer to Pygmalian, King of Tyre and to a battle between Sardinians and Phoenicians at Tarshish!
It has been postulated that the Shardana, one of the Sea Peoples of the 2nd millennium BC, gave their name to Sardinia and were probably the builders of the hundreds of Nuraghi there. Leonardo Melis, a native Sardinian, has studied and written at length on the subject. David Rohl, the archaeologist and advocate of revising generally accepted ancient chronologies, has argued[0232] that the Shardana were in fact originally from Sardis in ancient Anatolia and that they migrated westward to Sardinia following the collapse of the Hittite Empire.
Angelo Paratico also proposed a connection between the Lydian capital Sardis and Sardinia in a lecture delivered in Hong Kong in 2004(an). Wikipedia includes the following information “According to Timaeus, one of Plato’s dialogues, Sardinia and its people as well, the “Sardonioi” or “Sardianoi”, might have been named after “Sardò”, a legendary woman from Sardis, capital of the ancient Kingdom of Lydia in Anatolia.”(ao)
Apart from the enigmatic remains of the Nuraghic period, Sardinia has presented archaeologists with a greater mystery in the form of a structure at Monte d’Accoddi that closely resembles a Mesopotamian ziggurat. The earliest parts of the monument have been dated to circa 3000 BC – the same period during which comparable step pyramids were being built in Mesopotamia. Leonardo Melis has speculated that the name of the site, Accoddi, may be connected to the Akkadian civilisation. Step pyramids are also found in Sicily(c) and additionally the Le Barnenez cairn(ad) (4500-4700 BC), in Brittany, has a superficial resemblance to some of the Western Mediterranean ‘pyramids’.
Philip Coppens, author of The New Pyramid Age [759] has also written a paper(az) on Sardinia’s only known pyramid Monte d’Accoddi concluded that “despite almost forty years of excavation on the site, we know little as to what Monte d’Accoddi was, beyond the “visually obvious”. We do not know its use, nor why it was built, or why it was unique. However, the fact that there are so many questions, illustrates how little we truly know about “the pyramid movement” and how it inspired people all over the world, whether in Egypt, Peru, Mesopotamia or here in Sardinia, to begin the construction of pyramids. Currently, the oldest pyramids have been found in Peru. And though in the “Old World” we link pyramids specifically with Egypt, one group of people in north-western Sardinia had built one long before the Egyptian Pyramid Age ever began. That’s all we know, and that’s not much, is it?”
 Recent discoveries of statue menhirs on Sardinia have suggested that in the 4th millennium BC the island was part of a culture which spread from the Black Sea to the Atlantic(f).
Recent discoveries of statue menhirs on Sardinia have suggested that in the 4th millennium BC the island was part of a culture which spread from the Black Sea to the Atlantic(f).
The ancient-wisdom.com website, in a well-illustrated article, has drawn attention to the fact that the nuraghi, while very numerous are not the only distinct form of megalithic monuments on the island, but there are two others known as ‘Tombes Gigantes’ (Giants Tombs) and ‘Domus de Janas’ (Spirit Homes).(ap)
Statue menhirs are also found on adjacent Corsica.
Apart from the Monte d’Accoddi feature, the statue menhirs and the thousands of nuraghi, Sardinia has another mystery to offer, in the form of cart ruts comparable with the better-known ruts on Malta. Dr Dominique Görlitz has also studied the cartruts found in Sardinia(ax). Images of these ruts can also be seen in a YouTube video(ay).
The end of the 18th and the beginning of the 19th centuries saw Antoine Court de Géblin and Delisle de Sales suggesting Sardinia as a remnant of Atlantis. However, the first person in more recent times to promote a Sardinian Atlantis was Paolo Valente Poddighe, who did so in 1982, but, it was 2006 before he published a book[711] supporting this claim.
It was nearly another twenty years before Robert Paul Ishoy was the first to have a website(a) that promoted Sardinia as the site of Atlantis. His contention is that Atlantis was a powerful state based in Sardinia that controlled most of the western Mediterranean and was at its peak between 2000 BC and 1400 BC. Ishoy further contends that the Keftiu, Atlantean and Nuraghi cultures were all one. He contends that they made attempts to conquer the principal civilisations of the eastern Mediterranean including the Minoans, Athenians and Egyptians. During one of these attacks, the Athenians with the unexpected support of floods and earthquakes defeated the Atlanteans. Ishoy has been planning an expedition to Sardinia to seek further evidence in support of his thesis.
In 2002, the Italian journalist, Sergio Frau, published a book[302], in Italian, which firmly located Atlantis just south of Sardinia, where it is now covered by water(ah). He argued that the Pillars of Heracles were at one time located as a boundary marker at the Strait of Sicily and later moved to Gibraltar as the Greek awareness of the western Mediterranean developed through expanded trade. Frau attributes this change of location to the geographer Eratosthenes who flourished more than a century after Plato. Understandably, his theory has been greeted with the usual hail of criticism but was given support by UNESCO when it organised a symposium on the theory in Paris in 2005 followed by an exhibition in Rome the following year.
In the interest of balance, Thorwald C. Franke’s critique(n) of Frau’s work is required reading, as well as a 21-point refutation of Frau’s book signed by 71 Sardinian historians, geologists and archaeologists(w). However, others such as Silvio Diego Novo have followed Frau’s lead(aq), while Aldo Bonincontro has also nominated Sardinia as Atlantis, which he did in a 2007 article, but without any reference to Frau!
It is obvious that there is considerable local support for the idea of a Sardinian Atlantis, but for some, this seems to be often linked with the independence movement on the island.
In June 2015 Frau together with a number of Italian scientists joined him when he visited Sardinia(x). They included historian Mario Lombardo; archaeologist Maria Teresa Giannotta; Claudio Giardino, a specialist in ancient metallurgy; cartographer Andrea Cantile; archivist Massimo Faraglia; and Stefano Tinti, a geophysicist and expert on tidal waves. Their objective was to study the evidence of a huge tsunami inundating the southern part of the island in ancient times.
A report in The Guardian (15/8/15) noted(y) that “Professor Tinti explained that until the 1980s no one was aware that tidal waves had occurred in the Mediterranean. But since 2004 scientists have identified 350 events of this type over a 2,500-year period,” and regarding the Sardinian tsunami “So what would have been required in our case?” he then asked. “We’re talking about a huge volume of water, some 500 metres high [the elevation up to which the nuraghi were affected]. Only a comet could do that if the impact occurred very close to the coast and in a very specific direction,” he asserted. An event of this sort may have occurred near Cagliari, with the resulting wave devastating the plain of Campidano.”
Afterwards, Frau’s claim was given further attention(u) when an exhibition in the museum in Sardara, focused on that catastrophe which hit the island around 1175 BC. This cataclysm mainly affected the southern portion of Sardinia covering it with a layer of mud. A geophysicist, Stefano Tinti, claims that the most likely cause of such an incursion would be an enormous tidal wave resulting from the impact of a comet in the Mediterranean. It was not surprising that Jason Colavito debunked(v) any linkage of Sardinia with Atlantis as well as the claim of a cometary impact, but avoided offering any explanation for the layer of mud.
A French website offers an interesting titbit regarding the extent of the mud, noting that “A nuraghe was discovered not far from the Sardinian town of Barumini.Les archéologues ont mis 14 ans pour ôter les 12 mètres de boue qui recouvraient ce monument. The archaeologists took 14 years to remove the 12 meters of mud that covered this monument”.
An alternative view of Sardinia and its nuraghi was offered(z) by Brian Cairns on the Thunderbolts website, where he claimed that the nuraghi were constructed to offer protection from cosmic electrical strikes. In his conclusion, he states that “while the evidence above is circumstantial, it seems that Sardinia had a very active electric environment.”
The late Vittorio Castellani who had advocated locating Atlantis in the British Isles was so impressed by Frau’s book that he changed his mind and supported the idea of a Sardinian Atlantis. Another keen supporter of Frau is Mario Tozzi who has also suggested that if Sardinia was Atlantis that the mysterious Etruscans may have been Sardinians(r)(s). Further support has come from Mario Cabriolu and architect Paolo Macoratti, who identifies the Plain of Campidano with the Plain of Atlantis and locates the Atlantean capital further south in the Gulf of Cagliari, illustrated on a map on the sardolog.com site(t).
As Sardinia is still very much above water, it might seem an unlikely choice as the location of Atlantis. However, if it is accepted that the Pillars of Heracles were in fact situated in the Strait of Sicily, there are a number of features on Sardinia that would support the theories of Ishoy and Frau. There is evidence that the large plain of Campidano was inundated, from the south, by a tsunami, following an earthquake, in the Central Mediterranean in the 2ndmillennium BC. Professor Mauro Perra has argued against this(o) using extensive stratigraphic evidence. However, this tsunami also covered Punic and Roman remains indicating a much later date.
Furthermore, there are mountains protecting the plain from cold northern winds and rich mineral deposits are also found in the locality. Sardinia was well-known in ancient times as a source of silver as well as copper, iron and lead(af). There is also some evidence that a small but important quantity of tin was available on the island according to Stephen L. Dyson and Robert J. Rowland Jnr., in their recent history of Sardinia[1530]. The excellent phoenicia.org website comments that Sardinia can scarcely have been occupied by the Phoenicians for anything but its metals. The southern and south-western parts of the island, where they made their settlements, were rich in copper and lead; and the position of the cities seems to indicate the intention to appropriate these metals.
In 2010, Giuseppe Mura published a book of nearly 600 pages, in which he identifies the Gulf of Cagliari as the location of the Pillars of Heracles that previously led to a channel which gave access to the Plain of Campidano, which he claims(g)(h) was the Plain of Atlantis described by Plato.
 Furthermore, another young Sardinian has recently pointed out that colours associated by Plato with Atlantis, namely red, white and black, are found naturally on the island as well as excavated buildings of the Nuraghic period being painted in red and black stripes. The Sardinian regional flag also uses these colours.
Furthermore, another young Sardinian has recently pointed out that colours associated by Plato with Atlantis, namely red, white and black, are found naturally on the island as well as excavated buildings of the Nuraghic period being painted in red and black stripes. The Sardinian regional flag also uses these colours.
We can expect that the future will see further development of the Sardinian Theory, which shows more promise than many of the other suggested locations.
For those interested in reading more about the history of Sardinia from its prehistory until the present should visit Claudio de Tisi’s website(i) (In Italian and English). It includes a review of Sergio Frau’s book on Atlantis. In 2011, travel writer Angela Corrias wrote a two-part article)(ab)(ac), which also includes a review of Frau’s theory.
There would appear to be growing support from local researchers on the island for a Sardinian Atlantis. One of the more recent is Giorgio Valdés who equates Sardinia with Tartessos and Atlantis. This idea of Sardinia and Tartessos being identical goes back to the middle of the 20th century when Wikipedia(k) tells us “that W.F. Albright (1941) and F.M. Cross (1972) suggested Tarshish was Sardinia because of the discovery of the ‘Nora Stone’ or ‘Nora Fragment’.” An extensive article(l) on the Nora Stele, in Italian, was written in January 2014, based on a translation by Jose Stromboni.
In 2013, Marin, Minella & Schievenin stated [972.43] that Sardinia was called Tartessos in ancient times, unfortunately, without providing any references.
In August 2016, Frau’s theory received a further spurt of publicity with an interview in Sputnik News, which was followed a few days later by the announcement that National Geographic was planning a documentary, co-produced by James Cameron and Simcha Jacobovici, based on Robert Ishoy’s Atlantis in Sardinia theory(ae).
However, Diaz-Montexano is also certain that the documentary will focus on his theory(ai). In the end, both theories were featured in what turned out to be a disappointing documentary.
In late 2016, Nicola Betti, Luciano Melis & Alessandro Mugria published Il mare addosso. L’isola che fu Atlantide e poi divenne Sardegna [1571] in which they add their support to the idea of Atlantis in Sardinia. They believe “with reasonable certainty that a large area of south-west Sardinia was hit by a swarm of iron meteorites in a period between 11,000 and 9000 BC,” which would have caused a catastrophic mega-tsunami(am).
Pier Paolo Saba, another Sardinian, suggests in his book Atlantide [739], that following a catastrophe around 10,000 BC Atlantis was destroyed and survivors were dispersed to the Americas, Northern Europe and the Mediterranean. One group settled in Saba’s native Sardinia, where they became the Shardana and were responsible for the building of the thousands of nuraghi found throughout the island and were part of the Sea Peoples who attacked Egypt(au)(av).
In 2020, Marc Deneux published an ebook Voyage en Atlantide (Voyage to Atlantis) in which he offers a ‘new hypothesis’ that places Atlantis off the coast of Sardinia. As you can see from the data above, the idea is far from new as it can be traced back to the 18th century!
Luigi Usai is now promoting [1814] the idea that a conjoined Sardinia and Corsica had constituted the island of Atlantis and its capital located at Sulcis at the southern end of Sardinia!(at) In 2024, Usai published a revised version of his thesis(ba). An important Phoenician city called Sulci was situated on the island of Sant’antioco, while the smaller island of San Pietro, just a short distance to the north, has two seastacks of the town of Carloforte, identified as the Pillars of Heracles by Professor Giorgio Saba. Usai has endorsed this identification.
In July 2021 I was sent a number of images that purported to show anomalous underwater images in the Central Mediterranean northeast of Malta. At first sight, they appeared to show extensive manmade features. However, further investigation by the person who sent them to me eventually discovered that the images were the consequence of the flawed computer interpretation of sonar data. In December 2021 Luigi Usai produced the same flawed imagery as evidence that he had discovered a lost submerged civilisation!
So that there is no misunderstanding let me state that I have advocated a Central Mediterranean location for Atlantis for some years. If Sardinia holds that location, I am more than happy to congratulate Usai and Frau. But, I am not convinced by satellite imagery that has so often been proven to be flawed.
I must include here a mention of the website of Pierluigi Montalbano where he and various guest authors have written many interesting articles about Sardinia and its Nuraghic past as well as Atlantis. The site is well worth a browse and as it has Google Translate built-in, making it easily accessible to all(aw).
(a) http://www.atlantisdiscovered.org/Thesis.htm
(b) See Archive 2139)
(c) See: Archive 2650
(e) https://www.migration-diffusion.info/article.php?authorid=22
(f) Stone Pages Archaeo News: Huge number of statue menhirs found on a Sardinian wall (archive.org)
(g) https://gianfrancopintore.blogspot.com/2011/03/atlantide-in-sardegna-e-cagliari-i.html
(h) https://gianfrancopintore.blogspot.com/2011/03/atlantide-in-sardegna-e-cagliari-ii.html
(i) See: https://web.archive.org/web/20180204153209/https://www.lamiasardegna.it/files/storia-index.htm
(j) http://www.museodeidolmen.it/englishdefault.html
(k) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tarshish
(m) See: https://web.archive.org/web/20180204153209/https://www.lamiasardegna.it/files/storia-index.htm
(n) https://www.atlantis-scout.de/atlantis-sergio-frau-english.htm
(o) https://pierluigimontalbano.blogspot.ie/2014/04/uno-tsunami-cancello-la-civilta-nuragica.html (Italian)
(p) In Search Of Atlantis: Clues In Cagliari, Sardinia (archive.org)
(q) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nora_Stone
(r) https://tozzi-national-geographic.blogautore.espresso.repubblica.it/2010/11/17/atlantide-sardegna/ (Italian)
(t) SardoLog – Sardegna è Atlantide? (archive.org)
(u) https://www.theguardian.com/science/2015/aug/15/bronze-age-sardinia-archaeology-atlantis
(v) https://www.jasoncolavito.com/blog/did-a-comet-destroy-atlantis-in-bronze-age-Sardinia
(w) “La Sardegna (che non esiste) di Sergio Frau”, l’invito di Alessandro (…) – Atlantikà (archive.org) (Italian)
(x) https://anthropologistintheattic.blogspot.ie/2015/11/was-sardinia-home-to-mythical.html
(y) https://www.theguardian.com/science/2015/aug/15/bronze-age-sardinia-archaeology-atlantis
(z) https://www.thunderbolts.info/wp/2015/11/20/neolithic-man-and-the-electric-universe/
(aa) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sardus
(ab) See Archive 2898
(af) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_mining_in_Sardinia
(ag) https://phoenicia.org/minning.html
(ah) https://en.yibada.com/articles/155860/20160831/atlantis-really-sardinia-claims-expert.htm
(ai) https://translate.google.co.uk/translate?hl=en&sl=es&u=https://atlantisng.com/blog/&prev=search
(aj) https://fr.sputniknews.com/sci_tech/201608241027440170-sardaigne-atlantide-hypothese/
(ak) https://www.academia.edu/4635111/Were_the_Sea_Peoples_Mycenaeans_The_Evidence_of_Ship_Iconography
(al) Archaeogenetic findings unlock ancestral orig | EurekAlert! (archive.org) *
(an) https://www.gingkoedizioni.it/is-there-an-association-between-sardis-and-sardinia/
(ao) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sardinian_people
(ap) http://www.ancient-wisdom.com/italysardinia.htm
(aq) See: Archive 2353 (Italian)
(ar) https://www.researchgate.net/publication/236000049_Cartography_on_Carthaginian_Gold_Staters
(at) https://www.atlantisfound.it/2021/01/24/why-didnt-scientists-find-atlantis-before-usai-luigi/
(au) http://www.abovetopsecret.com/forum/thread345932/pg1
(av) http://www.commuicati-stampa.ws/2009/02/10/1413
(aw) https://pierluigimontalbano.blogspot.com/2014/04/uno-tsunami-cancello-la-civilta-nuragica.html
(ax) On the trail of the Cart Rut mystery – Atlantisforschung.de (atlantisforschung-de.translate.goog)
(az) https://www.eyeofthepsychic.com/nap_art13/